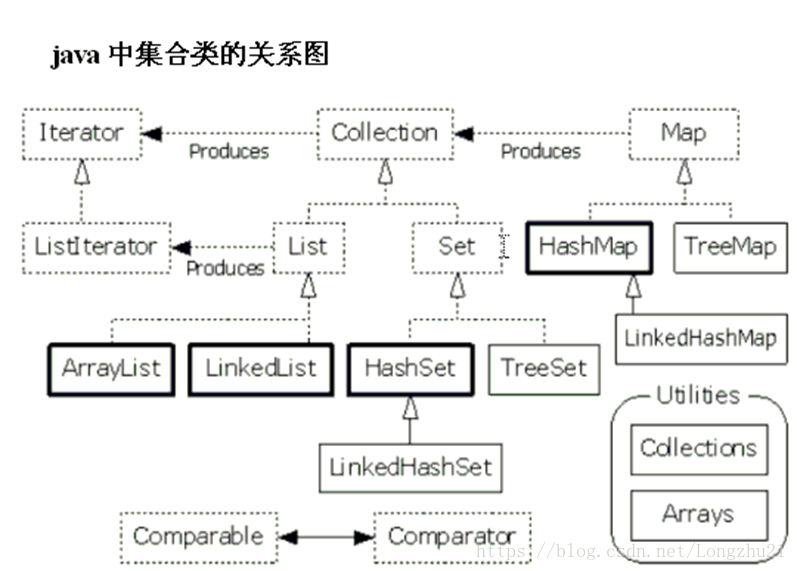
一、为什么会出现集合类
1.集合是一个容器,为了方便的对多个对象进行操作。
2.集合容器同数组容器的不同:数组长度固定,集合长度可变;数组可以存储基本数据类型,而集合只能存储引用数据类型;但是集合可以存储不同类型的对象。
二、Collection
Collection 表示一组对象,这些对象也称为 collection 的元素。一些 collection 允许有重复的元素(List集合),而另一些则不允许(set集合)。一些 collection 是有序的(List集合),而另一些则是无序的(Hashset)。
Collection的成员方法以及示例:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
public class CollectionDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// boolean add(E e)确保此 collection 包含指定的元素(可选操作)。
Collection arr=new ArrayList();
arr.add("张三");
arr.add("李四");
arr.add("王五");
arr.add("赵六");
System.out.println(arr);
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------");
// boolean remove(Object o) 从此 collection 中移除指定元素的单个实例,如果存在的话(可选操作)。
arr.remove("王五");
System.out.println(arr);
System.out.println("------------------------------------------");
// void clear()移除此 collection 中的所有元素(可选操作)。
//arr.clear();
//System.out.println(arr);
// boolean contains(Object o)如果此 collection 包含指定的元素,则返回 true。
boolean b = arr.contains("赵六");
System.out.println(b);//true
// boolean isEmpty()如果此 collection 不包含元素,则返回 true。
boolean c = arr.isEmpty();
System.out.println(c);
// int size()返回此 collection 中的元素数。
int size = arr.size();
System.out.println(size);
}
}
public class CollectionDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection arr=new ArrayList<>();
arr.add("张三");
arr.add("李四");
arr.add("王五");
arr.add("赵六");
System.out.println(arr);
Collection arr2=new ArrayList<>();
arr2.add("javase");
arr2.add("javame");
arr2.add("javaee");
arr2.add("hadoop");
arr2.add("spark");
System.out.println(arr2);
// boolean addAll(Collection c) 将指定 collection 中的所有元素都添加到此 collection 中(可选操作)。
arr.addAll(arr2);
System.out.println(arr);
// boolean removeAll(Collection c) 移除此 collection 中那些也包含在指定 collection 中的所有元素(可选操作)。
//arr.removeAll(arr2);
//System.out.println(arr);
// boolean containsAll(Collection c) 如果此 collection 包含指定 collection 中的所有元素,则返回 true。
boolean b = arr.containsAll(arr2);
System.out.println(b);
// boolean retainAll(Collection c) 仅保留此 collection 中那些也包含在指定 collection 的元素(可选操作)。
arr.retainAll(arr2);
System.out.println(arr);
}
}
Object[] toArray()集合转成数组,可以实现集合的遍历
Iterator iterator()迭代器,集合的专用遍历方式
但是使用迭代器遍历集合时,不能通过集合的引用操作元素。
Iterator中有两个常用的方法,一个是hasNext(),即判断集合中是否有下一个元素,另一个是next()方法,即返回集合中的下一个方法。
public class CollectionDemo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection c = new ArrayList();
