LinkedList的底层本质是一个双向链表,它实现了List接口(其提供了相关的添加、删除、修改、遍历等功能)。此次模拟以简单的单链表为例。
1.新建Node类,用来保存数据和指针,此时的data属性和next属性不加private修饰,方便同一包中的其它类访问。
包及控制权限:
| 修饰符\权限 | 本类 | 同包子类 | 同包非子类 | 不同包子类 | 不同包非子类 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| private | √ | × | × | × | × |
| 缺省 | √ | √ | √ | × | × |
| protected | √ | √ | √ | √ | × |
| public | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
package com.util;
/**
* 单链表的结点
*/
public class Node {
Object data;//要存储的数据
Node next;
public Node() {
}
public Node(Object data, Node next) {
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
}
public Node(Object data) {
this.data = data;
}
public Object getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(Object data) {
this.data = data;
}
public Node getNext() {
return next;
}
public void setNext(Node next) {
this.next = next;
}
}
2.新建SingleLinkedList类并实现List接口
package com.util;
import com.data.List;
import com.exception.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
public class SingleLinkedList implements List {
private Node head = new Node();//头节点,不存储数据,为了编程方便
private int size;//表示单链表长度
@Override
public int size() {
return this.size;
}
@Override
public Object get(int index) {
if(index>this.size){
return null;
}else{
Node node = this.head;
for(int x=0;x<=index;x++){
node = node.next;
}
return node.data;
}
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.size==0;
}
@Override
public boolean contains(Object e) {
return this.indexOf(e)!=-1;
}
@Override
public int indexOf(Object e) {
Node currentNode = this.head;
for(int x=0;x<this.size;x++){
currentNode = currentNode.next;
if(e.equals(currentNode.data)){
return x;
}
}
return -1;
}
@Override
public void add(int index, Object e) {
if(index>this.size||index<0){
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("数组指针越界异常:"+index);
}else{
Node beforeNode = this.head;//找到前一个结点
for(int x=0;x<index;x++){
beforeNode = beforeNode.next;
}
Node newNode = new Node(e);//创建一个新结点,并赋值
newNode.next = beforeNode.next;//指明新节点的后继节点
beforeNode.next = newNode;//指明新节点的前驱节点
this.size++;//列表长度+1
}
}
@Override
public void add(Object e) {
this.add(this.size,e);
}
@Override
public boolean addBefore(Object obj, Object e) {
int index = this.indexOf(obj);
if(index!=-1){
this.add(index,e);
return true;
}
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean addAfter(Object obj, Object e) {
int index = this.indexOf(obj);
if(index!=-1){
this.add(index+1,e);
return true;
}
return false;
}
@Override
public Object remove(int index) {
if(index>=0&&index<this.size){
Node beforeNode = this.head;
for(int x=0;x<index;x++){
beforeNode = beforeNode.next;
}
Node removedNode = beforeNode.next;
beforeNode.next = beforeNode.next.next;
this.size--;
return removedNode.data;
}else{
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("链表指针越界:"+index);
}
}
@Override
public Object remove(Object e) {
Node beforeNode = this.head;//要删除节点的前驱结点
for(int x=0;x<this.size;x++){
if(e.equals(beforeNode.next.data)){//如果下一个节点是要被删除的节点
Node removedNode = beforeNode.next;//保存要被删除的节点
beforeNode.next = beforeNode.next.next;//改变指针,删除节点
this.size--;//链表长度-1
return removedNode.data;
}
beforeNode = beforeNode.next;
}
return null;
}
@Override
public Object replace(int index, Object e) {
if(index>=0&&index<this.size){
Node beforeNode = this.head;//要删除结点的前驱节点
for(int x=0;x<index;x++){
beforeNode = beforeNode.next;
}
Node newNode = new Node(e);//创建新节点
Object data = beforeNode.next.data;//保存要删除的数据
newNode.next = beforeNode.next.next;//新结点指针指向被删除节点指针的后继节点
beforeNode.next = newNode;//被删除节点的前驱节点指针指向新结点
return data;
}else{
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("链表指针越界:"+index);
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
if(this.size==0){
return "[]";
}
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
Node currentNode = this.head;
builder.append("[");
for(int x=0;x<this.size;x++){
currentNode = currentNode.next;
builder.append(currentNode.data).append(',');
}
builder.delete(builder.length()-1,builder.length()).append("]");
return builder.toString();
}
}
3.编写测试代码
package com.test;
import com.data.List;
import com.util.SingleLinkedList;
public class TestLinkedList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new SingleLinkedList();
list.add("123");
list.add(456);
list.add(789);
list.add("555");
list.add(3,"haha");
System.out.println("数组长度:"+list.size());
System.out.println("是否为空:"+list.isEmpty());
System.out.println("是否包含haha:"+list.contains("haha"));
System.out.println("haha位置:"+list.indexOf("haha"));
System.out.println("输出集合:"+list);
System.out.println("在haha之前插入hello:"+list.addBefore("haha","hello"));
System.out.println("输出集合:"+list);
System.out.println("在haha之后插后world:"+list.addAfter("haha","world"));
System.out.println("输出集合:"+list);
System.out.println("删除第5个元素:"+list.remove(5));
System.out.println("输出集合:"+list);
System.out.println("删除haha:"+list.remove("haha"));
System.out.println("输出集合:"+list);
System.out.println("将最后一个元素换成haha:"+list.replace(list.size()-1,"haha"));
System.out.println("输出集合:"+list);
}
}
4.运行程序查看控制台输出,发现所有操作都能正常完成。
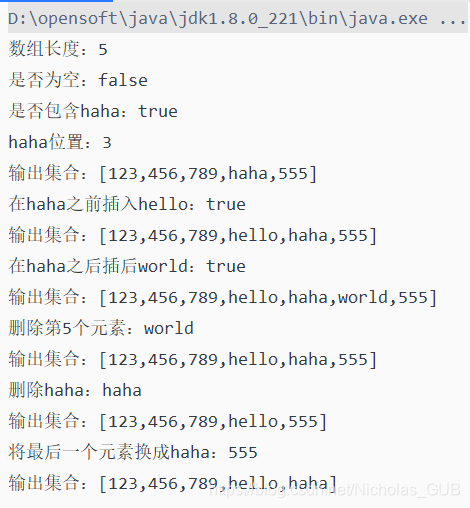





 本文详细介绍了一种基于单链表实现的LinkedList数据结构,包括结点类定义、链表类实现以及各种链表操作如添加、删除、查找等。通过具体代码示例,展示了如何在Java中手动构建和维护链表。
本文详细介绍了一种基于单链表实现的LinkedList数据结构,包括结点类定义、链表类实现以及各种链表操作如添加、删除、查找等。通过具体代码示例,展示了如何在Java中手动构建和维护链表。
















 12万+
12万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








