Linux102系列会详细讲解Linux0.11版本中的102个文件,本文讲解linux0.11的第14个文件
kernel/system_call.s的文件源码。
1.kernel/system_call.s的主要作用
本程序主要实现系统调用(system_call)中断int0x80的入口处理过程以及信号检测处理(从代码80行开始),同时给出了两个系统功能的底层接口,分别是sys_execve和sys_fork。
还列出了类似处理协处理器出错(int 16)、设备不存在(int 7)、时钟中断(int 32)、硬盘中断(int 46)、软盘中断(int 38)的中断处理程序。
2. 软硬中断的不同处理方式
1.软中断
首先调用相应的C函数处理程序作为准备,将一些参数压入栈帧,然后调用C函数进行相应功能的处理,处理返回后,再去检测当前任务的信号位图,对值小的一个信号进行处理并复位信号位图中的该信号。
系统调用的C函数分布在整个Linux内核代码中,由include/linux/sys.h头文件中的系统函数指针数组表如下:
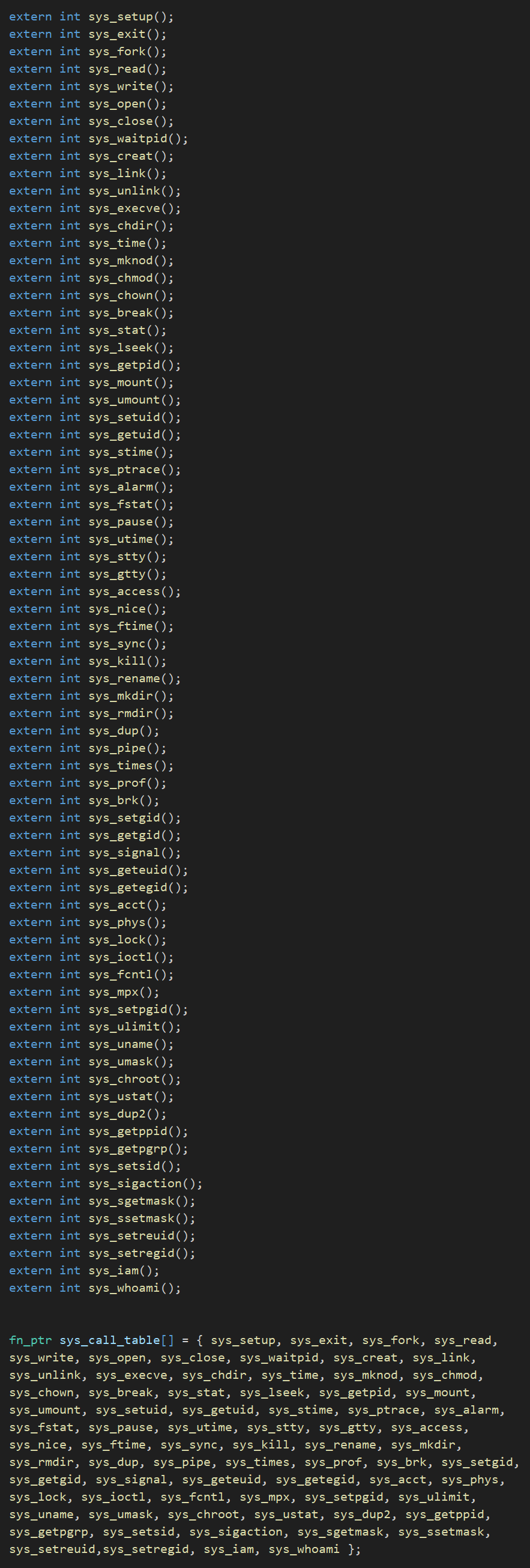
来匹配。
2.硬中断
对于硬件中断请求信号IRQ发来的中断,其处理过程首先是向中断控制芯片8259A发送结束硬件中断控制字指令EOI,然后调用相应的C函数处理程序。对于时钟中断也要对当前任务的信号位图进行检测处理。
系统中断调用处理的整个流程如下:
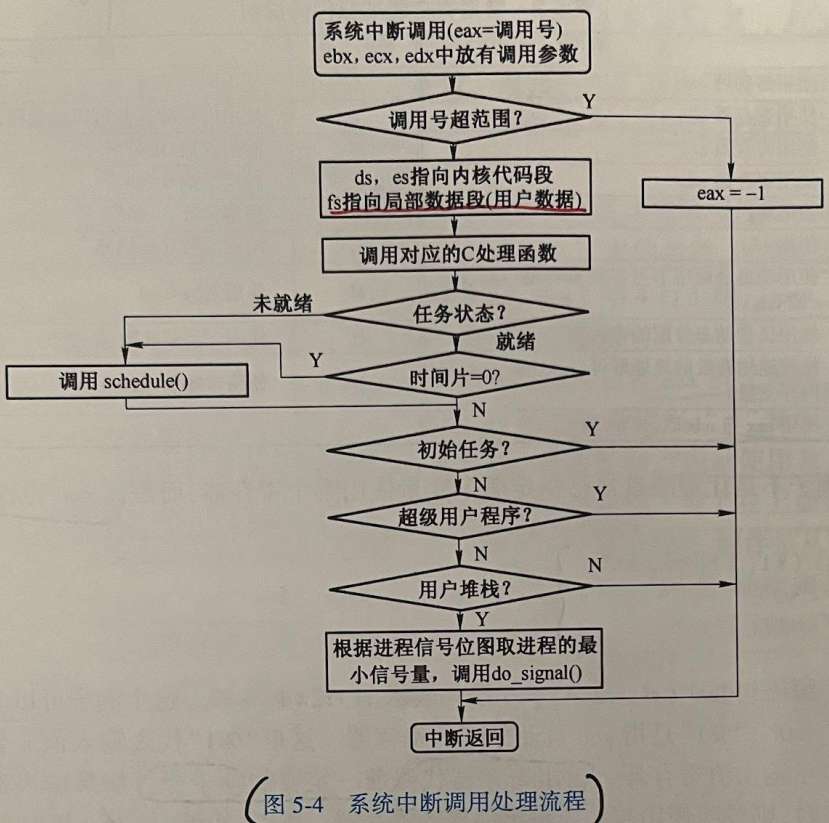
注,本节源码涉及写外部端口,所以这里需要掌握端口的知识:【汇编语言】14-端口
3.源码注释版本
; system_call.s文件包含系统调用底层处理子程序。由于有些代码比较类似,所以同时也包括时钟处理(timer-interrupt)句柄。
;硬盘和软盘的中断处理程序也在这里。注意,这段代码处理信号(signal)识别,在每次时钟中断和系统调用之后都会进行识别。
; 一般中断过程不就进行信号识别,因为会给系统造成混乱。
; 从系统调用返回时,堆栈的内容如下:
/*
* Stack layout in 'ret_from_system_call':
