RabbitMQ提供了7中工作模式,来进行消息的传递。
官⽅⽂档:RabbitMQ Tutorials | RabbitMQ
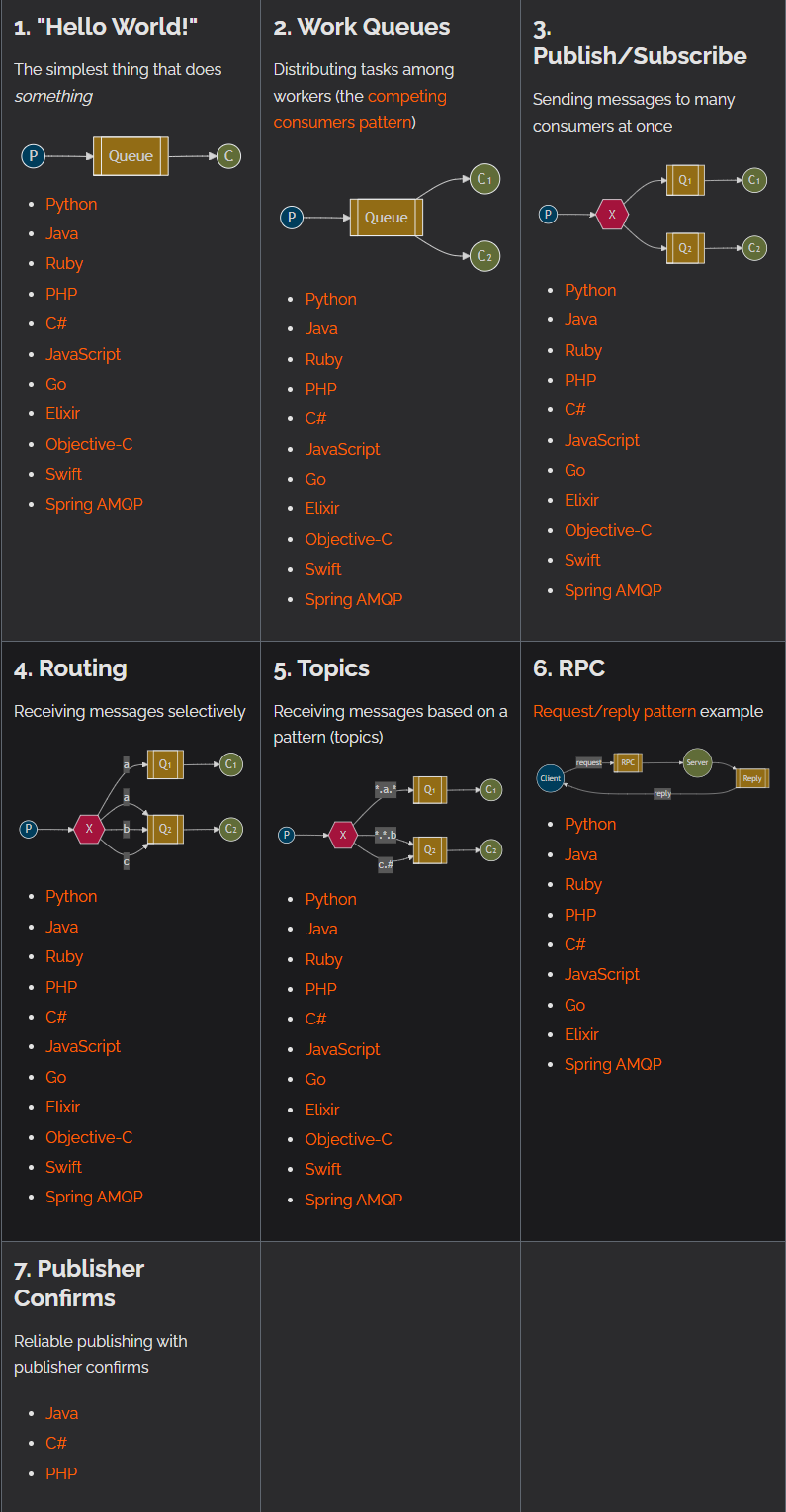
7种工作模式
Simple(简单模式)
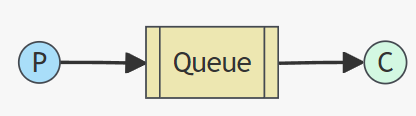
P: ⽣产者, 也就是要发送消息的程序
C: 消费者,消息的接收者
Queue: 消息队列, 可以缓存消息; ⽣产者向其中投递消息, 消费者从其中取出消息.
