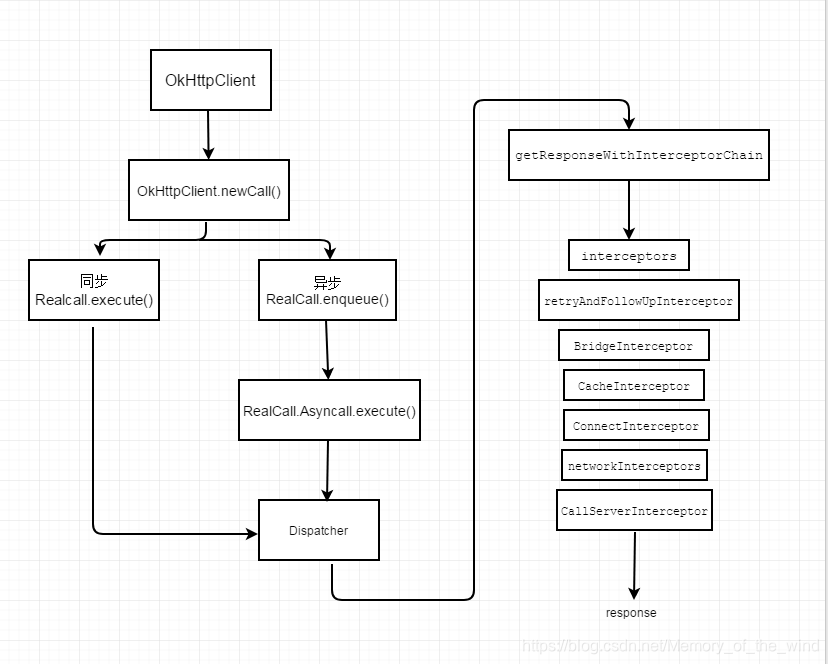
上面是Okhttp发起一个同步/异步请求时,方法调用流程图。
Okhttp的使用
//设置超时的时间
OkHttpClient.Builder builder = new OkHttpClient.Builder()
.connectTimeout(15, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.writeTimeout(20, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.readTimeout(20, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
;
OkHttpClient okHttpClient = builder.build();
Request request = new Request.Builder()
.get() //设置请求模式
.url("https://www.baidu.com/")
.build();
Call call = okHttpClient.newCall(request);
call.enqueue(new Callback() {
@Override
public void onFailure(Call call, IOException e) {
}
@Override
public void onResponse(Call call, Response response) throws IOException {
}
});
我们看到,通过okHttpClient.newCall()方法,拿到这个call对象,然后调用了Call.enqueue,我们先看看newCall是怎么走的。
@Override public Call newCall(Request request) {
return new RealCall(this, request, false /* for web socket */);
}
里面就new了一个RealCall,所以再看RealCall的enqueue方法。
@Override public void enqueue(Callback responseCallback) {
synchronized (this) {
if (executed) throw new IllegalStateException("Already Executed");
executed = true;
}
captureCallStackTrace();
client.dispatcher().enqueue(new AsyncCall(responseCallback));
}
可以看到client.dispatcher().enqueue(new AsyncCall(responseCallback));这句代码,也就是说,最终是有的请求是有dispatcher来完成,我们看看dispatcher。
public final class Dispatcher {
//最大请求的并发数
private int maxRequests = 64;
//每个主机最大请求数
private int maxRequestsPerHost = 5;
private @Nullable Runnable idleCallback;
/** 消费线程池 */
private @Nullable ExecutorService executorService;
/** 准备运行的异步请求队列 */
private final Deque<AsyncCall> readyAsyncCalls = new ArrayDeque<>();
/** 正在运行的异步请求队列 */
private final Deque<AsyncCall> runningAsyncCalls = new ArrayDeque<>();
/** 正在运行的同步请求队列 */
private final Deque<RealCall> runningSyncCalls = new ArrayDeque<>();
/** 构造方法 */
public Dispatcher(ExecutorService executorService) {
this.executorService = executorService;
}
public Dispatcher() {
}
.........
/**
*设置并发执行最大的请求数量
* <p>If more than {@code maxRequests} requests are in flight when this is invoked, those requests
* will remain in flight.
