22.文件和文件流
22.1.File类
Java.io.File类可以获取文件以及文件夹的一些基本的属性
常用的方法 文件名称,路径,大小,判断是否存在,删除,创建
// 创建一个文件对象(可以是文件,可以是文件夹)
File file = new File("e:/java_text.txt");
// 基本属性
boolean canWriter = file.canWrite();
System.out.println("是否可写:" + canWriter);
boolean canRead = file.canRead();
System.out.println("是否可读:" + canRead);
long size = file.length(); // 常用
System.out.println("文件大小:" + size);
boolean isFile = file.isFile(); // 常用
System.out.println("是否是文件:" + isFile);
boolean isDirectory = file.isDirectory();
System.out.println("是否是文件夹:" + isDirectory);
String filename = file.getName(); // 常用
System.out.println("文件的名称:" + filename);
String absolutePath = file.getAbsolutePath(); // 常用
System.out.println("文件的绝对路径:" + absolutePath);
String filepath = file.getPath();
System.out.println("文件的绝对路径:" + filepath);
boolean isExists = file.exists(); // 常用
System.out.println("是否存在:" + isExists);
boolean isDelete = file.delete(); // 常用
System.out.println("是否已经被删除:" + isDelete);
boolean isCreate = file.createNewFile();
System.out.println("创建了没有:" + isCreate);
File类的listFile获取文件夹下面的所有文件内容,可以通过递归调用的方法把某一个文件夹下的所有的文件查询出来
// 测试文件目录的属性(递归遍历文件夹中所有的文件信息)
public static void testDirectoryDeme(File file) {
if (file.isDirectory()) {
File[] files = file.listFiles();
System.out.println("文件夹"+file.getName()+"有"+files.length+"个文件");
// 利用for遍历所有的文件
for (int i = 0; i < files.length; i++) {
File childFile = files[i];
if (childFile.isFile()) {
// 这是一个文件
System.out.println("\t这是一个文件:" + childFile.getName());
} else {
// 文件夹:继续递归调用
testDirectoryDeme(childFile);
}
}
} else {
// 这是一个文件
System.out.println("\t这是一个文件:" + file.getName());
}
}
22.2.Files 和 paths是一个工具类,提供了对文件的基本功能的实现在java.nio包下面
文件的创建,删除,判断是否存在,移动,拷贝. 因为提供了静态的方法,所以不需要创建对象直接调用方法即可
// 如果文件不存在复制
if (!Files.exists(Paths.get("e:/a/cart1.jpg"))) {
// java.nio.Files(文件的工具类) Paths(文件路径工具类)
Files.copy(Paths.get("e:/cart1.jpg"), Paths.get("e:/a/cart1.jpg"));
}
Files.move(Paths.get("e:/a/cart1.jpg"), Paths.get("e:/a/b/cart1" + ((int) (Math.random() * 100)) + ".jpg"));
Files.delete(Paths.get("e:/cart1.jpg"));
22.3.文件流
文件流的分类:
根据功能分为:输入流(读取文件) 和 输出流(写入文件)
根据操作内容:字符流(读取字符数组) 和 字节流(读取字节数组)
字节输入流,字节输出流,字符输入流,字符输出流
文件流
