非阻塞式IO
- 使用channel代替stream
- 使用selector监控多条channel
- 可以在一个线程里处理多个channel I/O
Buffer解析
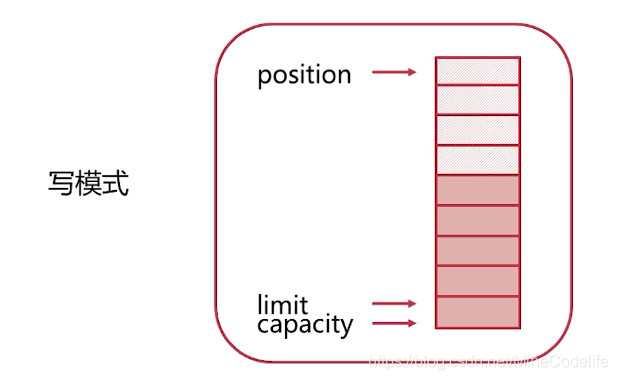
buffer既可以写也可以读,一开始我们向buffer写入到了position位置个数据
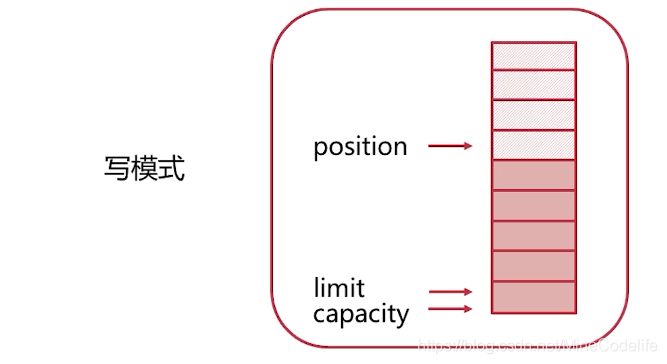
现在想从buffer里面读出数据,调用buffer的flip()方法 调整为读模式
将position位置指向开始的位置。limit指向已有数据的尾部
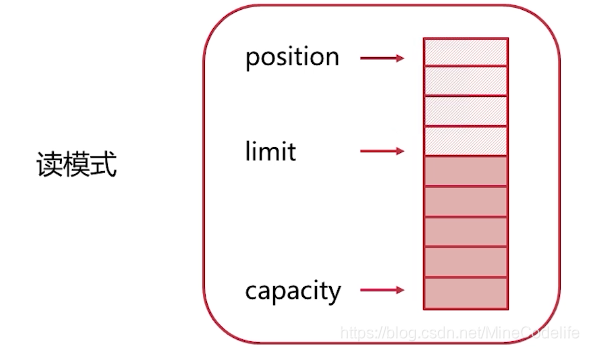
读完以后我们又想开始写入数据到buffer,调用buffer的clear()方法,调整为写模式。limit指向capacity,position指向开始位置
clear()并没有真正的清除数据只是调整了指针。
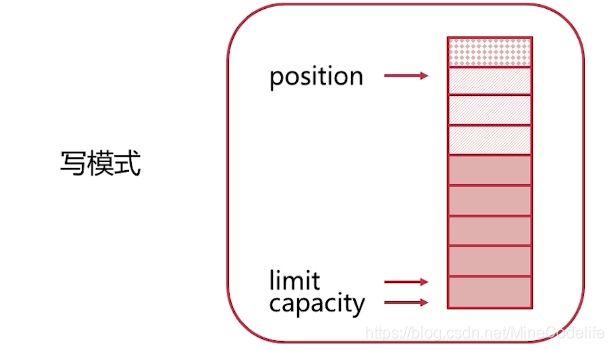
如果buffer未读完。又想写入。调用buffer的compact()方法,把未读完的数据放到buffer前部,
将position指向未读完数据的下面开始写入
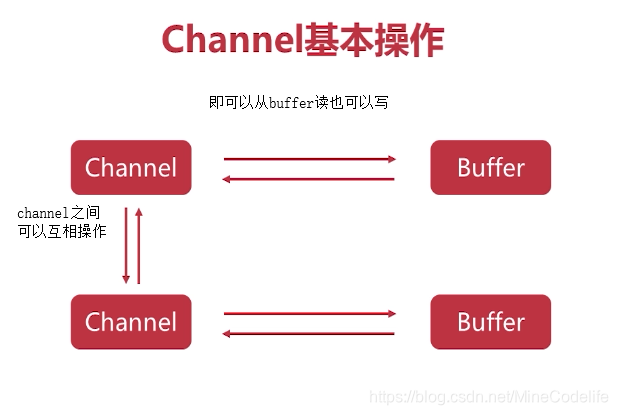
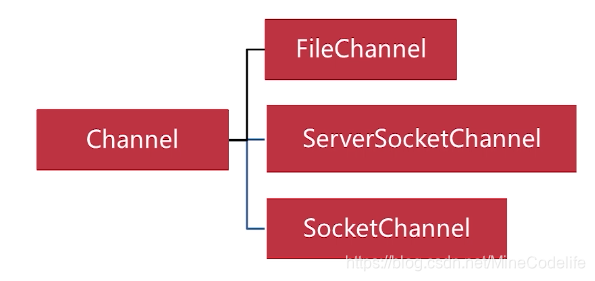
Channel解析
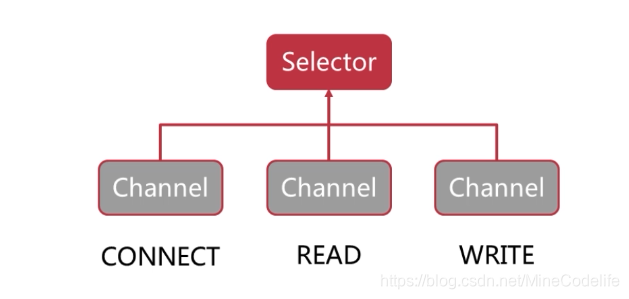
selector 解析
在selector上注册channel,监听channel的状态
代码示例
package main.java.com.founder.study.javaio.nio;
import java.io.*;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
/**
* Created by Founder on 2020/6/28.
*/
interface FileCopyRunner {
void copyFile(File source, File target);
}
public class FileCopyDemo{
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileCopyRunner noBufferStreamCopy = new FileCopyRunner() {
@Override
public void copyFile(File source, File target) {
FileInputStream in =null;
FileOutputStream os = null;
try {
in = new FileInputStream(source);
os = new FileOutputStream(target);
int result ;
while( (result = in.read()) != -1){
os.write(result);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
close(os);
close(in);
}
}
};
FileCopyRunner bufferStreamCopy = new FileCopyRunner() {
@Override
public void copyFile(File source, File target) {
FileInputStream in =null;
FileOutputStream os = null;
byte[] buffer =new byte[1024];
try {
in = new FileInputStream(source);