特点: ⼀个⽣产者P,⼀个消费者C, 消息只能被消费⼀次. 也称为点对点(Point-to-Point)模式.
适⽤场景: 消息只能被单个消费者处理
代码模拟:
生产者:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
//1.建立连接
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.setHost(ip地址);
connectionFactory.setPort(5672); //需提前开放端口号
connectionFactory.setUsername("admin");//账号
connectionFactory.setPassword("admin");//密码
connectionFactory.setVirtualHost("study");//虚拟主机
Connection connection = connectionFactory.newConnection();
//2.开启信道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//3.声明交换机 使用内置的交换机
//4.声明队列
/**
* Queue.DeclareOk queueDeclare(String queue, boolean durable, boolean exclusive, boolean autoDelete,
* Map<String, Object> arguments) throws IOException;
*
* 参数说明:
* queue:队列名称
* durable:可持久化
* exclusive:是否独占
* autoDelete:是否自动删除
* arguments:额外参数
*/
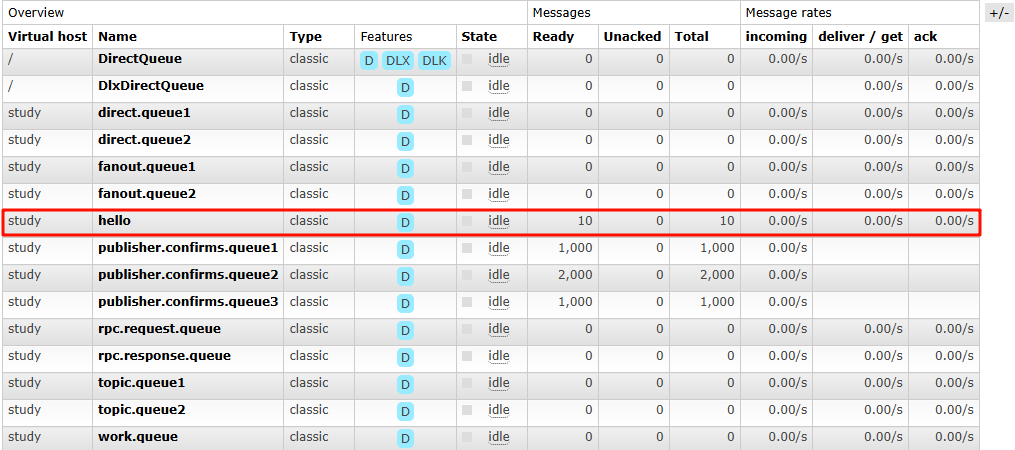
channel.queueDeclare("hello",true,false,false,null);
//5.发消息
/**
* void basicPublish(String exchange, String routingKey, BasicProperties props, byte[] body) throws IOException;
*
* 参数声明:
* exchange:交换机名称,不写代表使用内置交换机
* routingKey:路由名称, routingKey = 队列名称 (使用内置交换机,routingKey与队列名称保持一致)
* props:属性配置
* body:消息
*/
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
String msg = "hello rabbitmq ~" + i;
channel.basicPublish("","hello",null,msg.getBytes());
}
System.out.println("消息发送成功~");
//6.资源释放
channel.close();
connection.close();
}
消费者:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException, InterruptedException {
//1.建立链接
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.setHost(ip地址);
connectionFactory.setPort(5672);
connectionFactory.setUsername("admin");
connectionFactory.setPassword("admin");
connectionFactory.setVirtualHost("study");
Connection connection = connectionFactory.newConnection();
//2.创建Channel
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//3.声明队列(可以省略)
channel.queueDeclare("hello",true,false,false,null);
//4.消费消息
DefaultConsumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel){
//从队列中收到消息,就会执行的方法
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println("接收到消息: " + new String(body));
}
};
/**
* String basicConsume(String queue, boolean autoAck, Consumer callback) throws IOException;
* 参数说明:
* queue:队列名称
* autoAck:是否自动确认
* callback:接收到消息后,执行的逻辑
*/
channel.basicConsume("hello",true,consumer);
//等待程序完成
Thread.sleep(5000);
//5.释放资源
channel.close();
connection.close();
}
接收到消息: hello rabbitmq ~0
接收到消息: hello rabbitmq ~1
接收到消息: hello rabbitmq ~2
接收到消息: hello rabbitmq ~3
接收到消息: hello rabbitmq ~4
接收到消息: hello rabbitmq ~5
接收到消息: hello rabbitmq ~6
接收到消息: hello rabbitmq ~7
接收到消息: hello rabbitmq ~8
接收到消息: hello rabbitmq ~9
Work Queue(⼯作队列)
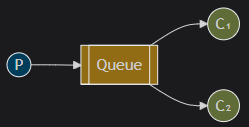
⼀个⽣产者P,多个消费者C1,C2. 在多个消息的情况下, Work Queue 会将消息分派给不同的消费者,
每个消费者都会接收到不同的消息.
