Convolutional Neural Networks: Step by Step
Welcome to Course 4's first assignment! In this assignment, you will implement convolutional (CONV) and pooling (POOL) layers in numpy, including both forward propagation and (optionally) backward propagation.
Notation:
- Superscript [l] denotes an object of the lth layer.
- Example: a[4] is the 4th layer activation. W[5] and b[5] are the 5th layer parameters.
- Superscript (i) denotes an object from the ith example.
- Example: x(i) is the ith training example input.
- Lowerscript i denotes the ith entry of a vector.
- Example: a[l]i denotes the ith entry of the activations in layer l, assuming this is a fully connected (FC) layer.
- nH, nW and nC denote respectively the height, width and number of channels of a given layer. If you want to reference a specific layer l, you can also write n[l]H, n[l]W, n[l]C.
- nHprev, nWprev and nCprev denote respectively the height, width and number of channels of the previous layer. If referencing a specific layer l, this could also be denoted n[l−1]H, n[l−1]W, n[l−1]C.
We assume that you are already familiar with numpy and/or have completed the previous courses of the specialization. Let's get started!
1 - Packages
Let's first import all the packages that you will need during this assignment.
- numpy is the fundamental package for scientific computing with Python.
- matplotlib is a library to plot graphs in Python.
- np.random.seed(1) is used to keep all the random function calls consistent. It will help us grade your work.
-
import numpy as np import h5py import matplotlib.pyplot as plt %matplotlib inline plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (5.0, 4.0) # set default size of plots plt.rcParams['image.interpolation'] = 'nearest' plt.rcParams['image.cmap'] = 'gray' %load_ext autoreload %autoreload 2 np.random.seed(1)2 - Outline of the Assignment
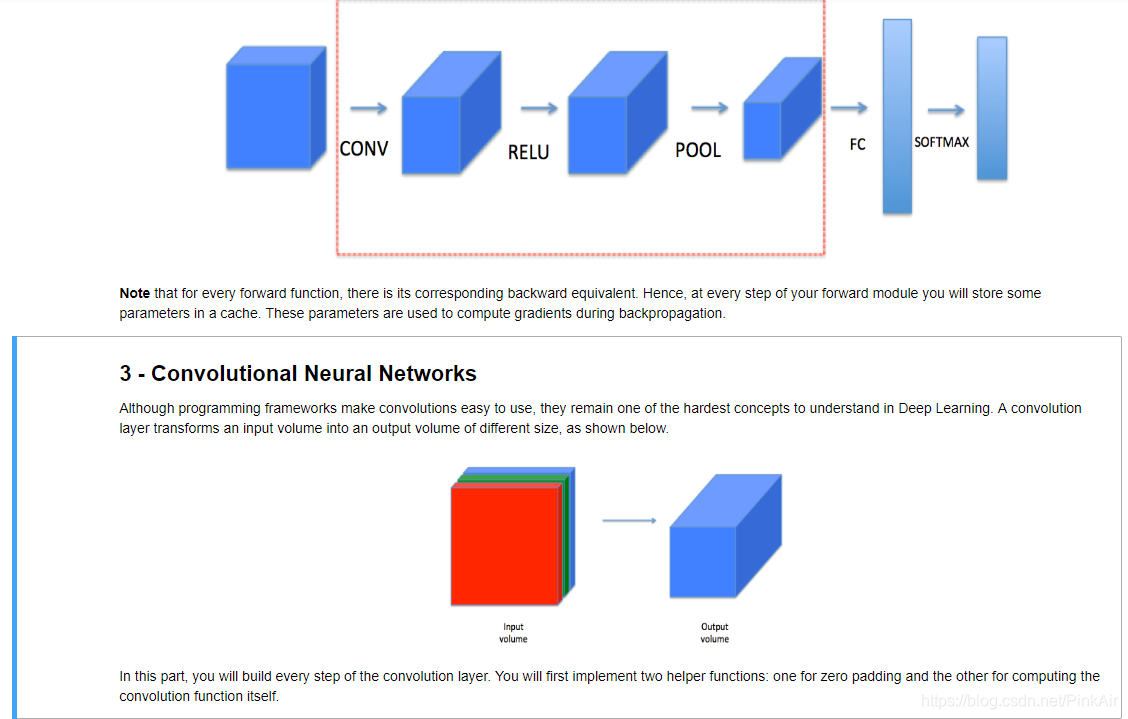
You will be implementing the building blocks of a convolutional neural network! Each function you will implement will have detailed instructions that will walk you through the steps needed:
- Convolution functions, including:
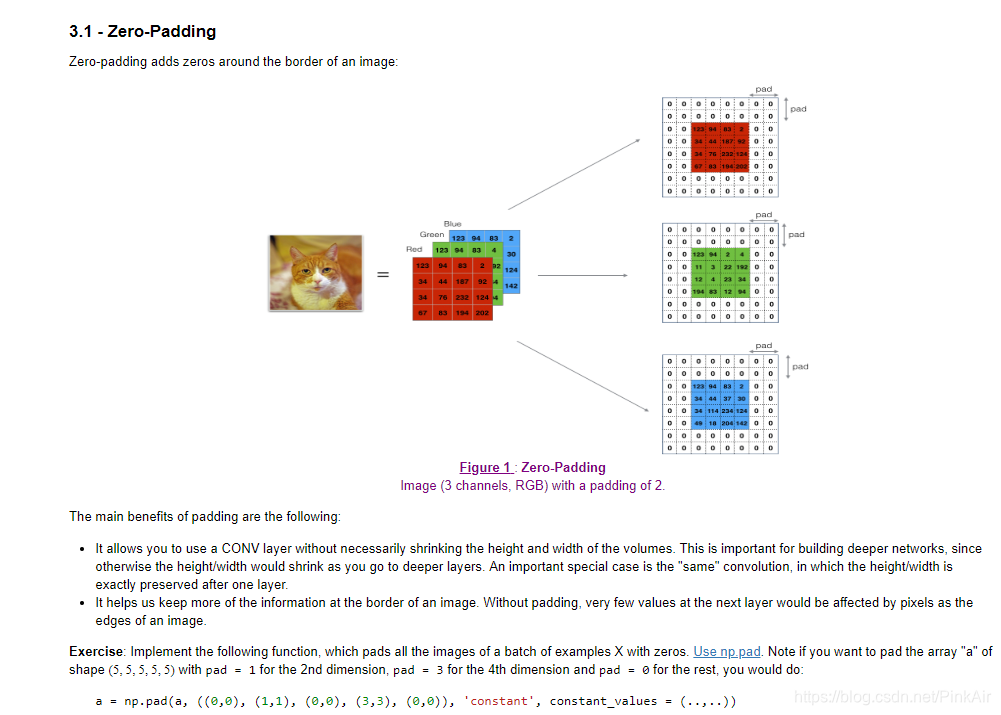
- Zero Padding
- Convolve window
- Convolution forward
- Convolution backward (optional)
- Pooling functions, including:
- Pooling forward
- Create mask
- Distribute value
- Pooling backward (optional)
-
This notebook will ask you to implement these functions from scratch in
numpy. In the next notebook, you will use the TensorFlow equivalents of these functions to build the following model: -
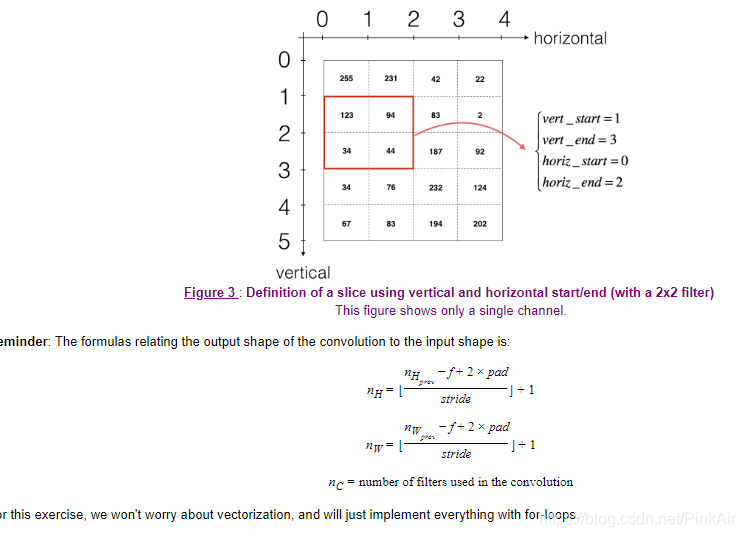
-
-
# GRADED FUNCTION: zero_pad def zero_pad(X, pad): """ Pad with zeros all images of the dataset X. The padding is applied to the height and width of an image, as illustrated in Figure 1. Argument: X -- python numpy array of shape (m, n_H, n_W, n_C) representing a batch of m images pad -- integer, amount of padding