一维函数的梯度检查
软件包导入
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
反向传播计算梯度 ∂J∂θ\frac{\partial J}{\partial \theta}∂θ∂J, θ\thetaθ 表示模型中的参数,使用前向传播和损失函数计算 JJJ ,因为向前传播相对容易实现,所以您确信自己得到了正确的结果,所以您几乎100%确定您正确计算了 JJJ。因此,您可以使用您的代码来计算 JJJ验证反向传播计算的梯度 ∂J∂θ\frac{\partial J}{\partial \theta}∂θ∂J。
导数(或梯度)的定义:
∂J∂θ=limε→0J(θ+ε)−J(θ−ε)2ε \frac{\partial J}{\partial \theta} = \lim_{\varepsilon \to 0} \frac{J(\theta + \varepsilon) - J(\theta - \varepsilon)}{2 \varepsilon} ∂θ∂J=ε→0lim2εJ(θ+ε)−J(θ−ε)
一维函数传播示意图
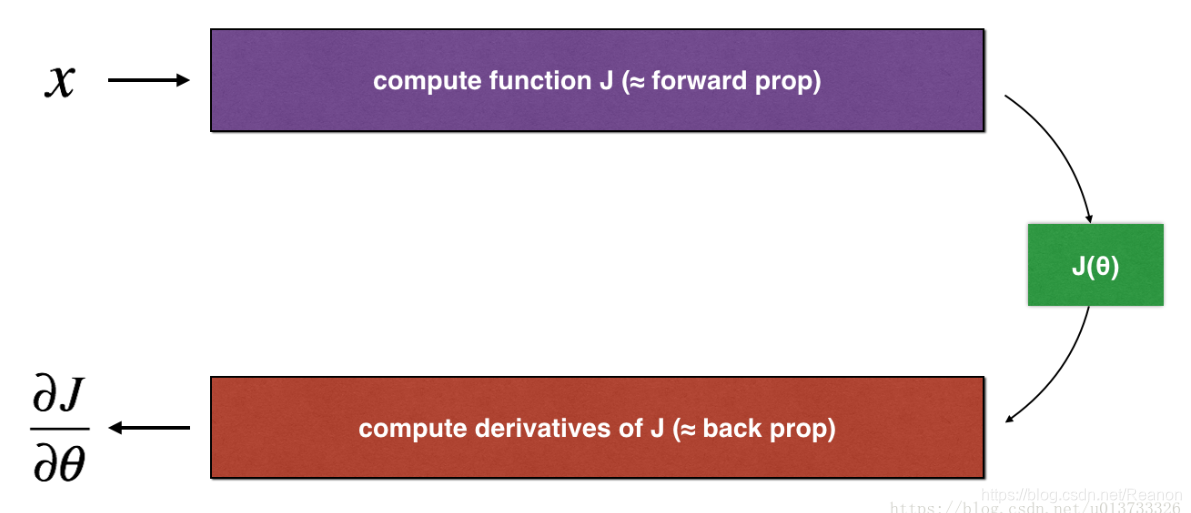
首先需用xxx前向传播计算得到J(x)=θ∗xJ(x)= \theta * xJ(x)=θ∗x ,然后由反向传播计算得到∂J∂θ\frac{\partial J}{\partial \theta}∂θ∂J
def forward_propagation(x, theta):
'''
实现一元函数的线性前向传播(计算J) J(theta)= theta * X
:param x: 输入
:param theta: θ,乘数
:return:
J:函数J(θ)= θ * X的值
'''
J = np.dot(theta, x)
return J
def backward_propagation(x, theta):
'''
计算J(theta)= theta * X相对于θ的导数
:param x: 输入
:param theta: θ,实数
:return:
dtheta:相对于θc的成本梯度
'''
dtheta = x
return dtheta
一维函数梯度检查
梯度检查的步骤如下,首先计算线性误差"gradapprox",精度是 ε\varepsilonε.