特点: 消息不会重复, 分配给不同的消费者.
适⽤场景: 集群环境中做异步处理
代码模拟:
生产者:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
//1.建立连接
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.setHost(Constants.HOST);
connectionFactory.setPort(Constants.PORT);
connectionFactory.setUsername(Constants.USER_NAME);
connectionFactory.setPassword(Constants.PASSWORD);
connectionFactory.setVirtualHost(Constants.VIRTUAL_HOST);
Connection connection = connectionFactory.newConnection();
//2.创建channel
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//3.声明队列 使用内置交换机
// 如果队列不存在 ,则创建,如果队列存在,则不创建
channel.queueDeclare(Constants.WORK_QUEUE,true,false,false,null);
//4.发送消息
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
String msg = "hello work queue ...." + i;
channel.basicPublish("", Constants.WORK_QUEUE,null,msg.getBytes());
}
System.out.println("发送消息成功!");
//6.释放资源
channel.close();
connection.close();
}
消费者1:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
//1.建立连接
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.setHost(Constants.HOST);
connectionFactory.setPort(Constants.PORT);
connectionFactory.setUsername(Constants.USER_NAME);
connectionFactory.setPassword(Constants.PASSWORD);
connectionFactory.setVirtualHost(Constants.VIRTUAL_HOST);
Connection connection = connectionFactory.newConnection();
//2.创建管道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//3.声明队列 使用内置交换机
//如果队列不存在,则创建
channel.queueDeclare(Constants.WORK_QUEUE,true,false,false,null);
//4.消费消息
DefaultConsumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel){
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println("接收到消息:" + new String(body));
}
};
channel.basicConsume(Constants.WORK_QUEUE,true,consumer);
//6.释放资源
/* channel.close();
connection.close();*/
}
接收到消息:hello work queue ....0
接收到消息:hello work queue ....2
接收到消息:hello work queue ....4
接收到消息:hello work queue ....6
接收到消息:hello work queue ....8
消费者2:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
//1.建立连接
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.setHost(Constants.HOST);
connectionFactory.setPort(Constants.PORT);
connectionFactory.setUsername(Constants.USER_NAME);
connectionFactory.setPassword(Constants.PASSWORD);
connectionFactory.setVirtualHost(Constants.VIRTUAL_HOST);
Connection connection = connectionFactory.newConnection();
//2.创建管道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//3.声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(Constants.WORK_QUEUE,true,false,false,null);
//4.消费消息
DefaultConsumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel){
//从队列中收到消息,就会执行的方法
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println("接收到消息:" + new String(body));
}
};
channel.basicConsume(Constants.WORK_QUEUE,true,consumer);
//6.释放资源
/* channel.close();
connection.close();*/
}
接收到消息:hello work queue ....1
接收到消息:hello work queue ....3
接收到消息:hello work queue ....5
接收到消息:hello work queue ....7
接收到消息:hello work queue ....9
Publish/Subscribe(发布/订阅)
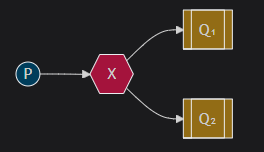
图中X表⽰交换机.
Exchange: 交换机 (X).只负责转发消息, 不具备存储消息的能⼒,
作⽤: ⽣产者将消息发送到Exchange, 由交换机将消息按⼀定规则路由到⼀个或多个队列中。
RabbitMQ交换机有四种类型: fanout,direct, topic, headers, 不同类型有着不同的路由策略.
1.Fanout:⼴播,将消息交给所有绑定到交换机的队列(Publish/Subscribe模式)
Direct:定向,把消息交给符合指定routing key的队列(Routing模式)
Topic:通配符,把消息交给符合routing pattern(路由模式)的队列(Topics模式)
headers类型的交换器不依赖于路由键的匹配规则来路由消息, ⽽是根据发送的消息内容中的headers属性进⾏匹配. headers类型的交换器性能会很差,⽽且也不实⽤,基本上不会看到它的存在
RoutingKey: 路由键.⽣产者将消息发给交换器时, 指定的⼀个字符串, ⽤来告诉交换机应该如何处理这
个消息.
