文章目录
简单概述
此文章是自己进行java学习的一个总结内容, 可能会有多篇内容.
集合
单列集合体系结构
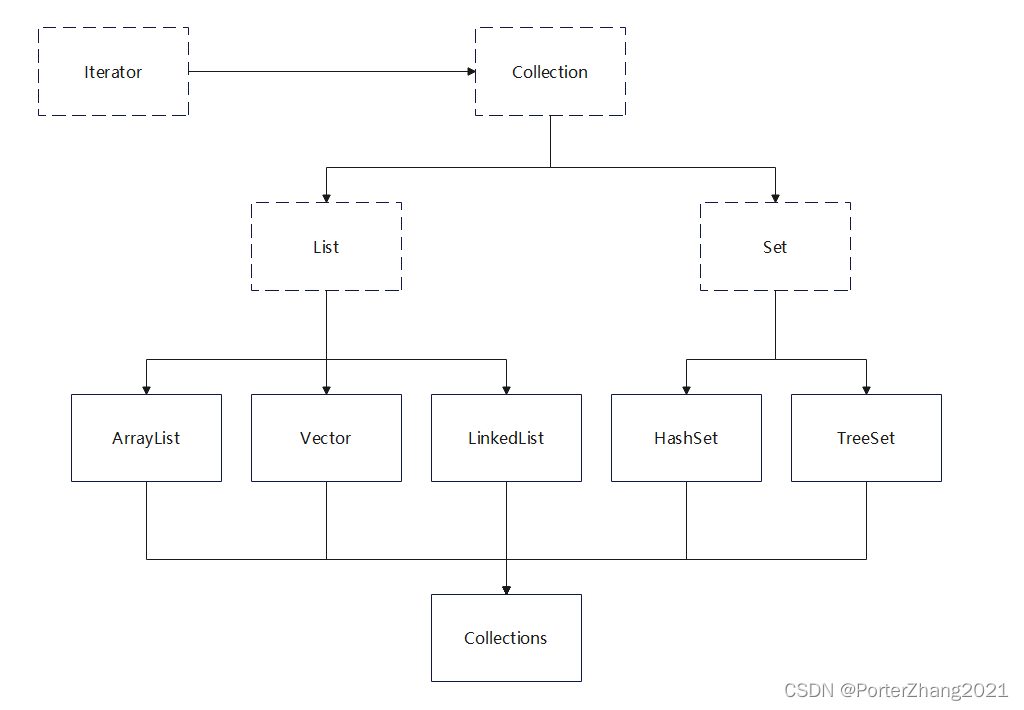
Collection接口
常用方法
| 方法名称 | 方法描述-JDK1.8-英文 |
|---|---|
| boolean add(E e) | Ensures that this collection contains the specified element (optional operation). |
| void clear() | Removes all of the elements from this collection (optional operation). |
| boolean remove(Object o) | Removes a single instance of the specified element from this collection, if it is present (optional operation). |
| boolean contains(Object o) | Returns true if this collection contains the specified element. |
| boolean isEmpty() | Returns true if this collection contains no elements. |
| int size() | Returns the number of elements in this collection. |
| Object[] toArray() | Returns an array containing all of the elements in this collection. |
| Iterator iterator() | Returns an iterator over the elements in this collection. |
List
特点
- 存取有序
- 允许重复元素
底层由动态数组组成, 底层相似的代码后期参考数据结构的文章.
ArrayList
特点
- 底层由数组构成
- 适合做查询操作
常用构造方法
| 构造方法 | 构造方法描述-1.8 |
|---|---|
| ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) | Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified collection, in the order they are returned by the collection’s iterator. |
常用方法
| 常用方法 | 方法描述 |
|---|---|
| E get(int index) | Returns the element at the specified position in this list. |
| E set(int index, E element) | Replaces the element at the specified position in this list with the specified element. |
| int indexOf(Object o) | Returns the index of the first occurrence of the specified element in this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element. |
| E remove(int index) | Removes the element at the specified position in this list. |
LinkedList
特点
- 底层由双向链表构成
常用构造方法
| 构造方法 | 构造方法描述-1.8 |
|---|---|
| LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) | Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified collection, in the order they are returned by the collection’s iterator. |
常用方法
| 常用方法 | 方法描述 |
|---|---|
| void addFirst(E e) | Inserts the specified element at the beginning of this list. |
| void addLast(E e) | Appends the specified element to the end of this list. |
| E getFirst() | Returns the first element in this list. |
| E getLast() | Returns the last element in this list. |
| E removeFirst() | Removes and returns the first element from this list. |
| E removeLast() | Removes and returns the last element from this list. |
| E pop() | Pops an element from the stack represented by this list. |
| void push(E e) | Pushes an element onto the stack represented by this list. |
底层由双向链表构成, 底层相似的代码后期参考数据结构的文章.
Set
特点
- 存取无序
- 不允许重复元素
TreeSet
特点
- 底层是由红黑树构成
常用构造方法
| 构造方法 | 构造方法描述-1.8 |
|---|---|
| TreeSet(Collection<? extends E> c) | Constructs a new tree set containing the elements in the specified collection, sorted according to the natural ordering of its elements. |
| TreeSet(Comparator<? super E> comparator) | Constructs a new, empty tree set, sorted according to the specified comparator. |
HashSet
特点
- 底层由哈希表构成(1.8-: 哈希表中由数组+链表 1.8+ 哈希表中由数组+链表(大于8转红黑树)+红黑树构成)
常用构造方法
| 构造方法 | 构造方法描述 |
|---|---|
| HashSet(Collection<? extends E> c) | Constructs a new set containing the elements in the specified collection. |
LinkedHashSet
特点
- 存取有序的set集合
Collections
定义
collections是一个集合工具类, 其功能可以被集合对象使用.
