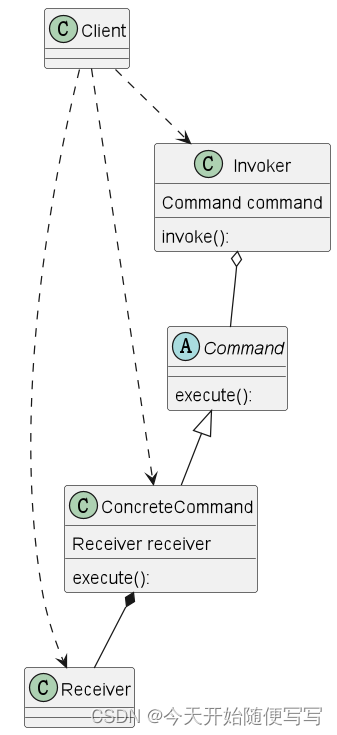
命令模式主要实现接受者(Receiver)与调用者(Invoker)之间的解耦,两者之间不是传统的调用者依赖接受者执行,而是通过具体的命令对象(ConcreteCommand)
1,优点:
- 降低系统的耦合度。命令模式能将调用操作的对象与实现该操作的对象解耦。
- 增加或删除命令非常方便。采用命令模式增加与删除命令不会影响其他类,它满足“开闭原则”,对扩展比较灵活。
- 可以实现宏命令。命令模式可以与组合模式结合,将多个命令装配成一个组合命令,即宏命令。 方便实现 Undo 和 Redo操作。
- 命令模式可以与后面介绍的备忘录模式结合,实现命令的撤销与恢复。
2,缺点:
- 使用命令模式可能会导致某些系统有过多的具体命令类。
- 系统结构更加复杂。
3, 使用场景
- 系统需要将请求调用者和请求接收者解耦,使得调用者和接收者不直接交互。
- 系统需要在不同的时间指定请求、将请求排队和执行请求。
- 系统需要支持命令的撤销(Undo)操作和恢复(Redo)操作。
原文链接https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/glass__sky/article/details/125224897
/**
* 角色(Receiver)
*/
public class Light {
public void on(){
System.out.println("开灯......");
}
public void off(){
System.out.println("关灯......");
}
}
/**
* 角色(Command)
*/
public abstract class Command {
public abstract void execute();
}
/**
* 角色(ConcreteCommand)
*/
public class LightOnCommand extends Command{
private Light light;
public LightOnCommand(Light light) {
this.light = light;
}
@Override
public void execute() {
light.on();
}
}
/**
* 角色(ConcreteCommand)
*/
public class LightOffCommand extends Command{
private Light light;
public LightOffCommand(Light light) {
this.light = light;
}
@Override
public void execute() {
light.off();
}
}
/**
* 空命令,方便封装
*/
public class EmptyCommand extends Command{
@Override
public void execute() {
System.out.println("暂无操作");
}
}
/**
* 角色(Invoker)
*/
public class Controller {
private Command[] onCommand;
private Command[] offCommand;
public Controller() {
this.onCommand = new Command[5];
this.offCommand = new Command[5];
for (Command command : onCommand) {
command = new EmptyCommand();
}
for (Command command : offCommand) {
command = new EmptyCommand();
}
}
public void setCommand(int index, Command onCommand, Command offCommand){
this.onCommand[index] = onCommand;
this.offCommand[index] = offCommand;
}
public void on(int index){
this.onCommand[index].execute();
}
public void off(int index){
this.offCommand[index].execute();
}
}
测试类
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Controller controller = new Controller();
Light light = new Light();
controller.setCommand(0, new LightOnCommand(light), new LightOffCommand(light));
controller.on(0);
controller.off(0);
}
}
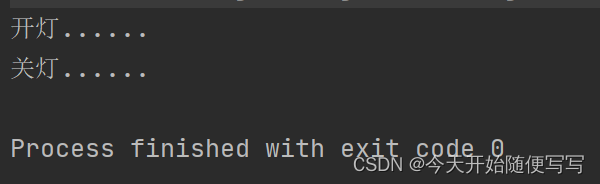
结果
jdk源码应用——runnable
public class JdkInstance {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("woca");
}
};
// 显然此处调用命令
thread.start();
}
}
进入thread.start()
public synchronized void start() {
/**
* This method is not invoked for the main method thread or "system"
* group threads created/set up by the VM. Any new functionality added
* to this method in the future may have to also be added to the VM.
*
* A zero status value corresponds to state "NEW".
*/
if (threadStatus != 0)
throw new IllegalThreadStateException();
/* Notify the group that this thread is about to be started
* so that it can be added to the group's list of threads
* and the group's unstarted count can be decremented. */
group.add(this);
boolean started = false;
try {
start0();
started = true;
} finally {
try {
if (!started) {
group.threadStartFailed(this);
}
} catch (Throwable ignore) {
/* do nothing. If start0 threw a Throwable then
it will be passed up the call stack */
}
}
}
private native void start0();
通过本地方法start0()开启线程,等待系统调用
runnable相当于是抽象命令,Thread相当于具体调用者,通过匿名内部类创建的Thread相当于是组合了具体命令的调用者





















 1115
1115

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