**Binding Key:**绑定. RabbitMQ中通过Binding(绑定)将交换器与队列关联起来, 在绑定的时候⼀般会指
定⼀个Binding Key, 这样RabbitMQ就知道如何正确地将消息路由到队列了.
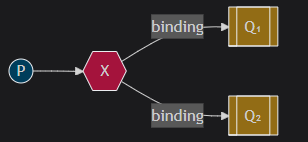
适合场景: 消息需要被多个消费者同时接收的场景. 如: 实时通知或者⼴播消息。
代码模拟:
生产者:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
//1.建立连接
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.setHost(Constants.HOST);
connectionFactory.setPort(Constants.PORT);
connectionFactory.setUsername(Constants.USER_NAME);
connectionFactory.setPassword(Constants.PASSWORD);
connectionFactory.setVirtualHost(Constants.VIRTUAL_HOST);
Connection connection = connectionFactory.newConnection();
//2.创建信道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//3.声明交换机
channel.exchangeDeclare(Constants.FANOUT_EXCHANGE, BuiltinExchangeType.FANOUT,true);
//4.声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(Constants.FANOUT_QUEUE1,true,false,false,null);
channel.queueDeclare(Constants.FANOUT_QUEUE2,true,false,false,null);
//5.交换机和队列绑定
channel.queueBind(Constants.FANOUT_QUEUE1,Constants.FANOUT_EXCHANGE,"");
channel.queueBind(Constants.FANOUT_QUEUE2,Constants.FANOUT_EXCHANGE,"");
//6.发布消息
String msg = "hello fanout....";
channel.basicPublish(Constants.FANOUT_EXCHANGE,"",null,msg.getBytes());
System.out.println("消息发送成功");
//7.释放资源
channel.close();
connection.close();
}
消费者1:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
//1.建立连接
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.setHost(Constants.HOST);
connectionFactory.setPort(Constants.PORT);
connectionFactory.setUsername(Constants.USER_NAME);
connectionFactory.setPassword(Constants.PASSWORD);
connectionFactory.setVirtualHost(Constants.VIRTUAL_HOST);
Connection connection = connectionFactory.newConnection();
//2.创建信道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//3.声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(Constants.FANOUT_QUEUE1,true,false,false,null);
//4.消费消息
DefaultConsumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel){
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println("接收到消息:" + new String(body));
}
};
channel.basicConsume(Constants.FANOUT_QUEUE1,true,consumer);
}
接收到消息:hello fanout....
消费者2:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
//1.建立连接
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.setHost(Constants.HOST);
connectionFactory.setPort(Constants.PORT);
connectionFactory.setUsername(Constants.USER_NAME);
connectionFactory.setPassword(Constants.PASSWORD);
connectionFactory.setVirtualHost(Constants.VIRTUAL_HOST);
Connection connection = connectionFactory.newConnection();
//2.创建信道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//3.声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(Constants.FANOUT_QUEUE2,true,false,false,null);
//4.消费消息
DefaultConsumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel){
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println("接收到消息:" + new String(body));
}
};
channel.basicConsume(Constants.FANOUT_QUEUE2,true,consumer);
}
接收到消息:hello fanout....
Routing(路由模式)
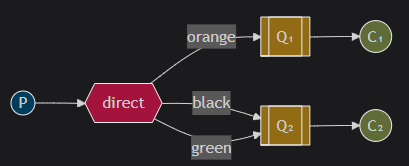
路由模式是发布订阅模式的变种, 在发布订阅基础上, 增加路由key
发布订阅模式是⽆条件的将所有消息分发给所有消费者, 路由模式是Exchange根据RoutingKey的规则,
将数据筛选后发给对应的消费者队列
适合场景: 需要根据特定规则分发消息的场景.