1. θ+=θ+ε\theta^{+} = \theta + \varepsilonθ+=θ+ε
2. θ−=θ−ε\theta^{-} = \theta - \varepsilonθ−=θ−ε
3. J+=J(θ+)J^{+} = J(\theta^{+})J+=J(θ+)
4. J−=J(θ−)J^{-} = J(\theta^{-})J−=J(θ−)
5. gradapprox=J+−J−2εgradapprox = \frac{J^{+} - J^{-}}{2 \varepsilon}gradapprox=2εJ+−J−
- 反向传播计算得到各个值的梯度值 “grad”,然后与"gradapprox"计算出两者的欧几里得范数:
(2)difference=∣∣grad−gradapprox∣∣2∣∣grad∣∣2+∣∣gradapprox∣∣2 difference = \frac {\mid\mid grad - gradapprox \mid\mid_2}{\mid\mid grad \mid\mid_2 + \mid\mid gradapprox \mid\mid_2} \tag{2}difference=∣∣grad∣∣2+∣∣gradapprox∣∣2∣∣grad−gradapprox∣∣2(2)
需要计算上面的公式:- 1’. 计算分子用
np.linalg.norm(...) - 2’. 计算分母用两次
np.linalg.norm(...) - 3’. 然后相除
当difference小于10−710^{-7}10−7时,通常认为计算结果是正确的。
- 1’. 计算分子用
def gradient_check(x, theta, epsilon=1e-7):
"""
实现微分和导数间的计算,进行梯度检验
Arguments:
x:实值输入
theta :参数,也是实值
epsilon :微小偏移以计算近似梯度
Returns:
difference:近似梯度gradapprox和后向传播梯度grad之间的差值
"""
# 计算gradapprox
thetaplus = theta + epsilon # Step 1
thetaminus = theta - epsilon # Step 2
J_plus = forward_propagation(x, thetaplus) # Step 3
J_minus = forward_propagation(x, thetaminus) # Step 4
gradapprox = (J_plus - J_minus) / (2 * epsilon) # Step 5
# 检查gradapprox是否和反向传播backward_propagation()输出grad相接近
grad = backward_propagation(x, theta)
numerator = np.linalg.norm(grad - gradapprox) # Step 1'
denominator = np.linalg.norm(grad) + np.linalg.norm(gradapprox) # Step 2'
difference = numerator / denominator # Step 3'
if difference < 1e-7:
print("梯度检查:梯度正常")
else:
print("梯度检查:超出阈值")
return difference
测试一下
#测试gradient_check
print("-----------------测试gradient_check-----------------")
x, theta = 2, 4
difference = gradient_check(x, theta)
print("difference = " + str(difference))
测试结果
-----------------测试gradient_check-----------------
梯度检查:梯度正常!
difference = 2.91933588329e-10
多层神经网络参数的梯度检查
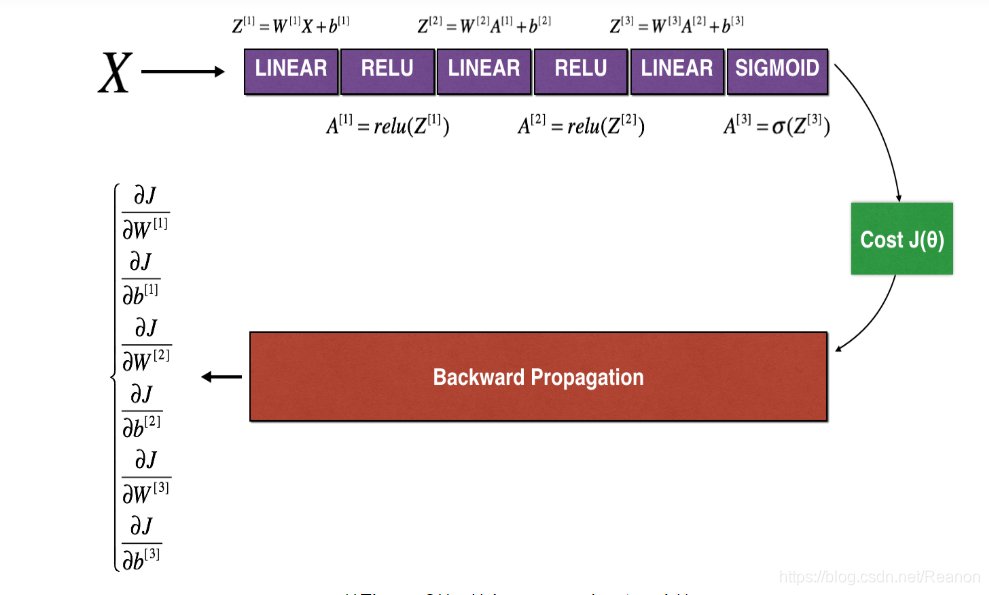
前向传播计算
def sigmoid(x):
"""
Compute the sigmoid of x
Arguments:
x -- A scalar or numpy array of any size.