*/
public synchronized void setMaxRequests(int maxRequests) {
if (maxRequests < 1) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("max < 1: " + maxRequests);
}
this.maxRequests = maxRequests;
promoteCalls();
}
//获取到最大请求的数量
public synchronized int getMaxRequests() {
return maxRequests;
}
/**
* 设置每个主机并发执行的请求的最大数量
*/
public synchronized void setMaxRequestsPerHost(int maxRequestsPerHost) {
if (maxRequestsPerHost < 1) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("max < 1: " + maxRequestsPerHost);
}
this.maxRequestsPerHost = maxRequestsPerHost;
promoteCalls();
}
//获取每个主机最大并发数量
public synchronized int getMaxRequestsPerHost() {
return maxRequestsPerHost;
}
synchronized void enqueue(AsyncCall call) {
if (runningAsyncCalls.size() < maxRequests && runningCallsForHost(call) < maxRequestsPerHost) {
runningAsyncCalls.add(call);
executorService().execute(call);
} else {
readyAsyncCalls.add(call);
}
}
.........
}
可以发现Dispatcher是一个任务分发器,主要负责为每个网络请求找到合适的执行线程。下面主要看一下enqueue方法:
synchronized void enqueue(AsyncCall call) {
if (runningAsyncCalls.size() < maxRequests && runningCallsForHost(call) < maxRequestsPerHost) {
runningAsyncCalls.add(call);
executorService().execute(call);
} else {
readyAsyncCalls.add(call);
}
}
当正在运行的异步请求队列中的数量小于64并且正在运行的请求主机数小于5时则把请求加载到runningAsyncCalls中并在线程池中执行,否则就再入到readyAsyncCalls中进行缓存等待。而runningAsyncCalls这个请求队列存放的就是AsyncCall对象,而这个AsyncCall就是RealCall的内部类,AsyncCall的execute源码如下。
@Override protected void execute() {
boolean signalledCallback = false;
try {
Response response = getResponseWithInterceptorChain();
if (retryAndFollowUpInterceptor.isCanceled()) {
signalledCallback = true;
responseCallback.onFailure(RealCall.this, new IOException("Canceled"));
} else {
signalledCallback = true;
responseCallback.onResponse(RealCall.this, response);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
if (signalledCallback) {
// Do not signal the callback twice!
Platform.get().log(INFO, "Callback failure for " + toLoggableString(), e);
} else {
responseCallback.onFailure(RealCall.this, e);
}
} finally {
client.dispatcher().finished(this);
}
}
}
可以发现是getResponseWithInterceptorChain()这句代码里面进行了网络请求。我们看看是怎么执行的。
Response getResponseWithInterceptorChain() throws IOException {
// Build a full stack of interceptors.
List<Interceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<>();
interceptors.addAll(client.interceptors());
interceptors.add(retryAndFollowUpInterceptor);
interceptors.add(new BridgeInterceptor(client.cookieJar()));
interceptors.add(new CacheInterceptor(client.internalCache()));
interceptors.add(new ConnectInterceptor(client));
if (!forWebSocket) {
interceptors.addAll(client.networkInterceptors());
}
interceptors.add(new CallServerInterceptor(forWebSocket));
Interceptor.Chain chain = new RealInterceptorChain(
interceptors, null, null, null, 0, originalRequest);
return chain.proceed(originalRequest);
}
}
1.创建一系列拦截器,并将其放入一个拦截器数组中。这部分拦截器即包括用户自定义的拦截器也包括框架内部拦截器;
2.创建一个拦截器链RealInterceptorChain,并执行拦截器链的proceed方法;
接下来再看看拦截器链的proceed方法:
public Response proceed(Request request, StreamAllocation streamAllocation, HttpCodec httpCodec,
RealConnection connection) throws IOException {
...
// Call the next interceptor in the chain.