代码模拟:
生产者:
/**/public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
//1.建立连接
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.setHost(Constants.HOST);
connectionFactory.setPort(Constants.PORT);
connectionFactory.setUsername(Constants.USER_NAME);
connectionFactory.setPassword(Constants.PASSWORD);
connectionFactory.setVirtualHost(Constants.VIRTUAL_HOST);
Connection connection = connectionFactory.newConnection();
//2.创建信道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//3.声明交换机
channel.exchangeDeclare(Constants.DIRECT_EXCHANGE, BuiltinExchangeType.DIRECT,true);
//4.声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(Constants.DIRECT_QUEUE1,true,false,false,null);
channel.queueDeclare(Constants.DIRECT_QUEUE2,true,false,false,null);
//5.绑定交换机和队列
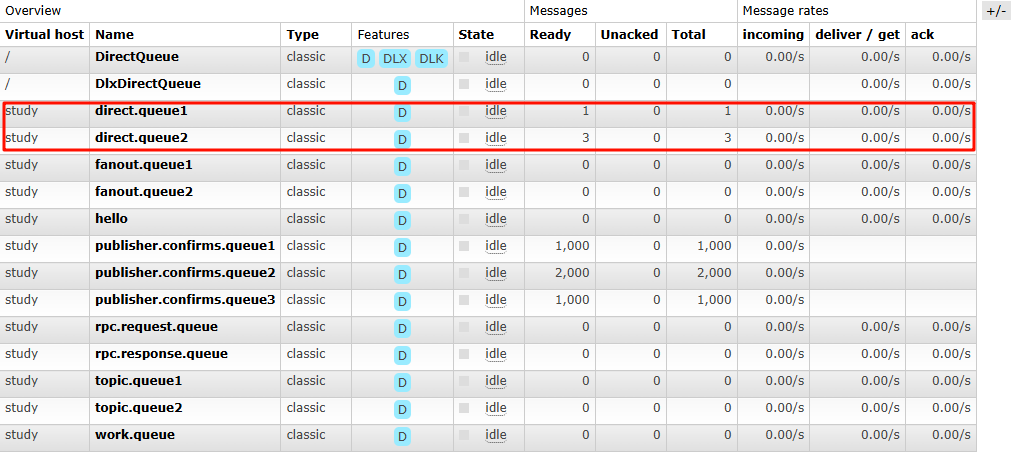
channel.queueBind(Constants.DIRECT_QUEUE1,Constants.DIRECT_EXCHANGE,"a");
channel.queueBind(Constants.DIRECT_QUEUE2,Constants.DIRECT_EXCHANGE,"a");
channel.queueBind(Constants.DIRECT_QUEUE2,Constants.DIRECT_EXCHANGE,"b");
channel.queueBind(Constants.DIRECT_QUEUE2,Constants.DIRECT_EXCHANGE,"c");
//6.发送消息
String msg_a = "hello direct, my routingkey is a .... ";
channel.basicPublish(Constants.DIRECT_EXCHANGE,"a",null,msg_a.getBytes());
String msg_b = "hello direct, my routingkey is b .... ";
channel.basicPublish(Constants.DIRECT_EXCHANGE,"b",null,msg_b.getBytes());
String msg_c = "hello direct, my routingkey is c .... ";
channel.basicPublish(Constants.DIRECT_EXCHANGE,"c",null,msg_c.getBytes());
System.out.println("发送消息成功");
//7.释放资源
channel.close();
connection.close();
}
消费者1:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
//1.建立连接
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.setHost(Constants.HOST);
connectionFactory.setPort(Constants.PORT);
connectionFactory.setUsername(Constants.USER_NAME);
connectionFactory.setPassword(Constants.PASSWORD);
connectionFactory.setVirtualHost(Constants.VIRTUAL_HOST);
Connection connection = connectionFactory.newConnection();
//2.开启信道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//3.声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(Constants.DIRECT_QUEUE1,true,false,false,null);
//4.消费消息
DefaultConsumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel){
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println("接收到消息: " + new String(body));
}
};
channel.basicConsume(Constants.DIRECT_QUEUE1,true,consumer);
}
接收到消息: hello direct, my routingkey is a ....
消费者2:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
//1.建立连接
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.setHost(Constants.HOST);
connectionFactory.setPort(Constants.PORT);
connectionFactory.setUsername(Constants.USER_NAME);
connectionFactory.setPassword(Constants.PASSWORD);
connectionFactory.setVirtualHost(Constants.VIRTUAL_HOST);
Connection connection = connectionFactory.newConnection();
//2.开启信道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//3.声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(Constants.DIRECT_QUEUE2,true,false,false,null);
//4.消费消息
DefaultConsumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel){
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println("接收到消息: " + new String(body));
}
};
channel.basicConsume(Constants.DIRECT_QUEUE2,true,consumer);
}
接收到消息: hello direct, my routingkey is a ....
接收到消息: hello direct, my routingkey is b ....
接收到消息: hello direct, my routingkey is c ....
