Initialization
Welcome to the first assignment of "Improving Deep Neural Networks".
Training your neural network requires specifying an initial value of the weights. A well chosen initialization method will help learning.
If you completed the previous course of this specialization, you probably followed our instructions for weight initialization, and it has worked out so far. But how do you choose the initialization for a new neural network? In this notebook, you will see how different initializations lead to different results.
A well chosen initialization can:
- Speed up the convergence of gradient descent
- Increase the odds of gradient descent converging to a lower training (and generalization) error
To get started, run the following cell to load the packages and the planar dataset you will try to classify.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import sklearn
import sklearn.datasets
from init_utils import sigmoid, relu, compute_loss, forward_propagation, backward_propagation
from init_utils import update_parameters, predict, load_dataset, plot_decision_boundary, predict_dec
%matplotlib inline
plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (7.0, 4.0) # set default size of plots
plt.rcParams['image.interpolation'] = 'nearest'
plt.rcParams['image.cmap'] = 'gray'
# load image dataset: blue/red dots in circles
train_X, train_Y, test_X, test_Y = load_dataset()You would like a classifier to separate the blue dots from the red dots.
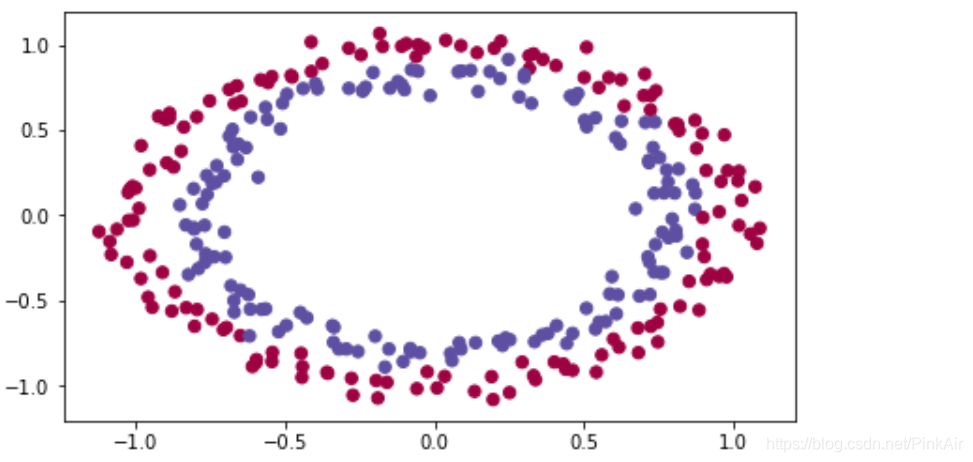
1 - Neural Network model
You will use a 3-layer neural network (already implemented for you). Here are the initialization methods you will experiment with:
- Zeros initialization -- setting
initialization = "zeros"in the input argument. - Random initialization -- setting
initialization = "random"in the input argument. This initializes the weights to large random values. - He initialization -- setting
initialization = "he"in the input argument. This initializes the weights to random values scaled according to a paper by He et al., 2015.
Instructions: Please quickly read over the code below, and run it. In the next part you will implement the three initialization methods that this model() calls.
def model(X, Y, learning_rate = 0.01, num_iterations = 15000, print_cost = True, initialization = "he"):
"""
Implements a three-layer neural network: LINEAR->RELU->LINEAR->RELU->LINEAR->SIGMOID.
Arguments:
X -- input data, of shape (2, number of examples)
Y -- true "label" vector (containing 0 for red dots; 1 for blue dots), of shape (1, number of examples)
learning_rate -- learning rate for gradient descent
num_iterations -- number of iterations to run gradient descent
print_cost -- if True, print the cost every 1000 iterations
initialization -- flag to choose which initialization to use ("zeros","random" or "he")
Returns:
parameters -- parameters learnt by the model
"""
grads = {}
costs = [] # to keep track of the loss
m = X.shape[1] # number of examples
layers_dims = [X.shape[0], 10, 5, 1]
# Initialize parameters dictionary.
if initialization == "zeros":
parameters = initialize_parameters_zeros(layers_dims)
elif initialization == "random":
parameters = initialize_parameters_random(layers_dims)
elif initialization == "he":
parameters = initialize_parameters_he(layers_dims)
# Loop (gradient descent)
for i in range(0, num_iterations):
# Forward propagation: LINEAR -> RELU -> LINEAR -> RELU -> LINEAR -> SIGMOID.
a3, cache = forward_propagation(X, parameters)
# Loss
cost = compute_loss(a3, Y)
# Backward propagation.
grads = backward_propagation(X, Y, cache)
# Update parameters.
parameters = update_parameters(parameters, grads, learning_rate)
# Print the loss every 1000 iterations
if print_cost and i % 1000 == 0:
print("Cost after iteration {}: {}".format(i, cost))
costs.ap




 本文探讨了神经网络权重初始化的重要性,包括零初始化、随机初始化和He初始化对模型训练效果的影响。通过实验发现,零初始化可能导致网络无法打破对称性,随机初始化虽有所改善但可能因数值过大导致梯度问题,而He初始化则根据ReLU激活函数特点进行优化,能有效提高训练效果。
本文探讨了神经网络权重初始化的重要性,包括零初始化、随机初始化和He初始化对模型训练效果的影响。通过实验发现,零初始化可能导致网络无法打破对称性,随机初始化虽有所改善但可能因数值过大导致梯度问题,而He初始化则根据ReLU激活函数特点进行优化,能有效提高训练效果。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 7万+
7万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








