目录
一、什么是红黑树
红黑树的定义
红黑树是一种自平衡的二叉搜索树,通过颜色标记和旋转操作确保树的高度始终保持在O(log n)范围内,从而保证插入、删除、查找等操作的高效性。
核心特性
- 每个节点非红即黑,根节点为黑。
- 红色节点的子节点必须为黑(无连续红节点)。
- 从任一节点到其叶子节点的路径包含相同数量的黑节点(黑高平衡)。//建议多看几遍这是核心
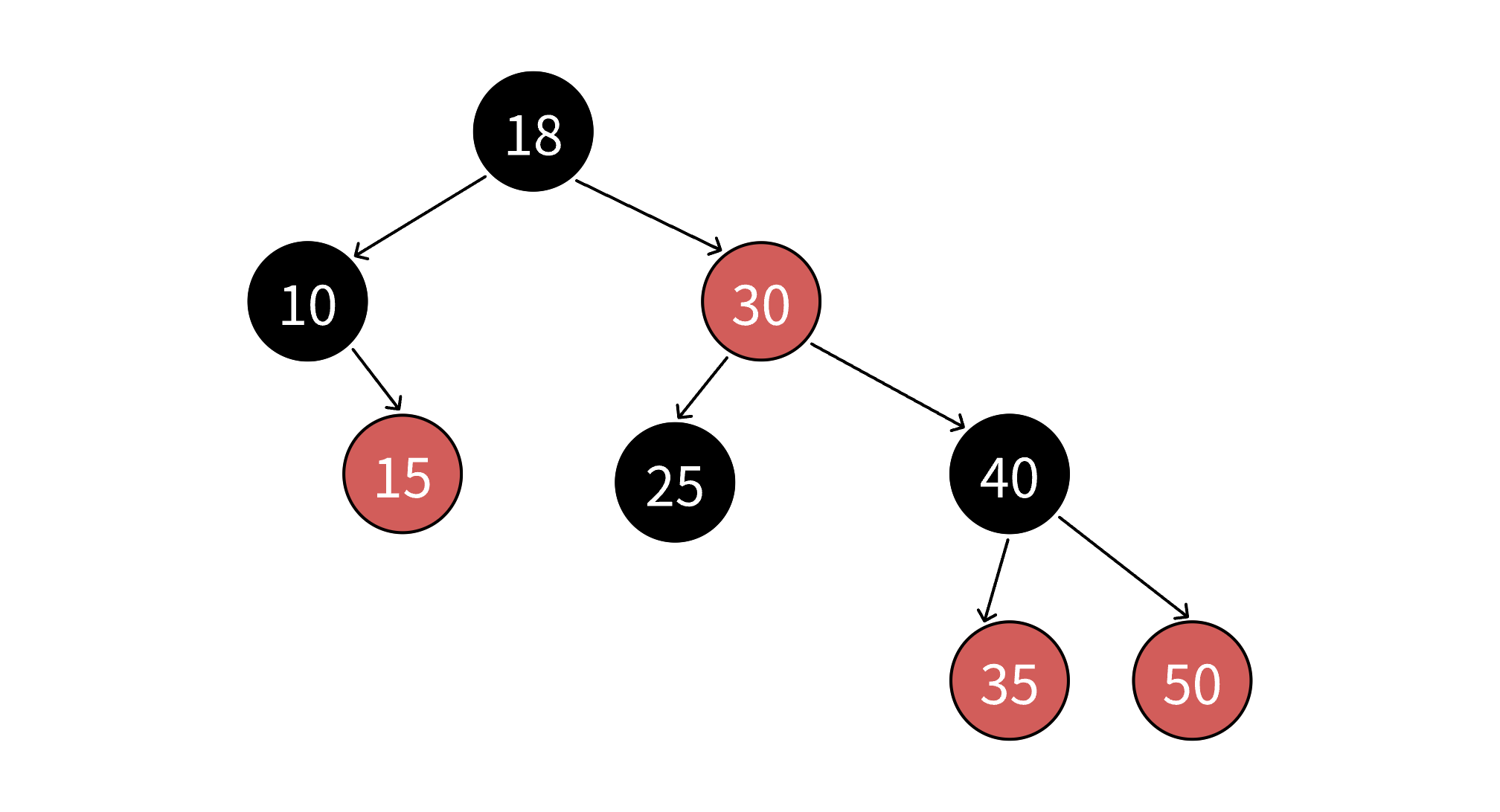
由此保证高度差永远是小于等于最短路径的二倍的
二、如何变色
我们可以把一颗红黑树抽象的表述为:
g 祖宗
p u 父亲 舅舅
c 要插入的孩子
由红黑树规则可知一个正常的红黑树c一定为红色(插入黑色会严重破坏树的结构),所以说如果父亲是黑色的直接插入即可什么都不用管;if(p->_color == black)
若父亲是红色那祖宗g必然是黑色此时的变量就只有u舅舅了;else
现在我们讨论舅舅的情况分为三种没有舅舅,舅舅是黑色的,舅舅是红色的;
2.1直接变色
我直接告诉答案:没有舅舅和舅舅是黑色的情况归位一类变化相同;此时情况就是:
{if(舅舅是红色的){} else{};}
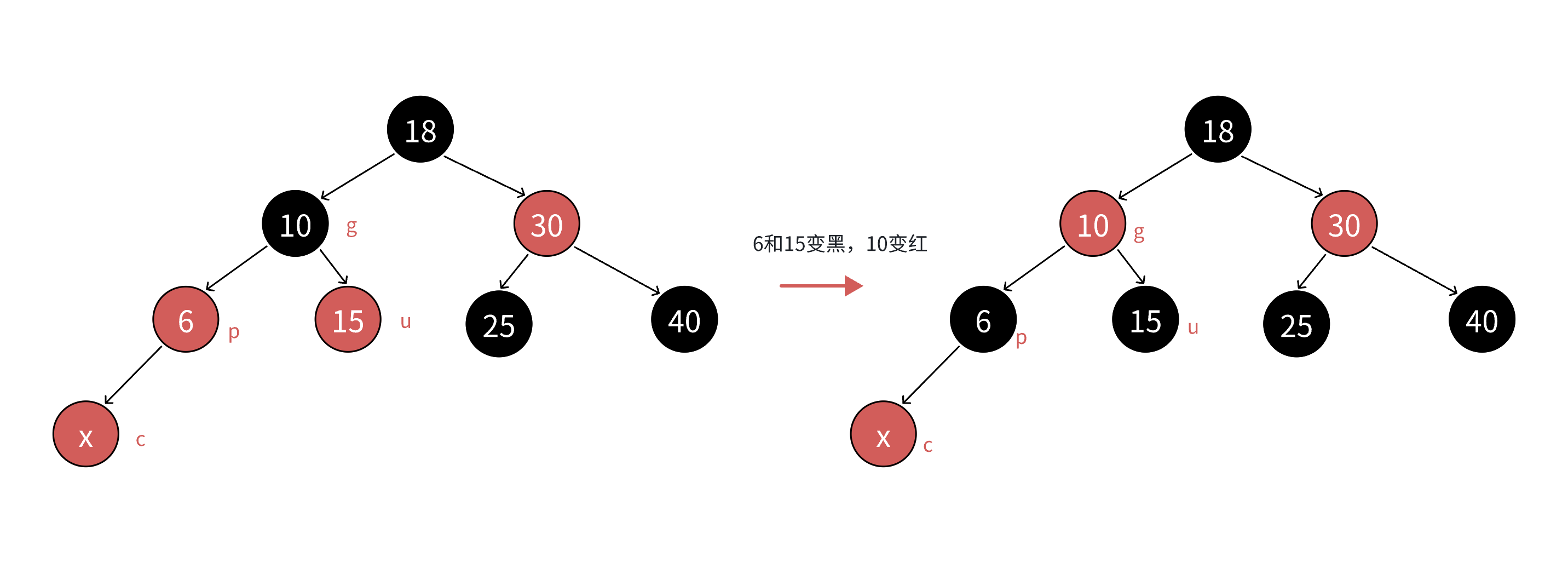
如图所示舅舅是红色的时候直接变色,让g变红,pu变黑就行了;
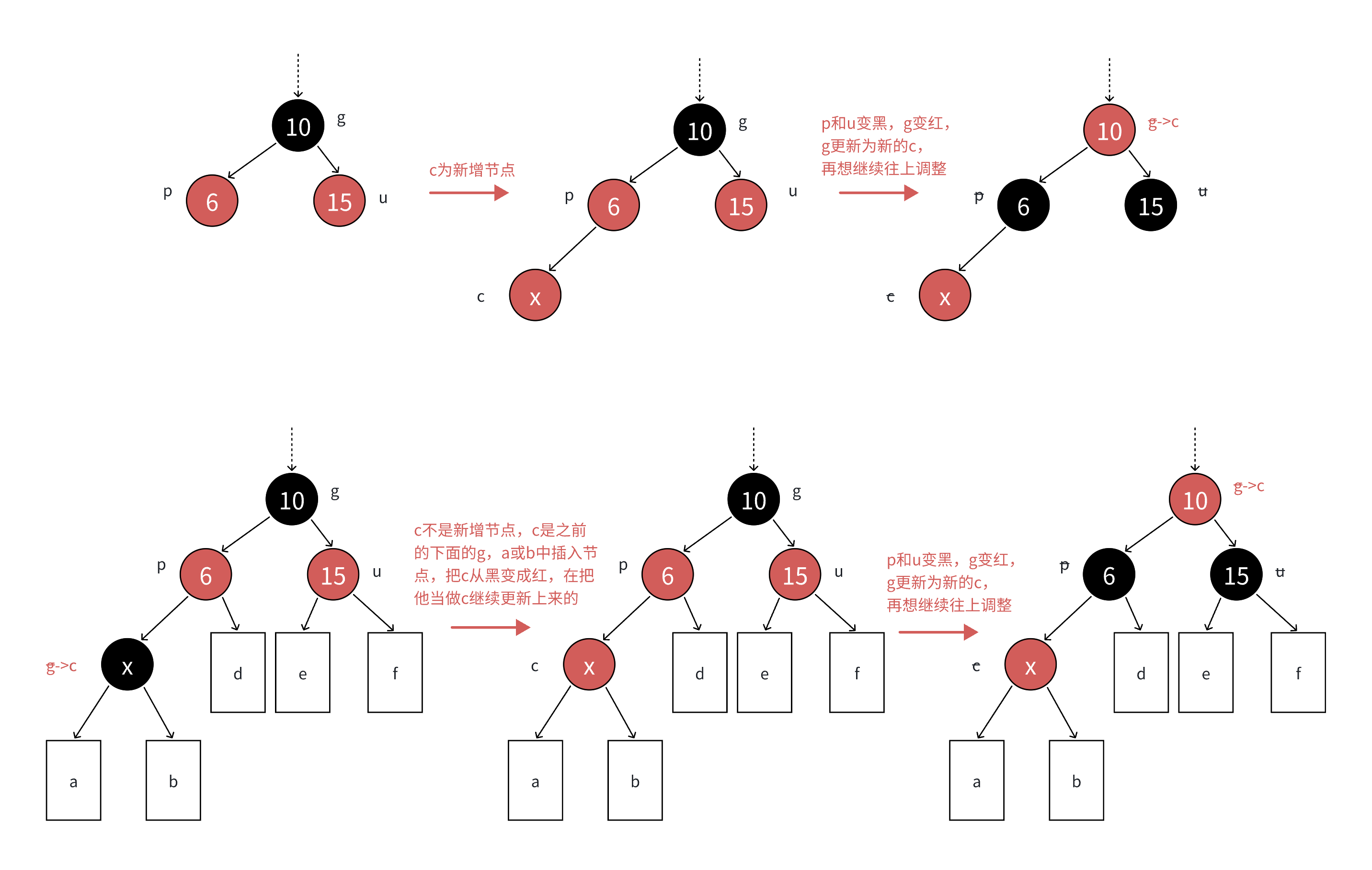
由上图可知在插入后变化可能会影响到上一级,在逐步向上是c可能不是新插入的结点而由新插入结点的祖宗g变过来的此时就需要逐级继续据徐变色while(c);
2.2旋转加变色
麻烦的是else(舅舅是黑色或者没有)
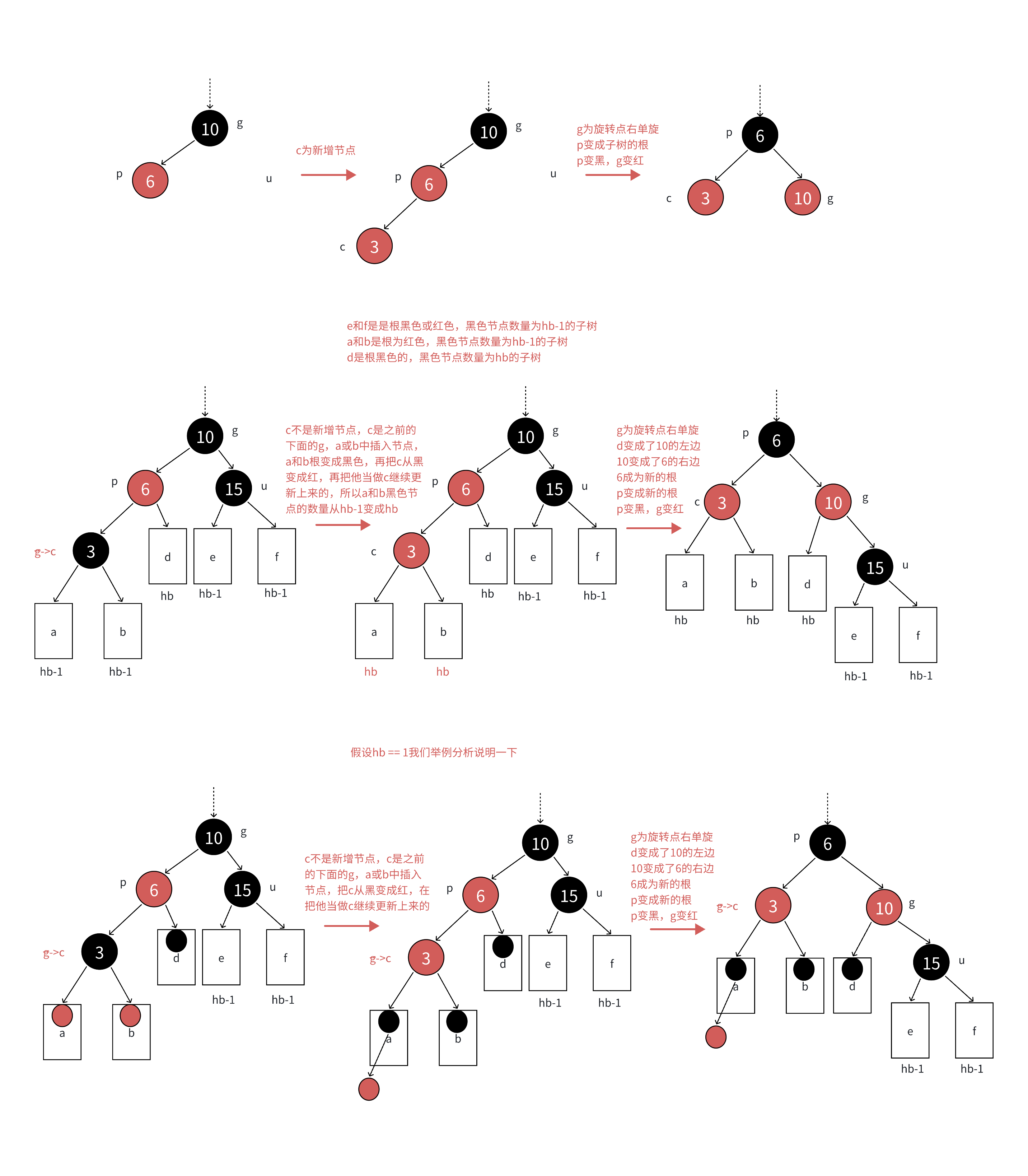
当没有舅舅或舅舅是黑色,我们只需要先判断舅舅是在祖宗的左还是右如果舅舅在右边,在继续判断新插入或变上来的新红色结点是在p父亲的左还是右就行,那p就是右旋转反之亦然;特殊情况:
