工程化部署:Stable Diffusion 3.5 FP8 从 Docker 到 Kubernetes 的完整落地指南
摘要
在AI模型从研究走向生产的过程中,工程化部署是决定成败的关键环节。
本文将深入探讨Stable Diffusion 3.5 FP8从单机容器化到大规模Kubernetes集群部署的完整解决方案,涵盖Python/Java混合技术栈、TensorRT加速优化、监控运维体系等核心内容,提供一套可落地的企业级部署框架。
1. 容器化部署:从单机到可复现
1.1 NVIDIA CUDA基础镜像选择策略
选择合适的CUDA基础镜像是AI模型部署的第一步。对于Stable Diffusion 3.5 FP8,我们需要考虑以下因素:
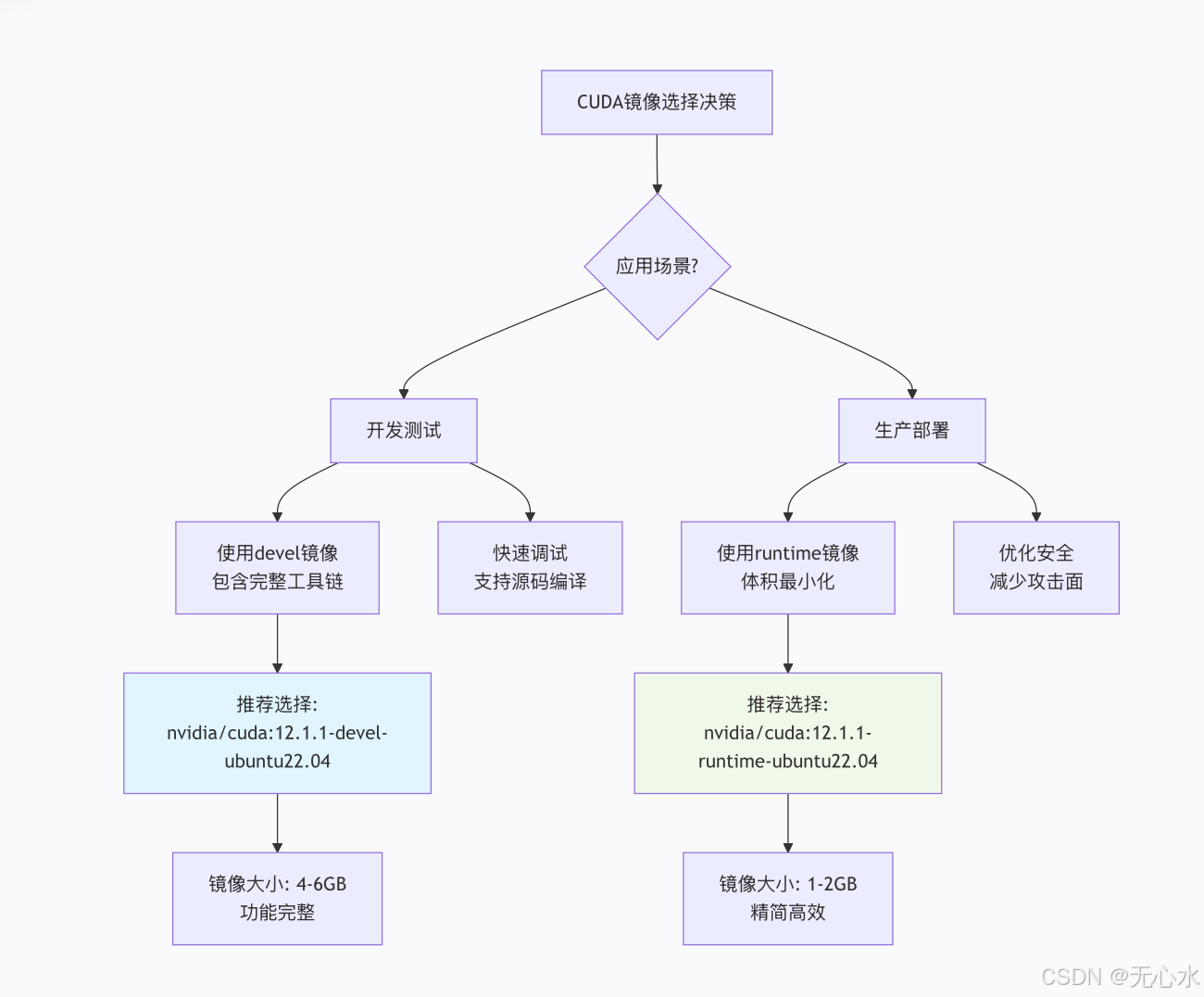
1.2 完整Dockerfile实现(Python+Java混合架构)
# 多阶段构建,优化镜像层
# 阶段1:基础CUDA环境
FROM nvidia/cuda:12.1.1-devel-ubuntu22.04 AS base
# 安装系统依赖
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y \
python3.10 \
python3-pip \
openjdk-17-jdk \
maven \
git \
wget \
libgl1-mesa-glx \
libglib2.0-0 \
&& rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
# 设置工作目录
WORKDIR /app
# 阶段2:Python依赖安装
FROM base AS python-deps
COPY requirements.txt .
# 安装PyTorch及相关库
RUN pip3 install --no-cache-dir \
torch==2.1.0+cu121 \
torchvision==0.16.0+cu121 \
--index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu121
# 安装Stable Diffusion相关库
RUN pip3 install --no-cache-dir \
diffusers==0.24.0 \
transformers==4.35.0 \
accelerate==0.25.0 \
xformers==0.0.23 \
safetensors==0.4.1 \
opencv-python==4.8.1.78 \
Pillow==10.1.0 \
scipy==1.11.4
# 阶段3:Java服务构建
FROM base AS java-builder
COPY pom.xml .
COPY src ./src
# Maven构建
RUN mvn clean package -DskipTests
# 阶段4:模型文件集成(单独层便于缓存)
FROM python-deps AS model-layer
ARG MODEL_VERSION=stable-diffusion-3.5-fp8
# 从模型仓库下载或复制模型
RUN mkdir -p /app/models
COPY models/${MODEL_VERSION} /app/models/
# 验证模型完整性
RUN python3 -c "
import torch
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
print('验证模型加载...')
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
'/app/models/${MODEL_VERSION}',
torch_dtype=torch.float16
)
print(f'模型验证成功: {pipe}')
"
# 阶段5:最终镜像组装
FROM nvidia/cuda:12.1.1-runtime-ubuntu22.04 AS runtime
# 安装最小化运行时依赖
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y \
python3.10 \
openjdk-17-jre-headless \
libgl1-mesa-glx \
&& rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
WORKDIR /app
# 复制Python环境
COPY --from=python-deps /usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages /usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages
COPY --from=python-deps /usr/local/bin /usr/local/bin
# 复制模型文件
COPY --from=model-layer /app/models /app/models
# 复制Java服务
COPY --from=java-builder /app/target/sd-api-service-1.0.0.jar /app/
COPY --from=java-builder /app/src/main/resources /app/config/
# 复制Python FastAPI服务
COPY python-service /app/python-service/
COPY configs /app/configs/
# 设置环境变量
ENV PYTHONPATH=/app/python-service
ENV MODEL_PATH=/app/models/stable-diffusion-3.5-fp8
ENV JAVA_OPTS="-Xms2g -Xmx4g -XX:MaxMetaspaceSize=512m"
ENV NVIDIA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=all
ENV CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0
# 暴露端口
EXPOSE 8080 8000
# 健康检查
HEALTHCHECK --interval=30s --timeout=10s --start-period=5s --retries=3 \
CMD curl -f http://localhost:8080/actuator/health || exit 1
# 启动脚本(同时启动Python和Java服务)
COPY entrypoint.sh /app/
RUN chmod +x /app/entrypoint.sh
ENTRYPOINT ["/app/entrypoint.sh"]
1.3 启动脚本与预热优化
#!/bin/bash
# entrypoint.sh
set -e
echo "正在启动Stable Diffusion 3.5 FP8服务..."
