目录
泛型 generic
定义
定义类,接口,方法时,同时声明了一个或者多个类型变量(如:<T>,<K>,<E>,<V>)
称为泛型类,泛型接口,泛型方法,它们统称为泛型
作用
泛型提供了在编译阶段所能操作的数据类型,并自动进行检查的能力!
这样可以避免强制类型转换及其可能出现的异常
注:泛型的本质是把具体的数据类型作为参数传给类型变量
实例:
1)自定义泛型类
// 不使用泛型的容器类
public class ContainerWithoutGenerics {
private Object item;
public void setItem(Object item) {
this.item = item;
}
public Object getItem() {
return item;
}
}
// 使用泛型的容器类
public class ContainerWithGenerics<T> { // T 是类型变量
private T item;
public void setItem(T item) {
this.item = item;
}
public T getItem() {
return item;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 使用没有泛型的容器
ContainerWithoutGenerics container1 = new ContainerWithoutGenerics();
container1.setItem("Hello");
String s1 = (String) container1.getItem(); // 需要强制类型转换
System.out.println(s1);
// 尝试放入错误类型的对象,编译器不会阻止
container1.setItem(123); // 这里是合法的
String s2 = (String) container1.getItem(); // 运行时会抛出ClassCastException
System.out.println(s2);
// 使用泛型的容器
ContainerWithGenerics<String> container2 = new ContainerWithGenerics<>();
container2.setItem("World");
String s3 = container2.getItem(); // 不需要强制类型转换
System.out.println(s3);
// 尝试放入错误类型的对象,编译器会阻止
// 下面这行代码会导致编译错误
// container2.setItem(456);
}
}2)自定义泛型接口
定义泛型接口
public interface DataProcessor<T> {
void process(T data); // 处理传入的数据
T getResult(); // 获取处理后的结果
}实现泛型接口 (实现功能:将输入的字符串转换为大写形式)
public class StringToUpperProcessor implements DataProcessor<String> {
private String result;
@Override
public void process(String data) {
if (data != null) {
this.result = data.toUpperCase();
} else {
this.result = null;
}
}
@Override
public String getResult() {
return result;
}
}使用泛型接口
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DataProcessor<String> processor = new StringToUpperProcessor();
processor.process("hello world");
System.out.println(processor.getResult()); // 输出: HELLO WORLD
}
}泛型方法
修饰符 <类型变量> 返回值类型 方法名(形参列表){ }
实例:实现功能:交换两个对象的值
1)不使用泛型方法
public void swap(Integer a, Integer b) {
Integer temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
public void swap(String a, String b) {
String temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
// ... 对于其他类型也需要类似的实现2)使用泛型方法
public class GenericMethodExample {
// 定义一个泛型方法
public <T> void swap(T a, T b) {
T temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
System.out.println("After swapping: a = " + a + ", b = " + b);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
GenericMethodExample example = new GenericMethodExample();
// 交换整数
Integer x = 10;
Integer y = 20;
example.swap(x, y); // 输出: After swapping: a = 20, b = 10
// 交换字符串
String s1 = "Hello";
String s2 = "World";
example.swap(s1, s2); // 输出: After swapping: a = World, b = Hello
}
}通配符
通配符就是 ? ,可以在"使用泛型"的时候代表一切
E,K,T,V是在定义泛型的时候使用
- 无界通配符
<?>:表示任何类型。- 上界通配符
<? extends T>:表示类型必须是T或T的子类型,主要用于读取数据。- 下界通配符
<? super T>:表示类型必须是T或T的父类型,主要用于写入数据。
实例:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class WildcardExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> intList = new ArrayList<>();
intList.add(1);
intList.add(2);
List<Double> doubleList = new ArrayList<>();
doubleList.add(1.5);
doubleList.add(2.5);
printList(intList); // 输出: 1, 2
printList(doubleList); // 输出: 1.5, 2.5
System.out.println("Sum of intList: " + sumOfNumbers(intList)); // 输出: 3.0
System.out.println("Sum of doubleList: " + sumOfNumbers(doubleList)); // 输出: 4.0
List<Number> numberList = new ArrayList<>();
addNumbers(numberList, 1, 2, 3);
System.out.println("numberList: " + numberList); // 输出: [1, 2, 3]
}
public static void printList(List<?> list) {
for (Object item : list) {
System.out.println(item);
}
}
public static double sumOfNumbers(List<? extends Number> numbers) {
double sum = 0.0;
for (Number num : numbers) {
sum += num.doubleValue();
}
return sum;
}
public static void addNumbers(List<? super Integer> list, int... numbers) {
for (int number : numbers) {
list.add(number);
}
}
}泛型支持的类型
泛型不支持基本数据类型,只能支持对象类型(引用数据类型)
解决方法:包装类
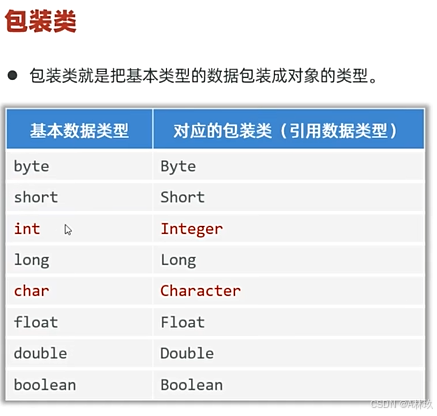
自动装箱:基本数据类型可以自动转换为包装类型
Integer i = 10; // int 被自动转换成 Integer自动拆箱:包装类型可以自动转换为基本数据类型
Integer i = new Integer(10);
int j = i; // Integer 被自动转换成 int包装类具备的其他功能
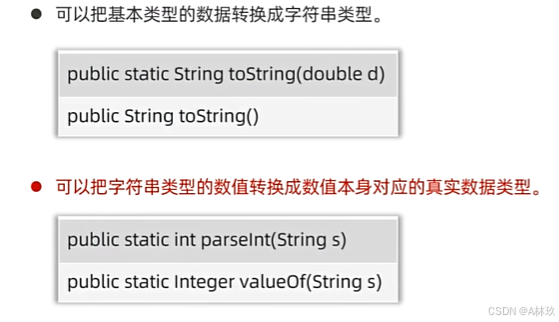
示例:
public class TypeConversionExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 基本类型转字符串
double num = 123.456;
String strNum = Double.toString(num);
System.out.println("基本类型转字符串: " + strNum);
//1.字符串转基本类型(int)
String strInt = "123";
//使用 parseInt 方法
int intValue = Integer.parseInt(strInt);
System.out.println("String to integer using parseInt: " + intValue);
// 使用 valueOf 方法
Integer intValueObj = Integer.valueOf(strInt);
System.out.println("String to integer using valueof: " + intValueObj);
// 2.字符串转基本类型 (double)
String strDouble = "123.456";
// 使用 parseDouble 方法
double doubleValue = Double.parseDouble(strDouble);
System.out.println("String to double using parseDouble: " + doubleValue);
// 使用 valueOf 方法
Double doubleValueObj = Double.valueOf(strDouble);
System.out.println("String to double using valueOf: " + doubleValueObj);
}
}





















 938
938

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