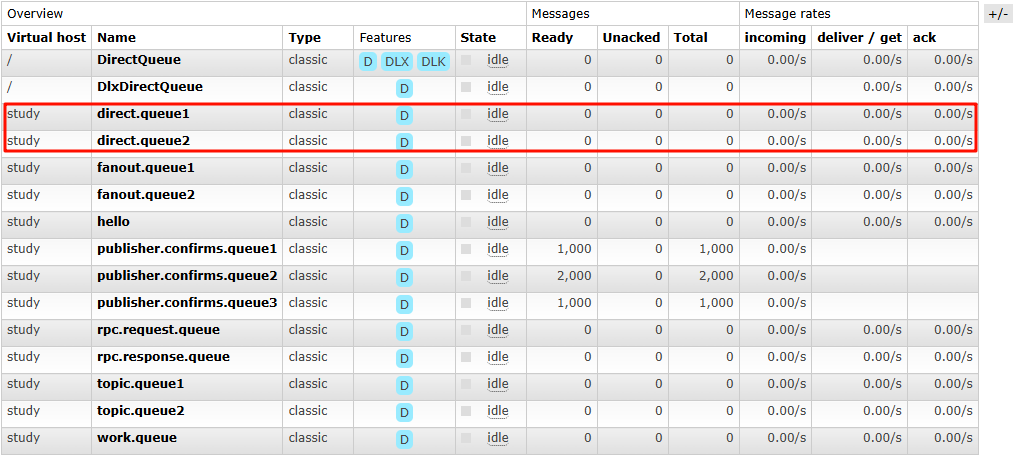
Topics(通配符模式)
路由模式的升级版, 在routingKey的基础上,增加了通配符的功能。
不同之处是:routingKey的匹配⽅式不同,Routing模式是相等匹配,topics模式是通配符匹配。
适合场景: 需要灵活匹配和过滤消息的场景。
代码模拟:
生产者:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
//1.建立连接
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.setHost(Constants.HOST);
connectionFactory.setPort(Constants.PORT);
connectionFactory.setUsername(Constants.USER_NAME);
connectionFactory.setPassword(Constants.PASSWORD);
connectionFactory.setVirtualHost(Constants.VIRTUAL_HOST);
Connection connection = connectionFactory.newConnection();
//2.开启信道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//3.声明交换机
channel.exchangeDeclare(Constants.TOPIC_EXCHANGE, BuiltinExchangeType.TOPIC,true);
//4.声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(Constants.TOPIC_QUEUE1,true,false,false,null);
channel.queueDeclare(Constants.TOPIC_QUEUE2,true,false,false,null);
//5.绑定交换机和队列
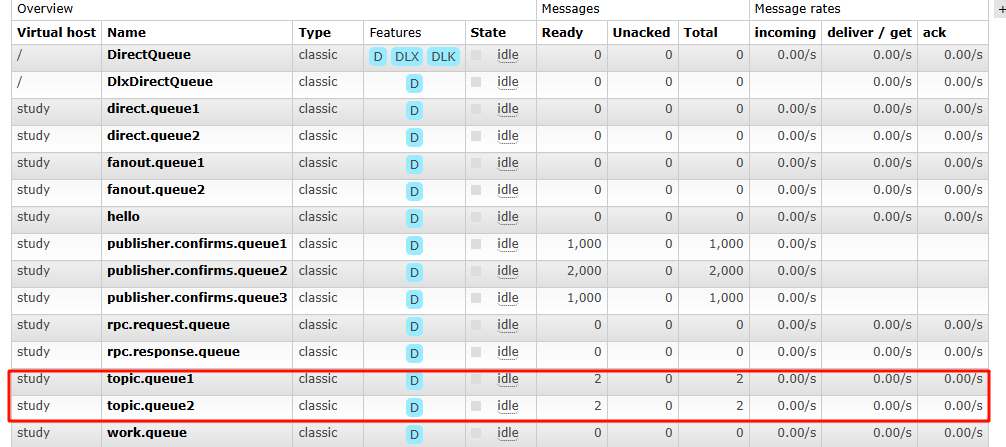
channel.queueBind(Constants.TOPIC_QUEUE1,Constants.TOPIC_EXCHANGE,"*.a.*");
channel.queueBind(Constants.TOPIC_QUEUE2,Constants.TOPIC_EXCHANGE,"*.*.b");
channel.queueBind(Constants.TOPIC_QUEUE2,Constants.TOPIC_EXCHANGE,"c.#");
//6.发送消息
String msg = "hello topic , my routingkey is ae.a.f...";
channel.basicPublish(Constants.TOPIC_EXCHANGE,"ae.a.f",null,msg.getBytes());
String msg_b = "hello topic , my routingkey is ef.a.b...";
channel.basicPublish(Constants.TOPIC_EXCHANGE,"ef.a.b",null,msg_b.getBytes());
String msg_c = "hello topic , my routingkey is c.ef.d...";
channel.basicPublish(Constants.TOPIC_EXCHANGE,"c.ef.d",null,msg_c.getBytes());
System.out.println("发送消息成功");
//7.释放资源
channel.close();
connection.close();
}
消费者1:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
//1.建立连接
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.setHost(Constants.HOST);
connectionFactory.setPort(Constants.PORT);
connectionFactory.setUsername(Constants.USER_NAME);
connectionFactory.setPassword(Constants.PASSWORD);
connectionFactory.setVirtualHost(Constants.VIRTUAL_HOST);
Connection connection = connectionFactory.newConnection();
//2.开启信道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//3.声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(Constants.TOPIC_QUEUE1,true,false,false,null);
//4.消费消息
DefaultConsumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel){
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println("接收到消息: " + new String(body));
}
};
channel.basicConsume(Constants.TOPIC_QUEUE1,true,consumer);
}
接收到消息: hello topic , my routingkey is ae.a.f...