# 模型预热函数
preheat_model() {
echo "开始预热模型..."
local PYTHON_SCRIPT=/app/python-service/preheat.py
# 预热主模型
python3 $PYTHON_SCRIPT --model-path $MODEL_PATH --warmup-steps 3
# 预热LoRA适配器(如果有)
if [ -d "/app/models/lora-adapters" ]; then
for adapter in /app/models/lora-adapters/*; do
echo "预热适配器: $(basename $adapter)"
python3 $PYTHON_SCRIPT --model-path $MODEL_PATH \
--lora-path $adapter --warmup-steps 2
done
fi
echo "模型预热完成"
}
# Java服务启动函数
start_java_service() {
echo "启动Java API服务..."
java $JAVA_OPTS \
-Dspring.profiles.active=production \
-Dmodel.path=$MODEL_PATH \
-jar /app/sd-api-service-1.0.0.jar &
JAVA_PID=$!
echo "Java服务启动,PID: $JAVA_PID"
}
# Python服务启动函数
start_python_service() {
echo "启动Python推理服务..."
cd /app/python-service
uvicorn main:app \
--host 0.0.0.0 \
--port 8000 \
--workers 1 \
--log-level info \
--access-log &
PYTHON_PID=$!
echo "Python服务启动,PID: $PYTHON_PID"
}
# 信号处理
cleanup() {
echo "接收到终止信号,优雅关闭服务..."
kill -TERM $JAVA_PID 2>/dev/null
kill -TERM $PYTHON_PID 2>/dev/null
wait $JAVA_PID $PYTHON_PID
echo "服务已关闭"
}
trap cleanup TERM INT
# 主执行流程
preheat_model
start_java_service
start_python_service
# 等待服务运行
wait
预热脚本实现:
# preheat.py
import torch
import time
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
import argparse
def preheat_model(model_path, lora_path=None, warmup_steps=3):
"""预热模型,填充GPU缓存"""
print(f"加载模型: {model_path}")
# 加载管道
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
model_path,
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
safety_checker=None,
requires_safety_checker=False
).to("cuda")
# 加载LoRA适配器
if lora_path:
print(f"加载LoRA适配器: {lora_path}")
pipe.load_lora_weights(lora_path)
# 预热循环
prompt = "a beautiful landscape"
negative_prompt = ""
for i in range(warmup_steps):
print(f"预热步骤 {i+1}/{warmup_steps}")
start_time = time.time()
# 生成测试图像
with torch.cuda.amp.autocast():
image = pipe(
prompt=prompt,
negative_prompt=negative_prompt,
num_inference_steps=5,
guidance_scale=7.5,
height=512,
width=512
).images[0]
elapsed = time.time() - start_time
print(f"步骤完成,耗时: {elapsed:.2f}s")
# 清理缓存
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
print("模型预热完成")
return pipe
if __name__ == "__main__":
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument("--model-path", required=True)
parser.add_argument("--lora-path")
parser.add_argument("--warmup-steps", type=int, default=3)
args = parser.parse_args()
preheat_model(args.model_path, args.lora_path, args.warmup_steps)
2. TensorRT加速:部署端性能翻倍技巧
2.1 PyTorch模型转TensorRT引擎
# convert_to_tensorrt.py
import torch
import tensorrt as trt
import os
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
from polygraphy.backend.trt import CreateConfig, EngineFromNetwork, NetworkFromOnnxPath, SaveEngine
from polygraphy.backend.onnx import OnnxFromPath
class SD35FP8ToTensorRTConverter:
def __init__(self, model_path, output_dir="./trt_engines"):
self.model_path = model_path
self.output_dir = output_dir
self.logger = trt.Logger(trt.Logger.INFO)
os.makedirs(output_dir, exist_ok=True)
def export_to_onnx(self, onnx_path):
"""将PyTorch模型导出为ONNX格式"""
print("导出ONNX模型...")
# 加载原始模型
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
self.model_path,
torch_dtype=torch.float16
)
pipe.to("cuda")
# 准备示例输入
batch_size = 1
latent_channels = 4
latent_height = 64 # 512/8
latent_width = 64
# UNet输入
sample = torch.randn(
batch_size, latent_channels, latent_height, latent_width,
device="cuda", dtype=torch.float16
)
timestep = torch.tensor([50], device="cuda", dtype=torch.int64)
encoder_hidden_states = torch.randn(
batch_size, 77, 768, device="cuda", dtype=torch.float16
)
# 导出UNet
torch.onnx.export(
pipe.unet,
(sample, timestep, encoder_hidden_states),
onnx_path,
export_params=True,
opset_version=17,
do_constant_folding=True,
input_names=["sample", "timestep", "encoder_hidden_states"],
output_names=["noise_pred"],
dynamic_axes={
"sample": {0: "batch_size"},
"encoder_hidden_states": {0: "batch_size"}
}
)
print(f"ONNX模型已导出到: {onnx_path}")
return onnx_path
def build_trt_engine(self, onnx_path, fp8_mode=True):
"""构建TensorRT引擎"""
print("构建TensorRT引擎...")
# 创建构建器
builder = trt.Builder(self.logger)
network = builder.create_network(1 << int(trt.NetworkDefinitionCreationFlag.EXPLICIT_BATCH))
parser = trt.OnnxParser(network, self.logger)
# 解析ONNX
with open(onnx_path, "rb") as f:
if not parser.parse(f.read()):
for error in range(parser.num_errors):
print(parser.get_error(error))
raise RuntimeError("ONNX解析失败")
# 配置优化参数
config = builder.create_builder_config()
config.set_memory_pool_limit(trt.MemoryPoolType.WORKSPACE, 1 << 30) # 1GB
# 启用FP8精度
if fp8_mode and builder.platform_has_fast_fp8:
print("启用FP8精度模式")
config.set_flag(trt.BuilderFlag.FP8)
config.set_flag(trt.BuilderFlag.PREFER_PRECISION_CONSTRAINTS)
# 设置优化配置
profile = builder.create_optimization_profile()
# 动态形状配置
profile.set_shape(
"sample",
min=(1, 4, 32, 32), # 最小分辨率
opt=(2, 4, 64, 64), # 优化分辨率
max=(4, 4, 96, 96) # 最大分辨率
)
profile.set_shape(
"encoder_hidden_states",
min=(1, 77, 768),
opt=(2, 77, 768),
max=(4, 77, 768)
)
config.add_optimization_profile(profile)
# 构建引擎
engine_path = os.path.join(self.output_dir, "sd35_fp8.engine")
serialized_engine = builder.build_serialized_network(network, config)
with open(engine_path, "wb") as f:
f.write(serialized_engine)
print(f"TensorRT引擎已保存到: {engine_path}")
return engine_path
def validate_engine(self, engine_path):
"""验证引擎功能"""
print("验证TensorRT引擎...")