c.add(11);
c.add(22);
c.add(33);
//Iterator iterator() 返回在此 collection 的元素上进行迭代的迭代器。
Iterator i=c.iterator();
while(i.hasNext()) {
//c.add(111);//java.util.ConcurrentModificationException并发的修改异常,在使用迭代器遍历集合时,不能直接通过
//集合的引用修改集合里面的元素,如果一定要修改里面的元素,一定要通过迭代器修改
Object obj = i.next();
System.out.println(obj);
}
}
}
三、List接口
有序的Collection(也称为序列),列表中通常允许重复的元素。List分为ArrayList和LinkedList。
ArrayList和LinkedList的大致区别如下:
1.ArrayList是实现了基于动态数组的数据结构,LinkedList基于链表的数据结构。
2.对于随机访问get和set,ArrayList觉得优于LinkedList,因为LinkedList要移动指针。
3.对于新增和删除操作add和remove,LinedList比较占优势,因为ArrayList要移动数据。
List接口的成员方法:(代码实现如下)
public class ArrayListDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list=new ArrayList();
list.add("哈哈");
list.add("javase");
list.add("javame");
list.add("javaee");
// void add(int index,E element)//插入
list.add(1, "ios");
System.out.println(list);
// E remove(int index)从列表中移除项的第一次出现。
list.remove(1);
System.out.println(list);
// E get(int index)返回列表中指定位置的元素。
list.get(0);
System.out.println(list.get(0));
// E set(int index,E element)//替换
list.set(0, "嘿嘿");
System.out.println(list);
// ListIterator listIterator()返回此列表元素的列表迭代器(按适当顺序)。
Iterator iterator = list.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
Object next = iterator.next();
System.out.println(next);
}
}
}
ListIterator<E> listIterator()返回此列表元素的列表迭代器(按适当顺序)。
常用的成员方法有两个:
boolean hasNext()以正向遍历列表时,如果列表迭代器有多个元素,则返回 true(换句话说,如果 next 返回一个元素而不是抛出异常,则返回 true)。
E next()返回列表中的下一个元素。可以重复调用此方法来迭代此列表,或混合调用 previous 来前后移动(注意交替调用 next 和 previous 将重复返回相同的元素)。
LinkedList底层数据结构是链表,增删快,查询慢。
LinkedList类中特有的成员方法:
public class LinkedListDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// public void addFirst(E e)及addLast(E e) 将指定元素插入此列表的开头。将指定元素添加到此列表的结尾。
LinkedList<String> list = new LinkedList<>();
list.add("哈哈");
list.add("呵呵");
list.add("嘻嘻");
list.add("嘿嘿");
list.addFirst("嘎嘎");
list.addLast("唧唧");
System.out.println(list);
// public E getFirst()及getLast()返回此列表的第一个元素。 返回此列表的最后一个元素。
System.out.println(list.getFirst());
System.out.println(list.getLast());
// public E removeFirst()及public E removeLast()移除并返回此列表的第一个元素。移除并返回此列表的最后一个元素。
String first = list.removeFirst();
System.out.println(list);
String last = list.removeLast();
System.out.println(list);
}
}
<2>泛型:
泛型是一种特殊的类型,它把指定类型的工作推迟到客户端代码声明并实例化类或方法的时候进行。
也被称为参数化类型,可以把类型当作参数一样传递过来,在传递过来之前我不明确,但是在使用的时候我就用明确了。
泛型定义在类上:格式:public class 类名<泛型类型1,…>
泛型定义在方法上:格式:public <泛型类型> 返回类型 方法名(泛型类型 .)
