if you want to make a great chart like the one below in reportlab, you need rotated text.it isn't very complicated - its just a bit hard to find som examples on the net.
the canvas in reportlab has a saveState and a restoreState method, and supports rotate and translate similarto openGL or processing. see the code example below who it is done.
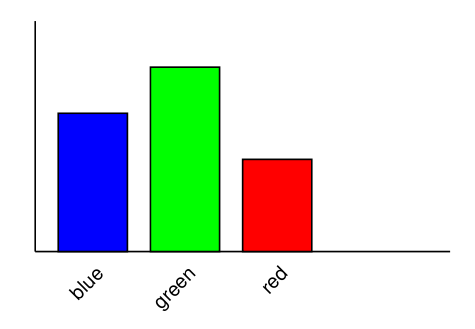
from reportlab.pdfgen import canvas
from reportlab.lib.units import cm
c = canvas.Canvas("rotate.pdf")
c.line( 2*cm, 21*cm, 2*cm, 16*cm)
c.line( 2*cm, 16*cm, 11*cm, 16*cm )
c.setFillColorRGB( 0, 0, 1 )
c.rect( 2.5*cm, 16*cm, 1.5*cm, 3*cm, fill = 1 )
c.setFillColorRGB( 0, 1, 0 )
c.rect( 4.5*cm, 16*cm, 1.5*cm, 4*cm, fill = 1 )
c.setFillColorRGB( 1, 0, 0 )
c.rect( 6.5*cm, 16*cm, 1.5*cm, 2*cm, fill = 1 )
c.setFillColorRGB( 0, 0, 0 )
i=0
for str in ["blue", "green", "red"]:
c.saveState()
c.translate( (i + 3.5) * cm, 15.5 * cm )
c.rotate( 45 )
c.drawRightString( 0, 0, str )
c.restoreState()
i += 2
c.showPage()
c.save()
引自:http://www.local-guru.net/blog/2009/4/9/rotated-text-in-reportlabs





 本文介绍如何使用ReportLab库在PDF中实现文本旋转效果,并提供了一个简单的示例代码,展示了如何通过saveState、translate、rotate等方法来绘制带有旋转文本的图表。
本文介绍如何使用ReportLab库在PDF中实现文本旋转效果,并提供了一个简单的示例代码,展示了如何通过saveState、translate、rotate等方法来绘制带有旋转文本的图表。
















 2163
2163

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








