最佳实践(Feign的使用方法)
最佳实践, 其实也就是经过历史的迭代, 在项⽬中的实践过程中, 总结出来的最好的使⽤⽅式.
通过观察, 我们也能看出来, Feign的客⼾端与服务提供者的controller代码⾮常相似.
Feign 客⼾端:
@FeignClient(value = "product-service", path = "/product")
public interface ProductApi {
@RequestMapping("/{productId}")
ProductInfo getProductById(@PathVariable("productId") Integer productId);
}
服务提供⽅Controller
@RequestMapping("/product")
@RestController
public class ProductController {
@RequestMapping("/{productId}")
public ProductInfo getProductById(@PathVariable("productId") Integer
productId){
//...
}
}
有没有⼀种⽅法可以简化这种写法呢?
方案一:Feign 继承⽅式
官⽅推荐Feign的使⽤⽅式为继承的⽅式, 但是企业开发中, 更多是把Feign接⼝抽取为⼀个独⽴的模块
(做法和继承相似, 但理念不同).
操作⽅法:
将Feign的Client抽取为⼀个独⽴的模块, 并把涉及到的实体类等都放在这个模块中, 打成⼀个Jar. 服务
消费⽅只需要依赖该Jar包即可. 这种⽅式在企业中⽐较常⻅, Jar包通常由服务提供⽅来实现.
1.创建⼀个module:
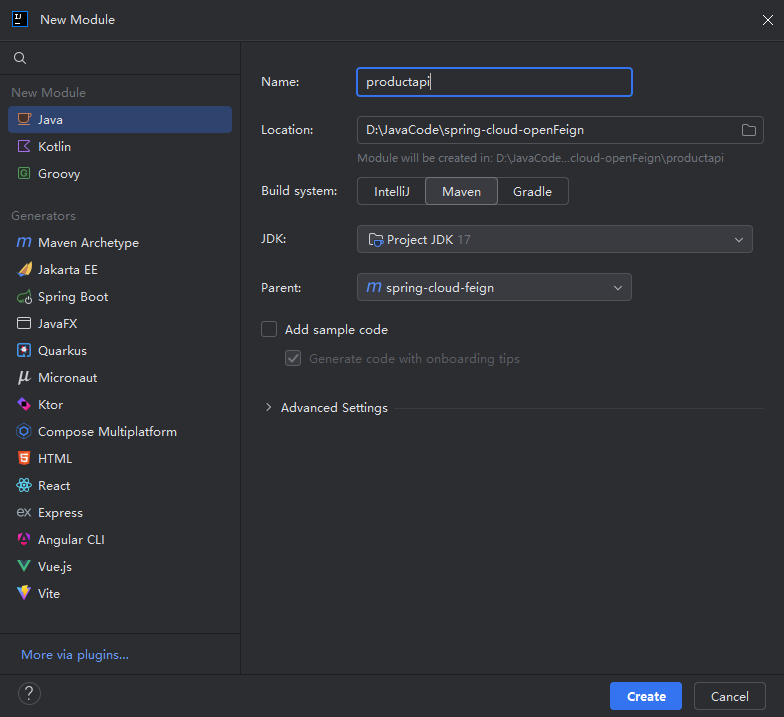
2.引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId>
</dependency>
3.编写接⼝
public interface ProductInterface {
@RequestMapping("/{productId}")
ProductInfo getProductInfo(@PathVariable("productId") Integer productId);
@RequestMapping("/p1")
String p1(@RequestParam("id") Integer id);
@RequestMapping("/p2")
String p2(@RequestParam("id") Integer id,@RequestParam("name") String name);
@RequestMapping("/p3")
String p3(@SpringQueryMap ProductInfo productInfo);
@RequestMapping("/p4")
String p4(@RequestBody ProductInfo productInfo);
}
相当于把ProductApi 和 ProductInfo 搬到 product-api 这个model里
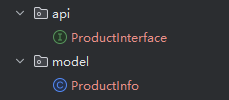
4.打jar包
通过Maven打包
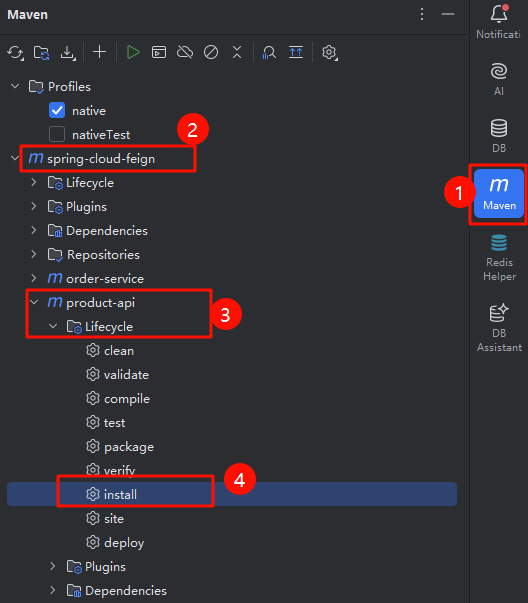
install:把当前工程打成 jar 包,放在maven本地仓库(不是远程仓库)
下面这个样子就代表打包成功,
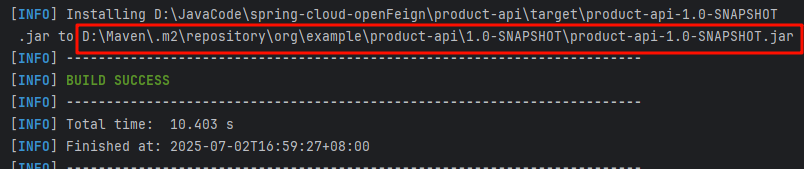
我们在复制包的路径看是否存在
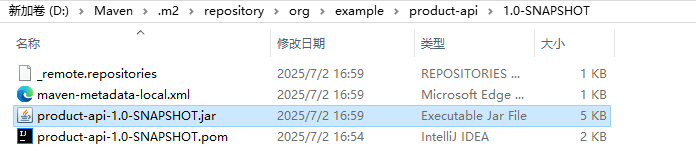