泛型定义在接口上:格式:public interface 接口名<泛型类型1…>
<3>增强for
为了简化数组和集合的遍历
格式:
for(元素数据类型 元素名 : 数组或者Collection集合) {
对元素进行你自己的操作
}
注意事项:遍历的目标不能是null
public class ForeachDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arr[]= {1,2,3,4};
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i]);
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("=============================================");
for(int value:arr) {
System.out.print(value);
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("======================================");
ArrayList<String> arrayList=new ArrayList<>();
arrayList.add("张三");
arrayList.add("李四");
arrayList.add("王五");
for(int i=0;i<arrayList.size();i++) {
System.out.print(arrayList.get(i));
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("========================================");
for(String value:arrayList) {
System.out.print(value);
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("========================================");
//String 集合的另一种遍历方式
Iterator<String> iterator = arrayList.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.print(iterator.next());
}
}
}
<4>可变参数
定义方法的时候不知道该定义多少个参数。
格式:修饰符 返回值类型 方法名(数据类型… 变量名){}
注意事项:
这里的变量其实是一个数组;如果一个方法有可变参数,并且有多个参数,那么,可变参数肯定是最后一个
Arrays工具类中提供了数组转换成集合的方法:
public class ChangeParamDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//将数组转换成集合
//public static <T> List<T> asList(T... a)//返回一个受指定数组支持的固定大小的集合
Integer[] arr= {1,2,3,4};
List<Integer> list=Arrays.asList(arr);
System.out.println(list);//[1, 2, 3, 4]
//将集合装换成数组Object[] toArray()返回包含此 collection 中所有元素的数组
Object[] array=list.toArray();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));//[1, 2, 3, 4]
//<T> T[] toArray(T[] a)返回包含此 collection 中所有元素的数组
//返回数组的运行时类型与指定数组的运行时类型相同。如果指定的数组能容纳该 collection,则返回包含此 collection 元素
//的数组。否则,将分配一个具有指定数组的运行时类型和此 collection 大小的新数组。
//Integer[] arr2=new Integer[1];//因为数组长度小,放不下。
Integer[] arr3=list.toArray(new Integer[1]);//这个虽然长度放不下,但是内部会重新分配一个指定数组的运行时类型和此collection
//大小的新数组
System.out.println("arr3"+Arrays.toString(arr3));
}
}
需要注意的是,将数组运用asList方法转换成的集合是固定长度的集合,所以如果要操作这个集合中的元素,一定要考虑到这一点,必要的时候可以新建一个集合,将该集合放入新集合中。
四、Set接口
set集合:一个不包含重复元素的collection,更确切的讲,set不包含满足e1.equals(e2)的元素对e1,e2,是依赖哈希表结构实现的,是依赖元素对象的hashcode和equals方法实现去重的。
去重步骤:
首先去判断要添加的元素和集合中现有的元素的哈希值是否相同
如果哈希值不相同就直接把当前元素添加集合中
如果哈希值相同再去调动equals方法进行比较是否相同
如果不相同就直接把当前元素添加集合中
如果相同就不添加
HashSet:存入和取出的顺序不保证一致,由哈希表结构保证元素不重复
LinkedHashSet:由链表保证存入和取出的顺序一致,由哈希表结构保证元素不重复
set代码实现:
public class SetListDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<Student> set=new LinkedHashSet<>();
set.add(new Student("张三",18,'男'));
set.add(new Student("李四",20,'男'));
set.add(new Student("张三",18,'男'));
set.add(new Student("张三",18,'女'));
set.add(new Student("王五",25,'男'));
show(set);
}
private static void show(Set<Student> set) {
for (Student s : set) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}
运行结果:Student [name=张三, age=18, sex=男]
Student [name=李四, age=20, sex=男]
Student [name=张三, age=18, sex=女]
Student [name=王五, age=25, sex=男]
五、map
键值对形式的双列集合,将键映射到对象,一个映射不能包含重复的键,每个键最多只能映射到一个值,
Map接口和Collection接口的不同,Map集合的数据结构值针对键有效,跟值无关; Collection集合的数据结构是针对元素有效
Map接口中的常用的成员方法(代码实现)
public class MapDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<Integer, String> map=new HashMap<Integer, String>();
// V put(K key,V value)将指定的值与此映射中的指定键关联(可选操作)。
System.out.println(map.put(110, "报警电话"));
System.out.println(map.put(110, "报警电话2"));