os = new FileOutputStream(target);
int len ;
while( (len = in.read(buffer)) != -1){
os.write(buffer,0,len);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
close(os);
close(in);
}
}
};
FileCopyRunner nioBufferCopy = new FileCopyRunner() {
@Override
public void copyFile(File source, File target) {
FileChannel fin =null;
FileChannel fout = null ;
try {
fin= new FileInputStream(source).getChannel();
fout = new FileOutputStream(target).getChannel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
// 从channel中读入数据写进buffer
while (fin.read(buffer)!= -1){
//将buffer调整为读模式
buffer.flip();
//从buffer中读出写进写进文件
while (buffer.hasRemaining()){
fout.write(buffer);
}
//循环读完buffer后将buffer转为写模式
buffer.clear();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
close(fin);
close(fout);
}
}
};
FileCopyRunner nioTransferCopy = new FileCopyRunner() {
@Override
public void copyFile(File source, File target) {
FileChannel fin =null;
FileChannel fout = null;
try {
fin = new FileInputStream(source).getChannel();
fout = new FileOutputStream(target).getChannel();
Long transferd = 0L;
while(transferd != fin.size()){
transferd +=fin.transferTo(0,fin.size(),fout);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
close(fin);
close(fout);
}
}
};
}
private static void close(Closeable closeable) {
try {
closeable.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}





 本文深入探讨了非阻塞式IO的概念及其在Java NIO中的应用,包括使用channel和selector进行多线程处理,以及buffer的读写操作。通过具体代码示例,展示了如何利用NIO进行文件复制,对比了不同方式的效率。
本文深入探讨了非阻塞式IO的概念及其在Java NIO中的应用,包括使用channel和selector进行多线程处理,以及buffer的读写操作。通过具体代码示例,展示了如何利用NIO进行文件复制,对比了不同方式的效率。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