Return:
s -- sigmoid(x)
"""
s = 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
return s
def relu(x):
"""
Compute the relu of x
Arguments:
x -- A scalar or numpy array of any size.
Return:
s -- relu(x)
"""
s = np.maximum(0, x)
return s
def forward_propagation_n(X, Y, parameters):
"""
实现图中的前向传播(并计算成本)。
参数:
X - 训练集为m个例子
Y - m个示例的标签
parameters - 包含参数“W1”,“b1”,“W2”,“b2”,“W3”,“b3”的python字典:
W1 - 权重矩阵,维度为(5,4)
b1 - 偏向量,维度为(5,1)
W2 - 权重矩阵,维度为(3,5)
b2 - 偏向量,维度为(3,1)
W3 - 权重矩阵,维度为(1,3)
b3 - 偏向量,维度为(1,1)
返回:
cost - 成本函数(logistic)
"""
m = X.shape[1]
W1 = parameters["W1"]
b1 = parameters["b1"]
W2 = parameters["W2"]
b2 = parameters["b2"]
W3 = parameters["W3"]
b3 = parameters["b3"]
# LINEAR -> RELU -> LINEAR -> RELU -> LINEAR -> SIGMOID
Z1 = np.dot(W1, X) + b1
A1 = relu(Z1)
Z2 = np.dot(W2, A1) + b2
A2 = relu(Z2)
Z3 = np.dot(W3, A2) + b3
A3 = sigmoid(Z3)
# 计算成本
logprobs = np.multiply(-np.log(A3), Y) + np.multiply(-np.log(1 - A3), 1 - Y)
cost = (1 / m) * np.sum(logprobs)
cache = (Z1, A1, W1, b1, Z2, A2, W2, b2, Z3, A3, W3, b3)
return cost, cache
反向传播
因为这里层数比较浅,没有直接用到relu_backward()和sigmoid_backward()。
def backward_propagation_n(X, Y, cache):
"""
实现图中所示的反向传播。
参数:
X - 输入数据点(输入节点数量,1)
Y - 标签
cache - 来自forward_propagation_n()的cache输出
返回:
gradients - 一个字典,其中包含与每个参数、激活和激活前变量相关的成本梯度。
"""
m = X.shape[1]
(Z1, A1, W1, b1, Z2, A2, W2, b2, Z3, A3, W3, b3) = cache
dZ3 = A3 - Y # 需要考究一下
dW3 = (1. / m) * np.dot(dZ3, A2.T)
dW3 = 1. / m * np.dot(dZ3, A2.T)
db3 = 1. / m * np.sum(dZ3, axis=1, keepdims=True)
dA2 = np.dot(W3.T, dZ3)
dZ2 = np.multiply(dA2, np.int64(A2 > 0))
