目录
一,map介绍
- map是关联容器,按照特定的次序存储元素(由键key和值value组合而成的键值对);
- 键key通常用于排序及唯一标识元素,而值value则存储与键key关联的内容;
- 键key和值value的类型可能不同,且在map的内部,key与value通过成员类型value_type绑定在一起;
- key是唯一的,并且不能修改;
- map中的元素如用迭代器去遍历,可以得到一个有序序列;
typedef pair<const Key, T> value_type;
- map中的元素始终根据其key按照其内部比较对象(compare)所指示的特定严格弱排序准则进行排序;
- map中通过键值访问元素的速度通常比unordered_map容器慢,但map允许根据顺序对元素进行直接迭代;
- map支持下标访问符,即在[ ]中放key,即可找到与key对应的value;
- map通常被实现为二叉搜索树(红黑树),查找效率比较高O(logN);
类pair
template <class T1, class T2> struct pair;- 此类将一对值组合在一起,类型可以不同;
- 可直接访问其公共成员变量first、second;
- pair是tuple的特殊形式;
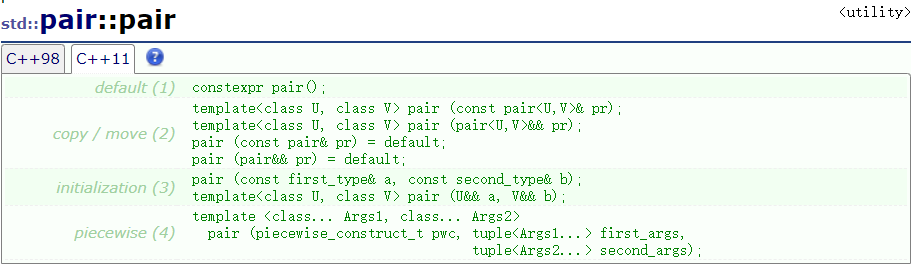
std::pair<int, double> p1(1, 2.5); //initialization (3) 初始化构造
std::pair<long, float> p2(p1); //copy/move (2) 调用模板拷贝构造函数,会进行类型转换
std::pair<long, float> p3(std::move(p1)); //copy/move (2) 调用模板移动构造函数,会进行类型转换
std::pair<int, double> p4(p1); //copy/move (2) 调用默认拷贝构造函数
std::pair<int, double> p5(std::move(p1)); //copy/move (2) 调用默认移动构造函数函数模板make_pair
- 构建一个pair对象,第一个元素为x,第二个元素为y;
- 通过传递的参数可隐式的推导模板类型;
template <class T1, class T2>
pair<V1,V2> make_pair (T1&& x, T2&& y);
//此函数返回,初始化构造一个pair对象,对参数进行完美转发
pair<V1,V2>(std::forward<T1>(x),std::forward<T2>(y))//自动推导类型,不需要显式指定类型
auto p1 = std::make_pair(1, "hello"); // pair<int, const char*>
auto p2 = std::make_pair(3.14, true); // pair<double, bool>
//隐式转化 pair<double,char>
std::pair <int, int> bar;
bar = std::make_pair(10.5, 'A');
//完美转发
string str = "world";
auto p3 = std::make_pair(std::move(str), 42); // 移动语义,str 被转移二,map成员函数
- Key,键值对中key的类型;
- T,键值对中value的类型;
- Compare,比较器类型,map中的元素是按照key来比较的,默认按照小于来比较;
- 一般情况下(内置类型)该参数不需传递;
- 如无法比较(自定义类型),需要用户自己显示传递比较规则(一般情况下按照函数指针或仿函数来传递);

注:
- map容器的元素是键值对(value_type),迭代器指向即为该元素的键值对;
- value_type = pair<const key_type, mapped_type>
构造函数