map.put(120, "急救电话");
map.put(119, "火警电话");
System.out.println(map);
// V remove(Object key) 如果存在一个键的映射关系,则将其从此映射中移除(可选操作)。返回的值是以前和key关联的值,如果没有针对Key的映射关系,则返回null
System.out.println(map.remove(110));
System.out.println(map);
// void clear()从此映射中移除所有映射关系(可选操作)。此调用返回后,该映射将为空
//map.clear();
//System.out.println(map);
// boolean containsKey(Object key)如果此映射包含指定键的映射关系,则返回 true。
System.out.println(map.containsKey(120));//true
// boolean containsValue(Object value)如果此映射将一个或多个键映射到指定值,则返回 true。
System.out.println(map.containsValue("火警电话"));//true
// boolean isEmpty()如果此映射未包含键-值映射关系,则返回 true。
System.out.println(map.isEmpty());//false
// int size()返回此映射中的键-值映射关系数。
System.out.println(map.size());//2
}
}
Map的遍历方法
Map<Integer,String> map = new HashMap<>();
....
1. Set<Integer> set = map.keySet();
String value = map.get(key);
2. Set<Map.Entry<Integer,String>> entrySet = map.entrySet();
for(Map.Entry<Integer,String> entry:entrySet){
entry.getKey();
ent
3. Collection c = map.values();
代码实现:
public class MapDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<Integer,String> map = new HashMap<Integer,String>();
map.put(1, "张三");
map.put(2, "李四");
map.put(3, "王五");
map.put(4, "赵六");
// V get(Object key)
String s = map.get(4);
System.out.println(s);
// Set<K> keySet()
Set<Integer> set = map.keySet();
for (Integer i : set) {
String value=map.get(i);
System.out.println(i+"="+value);
}
// Collection<V> values()
Collection<String> values = map.values();
for (String value : values) {
System.out.println(value);
}
// Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet()
Set<Entry<Integer,String>> entrySet = map.entrySet();
for (Entry<Integer, String> entry : entrySet) {
System.out.println(entry);
}
}
}
六、Collections工具类
Collection和Collections的区别
Collection:单列集合的根接口
Collections:集合的工具类
Arrays:数组的工具类
Collections中常用的成员方法:(代码实现)
public class CollectionsDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
list.add(12);
list.add(15);
list.add(18);
list.add(-8);
list.add(0);
list.add(5);
// public static <T> void sort(List<T> list) 根据元素的自然顺序 对指定列表按升序进行排序。
Collections.sort(list);
System.out.println(list);
// public static <T> int binarySearch(List<?> list,T key)
int search = Collections.binarySearch(list,12);
System.out.println(search);
// public static <T> T max(Collection<?> coll)
System.out.println(Collections.max(list));
// public static void reverse(List<?> list)
Collections.reverse(list);
System.out.println(list);
// public static void shuffle(List<?> list)
Collections.shuffle(list);
System.out.println(list);
// public static <T> void sort(List<T> list, Comparator<? super T> c)
Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return o1.compareTo(o2);
}
});
}
}
七、Comparator接口和Comparable接口
Comparable比较器接口:让自定义的对象具有比较规则,让自定义对象的类实现这个接口
Comparator比较器接口:覆盖元素对象已有的比较规则,还可以让没有比较规则的元素对象具有比较规则,当做参数传递给排序和二分查找的方法使用
一个集合或数组使用sort方法进行排序,那么这个集合和数组中的元素必须实现Comparable接口,或者传递一个Comparator比较器接口子类对象
提供排序的方法,可以通过实现接口中的compareTo方法来实现自定义排序规则
Comparable
Comparable 定义在 Person类的内部:
public class Persion implements Comparable {..比较Person的大小..},然后Person类再实现comparTo方法;
因为已经实现了比较器,那么我们的Person现在是一个可以比较大小的对象了,它的比较功能和String完全一样,可以随时随地的拿来
比较大小,因为Person现在自身就是有大小之分的。Collections.sort(personList)可以得到正确的结果。
Comparator
Comparator 是定义在Person的外部的, 此时我们的Person类的结构不需要有任何变化,如
public class Person{ String name; int age },
然后我们另外定义一个比较器:
Collections.sort( personList , new PersonComparator() ).