around each image on vertical and horizontal dimensions Returns: X_pad -- padded image of shape (m, n_H + 2*pad, n_W + 2*pad, n_C) """ ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 1 line) X_pad = np.pad(X, ((0,0), (pad,pad), (pad,pad),(0,0)), 'constant') ### END CODE HERE ### return X_pad np.random.seed(1) x = np.random.randn(4, 3, 3, 2) x_pad = zero_pad(x, 2) print ("x.shape =", x.shape) print ("x_pad.shape =", x_pad.shape) print ("x[1,1] =", x[1,1]) print ("x_pad[1,1] =", x_pad[1,1]) fig, axarr = plt.subplots(1, 2) axarr[0].set_title('x') axarr[0].imshow(x[0,:,:,0]) axarr[1].set_title('x_pad') axarr[1].imshow(x_pad[0,:,:,0])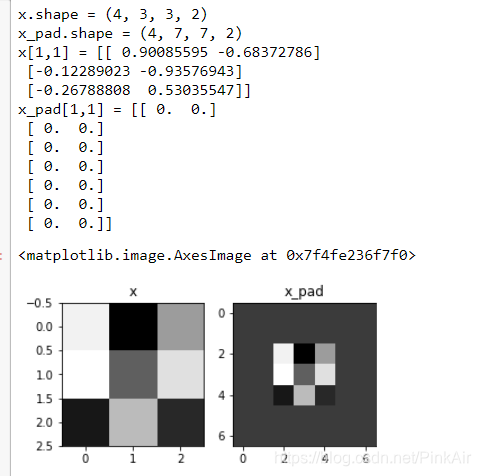
-
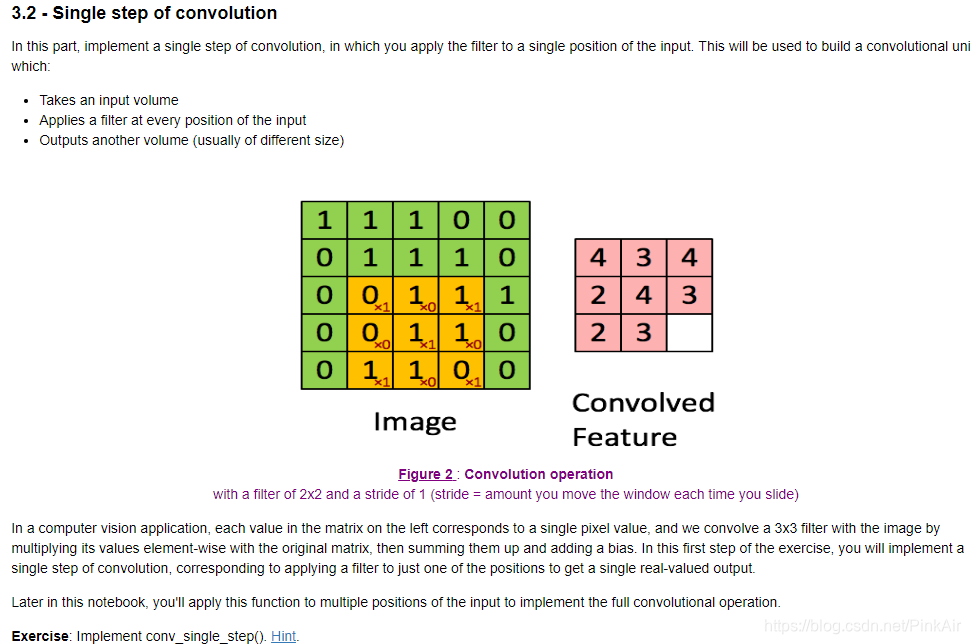
-
# GRADED FUNCTION: conv_single_step def conv_single_step(a_slice_prev, W, b): """ Apply one filter defined by parameters W on a single slice (a_slice_prev) of the output activation of the previous layer. Arguments: a_slice_prev -- slice of input data of shape (f, f, n_C_prev) W -- Weight parameters contained in a window - matrix of shape (f, f, n_C_prev) b -- Bias parameters contained in a wind





 本课程的作业中,你将从头实现卷积神经网络(CNN)的关键组件,包括卷积层(CONV)和池化层(POOL)。你将了解零填充、卷积窗口、前向传播和(可选)反向传播的实现。此外,还将涉及平均池化和最大池化的前后向过程。
本课程的作业中,你将从头实现卷积神经网络(CNN)的关键组件,包括卷积层(CONV)和池化层(POOL)。你将了解零填充、卷积窗口、前向传播和(可选)反向传播的实现。此外,还将涉及平均池化和最大池化的前后向过程。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 1020
1020

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