5.修改服务提供⽅代码
服务提供⽅实现接⼝ ProductInterface
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/product")
public class ProductController implements ProductInterface {
@Autowired
private ProductService productService;
@RequestMapping("/{productId}")
public ProductInfo getProductById(@PathVariable("productId") Integer productId){
return productService.selectProductById(productId);
}
@RequestMapping("/p1")
public String p1(Integer id){
return "product-service 接收到的参数,id=" + id;
}
@RequestMapping("/p2")
public String p2(Integer id,String name){
return "product-service 接收到的参数,id=" + id + "name = " + name;
}
@RequestMapping("/p3")
public String p3(ProductInfo productInfo){
return "product-service 接收到的参数 productInfo = " + productInfo.toString();
}
@RequestMapping("/p4")
public String p4(@RequestBody ProductInfo productInfo){
return "product-service 接收到的参数 productInfo = " + productInfo.toString();
}
}
由于我们要是用ProductInterface这个接口,刚才已经把product-api这个model已经达成jar包了,我们就可以把jar包引入,从而就可以实现ProductInterface接口了。
ProductInfo这个实体类也是,product-api里已经存在这个实体类了,那么product-service里的就可以删除了。
使用快捷键,按住 alt + 回车(enter),可以快速引入我们需要的jar包。
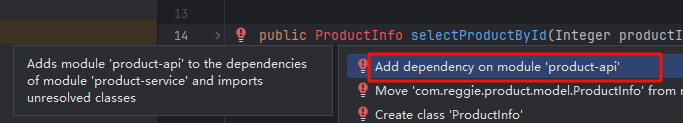
成功引入我们刚才创建好的jar包。
6.修改服务消费⽅
服务消费⽅继承ProductInterface
@FeignClient(value = "product-service" , path = "/product")
public interface ProductApi extends ProductInterface {
}
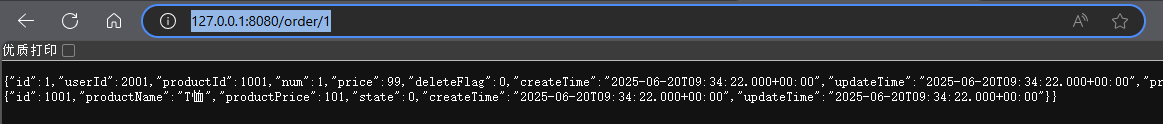
7.测试
方案二:Feign 抽取⽅式(抽取的模块,通常是由服务的提供方来写)
官⽅推荐Feign的使⽤⽅式为继承的⽅式, 但是企业开发中, 更多是把Feign接⼝抽取为⼀个独⽴的模块
(做法和继承相似, 但理念不同).
继承:在使用的时候仍需要再声明一个 Feign 的接口(ProductApi)
操作⽅法:
将Feign的Client抽取为⼀个独⽴的模块, 并把涉及到的实体类等都放在这个模块中, 打成⼀个Jar. 服务
消费⽅只需要依赖该Jar包即可. 这种⽅式在企业中⽐较常⻅, Jar包通常由服务提供⽅来实现.
