| Find them, Catch them |
|---|
| Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 10000K |
Description
The police office in Tadu City decides to say ends to the chaos, as launch actions to root up the TWO gangs in the city, Gang Dragon and Gang Snake. However, the police first needs to identify which gang a criminal belongs to. The present question is, given two criminals; do they belong to a same clan? You must give your judgment based on incomplete information. (Since the gangsters are always acting secretly.)
Assume N (N <= 10^5) criminals are currently in Tadu City, numbered from 1 to N. And of course, at least one of them belongs to Gang Dragon, and the same for Gang Snake. You will be given M (M <= 10^5) messages in sequence, which are in the following two kinds:
-
D [a] [b]
where [a] and [b] are the numbers of two criminals, and they belong to different gangs. -
A [a] [b]
where [a] and [b] are the numbers of two criminals. This requires you to decide whether a and b belong to a same gang.
Input
The first line of the input contains a single integer T (1 <= T <= 20), the number of test cases. Then T cases follow. Each test case begins with a line with two integers N and M, followed by M lines each containing one message as described above.
Output
For each message “A [a] [b]” in each case, your program should give the judgment based on the information got before. The answers might be one of “In the same gang.”, “In different gangs.” and “Not sure yet.”
Sample Input
1
5 5
A 1 2
D 1 2
A 1 2
D 2 4
A 1 4
Sample Output
Not sure yet.
In different gangs.
In the same gang.
题目大意:
有n个人分别属于两个团伙,接下来m组形如 ch, x, y的数据,ch为"D"表示 x, y属于不同的团伙;ch为"A"表示询问x,y是否属于同一个团伙,这种情况下要输出相应的回答;
解题思路:
把输入数据中能够形成关系的(即ch为"D"时的情况)用树形结构保存起来,结点到根结点的深度可用于判断与根结点的关系。当需要合并两棵树时,注意还需要一步额外的反转操作:

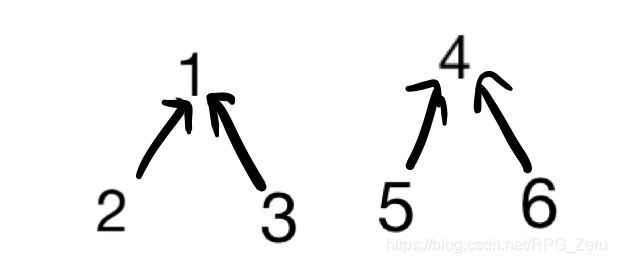
输入 D 3 5 后,上图中的两棵树将会进行合并

具体解释见代码注释
AC代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include<math.h>
using namespace std;
int pre[100005];//用于形成树结构
int n, m;
int rev[100005];//用于反转操作
void init() {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
pre[i] = -1;
}
}
int findroot(int x, int &y) {//返回根结点,y最终会变成结点x到根结点的长度
if (pre[x] == -1) { return x; }
else {
y++;
return findroot(pre[x], y);
}
}
int main() {
int t;
scanf("%d", &t);
while (t--) {
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
getchar();//吃掉回车
init();
char a; int b, c;
while (m--) {
scanf("%c%d%d", &a, &b, &c);//cin会超时
getchar();//吃掉回车
if (a == 'D') {//需要合并两棵树
int tmp = 0;
int fb = findroot(b, tmp);
int fc = findroot(c, tmp);
if (fb != fc) {//将c到原先根结点的那部分倒置
int now = 1; rev[0] = b; rev[1] = c;
while (pre[c] != -1) {
rev[++now] = pre[c];
c = pre[c];
}
for (; now > 0; now--) {
pre[rev[now]] = rev[now - 1];
}
}
}
if (a == 'A') {//需要给出判断
int tmp1 = 0; int tmp2 = 0;
int fb = findroot(b, tmp1);
int fc = findroot(c, tmp2);
if (fb != fc) { cout << "Not sure yet." << endl; }//两个结点属于两棵不同的树
else if (abs(tmp1 - tmp2) % 2 == 0) {//深度之差为偶数
cout << "In the same gang." << endl;
}
else cout << "In different gangs." << endl;//深度之差为奇数
}
}
}
}
做完之后,看了一些大神们的博客,发现大家普遍是按照种类并查集的方法来做的,类似于之前的那一题,仔细一想确实是这样,已经学习过种类并查集了,也需要多动动手,下面是按照种类并查集实现的代码:
poj1182食物链(并查集)
AC代码
/*
solution:
种类并查集
这道题有点类似poj1182(食物链),两题的关键点都在于如何维护不同集合的关系。
并查集的功能则正好与之相反,是维护相同集合间的关系。
如何用并查集来实现不同集合的维护呢?
方法是改变集合内元素的类型:本来unite(a,b)表示a,b属于同一个集合,现在用unite(a,b+n)来表示a,b属于不同集合,即a属于第一个集合,b属于第二个集合。
同理unite(a+n,b)表示a属于第二个集合,b属于第一个集合。
每次进行D操作时,将所有的可能都unite。
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 100005;
int n, m;
int par[maxn * 2];
void init(int n)
{
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){par[i] = i;}
}
int findroot(int x){
if (x == par[x]) return x;
else {
int tmp = findroot(par[x]);
par[x] = tmp;//实现路径压缩
return tmp;
}
}
void unite(int x, int y)
{
x = findroot(x);
y = findroot(y);
if (x == y) return;
par[x] = y;//左树合并到右树上
}
bool same(int x, int y)
{
return findroot(x) == findroot(y);
}
int main()
{
int T;
scanf("%d", &T);
while (T--){
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
init(2 * n);
char op;int a, b;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++){
scanf("\n%c%d%d", &op, &a, &b);
if (op == 'D'){
unite(a, b + n);
unite(a + n, b);
}
else{
if (same(a, b + n) || same(a + n, b)) printf("In different gangs.\n");
else if (same(a, b) || same(a + n, b + n)) printf("In the same gang.\n");
else printf("Not sure yet.\n");
}
}
}
return 0;
}







 本文介绍了一种算法,用于判断两个犯罪嫌疑人是否属于同一团伙。通过构建树形结构和使用并查集,算法能有效处理大量关系判断请求,即使信息不完全也能给出准确判断。
本文介绍了一种算法,用于判断两个犯罪嫌疑人是否属于同一团伙。通过构建树形结构和使用并查集,算法能有效处理大量关系判断请求,即使信息不完全也能给出准确判断。
















 2129
2129

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








