常用作用域函数使用区分
〰〰〰〰〰〰〰〰〰〰〰〰〰〰〰〰〰〰〰〰〰〰〰我是分隔线〰〰〰〰〰〰〰〰〰 〰〰〰〰〰〰〰〰〰〰〰〰〰〰
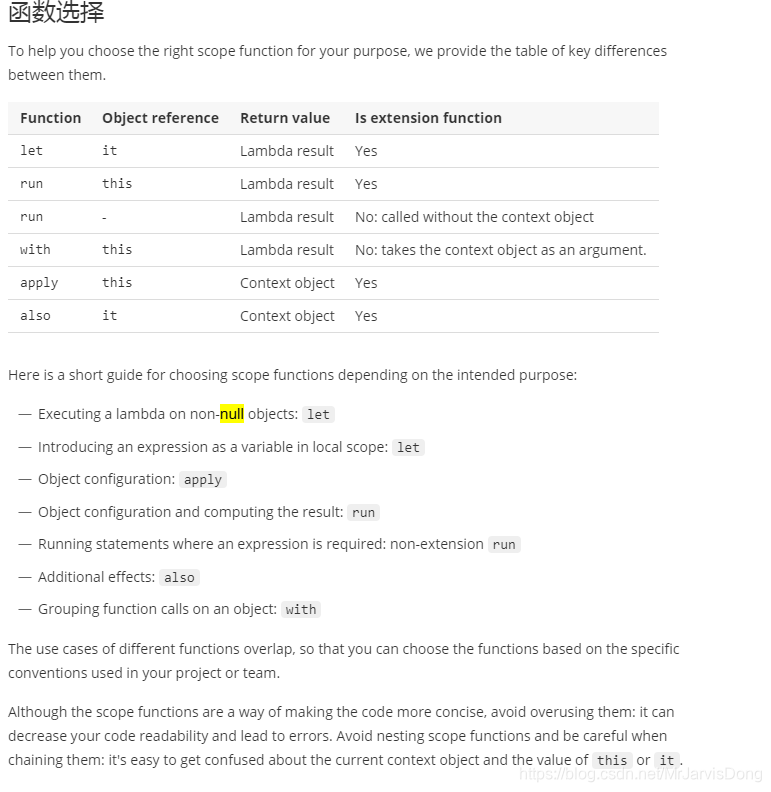
**作用域函数使用注意:**用于给定对象上下文中执行代码块;
apply: 有返回值自身;上下文对象可空;使用当前的接受者对象;root.apply{…}
Calls the specified function [block] with this value as its receiver and returns this value.
also: 将上下文对象的实例作为参数传递(it),返回值自身;上下文对象可空;使用当前的对象作为参数;
Calls the specified function [block] with this value as its argument and returns this value.
let: 将上下文对象的实例作为参数传递(it),有返回值方法体;上下文对象(调用对象)不可空;使用当前的对象作为参数;
Calls the specified function [block] with this value as its argument and returns its result.
with: 有返回值方法体;上下文对象不可空;使用的是给定的接受者eg: with(root){…}
Calls the specified function [block] with the given [receiver] as its receiver and returns its result.
run: 有返回值方法体;上下文对象可空;使用的是当前对象的接受者;
Calls the specified function [block] and returns its result.
Calls the specified function [block] with this value as its receiver and returns its result.
总结(结合例子看):
also和let差不多,使用方式 root.also{…} root.let{…};
使用当前对象(it指的是当前对象)作为参数;不可访问当前对象属性,但可使用it指代当前对象;
also 返回当前对象,let返回给定的值(最后一行);
一般用于使用当前对象作为参数进行下一步动作action;apply和with差不多, 使用方式 root.apply{…},with(root){…};
apply使用当前对象this作为接受者(代码块中的执行对象),可访问当前属性,但不可使用it;with使用给定的对象作为接受者,可访问属性,不可使用it;
apply返回值为当前对象;with返回给定的结果(最后一行);
一般用于使用当前对象的属性进行下一步动作action;run 使用当前对象this作为接受者,可访问当前属性,不可使用it;
返回值为给定的值;
// 上下文对象是“it”
//当前对象作为参数传入,不能访问属性;
class Baz {
var currentBar: Bar?
val observable: Observable
val foo = createBar().also {
currentBar = it // 访问 Baz 的属性
observable.registerCallback(it) // 将上下文对象作为参数传递
}
}
// 代码块中未使用接收者
val foo = createBar().also {
LOG.info("Bar created")
}
// 上下文对象是“this”
//当前对象作为接受者传入,color,text为当前对象的属性;
class Baz {
val foo: Bar = createBar().apply {
color = RED // 只访问 Bar 的属性
text = "Foo"
}
}
〰〰〰〰〰〰〰〰〰〰〰〰〰〰〰〰〰〰〰〰〰〰〰我是分隔线〰〰〰〰〰〰〰〰〰 〰〰〰〰〰〰〰〰〰〰〰〰〰〰
**额外的一些作用域函数说明:**takeIf: Returns this value if it satisfies the given [predicate] or null, if it doesn’t.
takeUnless: Returns this value if it does not satisfy the given [predicate] or null, if it does.
repeat: Executes the given function [action] specified number of [times].





 本文深入解析了作用域函数apply、also、let、with和run的使用场景与区别,通过对比不同函数的特点,如参数传递方式、上下文对象的使用及返回值类型,帮助读者掌握这些函数在实际编程中的应用。
本文深入解析了作用域函数apply、also、let、with和run的使用场景与区别,通过对比不同函数的特点,如参数传递方式、上下文对象的使用及返回值类型,帮助读者掌握这些函数在实际编程中的应用。
















 391
391

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








