结论:AtomicLong 底层CAS原理
LongAdder底层线程分组CAS操作原理
代理示例:
public class T02_AtomicVsSyncVsLongAdder {
static long count2 = 0L;
static AtomicLong count1 = new AtomicLong(0L);
static LongAdder count3 = new LongAdder();
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Thread[] threads = new Thread[1000];
for(int i=0; i<threads.length; i++) {
threads[i] =
new Thread(()-> {
for(int k=0; k<100000; k++) count1.incrementAndGet();
});
}
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(Thread t : threads ) t.start();
for (Thread t : threads) t.join();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
//TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(10);
System.out.println("Atomic: " + count1.get() + " time " + (end-start));
//-----------------------------------------------------------
Object lock = new Object();
for(int i=0; i<threads.length; i++) {
threads[i] =
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int k = 0; k < 100000; k++)
synchronized (lock) {
count2++;
}
}
});
}
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(Thread t : threads ) t.start();
for (Thread t : threads) t.join();
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("Sync: " + count2 + " time " + (end-start));
//----------------------------------
for(int i=0; i<threads.length; i++) {
threads[i] =
new Thread(()-> {
for(int k=0; k<100000; k++) count3.increment();
});
}
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(Thread t : threads ) t.start();
for (Thread t : threads) t.join();
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
//TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(10);
System.out.println("LongAdder: " + count1.longValue() + " time " + (end-start));
}
static void microSleep(int m) {
try {
TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS.sleep(m);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
运行结果:
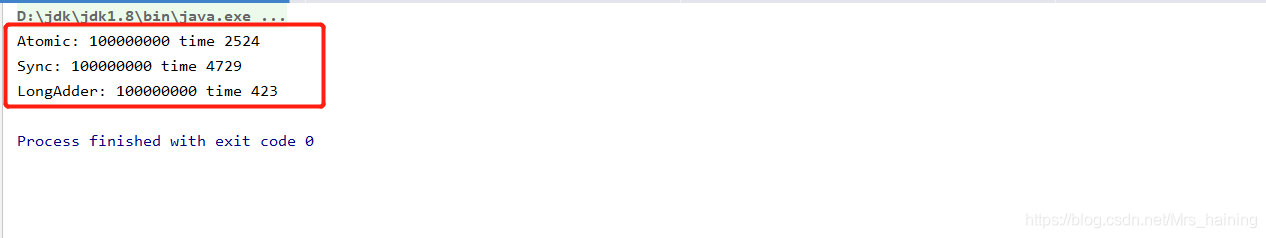
结论:
当线程数特别多的时候LongAdder有优势反之则AtomicLong或者Sync
高并发还得根据实际业务量进行分析适合用哪一种。





 本文通过并发测试展示了AtomicLong、同步锁和LongAdder在多线程环境下的性能差异。在高并发场景下,LongAdder表现出明显优势,而在线程较少的情况下,AtomicLong和同步锁的性能相近。选择哪种方式取决于实际的并发量和业务需求。
本文通过并发测试展示了AtomicLong、同步锁和LongAdder在多线程环境下的性能差异。在高并发场景下,LongAdder表现出明显优势,而在线程较少的情况下,AtomicLong和同步锁的性能相近。选择哪种方式取决于实际的并发量和业务需求。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