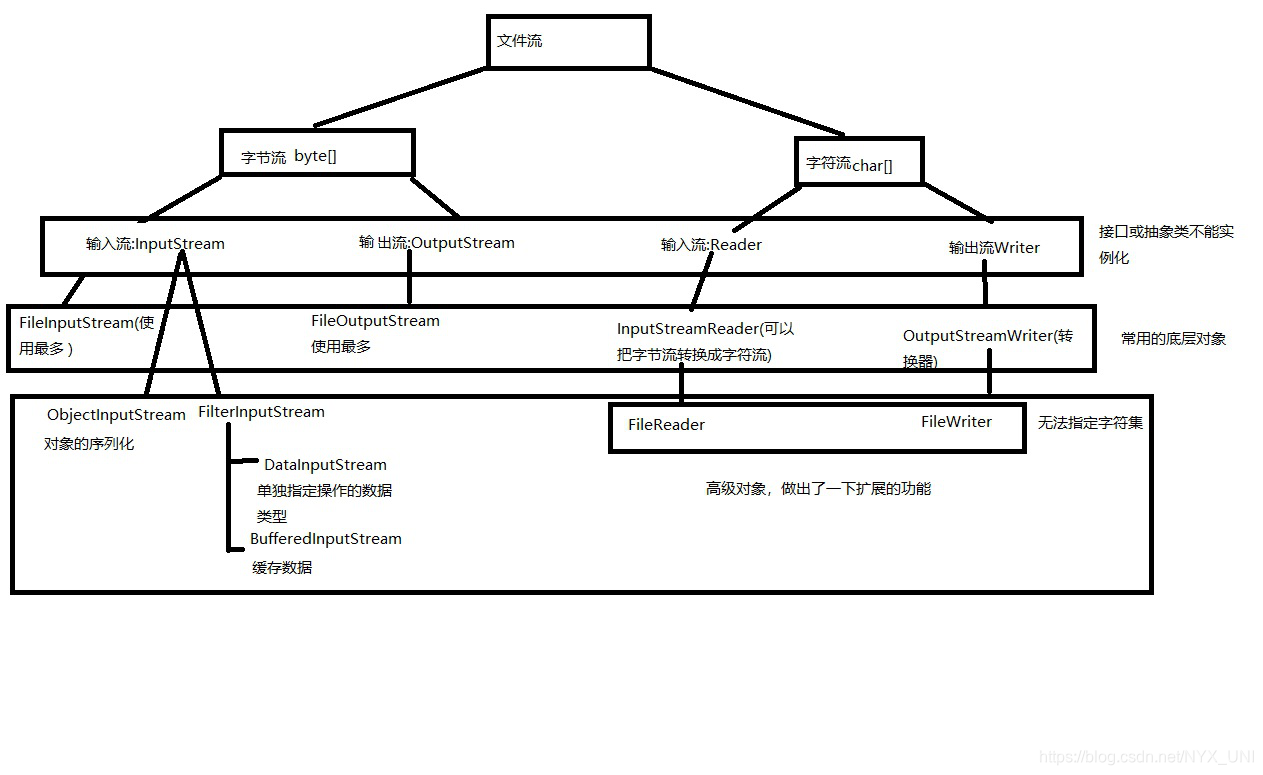
使用字节流实现文件的读取
//利用字节输入流实现文件的内容读取(inputStream 接口的 FileInputStream )
public static void testInputStream() throws Exception{
File file = new File("e:/a/file.txt");
InputStream is = new FileInputStream(file);
if(!file.exists()){
System.out.println("文件不存在");
}
//开始读取文件
byte[] temp_bytes = new byte[1024];
int size = 0; //用于记录读取文件的字节个数,如果没有读取任何的内容返回-1
//因为文件不可能一次读取完毕,需要循环读取
do{
size =is.read(temp_bytes);
if(size!=-1){
String info = new String(temp_bytes,0,size,"GBK");
System.out.println("读取的内容是:" + info);
}
}while(size !=-1);
//文件流是必须要关闭的(像水管子一样)
is.close();
}
利用字节输出流实现文件的写入
//利用字节输出流实现文件内容的写入(OutputStream 接口的FileOutputStream)
public static void testOuputStream() throws Exception{
File file = new File("e:/a/file_new.txt");
if(file.exists()){
file.createNewFile();
}
//文件写入
String info = "这就是我们要写入文件的内容";
//创建文件写入对象
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream(file);
os.write(info.getBytes());
//写入完毕后,关闭
os.flush(); //清空缓存区
os.close();
}
利用字节输入流和字节输出流实现文件的拷贝
//利用字节输入输入输出流,实现文件的复制,为了防止文件名称重复,需要对文件名称重命名
public static void testCopy(String filepath) throws Exception
{
//创建文件对象
File file = new File(filepath);
//判断文件是否存在,且必须是一个文件而不能是一个文件夹
if(!file.exists())
throw new Exception("文件不存在");
if(file.isDirectory())
throw new Exception("只能拷贝文件,不能拷贝文件夹");
//默认目标地址就是e:/a 文件夹
//开始拷贝
//创建一个文件输入流对象,读取文件的内容
InputStream is = new FileInputStream(file);
//创建一个文件输出流对象,写入文件的内容
String filename = getFileName(file.getName());
String targetpath="e:/a/"+filename;
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream(targetpath);
//利用循环,边读取内容,边写入内容即可
byte[] temp_info = new byte[1024]; //利用临时数组保存读取的内容
int size = 0; //保存读取的字节个数,如果没有读取到内容返回-1
do{
//先读取
size = is.read(temp_info);
//判断是否读取到了文件的内容
if(size!=-1){
//写入文件
os.write(temp_info, 0, size);
}
}while(size!=-1);
//关闭,先关闭输出流,后关闭输入流
os.flush();
os.close();
is.close();
}
//根据原有的文件名称获取新的文件名称
public static String getFileName(String fileName){
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyyMMddhhmmss");
//abc.mp4 ---abc_20190805164520.mp4
//根据.分别获取文件名称和扩展名
String[] name_infos = fileName.split("\\.");
//获取当前日期的字符串
Date date = new Date();
String dateStr = sdf.format(date);
