第一种:原型链继承
原型链继承是比较常见的继承方式之一,其中涉及的构造函数、原型和实例,三者之间存在着一定的关系,即每一个构造函数都有一个原型对象,原型对象又包含一个指向构造函数的指针,而实例则包含一个原型对象的指针。
function one1() {
this.name = '科技改变世界'
this.array = [1, 2, 3]
}
function two() {
this.type = '名字'
}
two.prototype = new one1()
let two2= new two()
console.log(two2)
上面的代码看似没有问题,虽然父类的方法和属性都能够访问,但其实有一个潜在的问题
let c1 = new one1();
let c2 = new one1();
c1.play.push(4);
console.log(c1.play, c2.play);
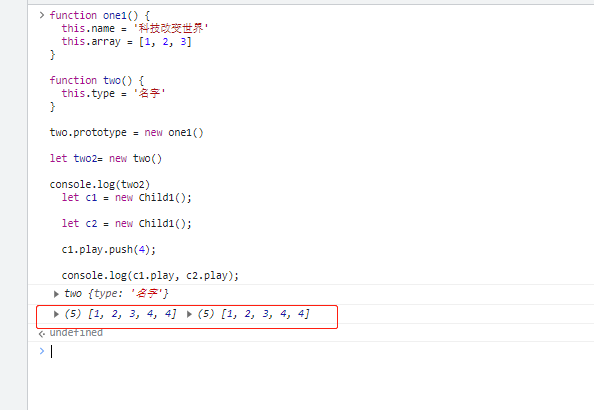
明明只改变了 c1 的 play 属性,为什么 c2 也跟着变了呢?原因很简单,因为两个实例使用的是同一个原型对象。它们的内存空间是共享的,当一个发生变化的时候,另外一个也随之进行了变化,这就是使用原型链继承方式的一个缺点。
第二种:构造函数继承(借助 call)
// 借用构造函数实现的继承,只能继承属性,不能继承方法
function one1(name,sex){
this.name = name
this.sex = sex
}
function tow2(sco,name,sex){
// 学生对象实例中的this指向实例对象
// tow2构造函数通过call方法,改变this指向
one1.call(this,name,sex)
this.sco = sco
}
// 创建学生对象
let stu1 = new tow2(100,'kk','man')
let stu2 = new tow2(98,'hh','female')
// stu1.sleep()
// stu1.sleep is not a function
console.log(stu1);
console.log(stu2);
第三种:组合继承(前两种组合)
// 组合继承:改变原型指向和和借用构造函数实现继承组合使用
// 人的构造函数
function one1(name,sex){
this.name = name
this.sex = sex
}
function tow2(sco,name,sex){
// 学生对象实例中的this指向实例对象
// one1构造函数通过call方法,改变this指向,实现Stu继承one1的属性
one1.call(this,name,sex)
this.sco = sco
}
// 改变Stu原型指向,实现Stu继承one1的方法
tow2.prototype = new one1()
tow2.prototype.constructor = tow2
let stu1 = new Stu(100,'kk','man')
let stu2 = new Stu(98,'hh','female')
console.log(stu1);
console.log(stu2);
console.log(stu1.sleep == stu2.sleep)第四种:原型式继承
let one = {
name: '科技改变世界',
friends: ['p1', 'p2', 'p3'],
getName: function () {
return this.name
},
}
let person = Object.create(one)
person.name = '科技'
person.friends.push('p4')
let person2 = Object.create(one)
person2.friends.push('p5')
console.log(person.name)
console.log(person.name === person.getName())
console.log(person2.name)
console.log(person.friends)
console.log(person2.friends)
第五种:寄生式继承
let parent5 = {
name: 'parent5',
friends: ['p1', 'p2', 'p3'],
getName: function () {
return this.name
},
}
function clone(original) {
let clone = Object.create(original)
clone.getFriends = function () {
return this.friends
}
return clone
}
let person = clone(parent5)
console.log(person.getName())
console.log(person.getFriends())第六种:寄生组合式继承
function Parent6() {
this.name = 'parent6'
this.play = [1, 2, 3]
}
Parent6.prototype.getName = function () {
return this.name
}
function Child6() {
Parent6.call(this)
this.friends = 'child5'
}
function clone(parent, child) {
child.prototype = Object.create(parent.prototype)
child.prototype.constructor = child
}
clone(Parent6, Child6)
Child6.prototype.getFriends = function () {
return this.friends
}
let person = new Child6()
console.log(person)
console.log(person.getName())
console.log(person.getFriends())




 文章详细介绍了JavaScript中五种常见的继承实现方式:原型链继承、构造函数继承、组合继承、原型式继承、寄生式继承,以及它们的特点和潜在问题。例如,原型链继承可能导致实例间属性共享,而构造函数继承无法继承方法。组合继承结合了两者优点,但仍有冗余。寄生式继承用于创建对象副本并添加新方法。最后提到了寄生组合式继承,它能更有效地避免上述问题。
文章详细介绍了JavaScript中五种常见的继承实现方式:原型链继承、构造函数继承、组合继承、原型式继承、寄生式继承,以及它们的特点和潜在问题。例如,原型链继承可能导致实例间属性共享,而构造函数继承无法继承方法。组合继承结合了两者优点,但仍有冗余。寄生式继承用于创建对象副本并添加新方法。最后提到了寄生组合式继承,它能更有效地避免上述问题。
















 662
662

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








