
在 Spring 框架中,Bean 的生命周期是指从 Bean 的创建到销毁的整个过程,Spring 容器负责管理 Bean 的整个生命周期。
完整生命周期:实例化 -> 属性赋值 -> BeanPostProcessor 的前置处理 -> 初始化 -> BeanPostProcessor 的后置处理 -> 使用 -> 销毁。
在整个生命周期中,
BeanPostProcessor可以在初始化前后修改Bean的实例,为扩展和自定义Spring的行为提供了强大的功能。初始化和销毁方法可以通过多种方式指定,可以根据项目需求和编码风格选择合适的方式。
通过掌握Bean的生命周期,可以在不同阶段对Bean进行自定义操作,确保资源的正确使用和释放,以及利用 BeanPostProcessor 实现一些高级功能,如 AOP 代理等。理解Bean的生命周期有助于更好地管理Bean的创建、使用和释放资源,同时也有助于理解Spring框架的内部工作原理,为开发更健壮、可维护的Spring应用程序打下基础。
文章目录
- 一、总结 Bean 生命周期的阶段
- 二、分解 Bean 生命周期的阶段
- 01、实例化(Instantiation)
- 02、属性赋值(Populate Properties)
- 03、BeanNameAware.setBeanName()
- 04、BeanFactoryAware.setBeanFactory()
- 05、ApplicationContextAware.setApplicationContext()
- 06、前置处理:BeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization()
- 07、@PostConstruct 或 InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet()
- 08、自定义初始化方法(init-method)
- 09、后置处理:BeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization(),
- 10、Bean的使用
- 11、@PreDestroy 或 DisposableBean.destroy()
- 12、自定义销毁方法(destroy-method)
- 13、垃圾回收(Garbage Collection)
- 三、整体示例代码
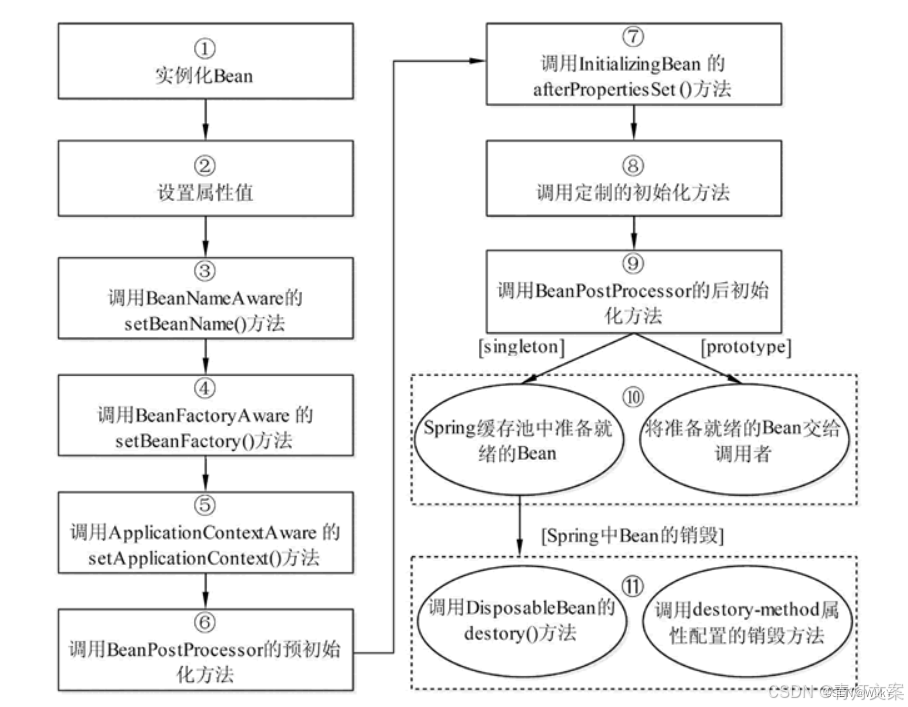
一、总结 Bean 生命周期的阶段
由上图可以看出,Spring Bean的生命周期可以分为以下几个阶段:
- 实例化:创建Bean实例。
- 属性赋值:注入依赖和配置。
- Aware接口回调:设置Bean名称、BeanFactory、ApplicationContext等。这里有三步。
- 初始化前处理:
BeanPostProcessor的postProcessBeforeInitialization(),也就是预初始化方法。 - 初始化:
@PostConstruct、InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet()、自定义初始化方法。这里有两步。 - 初始化后处理:
BeanPostProcessor的postProcessAfterInitialization()。 - 使用:Bean已准备好,可以被应用程序使用。
- 销毁:
@PreDestroy、DisposableBean.destroy()、自定义销毁方法。 - 垃圾回收:Bean实例被回收。
二、分解 Bean 生命周期的阶段
01、实例化(Instantiation)
Spring容器根据配置信息(XML、注解或Java配置)创建Bean的实例。可以通过构造函数或者工厂方法来实例化Bean。对于采用默认构造函数创建Bean的情况,Spring会直接调用其构造函数创建实例;对于使用工厂方法创建Bean的情况,会调用工厂方法。
@Component
public class MyBean {
public MyBean() {
System.out.println("MyBean 实例化");
}
}
当Spring容器启动时,会调用 MyBean 的无参构造函数进行实例化操作。
02、属性赋值(Populate Properties)
- 触发时机:在实例化Bean之后。
在实例化Bean之后,Spring容器会将配置的属性值或依赖注入(Dependency Injection)到Bean的属性中。这可以通过 @Autowired、@Resource 等注解,或者在XML配置文件中使用 <property> 元素来完成。
@Component
public class MyBean {
@Autowired
private AnotherBean anotherBean;
public MyBean() {
System.out.println("MyBean 实例化");
}
}
上面示例中 anotherBean 属性会在实例化 MyBean 之后被注入。
03、BeanNameAware.setBeanName()
- 触发时机:属性赋值之后。
在属性赋值后,如果Bean实现了BeanNameAware接口,Spring会调用setBeanName()方法,传入 Bean 的 ID 或名称。
04、BeanFactoryAware.setBeanFactory()
- 触发时机:
setBeanName()之后。
如果Bean实现了BeanFactoryAware接口,Spring会调用setBeanFactory()方法,传入 BeanFactory 实例。
05、ApplicationContextAware.setApplicationContext()
- 触发时机:
setBeanFactory()之后。
如果Bean实现了 ApplicationContextAware 接口,Spring会调用 setApplicationContext() 方法,传入 ApplicationContext 实例。
06、前置处理:BeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization()
- 触发时机:
setApplicationContext()之后,初始化之前。
如果存在 BeanPostProcessor,在调用初始化方法之前,会调用其 postProcessBeforeInitialization 方法。BeanPostProcessor 允许对Bean的实例进行修改,如包装或替换。
@Component
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (bean instanceof MyBean) {
System.out.println("在 MyBean 初始化前处理");
}
return bean;
}
}
当 MyBean 处于生命周期的这个阶段时,上述 MyBeanPostProcessor 会被调用,执行 postProcessBeforeInitialization 方法。
07、@PostConstruct 或 InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet()
- 触发时机:
postProcessBeforeInitialization()之后。
如果Bean使用了@PostConstruct注解,Spring会调用该注解标记的方法。
如果Bean实现了InitializingBean接口,Spring会调用afterPropertiesSet()方法。