runtime = trt.Runtime(self.logger)
with open(engine_path, "rb") as f:
engine = runtime.deserialize_cuda_engine(f.read())
# 创建执行上下文
context = engine.create_execution_context()
# 测试推理
import numpy as np
# 准备输入
batch_size = 1
sample_shape = (batch_size, 4, 64, 64)
encoder_shape = (batch_size, 77, 768)
# 分配内存
inputs, outputs, bindings = [], [], []
stream = torch.cuda.Stream()
for binding in engine:
size = trt.volume(engine.get_binding_shape(binding))
dtype = trt.nptype(engine.get_binding_dtype(binding))
# 分配页锁定内存
mem = torch.cuda.alloc_pinned_memory(size * dtype().itemsize)
arr = np.frombuffer(mem, dtype=dtype)
if engine.binding_is_input(binding):
inputs.append(arr)
else:
outputs.append(arr)
bindings.append(int(arr.ctypes.data))
print("引擎验证成功")
return engine, context, bindings, inputs, outputs, stream
# 使用示例
if __name__ == "__main__":
converter = SD35FP8ToTensorRTConverter(
model_path="/app/models/stable-diffusion-3.5-fp8",
output_dir="/app/trt_engines"
)
# 导出ONNX
onnx_path = os.path.join(converter.output_dir, "sd35_fp8.onnx")
converter.export_to_onnx(onnx_path)
# 构建TensorRT引擎
engine_path = converter.build_trt_engine(onnx_path, fp8_mode=True)
# 验证
converter.validate_engine(engine_path)
2.2 TensorRT引擎的Java JNI集成
// TensorRTEngine.java
package com.sd.deployment.tensorrt;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.FloatBuffer;
public class TensorRTEngine {
static {
System.loadLibrary("tensorrt_jni");
}
// Native方法声明
private native long initEngine(String enginePath);
private native void destroyEngine(long enginePtr);
private native float[] infer(
long enginePtr,
float[] sample,
int timestep,
float[] encoderStates
);
private long enginePtr;
private boolean initialized = false;
public TensorRTEngine(String enginePath) {
this.enginePtr = initEngine(enginePath);
if (this.enginePtr != 0) {
this.initialized = true;
System.out.println("TensorRT引擎初始化成功");
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("TensorRT引擎初始化失败");
}
}
public float[] inference(
float[] latentNoise,
int timestep,
float[] textEmbeddings
) {
if (!initialized) {
throw new IllegalStateException("引擎未初始化");
}
return infer(enginePtr, latentNoise, timestep, textEmbeddings);
}
public void close() {
if (initialized) {
destroyEngine(enginePtr);
enginePtr = 0;
initialized = false;
System.out.println("TensorRT引擎已释放");
}
}
@Override
protected void finalize() throws Throwable {
try {
close();
} finally {
super.finalize();
}
}
}
// JNI实现(C++部分)
// tensorrt_jni.cpp
#include <jni.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include <vector>
#include <NvInfer.h>
#include <cuda_runtime_api.h>
using namespace nvinfer1;
class TRTLogger : public ILogger {
void log(Severity severity, const char* msg) override {
if (severity <= Severity::kWARNING) {
std::cout << "TensorRT: " << msg << std::endl;
}
}
};
class TensorRTEngineWrapper {
private:
TRTLogger logger;
IRuntime* runtime;
ICudaEngine* engine;
IExecutionContext* context;
public:
TensorRTEngineWrapper(const std::string& enginePath) {
// 加载引擎文件
std::ifstream engineFile(enginePath, std::ios::binary);
if (!engineFile) {
throw std::runtime_error("无法打开引擎文件");
}
engineFile.seekg(0, std::ios::end);
size_t size = engineFile.tellg();
engineFile.seekg(0, std::ios::beg);
std::vector<char> engineData(size);
engineFile.read(engineData.data(), size);
// 创建运行时和引擎
runtime = createInferRuntime(logger);
engine = runtime->deserializeCudaEngine(engineData.data(), size);
context = engine->createExecutionContext();
if (!engine || !context) {
throw std::runtime_error("TensorRT引擎创建失败");
}
}
~TensorRTEngineWrapper() {
if (context) context->destroy();
if (engine) engine->destroy();
if (runtime) runtime->destroy();
}
std::vector<float> inference(
const std::vector<float>& sample,
int timestep,
const std::vector<float>& encoderStates
) {
// 准备输入输出缓冲区
void* buffers[3];
// 分配GPU内存
float *d_sample, *d_encoder, *d_output;
size_t sample_size = sample.size() * sizeof(float);
size_t encoder_size = encoderStates.size() * sizeof(float);
cudaMalloc(&d_sample, sample_size);
cudaMalloc(&d_encoder, encoder_size);
cudaMalloc(&d_output, sample_size); // 输出大小与sample相同
// 复制数据到GPU
cudaMemcpy(d_sample, sample.data(), sample_size, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
cudaMemcpy(d_encoder, encoderStates.data(), encoder_size, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
// 设置绑定
int sample_idx = engine->getBindingIndex("sample");
int timestep_idx = engine->getBindingIndex("timestep");
int encoder_idx = engine->getBindingIndex("encoder_hidden_states");
int output_idx = engine->getBindingIndex("noise_pred");
buffers[sample_idx] = d_sample;
buffers[timestep_idx] = ×tep;
buffers[encoder_idx] = d_encoder;
buffers[output_idx] = d_output;
// 执行推理
context->executeV2(buffers);
// 获取结果
std::vector<float> output(sample.size());
cudaMemcpy(output.data(), d_output, sample_size, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
// 清理
cudaFree(d_sample);
cudaFree(d_encoder);
cudaFree(d_output);
return output;
}
};
// JNI函数实现
extern "C" {
JNIEXPORT jlong JNICALL
Java_com_sd_deployment_tensorrt_TensorRTEngine_initEngine(
JNIEnv* env, jobject obj, jstring enginePath
) {
const char* path = env->GetStringUTFChars(enginePath, nullptr);
try {
auto* wrapper = new TensorRTEngineWrapper(path);
env->ReleaseStringUTFChars(enginePath, path);
return reinterpret_cast<jlong>(wrapper);
} catch (const std::exception& e) {
env->ReleaseStringUTFChars(enginePath, path);
env->ThrowNew(env->FindClass("java/lang/RuntimeException"), e.what());
return 0;
}
}
JNIEXPORT void JNICALL
Java_com_sd_deployment_tensorrt_TensorRTEngine_destroyEngine(
JNIEnv* env, jobject obj, jlong ptr
) {
auto* wrapper = reinterpret_cast<TensorRTEngineWrapper*>(ptr);
delete wrapper;
}
JNIEXPORT jfloatArray JNICALL
Java_com_sd_deployment_tensorrt_TensorRTEngine_infer(
JNIEnv* env, jobject obj, jlong ptr,