1.创建一个model
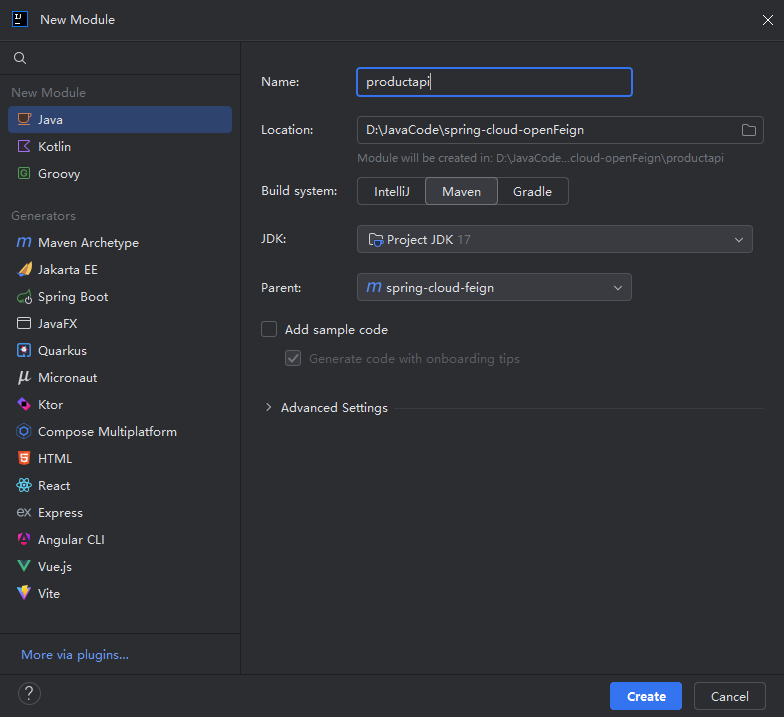
2.引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId>
</dependency>
3.完成抽取
把order-service模块里的 ProductApi 和 ProductInfo 抽取到 product-api。
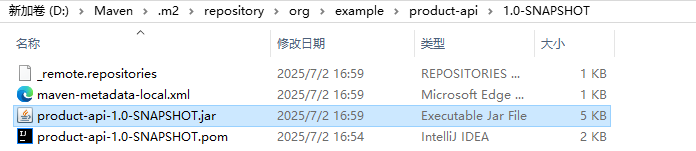
4.打包 install
通过Maven打包
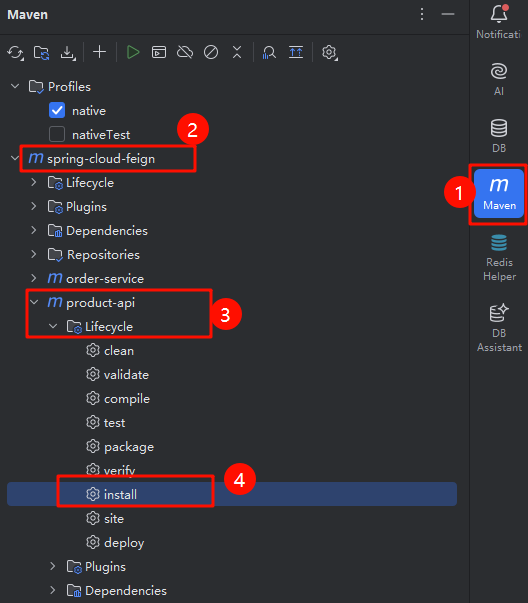
install:把当前工程打成 jar 包,放在maven本地仓库(不是远程仓库)
下面这个样子就代表打包成功,
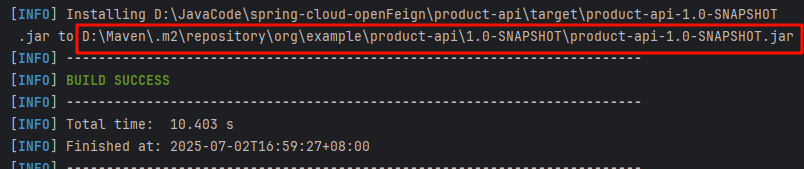
我们在复制包的路径看是否存在
5.服务调用方,引入抽取出来的模块(order-service)
- 删除 ProductApi, ProductInfo
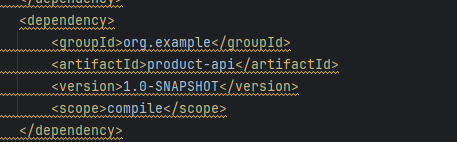
- 引⼊依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<artifactId>product-api</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
修改项⽬中ProductApi, ProductInfo的路径为product-api中的路径
- 指定扫描类: ProductApi(最重要,必不可少)
由于我们进行了抽取,ProductApi就属于第三方的了,我们又需要依赖注入@Autowired ,而我们的扫描路径只能扫描启动类的同一级文件及子文件,所以为了能够成功注入ProductApi我们需要 在启动类添加扫描路径
@EnableFeignClients(basePackages = {"com.bite.api"})
完整代码
@EnableFeignClients(basePackages = {"com.bite.api"})
@SpringBootApplication
public class OrderServiceApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(OrderServiceApplication.class, args);
}
}
或者也可以指定需要加载的Feign客⼾端(通过@EnableFeignClients(clients = {ProductApi.class}))
@EnableFeignClients(clients = {ProductApi.class})
@SpringBootApplication
public class OrderServiceApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(OrderServiceApplication.class,args);
}
}
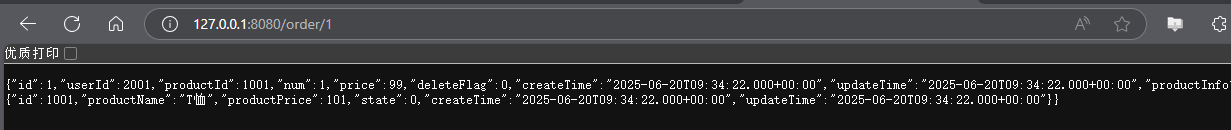
6.测试




















 1716
1716

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