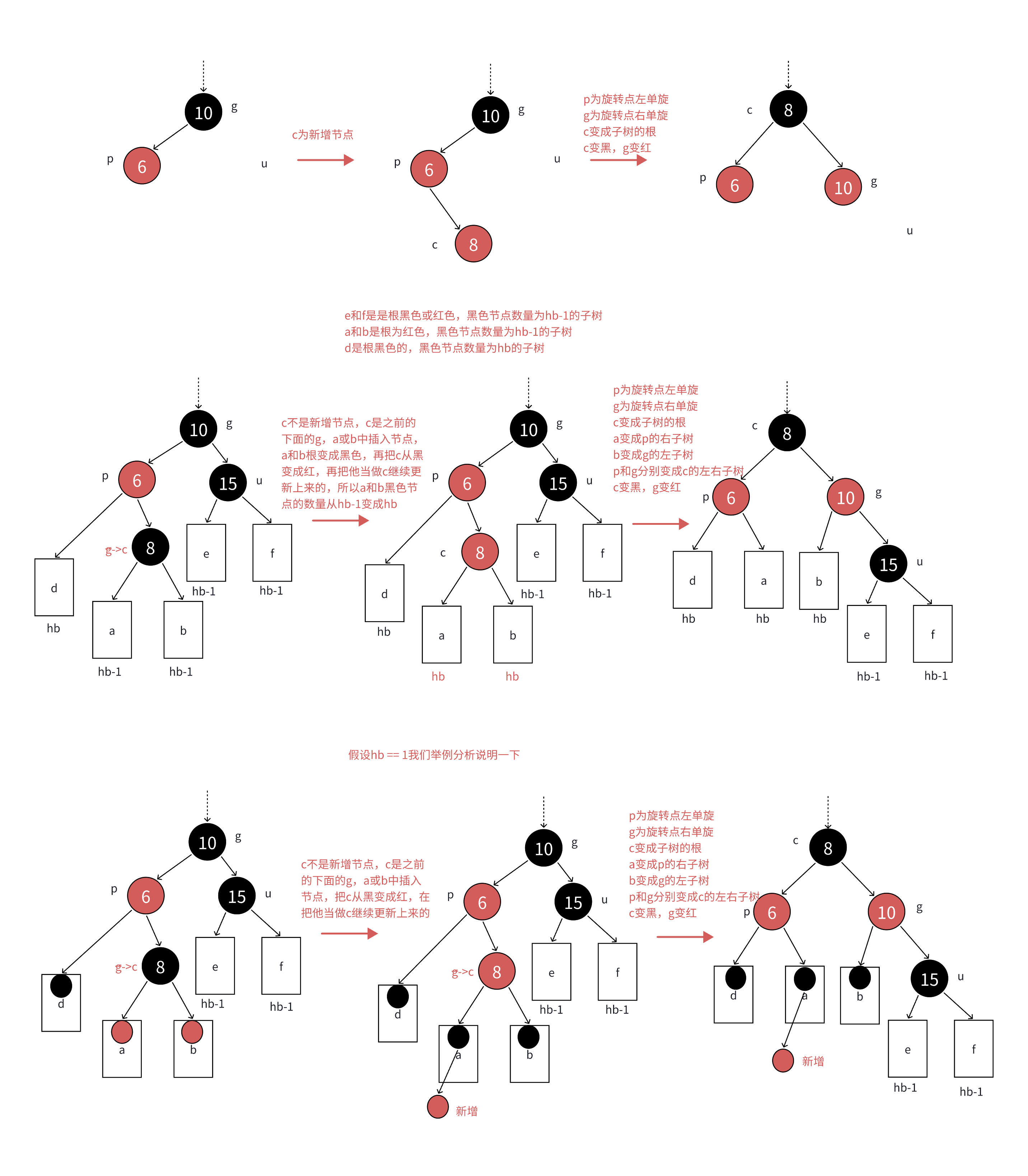
g和p和c不在同一条方向上此时需要进行双旋,以(舅舅在右边的情况为例子)先把p左旋转,再把旋转上来的c进行右旋转;之后c变黑色,g变红;
三、代码加注释
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<iostream>
enum color
{
RED,
BLACK
};
template<class K, class T>
struct pair
{
K _first;
T _second;
pair(K key, T val)
{
_first = key;
_second = val;
}
};//与map里的pair类似;
template<class K, class T>
struct RBtreeNode
{
pair<K, T>* _kt;
RBtreeNode<K, T>* _left = nullptr;
RBtreeNode<K, T>* _right = nullptr;
RBtreeNode* _parent = nullptr;
color _col;
RBtreeNode(K key, T val)
{
_kt = new pair<K, T>(key, val);
_left = nullptr;
_right = nullptr;
_parent = nullptr;
}
};//RB树的结点
template<class K, class T>
class RBtree
{
public:
RBtree()
{
_root = nullptr;
}
typedef RBtreeNode<K, T> node;
void insert(const K& key, const T& val)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new node(key, val);
_root->_col = BLACK;
}//根空则先给根;