jfloatArray sample, jint timestep, jfloatArray encoderStates
) {
auto* wrapper = reinterpret_cast<TensorRTEngineWrapper*>(ptr);
// 转换Java数组到C++向量
jsize sample_len = env->GetArrayLength(sample);
jsize encoder_len = env->GetArrayLength(encoderStates);
jfloat* sample_data = env->GetFloatArrayElements(sample, nullptr);
jfloat* encoder_data = env->GetFloatArrayElements(encoderStates, nullptr);
std::vector<float> sample_vec(sample_data, sample_data + sample_len);
std::vector<float> encoder_vec(encoder_data, encoder_data + encoder_len);
// 执行推理
auto result = wrapper->inference(sample_vec, timestep, encoder_vec);
// 释放资源
env->ReleaseFloatArrayElements(sample, sample_data, JNI_ABORT);
env->ReleaseFloatArrayElements(encoderStates, encoder_data, JNI_ABORT);
// 返回结果
jfloatArray result_array = env->NewFloatArray(result.size());
env->SetFloatArrayRegion(result_array, 0, result.size(), result.data());
return result_array;
}
}
3. Kubernetes集群部署:企业级方案
3.1 完整的Kubernetes部署清单
# stable-diffusion-deployment.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: ai-inference
---
# GPU节点选择器
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: sd-gpu-config
namespace: ai-inference
data:
cuda-version: "12.1.1"
model-path: "/app/models/stable-diffusion-3.5-fp8"
trt-engine-path: "/app/trt_engines/sd35_fp8.engine"
---
# 持久化存储声明(用于缓存模型)
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: sd-model-pvc
namespace: ai-inference
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
storageClassName: fast-ssd
resources:
requests:
storage: 50Gi
---
# 模型预热Job(首次部署时运行)
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
name: sd-model-warmup
namespace: ai-inference
spec:
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: warmup
image: sd-3.5-fp8:latest
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
command: ["python3", "/app/python-service/preheat.py"]
args: ["--model-path", "/app/models/stable-diffusion-3.5-fp8"]
env:
- name: CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES
value: "0"
resources:
limits:
nvidia.com/gpu: 1
requests:
nvidia.com/gpu: 1
volumeMounts:
- name: model-storage
mountPath: /app/models
restartPolicy: Never
volumes:
- name: model-storage
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: sd-model-pvc
backoffLimit: 1
---
# 主部署:Stable Diffusion推理服务
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: stable-diffusion-deployment
namespace: ai-inference
labels:
app: stable-diffusion
component: inference
spec:
replicas: 2 # 根据GPU数量调整
selector:
matchLabels:
app: stable-diffusion
component: inference
strategy:
type: RollingUpdate
rollingUpdate:
maxSurge: 1
maxUnavailable: 0
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: stable-diffusion
component: inference
annotations:
prometheus.io/scrape: "true"
prometheus.io/port: "8080"
prometheus.io/path: "/actuator/prometheus"
spec:
# 节点选择器:选择有GPU的节点
nodeSelector:
accelerator: nvidia-gpu
# 优先级类
priorityClassName: high-priority
# 亲和性配置
affinity:
podAntiAffinity:
preferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
- weight: 100
podAffinityTerm:
labelSelector:
matchExpressions:
- key: app
operator: In
values:
- stable-diffusion
topologyKey: kubernetes.io/hostname
containers:
- name: sd-inference
image: registry.example.com/sd-3.5-fp8:v1.0.0
imagePullPolicy: Always
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
name: http
protocol: TCP
- containerPort: 8000
name: fastapi
protocol: TCP
# 环境变量
env:
- name: MODEL_PATH
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: sd-gpu-config
key: model-path
- name: CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES
value: "0"
- name: NVIDIA_VISIBLE_DEVICES
value: "all"
- name: TF_FORCE_GPU_ALLOW_GROWTH
value: "true"
# 资源限制
resources:
limits:
cpu: "4"
memory: "16Gi"
nvidia.com/gpu: 1
ephemeral-storage: "10Gi"
requests:
cpu: "2"
memory: "8Gi"
nvidia.com/gpu: 1
ephemeral-storage: "5Gi"
# 生命周期钩子
lifecycle:
postStart:
exec:
command: ["/bin/sh", "-c", "python3 /app/python-service/preheat.py"]
preStop:
exec:
command: ["/bin/sh", "-c", "sleep 30"]
# 就绪和存活探针
readinessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /actuator/health/readiness
port: 8080
initialDelaySeconds: 60
periodSeconds: 10
failureThreshold: 3
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /actuator/health/liveness
port: 8080
initialDelaySeconds: 90
periodSeconds: 15
failureThreshold: 3
# 卷挂载
volumeMounts:
- name: model-storage
mountPath: /app/models
- name: trt-engine
mountPath: /app/trt_engines
- name: cache-volume
mountPath: /tmp
- name: shared-memory
mountPath: /dev/shm
# 安全上下文
securityContext:
capabilities:
add: ["SYS_ADMIN"]
privileged: false
readOnlyRootFilesystem: false
# 卷定义
volumes:
- name: model-storage
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: sd-model-pvc
- name: trt-engine
hostPath:
path: /opt/trt-engines
type: DirectoryOrCreate
- name: cache-volume
emptyDir: {}
- name: shared-memory
emptyDir:
medium: Memory
sizeLimit: 8Gi
# 重启策略
restartPolicy: Always
---
# 水平Pod自动伸缩器
apiVersion: autoscaling/v2
kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
metadata:
name: sd-inference-hpa
namespace: ai-inference
spec:
scaleTargetRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: stable-diffusion-deployment
minReplicas: 1
maxReplicas: 10
metrics:
- type: Resource
resource:
name: nvidia.com/gpu
target:
type: Utilization
averageUtilization: 70
- type: Pods
pods:
metric:
name: inference_latency_p99
target:
type: AverageValue
averageValue: 500ms
behavior:
scaleUp:
stabilizationWindowSeconds: 60
policies:
- type: Percent
value: 100
periodSeconds: 60
scaleDown:
stabilizationWindowSeconds: 300
policies:
- type: Percent
value: 50
periodSeconds: 60
---
# 服务暴露(LoadBalancer)
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: stable-diffusion-service
namespace: ai-inference
annotations:
service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-type: "nlb"