# dW2 = 1. / m * np.dot(dZ2, A1.T) * 2 # Should not multiply by 2
dW2 = 1. / m * np.dot(dZ2, A1.T)
db2 = 1. / m * np.sum(dZ2, axis=1, keepdims=True)
dA1 = np.dot(W2.T, dZ2)
dZ1 = np.multiply(dA1, np.int64(A1 > 0))
dW1 = 1. / m * np.dot(dZ1, X.T)
# db1 = 4. / m * np.sum(dZ1, axis=1, keepdims=True) # Should not multiply by 4
db1 = 1. / m * np.sum(dZ1, axis=1, keepdims=True)
gradients = {"dZ3": dZ3, "dW3": dW3, "db3": db3,
"dA2": dA2, "dZ2": dZ2, "dW2": dW2, "db2": db2,
"dA1": dA1, "dZ1": dZ1, "dW1": dW1, "db1": db1}
return gradients
参数格式转换
如果想比较"gradapprox" 与反向传播计算的梯度。 该公式仍然是:
∂J∂θ=limε→0J(θ+ε)−J(θ−ε)2ε \frac{\partial J}{\partial \theta} = \lim_{\varepsilon \to 0} \frac{J(\theta + \varepsilon) - J(\theta - \varepsilon)}{2 \varepsilon} ∂θ∂J=ε→0lim2εJ(θ+ε)−J(θ−ε)
然而,θ\thetaθ不再是标量。 这是一个名为"parameters"的字典。 我们为你实现了一个函数"dictionary_to_vector()"。 它将"parameters" 字典转换为一个称为 “values"的向量,通过将所有参数(W1,b1,W2,b2,W3,b3)重塑为向量并将它们连接起来而获得。反函数是”vector_to_dictionary",它返回“parameters”字典。
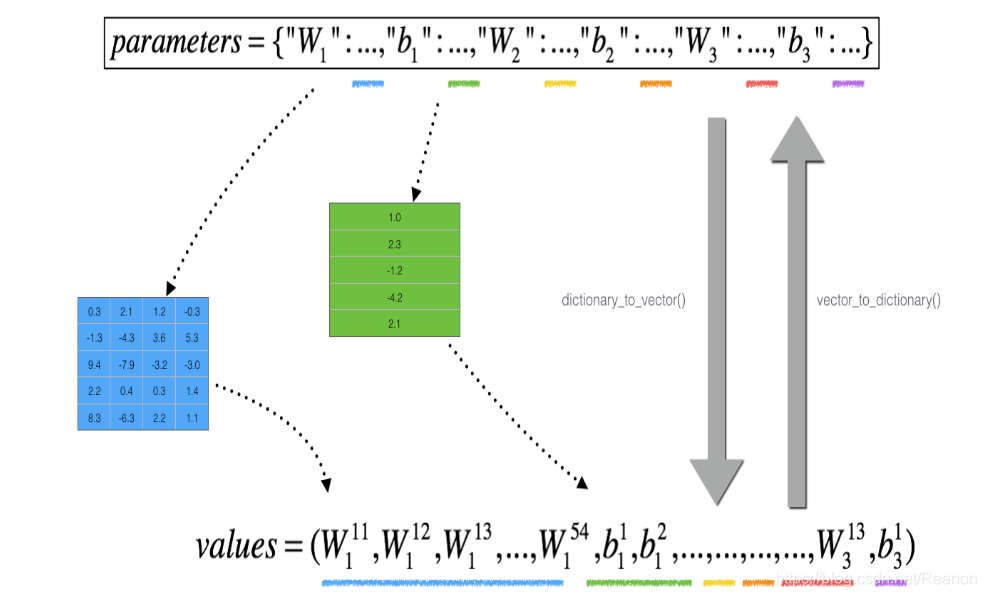
def dictionary_to_vector(parameters):
"""
Roll all our parameters dictionary into a single vector satisfying our specific required shape.
"""
keys = []
count = 0
for key in ["W1", "b1", "W2", "b2", "W3", "b3"]:
# flatten parameter
new_vector = np.reshape(parameters[key], (-1, 1)) # 将元素转化为一行(列值为1)
keys = keys + [key] * new_vector.shape[0]
if count == 0:
theta = new_vector
else:
theta = np.concatenate((theta, new_vector), axis=0)
count = count + 1
return theta, keys
def vector_to_dictionary(theta):
"""
Unroll all our parameters dictionary from a single vector satisfying our specific required shape.