return name_infos[0]+"_"+dateStr+"."+name_infos[1];
}
重点是熟练使用FileInputStream 和FileOutputStream 的使用
// 利用字节流复制某一个文件夹中的所有文件
public static void testCopyDirectory() throws Exception {
File file = new File("e:/file_source");
// 实现复制
// 创建文件输入输出流对象
InputStream is = null;
OutputStream os = null;
try {
// 遍历这个文件夹下的所有的文件信息
File[] files = file.listFiles();
for (int i = 0; i < files.length; i++) {
File childFile = files[i];
// 如果是一个文件就复制
if (childFile.isFile()) {
is = new FileInputStream(childFile);
// 根据原有的文件名称获取新的文件名称
String newFileName = getNewFileName(childFile.getName());
os = new FileOutputStream("e:/a/b/" + newFileName);
byte[] temp_info = new byte[1024];
int size = -1;
do {
// 先读取
size = is.read(temp_info);
// 后写入(写入的内容多去取决于读取的内容多少)
if (size != -1) {
os.write(temp_info, 0, size);
}
} while (size != -1);
}
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
throw new Exception(ex);
} finally {
if (os != null)
os.close();
if (is != null)
is.close();
}
}
// 根据原有的文件名称,获取新的文件名称
public static String getNewFileName(String oldFileName) {
// oldname :上机作业.docx newnmae : 上机作业_20180222.docx;
// 根据原有的文件名称获取文件名字和文件的类型
int index = oldFileName.lastIndexOf(".");
if (index == -1) {
return oldFileName;
}
// 获取文件名: 上机作业
String name = oldFileName.substring(0, index);
// 获取文件类型: docx
String type = oldFileName.substring(index + 1);
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyyMMddhhmmss");
Date date = new Date();
String formatstr = sdf.format(date);
// 上机作业_20180222.docx;
return name + "_" + formatstr + "." + type;
}
释放资源的新方法
//新的关闭资源的方法
//try( 定义必须要关闭的对象; ){}catch(Exception ex){};
// 创建输出流对象
try( OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream(FILE_PATH);
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(os); ) {
oos.writeObject(stuList);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new Exception(e);
}





 本文深入讲解Java中文件和文件流的操作,包括File类的基本属性获取、文件夹内容遍历、Files和Paths工具类的使用、字节流和字符流的概念及应用。通过实例演示如何进行文件读写、复制和删除等常见操作。
本文深入讲解Java中文件和文件流的操作,包括File类的基本属性获取、文件夹内容遍历、Files和Paths工具类的使用、字节流和字符流的概念及应用。通过实例演示如何进行文件读写、复制和删除等常见操作。
















 2927
2927

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