service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-internal: "false"
prometheus.io/scrape: "true"
spec:
selector:
app: stable-diffusion
component: inference
ports:
- name: http
port: 80
targetPort: 8080
protocol: TCP
- name: fastapi
port: 8000
targetPort: 8000
protocol: TCP
type: LoadBalancer
loadBalancerSourceRanges:
- 0.0.0.0/0 # 生产环境应限制IP范围
---
# Ingress路由配置
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: sd-ingress
namespace: ai-inference
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: "nginx"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-redirect: "true"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/backend-protocol: "HTTP"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-body-size: "50m"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-connect-timeout: "60"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-read-timeout: "300"
spec:
tls:
- hosts:
- sd-api.example.com
secretName: sd-tls-secret
rules:
- host: sd-api.example.com
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: stable-diffusion-service
port:
number: 80
- path: /v2/
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: stable-diffusion-service
port:
number: 8000
3.2 GPU节点标签和污点配置
# gpu-node-config.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Node
metadata:
name: gpu-node-1
labels:
accelerator: nvidia-gpu
gpu-type: a100
gpu-memory: "40Gi"
zone: us-west-2a
annotations:
nvidia.com/gpu.count: "4"
nvidia.com/gpu.product: "NVIDIA-A100-SXM4-40GB"
spec:
taints:
- key: "nvidia.com/gpu"
value: "present"
effect: "NoSchedule"
---
# 容忍性配置(在Pod Spec中)
tolerations:
- key: "nvidia.com/gpu"
operator: "Equal"
value: "present"
effect: "NoSchedule"
- key: "critical-addons-only"
operator: "Exists"
3.3 NVIDIA Device Plugin配置
# nvidia-device-plugin.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: DaemonSet
metadata:
name: nvidia-device-plugin-daemonset
namespace: kube-system
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
name: nvidia-device-plugin-ds
updateStrategy:
type: RollingUpdate
rollingUpdate:
maxUnavailable: 1
template:
metadata:
labels:
name: nvidia-device-plugin-ds
spec:
priorityClassName: "system-node-critical"
tolerations:
- key: nvidia.com/gpu
operator: Exists
effect: NoSchedule
nodeSelector:
accelerator: nvidia-gpu
containers:
- image: nvcr.io/nvidia/k8s-device-plugin:v0.14.1
name: nvidia-device-plugin-ctr
securityContext:
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
capabilities:
drop: ["ALL"]
volumeMounts:
- name: device-plugin
mountPath: /var/lib/kubelet/device-plugins
volumes:
- name: device-plugin
hostPath:
path: /var/lib/kubelet/device-plugins
4. 监控与运维体系
4.1 Prometheus监控指标配置
# prometheus-monitoring.yaml
apiVersion: monitoring.coreos.com/v1
kind: ServiceMonitor
metadata:
name: stable-diffusion-monitor
namespace: monitoring
labels:
release: prometheus-stack
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: stable-diffusion
namespaceSelector:
matchNames:
- ai-inference
endpoints:
- port: http
interval: 30s
scrapeTimeout: 25s
path: /actuator/prometheus
metricRelabelings:
- sourceLabels: [__name__]
regex: '(gpu|inference|memory).*'
action: keep
- port: fastapi
interval: 30s
path: /metrics
自定义监控指标实现:
# metrics_collector.py
import time
import psutil
import torch
import prometheus_client as prom
from prometheus_client import Gauge, Histogram, Counter
class SDMetricsCollector:
def __init__(self):
# GPU指标
self.gpu_utilization = Gauge(
'sd_gpu_utilization_percent',
'GPU利用率百分比',
['gpu_id']
)
self.gpu_memory_used = Gauge(
'sd_gpu_memory_used_bytes',
'GPU显存使用量',
['gpu_id']
)
self.gpu_memory_total = Gauge(
'sd_gpu_memory_total_bytes',
'GPU显存总量',
['gpu_id']
)
self.gpu_temperature = Gauge(
'sd_gpu_temperature_celsius',
'GPU温度',
['gpu_id']
)
# 推理指标
self.inference_latency = Histogram(
'sd_inference_latency_seconds',
'推理延迟',
['model_name', 'resolution'],
buckets=[0.1, 0.5, 1.0, 2.0, 5.0, 10.0, 30.0]
)
self.inference_requests = Counter(
'sd_inference_requests_total',
'推理请求总数',
['model_name', 'status']
)
self.inference_queue_size = Gauge(
'sd_inference_queue_size',
'推理队列大小'
)
# 系统指标
self.cpu_usage = Gauge(
'sd_cpu_usage_percent',
'CPU使用率'
)
self.memory_usage = Gauge(
'sd_memory_usage_bytes',
'内存使用量'
)
self.disk_io = Counter(
'sd_disk_io_bytes_total',
'磁盘IO总量',
['direction']
)
# 业务指标
self.images_generated = Counter(
'sd_images_generated_total',
'生成图像总数',
['model_version', 'style']
)
self.prompt_length = Histogram(
'sd_prompt_length_chars',
'提示词长度分布',
buckets=[10, 50, 100, 200, 500, 1000]
)
def update_gpu_metrics(self):
"""更新GPU指标"""
if torch.cuda.is_available():
for i in range(torch.cuda.device_count()):
gpu_id = f'cuda:{i}'
# GPU利用率
util = torch.cuda.utilization(i)
self.gpu_utilization.labels(gpu_id=gpu_id).set(util)
# 显存使用
mem_alloc = torch.cuda.memory_allocated(i)
mem_reserved = torch.cuda.memory_reserved(i)
mem_total = torch.cuda.get_device_properties(i).total_memory
self.gpu_memory_used.labels(gpu_id=gpu_id).set(mem_alloc)
self.gpu_memory_total.labels(gpu_id=gpu_id).set(mem_total)
# GPU温度(需要nvidia-smi)
try:
import subprocess
result = subprocess.run(
['nvidia-smi', '--query-gpu=temperature.gpu', '--format=csv,noheader,nounits'],
capture_output=True, text=True
)
if result.returncode == 0:
temp = float(result.stdout.strip().split('\n')[i])
self.gpu_temperature.labels(gpu_id=gpu_id).set(temp)
except:
pass
def record_inference(self, model_name, resolution, latency, status='success'):
"""记录推理指标"""
self.inference_latency.labels(
model_name=model_name,
resolution=resolution
).observe(latency)
self.inference_requests.labels(
model_name=model_name,
status=status
).inc()
def update_system_metrics(self):
"""更新系统指标"""
# CPU使用率
cpu_percent = psutil.cpu_percent(interval=1)
self.cpu_usage.set(cpu_percent)
# 内存使用
memory = psutil.virtual_memory()
self.memory_usage.set(memory.used)