RealInterceptorChain next = new RealInterceptorChain(
interceptors, streamAllocation, httpCodec, connection, index + 1, request);
Interceptor interceptor = interceptors.get(index);
Response response = interceptor.intercept(next);
...
return response;
}
1.创建下一个拦截链。传入index + 1使得下一个拦截器链只能从下一个拦截器开始访问;
2.执行索引为index的拦截器的intercept方法,并将下一个拦截器链传入该方法;
接下来看一下Okhttp内部的第一个拦截器RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor的拦截方法:
public final class RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor implements Interceptor {
@Override public Response intercept(Chain chain) throws IOException {
Request request = chain.request();
streamAllocation = new StreamAllocation(
client.connectionPool(), createAddress(request.url()), callStackTrace);
int followUpCount = 0;
Response priorResponse = null;
while (true) {
if (canceled) {
streamAllocation.release();
throw new IOException("Canceled");
}
Response response = null;
boolean releaseConnection = true;
try {
//执行下一个拦截器链的proceed方法
response = ((RealInterceptorChain) chain).proceed(request, streamAllocation, null, null);
releaseConnection = false;
} catch (RouteException e) {
// The attempt to connect via a route failed. The request will not have been sent.
if (!recover(e.getLastConnectException(), false, request)) {
throw e.getLastConnectException();
}
releaseConnection = false;
continue;
} catch (IOException e) {
// An attempt to communicate with a server failed. The request may have been sent.
boolean requestSendStarted = !(e instanceof ConnectionShutdownException);
if (!recover(e, requestSendStarted, request)) throw e;
releaseConnection = false;
continue;
} finally {
// We're throwing an unchecked exception. Release any resources.
if (releaseConnection) {
streamAllocation.streamFailed(null);
streamAllocation.release();
}
}
...
}
}
}
1.对request进行处理;
2.调用下一个拦截器链的proceed方法,获取response;
3.对response进行处理,返回给上一个拦截器;
到这里,我们可以发现所有的拦截器对request和response的操作,都是由拦截器链RealInterceptorChain的递归调用来实现的。那么真正的网络请求是在哪里进行的呢,可以猜到肯定是在最后一个拦截器。下面看一下最后一个拦截器CallServerInterceptor:
@Override public Response intercept(Chain chain) throws IOException {
RealInterceptorChain realChain = (RealInterceptorChain) chain;
HttpCodec httpCodec = realChain.httpStream();
StreamAllocation streamAllocation = realChain.streamAllocation();
RealConnection connection = (RealConnection) realChain.connection();
Request request = realChain.request();
long sentRequestMillis = System.currentTimeMillis();
httpCodec.writeRequestHeaders(request);
Response.Builder responseBuilder = null;
if (HttpMethod.permitsRequestBody(request.method()) && request.body() != null) {
if ("100-continue".equalsIgnoreCase(request.header("Expect"))) {
httpCodec.flushRequest();
responseBuilder = httpCodec.readResponseHeaders(true);
}
if (responseBuilder == null) {
// Write the request body if the "Expect: 100-continue" expectation was met.
Sink requestBodyOut = httpCodec.createRequestBody(request, request.body().contentLength());
BufferedSink bufferedRequestBody = Okio.buffer(requestBodyOut);
request.body().writeTo(bufferedRequestBody);
bufferedRequestBody.close();
} else if (!connection.isMultiplexed()) {
streamAllocation.noNewStreams();
}
}
httpCodec.finishRequest();
if (responseBuilder == null) {
responseBuilder = httpCodec.readResponseHeaders(false);
}
Response response = responseBuilder
.request(request)
.handshake(streamAllocation.connection().handshake())
.sentRequestAtMillis(sentRequestMillis)
.receivedResponseAtMillis(System.currentTimeMillis())
.build();
int code = response.code();
if (forWebSocket && code == 101) {
// Connection is upgrading, but we need to ensure interceptors see a non-null response body.
response = response.newBuilder()
.body(Util.EMPTY_RESPONSE)
.build();
} else {
response = response.newBuilder()
.body(httpCodec.openResponseBody(response))
.build();
}
if ("close".equalsIgnoreCase(response.request().header("Connection"))
|| "close".equalsIgnoreCase(response.header("Connection"))) {
streamAllocation.noNewStreams();
}
if ((code == 204 || code == 205) && response.body().contentLength() > 0) {
throw new ProtocolException(
"HTTP " + code + " had non-zero Content-Length: " + response.body().contentLength());
}
return response;
}
可以发现真的网络请求确实是在CallServerInterceptor里面。























 579
579

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