else
{
node* parent = nullptr;
node* cur = _root;
while (cur) {
if (cur->_kt->_first > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else//(cur->_kt->_first < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
}//寻找插入点小的左子树大的右子树;
cur = new node(key, val);
if (parent->_kt->_first > cur->_kt->_first)
{
parent->_left = cur;
cur->_parent = parent;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur;
cur->_parent = parent;
}
cur->_col = RED;//插入之后再看变不变色;注意新插入的结点颜色固定为红;
node* ground = parent->_parent;
node* jojo = nullptr;//舅舅
while (cur != _root)
{
if (ground == nullptr)//如果父亲就是根直接插入不用管了
{
break;
}
else//如果父亲不是根分情况
{
if (ground->_left == parent)
{
jojo = ground->_right;
}
else
{
jojo = ground->_left;
}//找到舅舅也就是祖父除父亲外的另一个孩子
if (parent->_col == BLACK)
{
break;
}//要是父亲是黑色的也直接插入就完事
else
{
if (jojo && jojo->_col == RED)
{
parent->_col = BLACK;
jojo->_col = BLACK;
ground->_col = RED;
if (ground == _root)
{
ground->_col = BLACK;
break;
}
cur = ground;
parent = ground->_parent;
ground = parent->_parent;//之后在向上变化;
}//此时父亲和舅舅颜色都是红色那么我们直接把祖父颜色改成红色,父亲和舅舅改成黑色,就符合规则了;注意祖父是根的情况;
else//此时舅舅颜色是黑色或者没有舅舅
{
if (ground->_right == jojo)//舅舅在右侧
{
if (parent->_left == cur)
{
xuanR(ground);
parent->_col = BLACK;
ground->_col = RED;
//右单旋变色
}
else
{
xuanLR(parent);
cur->_col = BLACK;
ground->_col = RED;
//左右双旋变色;
}
}
else
{
if (parent->_right == cur)
{
xuanL(ground);
parent->_col = BLACK;
ground->_col = RED;
//左单旋变色
}
else
{
xuanRL(parent);
cur->_col = BLACK;
ground->_col = RED;
//左右双旋变色;
}
}
break;
}
}
}
}
}
}
void xuanR(node* parent)
{
node* subL = parent->_left;
node* subLR = subL->_right;
subL->_right = parent;
parent->_left = subLR;
if (subLR)
subLR->_parent = parent;
if (parent == _root)
{
subL->_parent = nullptr;
parent->_parent = subL;
_root = subL;