def start_metrics_server(self, port=8001):
"""启动指标服务器"""
prom.start_http_server(port)
print(f"指标服务器启动在端口 {port}")
# 定期更新指标
import threading
def update_metrics():
while True:
self.update_gpu_metrics()
self.update_system_metrics()
time.sleep(10)
thread = threading.Thread(target=update_metrics, daemon=True)
thread.start()
4.2 ELK日志收集配置
# filebeat-config.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: filebeat-config
namespace: logging
data:
filebeat.yml: |
filebeat.inputs:
- type: container
paths:
- /var/log/containers/*sd-inference*.log
processors:
- add_kubernetes_metadata:
host: ${NODE_NAME}
matchers:
- logs_path:
logs_path: "/var/log/containers/"
output.logstash:
hosts: ["logstash.logging.svc.cluster.local:5044"]
logging.level: info
---
# logstash-pipeline.conf
input {
beats {
port => 5044
}
}
filter {
# 解析JSON日志
if [message] =~ /^{.*}$/ {
json {
source => "message"
}
}
# 提取关键字段
grok {
match => { "message" => "\[%{TIMESTAMP_ISO8601:timestamp}\] %{LOGLEVEL:loglevel} %{GREEDYDATA:msg}" }
}
# 添加推理相关标签
if [msg] =~ /inference|generate|prompt/ {
mutate {
add_tag => ["inference"]
}
# 提取推理指标
grok {
match => { "msg" => "inference time: %{NUMBER:inference_time}ms" }
}
# 提取提示词(脱敏)
if [msg] =~ /prompt:.*/ {
mutate {
gsub => ["msg", "prompt: .*", "prompt: [REDACTED]"]
}
}
}
# GPU相关日志
if [msg] =~ /gpu|memory|cuda/ {
mutate {
add_tag => ["gpu"]
}
}
}
output {
# 生产环境输出到Elasticsearch
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["elasticsearch.logging.svc.cluster.local:9200"]
index => "sd-logs-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
user => "${ELASTICSEARCH_USERNAME}"
password => "${ELASTICSEARCH_PASSWORD}"
}
# 开发环境同时输出到控制台
stdout {
codec => rubydebug
}
}
4.3 基于GPU负载的自动扩缩容
# gpu-autoscaler.py
import json
import time
import requests
from kubernetes import client, config
from prometheus_api_client import PrometheusConnect
class GPUScaler:
def __init__(self, namespace="ai-inference", deployment="stable-diffusion-deployment"):
# 加载Kubernetes配置
config.load_incluster_config()
self.api = client.AppsV1Api()
self.core_api = client.CoreV1Api()
self.namespace = namespace
self.deployment = deployment
# Prometheus连接
self.prom = PrometheusConnect(url="http://prometheus.monitoring.svc.cluster.local:9090")
# 扩缩容参数
self.scale_up_threshold = 70 # GPU利用率超过70%时扩容
self.scale_down_threshold = 30 # GPU利用率低于30%时缩容
self.max_replicas = 10
self.min_replicas = 1
self.cooldown_period = 300 # 冷却时间(秒)
self.last_scale_time = 0
def get_gpu_utilization(self):
"""获取所有Pod的GPU利用率"""
query = 'avg(avg_over_time(sd_gpu_utilization_percent[5m])) by (pod)'
try:
result = self.prom.custom_query(query)
utilizations = {}
for item in result:
pod = item['metric'].get('pod', '')
value = float(item['value'][1])
utilizations[pod] = value
return utilizations
except Exception as e:
print(f"获取GPU利用率失败: {e}")
return {}
def get_pending_requests(self):
"""获取待处理的推理请求数"""
query = 'sd_inference_queue_size'
try:
result = self.prom.custom_query(query)
if result:
return float(result[0]['value'][1])
except:
pass
return 0
def get_current_replicas(self):
"""获取当前副本数"""
deployment = self.api.read_namespaced_deployment(
name=self.deployment,
namespace=self.namespace
)
return deployment.spec.replicas
def scale_deployment(self, replicas):
"""扩缩容部署"""
if replicas < self.min_replicas:
replicas = self.min_replicas
if replicas > self.max_replicas:
replicas = self.max_replicas
current_replicas = self.get_current_replicas()
# 检查冷却时间
current_time = time.time()
if current_time - self.last_scale_time < self.cooldown_period:
print(f"冷却时间中,跳过扩缩容")
return
if replicas != current_replicas:
print(f"正在调整副本数: {current_replicas} -> {replicas}")
# 更新部署
patch = {
'spec': {
'replicas': replicas
}
}
try:
self.api.patch_namespaced_deployment(
name=self.deployment,
namespace=self.namespace,
body=patch
)
self.last_scale_time = current_time
print(f"成功调整副本数为: {replicas}")
# 记录扩缩容事件
self.record_scale_event(replicas, current_replicas)
except Exception as e:
print(f"扩缩容失败: {e}")
def record_scale_event(self, new_replicas, old_replicas):
"""记录扩缩容事件"""
event = client.CoreV1Event(
metadata=client.V1ObjectMeta(
generate_name=f"{self.deployment}-scale-"
),
involved_object=client.V1ObjectReference(
api_version="apps/v1",
kind="Deployment",
name=self.deployment,
namespace=self.namespace,
uid=self.api.read_namespaced_deployment(
name=self.deployment,
namespace=self.namespace
).metadata.uid
),
reason="Scaled",
message=f"Scaled deployment from {old_replicas} to {new_replicas} replicas based on GPU utilization",
first_timestamp=datetime.now(timezone.utc),
last_timestamp=datetime.now(timezone.utc),
count=1,
type="Normal",
source=client.V1EventSource(component="gpu-autoscaler")
)
try:
self.core_api.create_namespaced_event(
namespace=self.namespace,
body=event
)
except:
pass
def evaluate_scaling(self):
"""评估是否需要扩缩容"""
# 获取GPU利用率
utilizations = self.get_gpu_utilization()
if not utilizations:
print("无法获取GPU利用率数据")
return
avg_utilization = sum(utilizations.values()) / len(utilizations)
pending_requests = self.get_pending_requests()
current_replicas = self.get_current_replicas()
print(f"当前状态: 副本数={current_replicas}, GPU利用率={avg_utilization:.1f}%, 待处理请求={pending_requests}")
# 扩容条件
if avg_utilization > self.scale_up_threshold and current_replicas < self.max_replicas:
# 基于负载计算需要的副本数
needed_replicas = min(
current_replicas * 2,
current_replicas + int(pending_requests / 10) + 1,
self.max_replicas
)
self.scale_deployment(needed_replicas)
# 缩容条件
elif avg_utilization < self.scale_down_threshold and current_replicas > self.min_replicas:
# 可以安全缩容
new_replicas = max(current_replicas - 1, self.min_replicas)
# 确保有足够的副本处理待处理请求
if pending_requests < 5: # 几乎没有待处理请求
self.scale_deployment(new_replicas)
def run(self, interval=30):
"""运行自动扩缩容器"""
print("GPU自动扩缩容器启动")
print(f"配置: 扩容阈值={self.scale_up_threshold}%, 缩容阈值={self.scale_down_threshold}%")