接收到消息: hello topic , my routingkey is ef.a.b...
消费者2:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
//1.建立连接
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.setHost(Constants.HOST);
connectionFactory.setPort(Constants.PORT);
connectionFactory.setUsername(Constants.USER_NAME);
connectionFactory.setPassword(Constants.PASSWORD);
connectionFactory.setVirtualHost(Constants.VIRTUAL_HOST);
Connection connection = connectionFactory.newConnection();
//2.开启信道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//3.声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(Constants.TOPIC_QUEUE2,true,false,false,null);
//4.消费消息
DefaultConsumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel){
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println("接收到消息: " + new String(body));
}
};
channel.basicConsume(Constants.TOPIC_QUEUE2,true,consumer);
}
接收到消息: hello topic , my routingkey is ef.a.b...
接收到消息: hello topic , my routingkey is c.ef.d...
RPC(RPC通信)
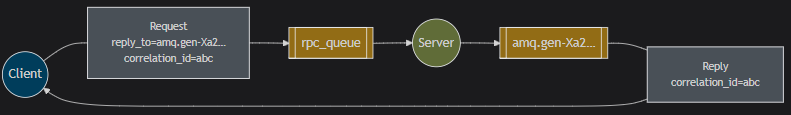
在RPC通信的过程中, 没有⽣产者和消费者, ⽐较像咱们RPC远程调⽤, ⼤概就是通过两个队列实现了⼀
个可回调的过程.
具体过程:
- 客⼾端发送消息到⼀个指定的队列, 并在消息属性中设置replyTo字段, 这个字段指定了⼀个回调队列, ⽤于接收服务端的响应.
- 服务端接收到请求后, 处理请求并发送响应消息到replyTo指定的回调队列
- 客⼾端在回调队列上等待响应消息. ⼀旦收到响应,客⼾端会检查消息的correlationId属性,以 确保它是所期望的响应
代码模拟:
客户端:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException, InterruptedException {
//1.建立连接
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.setHost(Constants.HOST);
connectionFactory.setPort(Constants.PORT);
connectionFactory.setUsername(Constants.USER_NAME);
connectionFactory.setPassword(Constants.PASSWORD);
connectionFactory.setVirtualHost(Constants.VIRTUAL_HOST);
Connection connection = connectionFactory.newConnection();
//2.开启信道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
channel.queueDeclare(Constants.RPC_REQUEST_QUEUE,true,false,false,null);
channel.queueDeclare(Constants.RPC_RESPONSE_QUEUE,true,false,false,null);
//3.发送请求
String msg = "hello , rpc...";
//设置请求的唯一标识
String correlationID = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
//设置请求的相关属性
AMQP.BasicProperties properties = new AMQP.BasicProperties().builder()
.correlationId(correlationID)
.replyTo(Constants.RPC_RESPONSE_QUEUE)
.build();
channel.basicPublish("",Constants.RPC_REQUEST_QUEUE,properties,msg.getBytes());
//4.接收响应
//使用阻塞队列,来储存响应信息
final BlockingQueue<String> response = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(1);
DefaultConsumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel){
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
String respMsg = new String(body);
System.out.println("j接收回调消息:" + respMsg);
if (correlationID.equals(properties.getCorrelationId())){
//如果correlationID 校验一致
response.add(respMsg);
}
}
};
channel.basicConsume(Constants.RPC_RESPONSE_QUEUE,true,consumer);
String result = response.take();
System.out.println("[RPC CLIENT 响应结果]: " + result);
}
服务器:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
//1.建立连接
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.setHost(Constants.HOST);
connectionFactory.setPort(Constants.PORT);
connectionFactory.setUsername(Constants.USER_NAME);
connectionFactory.setPassword(Constants.PASSWORD);
connectionFactory.setVirtualHost(Constants.VIRTUAL_HOST);
Connection connection = connectionFactory.newConnection();
//2.开启信道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//3.接收请求
DefaultConsumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel){
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
String request = new String(body,"UTF-8");
System.out.println("接收到请求" + request);
String response = "针对request:" + request + ",相应成功";
AMQP.BasicProperties basicProperties = new AMQP.BasicProperties().builder()
.correlationId(properties.getCorrelationId())
.build();
channel.basicPublish("",Constants.RPC_RESPONSE_QUEUE,basicProperties,response.getBytes());
channel.basicAck(envelope.getDeliveryTag(), false);
}
};
channel.basicConsume(Constants.RPC_REQUEST_QUEUE,true,consumer);
}
接收到请求hello , rpc...