}
else
{
subL->_parent = parent->_parent;
if (parent->_parent->_left == parent)
{
parent->_parent->_left = subL;
}
else
{
parent->_parent->_right = subL;
}
parent->_parent = subL;
}
}
void xuanL(node* parent)
{
node* subR = parent->_right;
node* subRL = subR->_left;
subR->_left = parent;
parent->_right = subRL;
if (subRL)
subRL->_parent = parent;
if (parent == _root)
{
subR->_parent = nullptr;
parent->_parent = subR;
_root = subR;
}
else
{
subR->_parent = parent->_parent;
if (parent->_parent->_left == parent)
{
parent->_parent->_left = subR;
}
else
{
parent->_parent->_right = subR;
}
parent->_parent = subR;
}
}
void xuanLR(node* parent)
{
node* ground = parent->_parent;
xuanL(parent);
xuanR(ground);
}
void xuanRL(node* parent)
{
node* ground = parent->_parent;
xuanR(parent);
xuanL(ground);
}
bool check()
{
if (this->_root->_col == RED)
{
return false;
}
int n = 0;
return blacknum(this->_root, 0, n);
}//检查
bool blacknum(node* root,int b,int& n)//b遇见黑色结点就+1;n再遍历一个路径后以这一个路径为黑色结点基础与其他路径的b进行比较;
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
if (n == 0)
{
n = b;
}
if (b != n)
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
if (root->_col == BLACK)
{
b++;
}
else
{
if (root->_parent&& root->_parent->_col==RED )
{
return false;
}
}
blacknum(root->_left,b,n);
std::cout << root->_kt->_first<<" ";
blacknum(root->_right,b,n);
return true;
}//检查黑色结点数量是否每一路径都相等;
private:
node* _root = nullptr;
};
int main()
{
RBtree<int, int> a;
int i[] = { 16, 3, 7, 11, 9, 26, 18, 14, 15 };
for (auto e : i)
{
a.insert(e, e);
}
std::cout << std::endl<< a.check() << std::endl;
int b = 0;
}再提一嘴在检查黑色结点个数的时候传进去的b是临时变量所以不会被保存下来而n用了引用所以会被保留以作为基准;
 红黑树原理与实现详解
红黑树原理与实现详解




















 177万+
177万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