print(f"副本范围: {self.min_replicas} - {self.max_replicas}")
while True:
try:
self.evaluate_scaling()
except Exception as e:
print(f"扩缩容评估失败: {e}")
time.sleep(interval)
# 运行自动扩缩容器
if __name__ == "__main__":
scaler = GPUScaler()
scaler.run()
5. 部署案例:小流量测试→全量上线流程
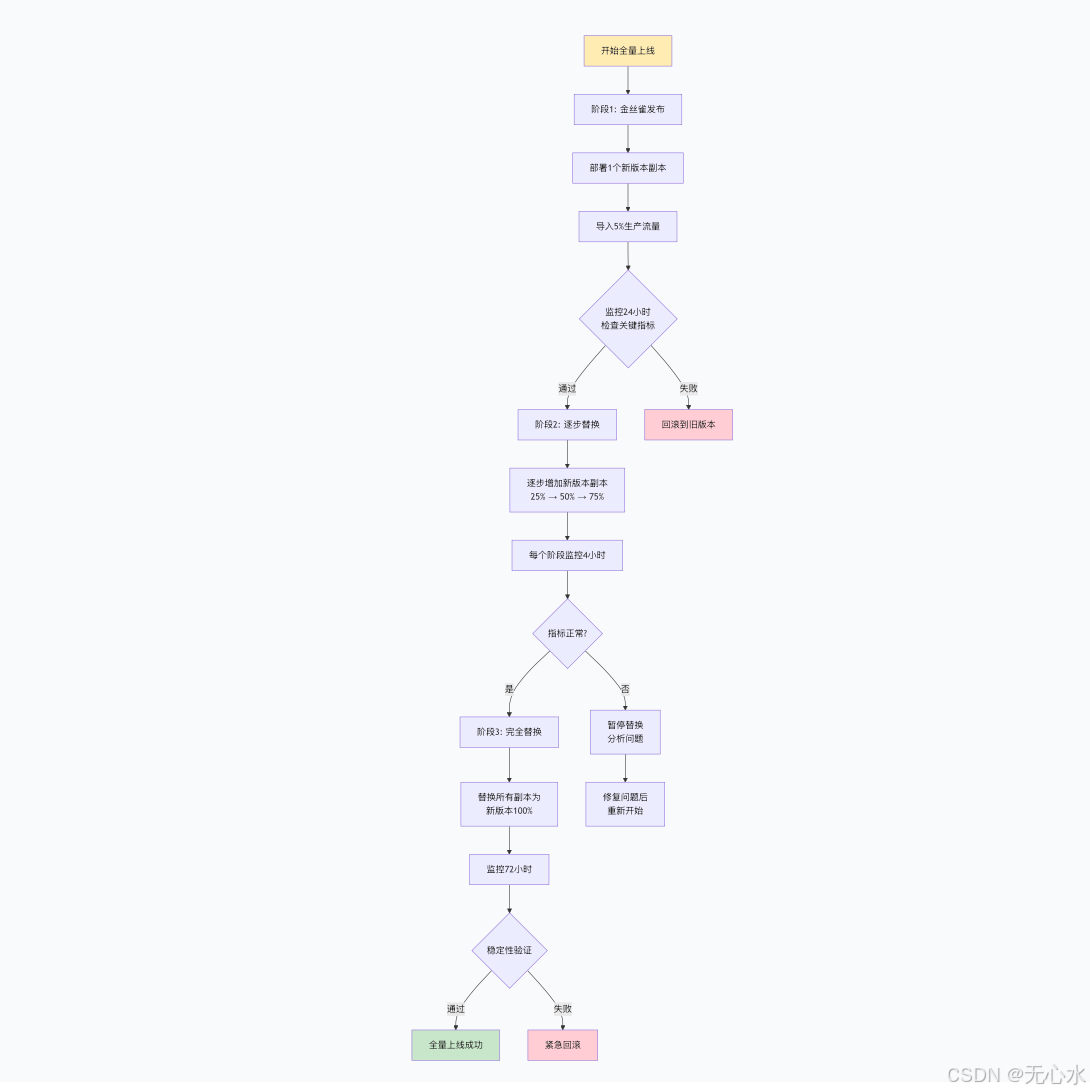
5.1 小流量测试阶段(金丝雀发布)
# canary-deployment.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: sd-canary-deployment
namespace: ai-inference
spec:
replicas: 1 # 仅部署1个副本用于测试
selector:
matchLabels:
app: stable-diffusion
track: canary
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: stable-diffusion
track: canary
spec:
containers:
- name: sd-canary
image: registry.example.com/sd-3.5-fp8:v1.1.0-canary
# 环境变量:启用详细日志和性能追踪
env:
- name: LOG_LEVEL
value: "DEBUG"
- name: ENABLE_TRACING
value: "true"
- name: REQUEST_LIMIT
value: "10" # 限制请求量
# 资源限制更宽松,便于观察
resources:
limits:
nvidia.com/gpu: 1
memory: "32Gi"
requests:
nvidia.com/gpu: 1
memory: "16Gi"
---
# 服务路由配置(Istio)
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1beta1
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: sd-virtual-service
namespace: ai-inference
spec:
hosts:
- sd-api.example.com
http:
- match:
- headers:
x-canary-test:
exact: "true"
route:
- destination:
host: sd-canary-service
port:
number: 80
weight: 100
- route:
- destination:
host: stable-diffusion-service
port:
number: 80
weight: 95
- destination:
host: sd-canary-service
port:
number: 80
weight: 5 # 5%的流量导向金丝雀版本
5.2 全量上线检查清单
# rollout_checklist.py
import requests
import json
import time
from datetime import datetime
class RolloutValidator:
def __init__(self, base_url="http://sd-api.example.com"):
self.base_url = base_url
self.results = {}
def check_health(self):
"""检查服务健康状态"""
try:
response = requests.get(f"{self.base_url}/actuator/health", timeout=10)
if response.status_code == 200:
data = response.json()
status = data.get("status", "UNKNOWN")
self.results['health'] = status == "UP"
return status == "UP"
except Exception as e:
print(f"健康检查失败: {e}")
self.results['health'] = False
return False
def check_latency(self, num_requests=10):
"""检查推理延迟"""
latencies = []
test_prompts = [
"a beautiful sunset over mountains",
"a cat sitting on a windowsill",
"futuristic cityscape at night"
]
for i in range(num_requests):
prompt = test_prompts[i % len(test_prompts)]
start_time = time.time()
try:
response = requests.post(
f"{self.base_url}/api/v1/generate",
json={"prompt": prompt, "steps": 20},
timeout=60
)
elapsed = time.time() - start_time
if response.status_code == 200:
latencies.append(elapsed)
else:
print(f"请求失败: {response.status_code}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"请求异常: {e}")
if latencies:
avg_latency = sum(latencies) / len(latencies)
p95_latency = sorted(latencies)[int(len(latencies) * 0.95)]
self.results['avg_latency'] = avg_latency
self.results['p95_latency'] = p95_latency
self.results['latency_check'] = p95_latency < 5.0 # P95延迟小于5秒
print(f"平均延迟: {avg_latency:.2f}s, P95延迟: {p95_latency:.2f}s")
return self.results['latency_check']
else:
self.results['latency_check'] = False
return False
def check_concurrency(self, concurrent_users=5):
"""检查并发处理能力"""
import threading
results = []
errors = []
def make_request(user_id):
try:
response = requests.post(
f"{self.base_url}/api/v1/generate",
json={
"prompt": f"test image for user {user_id}",
"steps": 15,
"width": 512,
"height": 512
},
timeout=30
)
results.append({
"user": user_id,
"success": response.status_code == 200,
"latency": response.elapsed.total_seconds()
})
except Exception as e:
errors.append(f"用户{user_id}: {e}")
threads = []
for i in range(concurrent_users):
thread = threading.Thread(target=make_request, args=(i,))
threads.append(thread)
thread.start()
for thread in threads:
thread.join()
success_rate = sum(1 for r in results if r['success']) / len(results) if results else 0
self.results['concurrency_success_rate'] = success_rate
self.results['concurrency_check'] = success_rate > 0.9 # 成功率大于90%
print(f"并发测试成功率: {success_rate:.1%}")
if errors:
print(f"错误信息: {errors}")
return self.results['concurrency_check']
def check_gpu_utilization(self, duration=60):
"""检查GPU利用率"""
print(f"监控GPU利用率 {duration}秒...")
utilizations = []
start_time = time.time()
while time.time() - start_time < duration:
try:
# 通过Prometheus查询GPU利用率
prom_url = "http://prometheus.monitoring.svc.cluster.local:9090"
query = 'avg(sd_gpu_utilization_percent)'
response = requests.get(
f"{prom_url}/api/v1/query",
params={"query": query},
timeout=5
)
if response.status_code == 200:
data = response.json()
if data['data']['result']:
value = float(data['data']['result'][0]['value'][1])
utilizations.append(value)
except Exception as e:
print(f"获取GPU利用率失败: {e}")
time.sleep(5)
if utilizations:
avg_utilization = sum(utilizations) / len(utilizations)
self.results['avg_gpu_utilization'] = avg_utilization
self.results['gpu_check'] = 20 < avg_utilization < 80 # 利用率在合理范围内
print(f"平均GPU利用率: {avg_utilization:.1f}%")
return self.results['gpu_check']
else:
self.results['gpu_check'] = False
return False
def run_full_check(self):
"""运行完整检查"""
print("=" * 50)
print(f"全量上线检查 - {datetime.now()}")
print("=" * 50)
checks = [
("健康检查", self.check_health),
("延迟检查", self.check_latency),
("并发检查", self.check_concurrency),
("GPU检查", self.check_gpu_utilization)
]
all_passed = True
for check_name, check_func in checks:
print(f"\n执行 {check_name}...")
try:
passed = check_func()
status = "✓ 通过" if passed else "✗ 失败"
print(f"{check_name}: {status}")
all_passed = all_passed and passed
except Exception as e:
print(f"{check_name}: ✗ 异常 - {e}")
all_passed = False
print("\n" + "=" * 50)
print(f"检查结果: {'全部通过' if all_passed else '存在失败'}")
print(f"详细结果: {json.dumps(self.results, indent=2)}")
return all_passed
# 执行检查
if __name__ == "__main__":
validator = RolloutValidator()
if validator.run_full_check():
print("检查通过,可以全量上线!")