client:
j接收回调消息:针对request:hello , rpc...,相应成功
[RPC CLIENT 响应结果]: 针对request:hello , rpc...,相应成功
Publisher Confirms(发布确认)
Publisher Confirms模式是RabbitMQ提供的⼀种确保消息可靠发送到RabbitMQ服务器的机制。
⽣产者可以等待RabbitMQ服务器的确认,以确保消息已经被服务器接收并处理。
⽣产者将信道设置成confirm(确认)模式, ⼀旦信道进⼊confirm模式, 所有在该信道上⾯发布的消息都
会被指派⼀个唯⼀的ID(从1开始), ⼀旦消息被投递到所有匹配的队列之后, RabbitMQ就会发送⼀个
认给⽣产者(包含消息的唯⼀ID), 这就使得⽣产者知道消息已经正确到达⽬的队列了, 如果消息和队
是可持久化的, 那么确认消息会在将消息写⼊磁盘之后发出. broker回传给⽣产者的确认消息中。
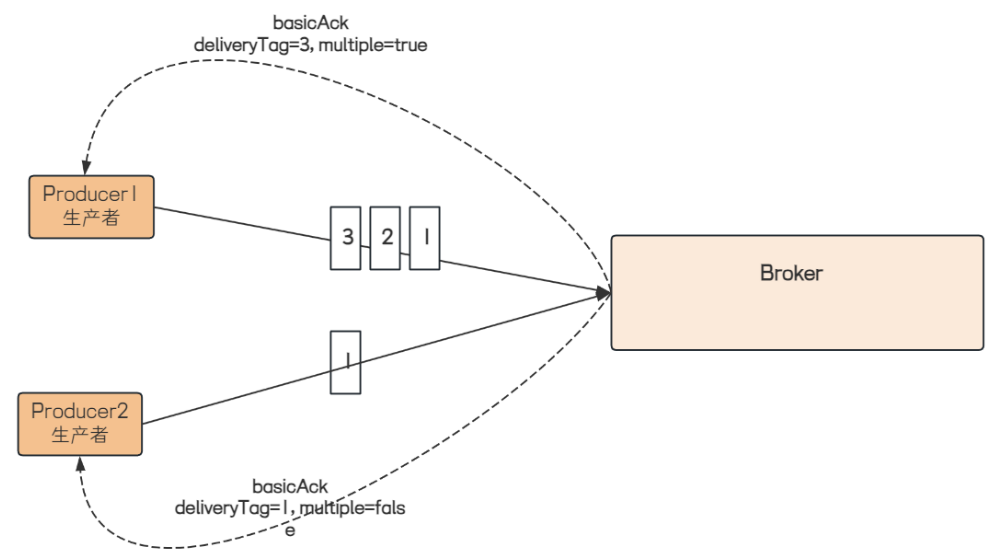
deliveryTag 包含了确认消息的序号, 此外 broker 也可以设置channel.basicAck⽅法中的multiple参
数, 表⽰到这个序号之前的所有消息都已经得到了处理。
发送⽅确认机制最⼤的好处在于它是异步的, ⽣产者可以同时发布消息和等待信道返回确认消息.
- 当消息最终得到确认之后, ⽣产者可以通过回调⽅法来处理该确认消息.
- 如果RabbitMQ因为⾃⾝内部错误导致消息丢失, 就会发送⼀条nack(Basic.Nack)命令, ⽣产者同样 可以在回调⽅法中处理该nack命令。




















 1667
1667

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