两种方式的代码实现如下:
public class Person implements Comparable<Person>{
private String name;
private int age;
public Person() {
super();
}
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name=name;
this.age=age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "[name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Person o) {
//this的成员和o的成员比较,升序
//以名字为主体进行比较,如果名字的内容一样比较他们的年龄,否则在比较姓名
//return this.name.equals(o.name)?this.age-o.age:this.name.compareTo(o.name);
//o的成员变量和this的成员变量进行比较 降序
//以年龄为主体
return (this.age==o.age)?this.name.compareTo(o.name):this.age-o.age;
}
}
public class ComparatorDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Person> list = new ArrayList<Person>();
list.add(new Person("zhangsan",18));
list.add(new Person("zhangsan",28));
list.add(new Person("lisi",18));
list.add(new Person("wangwu",38));
list.add(new Person("zhaoliu",18));
System.out.println(list);
Collections.sort(list);
System.out.println(list);
}
}
public class CollectionsDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>();
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.add(15);
list.add(-2);
list.add(23);
list.add(8);
System.out.println(list);
//匿名内部类本质上是一个继承了类或者实现接口的匿名子类对象
Comparator c=new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
//升序
//return o1.compareTo(o2);
//降序
return o2.compareTo(o1);
}
};
// public static <T> void sort(List<T> list, Comparator<? super T> c)根据指定比较器产生的顺序对指定列表进行排序。
Collections.sort(list, c);
System.out.println(list);
System.out.println(Collections.binarySearch(list, 1, c));
}
}
八、TreeSet&TreeMap
代码实现:
public class TreeSetDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeSet<Integer> set = new TreeSet<Integer>();
//public TreeSet(Comparator<? super E> comparator)构造一个新的空 TreeSet,它根据指定比较器进行排序。
set=new TreeSet<>(new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
//升序
//return o1-o2;
//降序
return o2-o1;
}
});
set.add(5);
set.add(-6);
set.add(15);
set.add(8);
set.add(3);
System.out.println(set);
}
}
public class TreeMapDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeMap<Integer,String> map = new TreeMap<Integer,String>();
map=new TreeMap<Integer,String>(new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o2-o1;
}
});
map.put(1, "haha");
map.put(15, "xixi");
map.put(-5, "test1");
map.put(6, "test2");
map.put(8, "test3");
Set<Entry<Integer, String>> entrySet = map.entrySet();
for (Entry<Integer, String> entry : entrySet) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey()+"="+entry.getValue());
}
}
}
以上,为我再次学习集合后的一个总结。





 本文深入讲解Java集合框架,包括Collection、List、Set、Map等核心接口及其实现类的特点与应用场景,对比不同集合类的优缺点,并介绍泛型、增强for循环、可变参数等实用功能。
本文深入讲解Java集合框架,包括Collection、List、Set、Map等核心接口及其实现类的特点与应用场景,对比不同集合类的优缺点,并介绍泛型、增强for循环、可变参数等实用功能。
















 4622
4622

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