exit(0)
else:
print("检查失败,需要修复问题后再上线。")
exit(1)
5.3 全量上线执行流程
6. 不同规模场景的部署方案选型
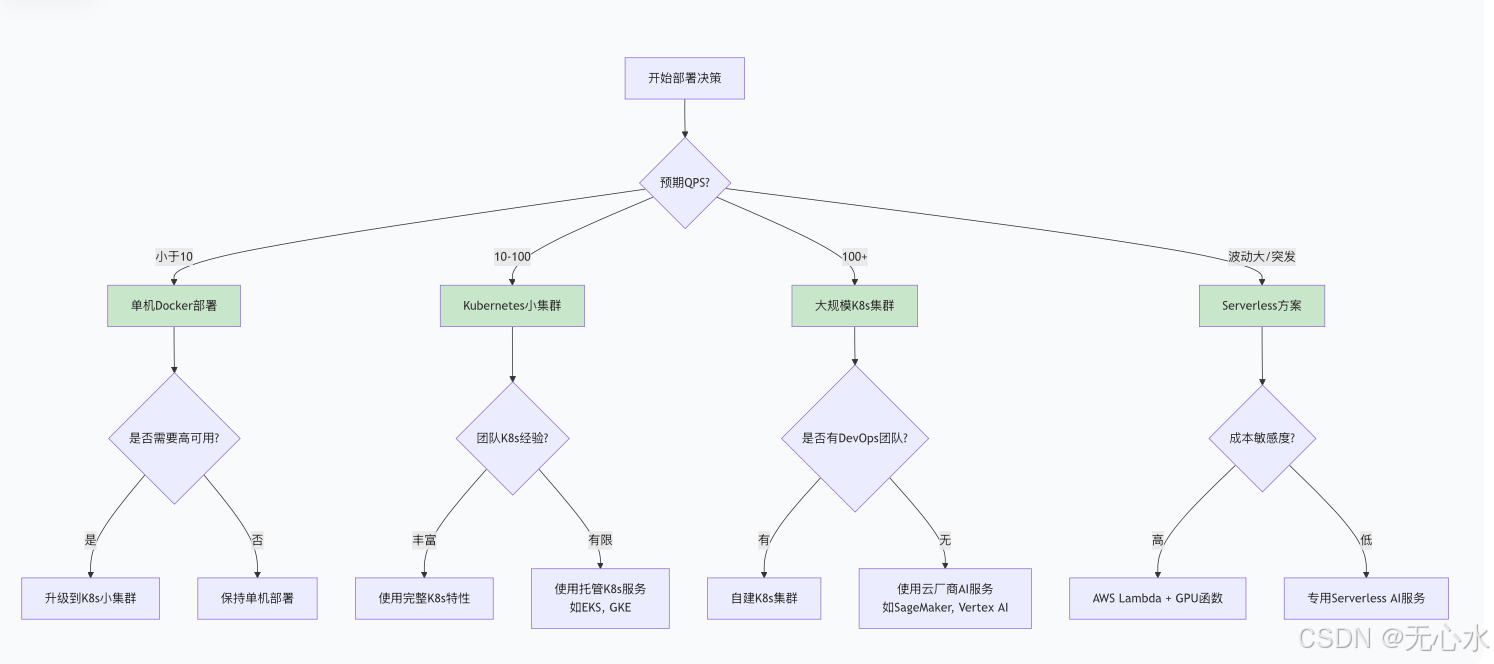
6.1 部署方案对比矩阵
| 维度 | 单机Docker部署 | Kubernetes小集群 | 大规模K8s集群 | Serverless函数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 适用场景 | 开发测试、小规模POC | 中小型企业、团队内部 | 大型企业、SaaS服务 | 突发流量、边缘计算 |
| GPU资源 | 单GPU或CPU | 2-8个GPU节点 | 数十至数百GPU | GPU函数实例 |
| 成本估算 | 最低 | 中等 | 较高 | 按使用量计费 |
| 部署复杂度 | 简单 | 中等 | 复杂 | 简单 |
| 可扩展性 | 差 | 良好 | 优秀 | 优秀 |
| 运维负担 | 低 | 中等 | 高 | 低 |
| 典型配置 | 1x A10/A100 | 4x A100节点 | 10+ A100/H100节点 | AWS Lambda + GPU |
| 适用模型 | SD 3.5 FP8 | SD 3.5 FP8 + 微调 | 多版本模型并行 | 轻量化SD模型 |
6.2 推荐方案
方案1:开发测试环境
# 单节点Docker Compose配置
version: '3.8'
services:
sd-inference:
image: sd-3.5-fp8:latest
deploy:
resources:
reservations:
devices:
- driver: nvidia
count: 1
capabilities: [gpu]
ports:
- "8080:8080"
volumes:
- ./models:/app/models
- ./cache:/root/.cache
environment:
- CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0
command: ["python3", "/app/python-service/main.py"]
方案2:中小企业生产环境
# Kubernetes轻量级配置
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
spec:
replicas: 2 # 两个副本提供高可用
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: sd-inference
image: sd-3.5-fp8:production
resources:
limits:
nvidia.com/gpu: 1
memory: "16Gi"
requests:
nvidia.com/gpu: 1
memory: "8Gi"
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
spec:
type: NodePort
方案3:大规模企业级部署
# 完整的K8s部署方案(如前文3.1节)
# 包括:
# 1. 多副本部署 + HPA
# 2. 负载均衡 + Ingress
# 3. 监控 + 日志收集
# 4. 持久化存储
# 5. 网络策略 + 安全配置
方案4:Serverless部署(AWS SageMaker示例)
# sagemaker_deployment.py
import sagemaker
from sagemaker.pytorch import PyTorchModel
from sagemaker.predictor import Predictor
class StableDiffusionEndpoint:
def __init__(self, model_path, role_arn):
self.model_path = model_path
self.role_arn = role_arn
def create_endpoint(self, instance_type="ml.g5.2xlarge"):
"""创建SageMaker端点"""
# 创建模型
model = PyTorchModel(
entry_point='inference.py',
source_dir='src',
model_data=self.model_path,
role=self.role_arn,
framework_version='2.0.0',
py_version='py310',
image_uri='763104351884.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/pytorch-inference:2.0.0-gpu-py310-cu118-ubuntu20.04-sagemaker'
)
# 部署端点
predictor = model.deploy(
initial_instance_count=1,
instance_type=instance_type,
endpoint_name='stable-diffusion-3.5-fp8',
wait=True
)
return predictor
def update_endpoint(self, new_model_path):
"""更新端点模型"""
# 创建新配置
new_model = PyTorchModel(
entry_point='inference.py',
source_dir='src',
model_data=new_model_path,
role=self.role_arn,
framework_version='2.0.0',
py_version='py310'
)
# 创建新端点配置
new_endpoint_config_name = f'sd-config-{int(time.time())}'
new_model.create(
name=new_endpoint_config_name,
instance_type='ml.g5.2xlarge',
initial_instance_count=1
)
# 更新端点
sagemaker_client = boto3.client('sagemaker')
sagemaker_client.update_endpoint(
EndpointName='stable-diffusion-3.5-fp8',
EndpointConfigName=new_endpoint_config_name
)
6.3 决策树:如何选择部署方案
7. 总结与最佳实践
通过本文的详细探讨,我们可以总结出Stable Diffusion 3.5 FP8工程化部署的核心要点:
7.1 关键成功因素
- 镜像优化:多阶段构建、合理分层、最小化体积
- 性能调优:TensorRT加速、预热机制、批处理优化
- 资源管理:GPU调度、内存限制、自动扩缩容
- 监控体系:全方位指标收集、智能告警、日志分析
- 部署策略:渐进式发布、金丝雀测试、快速回滚
7.2 避坑指南
- 避免在单个Pod中运行多个GPU密集型应用
- 不要将模型文件放在容器镜像内层(影响构建速度)
- 确保GPU驱动版本与CUDA版本兼容
- 测试不同批处理大小对性能的影响
- 监控显存泄漏和GPU内存碎片化
7.3 未来展望
随着AI模型部署技术的不断发展,未来趋势包括:
- 无服务器GPU计算的进一步成熟
- 混合精度推理的自动化优化
- 边缘AI部署的轻量化方案
- 多模型编排与智能路由
- 绿色计算与能效优化
Stable Diffusion 3.5 FP8的部署不仅仅是一个技术任务,更是一个系统工程。通过合理的架构设计、完善的运维体系和持续的优化迭代,才能确保AI模型在生产环境中稳定、高效地运行,真正发挥其商业价值。

























 632
632

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