常用方法
| 常用方法 | 方法描述-1.8 |
|---|---|
| static <T extends Comparable<? super T> void sort(List list) | Sorts the specified list into ascending order, according to the natural ordering of its elements. |
| static void sort(List list, Comparator<? super T> c) | Sorts the specified list according to the order induced by the specified comparator. |
| static void shuffle(List<?> list) | Randomly permutes the specified list using a default source of randomness. |
双列集合体系
Map接口
定义
数据存储时, 以键值对的方式进行数据的存储, 其中键列又称为key, 值列又称为value.
常用方法
| 常用方法 | 方法描述 |
|---|---|
| V put(K key, V value) | Associates the specified value with the specified key in this map (optional operation). |
| V remove(Object key) | Removes the mapping for a key from this map if it is present (optional operation). |
| V get(Object key) | Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped, or null if this map contains no mapping for the key. |
| Set keySet() | Returns a Set view of the keys contained in this map. |
| Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() | Returns a Set view of the mappings contained in this map. |
| boolean containsKey(Object key) | Returns true if this map contains a mapping for the specified key. |
| Collection values() | Returns a Collection view of the values contained in this map. |
HashMap
The HashMap class is roughly equivalent to Hashtable, except that it is unsynchronized and permits nulls.
HashTable
Hash table based implementation of the Map interface. This implementation provides all of the optional map operations, and permits null values and the null key.
TreeMap
A Red-Black tree based NavigableMap implementation. The map is sorted according to the natural ordering of its keys, or by a Comparator provided at map creation time, depending on which constructor is used.
常用构造方法
| 构造方法 | 方法描述 |
|---|---|
| TreeMap() | Constructs a new, empty tree map, using the natural ordering of its keys. |
| TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator) | Constructs a new, empty tree map, ordered according to the given comparator. |
| TreeMap(Map<? extends K,? extends V> m) | Constructs a new tree map containing the same mappings as the given map, ordered according to the natural ordering of its keys. |
常用方法
| 常用方法 | 方法描述 |
|---|---|
| Map.Entry<K,V> ceilingEntry(K key) | Returns a key-value mapping associated with the least key greater than or equal to the given key, or null if there is no such key. |
| K ceilingKey(K key) | Returns the least key greater than or equal to the given key, or null if there is no such key. |
| Map.Entry<K,V> firstEntry() | Returns a key-value mapping associated with the least key in this map, or null if the map is empty. |
| K firstKey() | Returns the first (lowest) key currently in this map. |
| Map.Entry<K,V> lastEntry() | Returns a key-value mapping associated with the greatest key in this map, or null if the map is empty. |
| K lastKey() | Returns the last (highest) key currently in this map. |
高级for循环
格式
for(数据类型 变量: 集合|数组名){
}
泛型
定义
其表示规范的类型看, 主要限制集合内部可以存储的数据的元素类型.
优势
- 强制规范集合中的元素类型
- 避免了集合由于内部元素类型不一致出现的运行期转换异常
- 将运行时异常提到了编译期
种类
泛型接口
public interface 接口名<E>{}
泛型类
public class 类名<E>{}
泛型方法
public <E> void 方法名(){}
通配符
?: 表示现在还无法确定要使用的类型
? extend 类: 通配符的向下限制
? super 类: 通配符的向上限制
可变参数
定义
在参数列表中, 可以接受多个相同的数据类型的值参数叫做可变参数.
格式
修饰符 返回值类型 方法名(参数类型... 形参名){ }
数据类型…参数名
注意事项:
- 可变参数必须在参数列表的末尾, 不能在开头
- 可变参数在参数列表中有且仅有一个
克隆操作
如果在Java中想要实现克隆操作, 需要我们对实现的类进行Cloneable的接口标记, 之后对类进行Object.clone重写.
浅克隆
浅克隆主要是上面所写的方式, 下面的代码就实现了浅克隆的操作:
public class Student implements Cloneable{
private String name;
private int age;
@Override
public Student clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return (Student) super.clone();
}
}
深克隆
深克隆, 则是对组合类, 即类中还有类的成员变量的情况下, 将类中的成员变量类进行克隆的操作, 以下是一个深克隆的例子:
student.class
//修改Student的clone方法
public class Student implements Cloneable{
private String name;
private int age;
private Car car;
//空参带参
//get/set
@Override
public Student clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
//调用克隆方法 获取到学生
Student clone = (Student) super.clone();
//将当前的car克隆 并设置到克隆后的学生中
Car car = this.car.clone();
clone.setCar(car);
return clone;
}
}
car.class
//首先 Car类实现克隆接口 重写clone方法
public class Car implements Cloneable{
private String brand;//品牌
public Car() {
}
public Car(String brand) {
this.brand = brand;
}
//get/set...
@Override
public Car clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return (Car) super.clone();
}
}






















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