08、自定义初始化方法(init-method)
- 触发时机:
afterPropertiesSet()或@PostConstruct之后。
如果Bean配置了自定义的初始化方法(通过XML的 init-method 属性或 @Bean(initMethod = "...") ),Spring会调用该方法,有多种方式可以指定Bean的初始化方法。
1、使用 @PostConstruct 注解:
@Component
public class MyBean {
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
System.out.println("MyBean 初始化");
}
}
2、实现 InitializingBean 接口:
@Component
public class MyBean implements InitializingBean {
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("MyBean 初始化");
}
}
3、在XML配置文件中使用 init-method 属性:
<bean id="myBean" class="com.example.MyBean" init-method="initMethod">
</bean>
其中 initMethod 是 MyBean 类中自定义的初始化方法。
09、后置处理:BeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization(),
- 触发时机:自定义初始化方法之后。
类似于前置处理,如果容器中有BeanPostProcessor,在初始化方法之后,会调用 BeanPostProcessor 的 postProcessAfterInitialization 方法。
@Component
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (bean instanceof MyBean) {
System.out.println("在 MyBean 初始化后处理");
}
return bean;
}
}
此时会对 MyBean 执行 postProcessAfterInitialization 操作。
10、Bean的使用
- 触发时机:初始化完成后。
Bean已准备好,可以被应用程序使用。
11、@PreDestroy 或 DisposableBean.destroy()
- 触发时机:容器关闭时。
1、如果Bean使用了 @PreDestroy 注解,Spring会在销毁前调用该注解标记的方法。
@Component
public class MyBean {
@PreDestroy
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("MyBean 销毁");
}
}
2、如果Bean实现了 DisposableBean 接口,Spring会调用 destroy() 方法。
@Component
public class MyBean implements DisposableBean {
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("MyBean 销毁");
}
}
3、在XML配置文件中使用 destroy-method 属性。
<bean id="myBean" class="com.example.MyBean" destroy-method="destroyMethod">
</bean>
12、自定义销毁方法(destroy-method)
- 触发时机:
destroy()或@PreDestroy之后。
如果Bean配置了自定义的销毁方法(通过XML的destroy-method属性或@Bean(destroyMethod = "...")),Spring会调用该方法。
13、垃圾回收(Garbage Collection)
- 触发时机:Bean销毁后。
Bean实例不再被引用,等待垃圾回收器回收。
三、整体示例代码
public class MyBean implements BeanNameAware, BeanFactoryAware, ApplicationContextAware, InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
private String name;
public MyBean() {
System.out.println("1. Instantiation: Constructor called");
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
System.out.println("2. Populate Properties: setName called");
}
@Override
public void setBeanName(String name) {
System.out.println("3. BeanNameAware: setBeanName called with " + name);
}
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("4. BeanFactoryAware: setBeanFactory called");
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("5. ApplicationContextAware: setApplicationContext called");
}
@PostConstruct
public void postConstruct() {
System.out.println("7. @PostConstruct: postConstruct called");
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("8. InitializingBean: afterPropertiesSet called");
}
public void customInit() {
System.out.println("9. Custom init-method: customInit called");
}
@PreDestroy
public void preDestroy() {
System.out.println("11. @PreDestroy: preDestroy called");
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("12. DisposableBean: destroy called");
}
public void customDestroy() {
System.out.println("13. Custom destroy-method: customDestroy called");
}
}
配置示例:
<bean id="myBean" class="com.example.MyBean" init-method="customInit" destroy-method="customDestroy">
<property name="name" value="MyBeanName"/>
</bean>






















 1748
1748

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