"""
parameters = {}
parameters["W1"] = theta[:20].reshape((5, 4))
parameters["b1"] = theta[20:25].reshape((5, 1))
parameters["W2"] = theta[25:40].reshape((3, 5))
parameters["b2"] = theta[40:43].reshape((3, 1))
parameters["W3"] = theta[43:46].reshape((1, 3))
parameters["b3"] = theta[46:47].reshape((1, 1))
return parameters
L层梯度检查具体实现
这里是伪代码,可以帮助你实现梯度检查:
For each i in num_parameters:
- To compute
J_plus[i]:- Set θ+\theta^{+}θ+ to
np.copy(parameters_values) - Set θi+\theta^{+}_iθi+ to θi++ε\theta^{+}_i + \varepsilonθi++ε
- Calculate Ji+J^{+}_iJi+ using to
forward_propagation_n(x, y, vector_to_dictionary(θ+\theta^{+}θ+)).
- Set θ+\theta^{+}θ+ to
- To compute
J_minus[i]: do the same thing with θ−\theta^{-}θ− - 计算近似梯度 gradapprox[i]=Ji+−Ji−2εgradapprox[i] = \frac{J^{+}_i - J^{-}_i}{2 \varepsilon}gradapprox[i]=2εJi+−Ji−, gradapprox是个向量, gradapprox[i]对应每个参数的近似梯度值。
- 反向传播计算gradsgradsgrads
- 计算误差
difference=∥grad−gradapprox∥2∥grad∥2+∥gradapprox∥2 difference = \frac {\| grad - gradapprox \|_2}{\| grad \|_2 + \| gradapprox \|_2 } difference=∥grad∥2+∥gradapprox∥2∥grad−gradapprox∥2
def gradient_check_n(parameters, gradients, X, Y, epsilon=1e-7):
"""
检查backward_propagation_n是否正确计算forward_propagation_n输出的成本梯度
参数:
parameters - 包含参数“W1”,“b1”,“W2”,“b2”,“W3”,“b3”的python字典:
gradient:后向传播的输出,包含对应于每个参数的成本函数的导数
x - 输入数据点,维度为(输入节点数量,1)
y - 标签
epsilon - 计算输入的微小偏移以计算近似梯度
返回:
difference - 近似梯度和后向传播梯度之间的误差
"""
# 初始化参数
parameters_values, keys = dictionary_to_vector(parameters) # keys用不到
grad = gradients_to_vector(gradients)
num_parameters = parameters_values.shape[0]
J_plus = np.zeros((num_parameters, 1))
J_minus = np.zeros((num_parameters, 1))
gradapprox = np.zeros((num_parameters, 1))
# 计算gradapprox
for i in range(num_parameters):
# 计算J_plus [i]。输入:“parameters_values,epsilon”。输出=“J_plus [i]”
thetaplus = np.copy(parameters_values) # Step 1
thetaplus[i][0] = thetaplus[i][0] + epsilon # Step 2
J_plus[i], cache = forward_propagation_n(X, Y, vector_to_dictionary(thetaplus)) # Step 3 ,cache用不到
# 计算J_minus [i]。输入:“parameters_values,epsilon”。输出=“J_minus [i]”。
thetaminus = np.copy(parameters_values) # Step 1
thetaminus[i][0] = thetaminus[i][0] - epsilon # Step 2
J_minus[i], cache = forward_propagation_n(X, Y, vector_to_dictionary(thetaminus)) # Step 3 ,cache用不到
# 计算gradapprox[i]
gradapprox[i] = (J_plus[i] - J_minus[i]) / (2 * epsilon)
# 通过计算差异比较gradapprox和后向传播梯度。
numerator = np.linalg.norm(grad - gradapprox) # Step 1'
denominator = np.linalg.norm(grad) + np.linalg.norm(gradapprox) # Step 2'
difference = numerator / denominator # Step 3'
if difference < 1e-7:
print("梯度检查:梯度正常!")
else:
print("梯度检查:梯度超出阈值!")
return difference
 一维与多层神经网梯度检查
一维与多层神经网梯度检查





 本文介绍了一维函数与多层神经网络的梯度检查方法,包括梯度定义、一维函数梯度检查流程及多层神经网络参数梯度检查的具体实现。
本文介绍了一维函数与多层神经网络的梯度检查方法,包括梯度定义、一维函数梯度检查流程及多层神经网络参数梯度检查的具体实现。
















 2125
2125

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