操作函数
//迭代器
iterator begin() noexcept;
const_iterator begin() const noexcept;
iterator end() noexcept;
const_iterator end() const noexcept;
reverse_iterator rbegin() noexcept;
const_reverse_iterator rbegin() const noexcept;
reverse_iterator rend() noexcept;
const_reverse_iterator rend() const noexcept;
//插入
single element (1)
pair<iterator,bool> insert (const value_type& val);
template <class P> pair<iterator,bool> insert (P&& val);
with hint (2)
iterator insert (const_iterator position, const value_type& val);
template <class P> iterator insert (const_iterator position, P&& val);
range (3)
template <class InputIterator>
void insert (InputIterator first, InputIterator last);
initializer list (4)
void insert (initializer_list<value_type> il);
//删除
iterator erase (const_iterator position);
size_type erase (const key_type& k);
iterator erase (const_iterator first, const_iterator last);
//查找
iterator find (const key_type& k);
const_iterator find (const key_type& k) const;
//访问
mapped_type& operator[] (const key_type& k);
mapped_type& operator[] (key_type&& k);
bool empty() const noexcept;
size_type size() const noexcept;
size_type count (const key_type& k) const;
void swap (map& x);
void clear() noexcept;key_compare key_comp() const;
value_compare value_comp() const;
iterator lower_bound (const key_type& k);
const_iterator lower_bound (const key_type& k) const;
iterator upper_bound (const key_type& k);
const_iterator upper_bound (const key_type& k) const;
pair<const_iterator,const_iterator> equal_range (const key_type& k) const;
pair<iterator,iterator> equal_range (const key_type& k);int main()
{
map<string, string> m;
m.insert(pair<string, string>("peach", "桃子")); //pair<string, string> p("peach", "桃子");
m.insert(make_pair("banan", "香蕉"));
m["apple"] = "苹果";
//m.at("waterme"); //不存在抛异常
cout << m.size() << endl;
cout << m.count("waterme") << endl;
pair<map<string, string>::iterator, bool> ret = m.insert(make_pair("banan", "香蕉"));
if (ret.second)
cout << "insert successful" << endl;
else
cout << "insert failed" << endl;
for (auto& e : m)
{
cout << e.first << "-->" << e.second << endl;
}
m.erase("apple");
map<string, string>::iterator it = m.begin();
while (it != m.end())
{
cout << (*it).first << "-->" << (*it).second << endl;
++it;
}
it = m.find("banan");
cout << (*it).first << "-->" << (*it).second << endl;
return 0;
}三,map应用
// 字典和查找表(最常用)
std::map<std::string, std::string> countryCodes = {
{"CN", "中国"},
{"US", "美国"},
{"JP", "日本"},
{"UK", "英国"},
{"FR", "法国"}
};
// 错误码映射
std::map<int, std::string> errorMessages = {
{0, "成功"},
{1, "文件未找到"},
{2, "权限不足"},
{3, "内存不足"},
{4, "网络超时"}
};
std::string getCountryName(const std::string& code) {
auto it = countryCodes.find(code);
return it != countryCodes.end() ? it->second : "未知国家";
}
std::string getErrorMessage(int errorCode) {
return errorMessages.count(errorCode) ? errorMessages[errorCode] : "未知错误";
}// 统计单词频率
void wordFrequency(const std::vector<std::string>& words) {
std::map<std::string, int> frequency;
for (const auto& word : words) {
frequency[word]++;
}
std::cout << "单词频率统计:" << std::endl;
for (const auto& [word, count] : frequency) {
std::cout << word << ": " << count << "次" << std::endl;
}
}
// 投票统计
void voteCounter() {
std::map<std::string, int> votes = {
{"候选人A", 0},
{"候选人B", 0},
{"候选人C", 0}
};
// 模拟投票
std::vector<std::string> voteResults = {"A", "B", "A", "C", "B", "A", "A"};
for (const auto& vote : voteResults) {
std::string candidate = "候选人" + vote;
if (votes.find(candidate) != votes.end()) {
votes[candidate]++;
}
}
// 显示结果(自动按键排序)
for (const auto& [candidate, count] : votes) {
std::cout << candidate << ": " << count << "票" << std::endl;
}
}






 本文详细介绍了C++中的map容器,包括它的特性,如作为关联容器存储键值对,内部基于红黑树实现高效查找。此外,还讲解了pair类和make_pair函数的用途,以及map的各种操作,如插入、删除、查找和访问元素的方法。
本文详细介绍了C++中的map容器,包括它的特性,如作为关联容器存储键值对,内部基于红黑树实现高效查找。此外,还讲解了pair类和make_pair函数的用途,以及map的各种操作,如插入、删除、查找和访问元素的方法。
















 3455
3455

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