*
* 0(%esp) - %eax
* 4(%esp) - %ebx
* 8(%esp) - %ecx
* C(%esp) - %edx
* 10(%esp) - %fs
* 14(%esp) - %es
* 18(%esp) - %ds
* 1C(%esp) - %eip
* 20(%esp) - %cs
* 24(%esp) - %eflags
* 28(%esp) - %oldesp
* 2C(%esp) - %oldss
*/
; 这是SIG_CHLD信号,当子进程终止时,会发送SIG_CHLD信号给父进程。通知子进程停止或者结束。
SIG_CHLD = 17
; 堆栈中每个寄存器的偏移位置。
EAX = 0x00
EBX = 0x04
ECX = 0x08
EDX = 0x0C
FS = 0x10
ES = 0x14
DS = 0x18
EIP = 0x1C
CS = 0x20
EFLAGS = 0x24
OLDESP = 0x28 # 当有特权级变化时,旧的ESP值。
OLDSS = 0x2C # 当有特权级变化时,旧的SS值。
; 以下是任务结构(task_struct)中变量的偏移值,参见include/linux/sched.h,77行。
state = 0 # 进程状态码
counter = 4 # 任务进行时间计数(递减)(滴答数),运行时间片
priority = 8 # 进程优先级,任务开始时counter=priority,越大则运行时间越长
signal = 12 # 信号位图,每一个比特位代表一种信号,信号值=位偏移值+1.
sigaction = 16 # sigaction结构体必须是16字节.信号执行属性结构数组的偏移值,对应信号将要执行的操作和标志信息。
blocked = (33*16) #受阻塞信号位图的偏移量。
# offsets within sigaction
# 这是定义在sigaction结构体中的偏移量,参见include/signal.h,第48行开始。
sa_handler = 0 # 信号处理过程的句柄
sa_mask = 4 # 信号屏蔽字,在信号处理过程中,屏蔽某些信号。
sa_flags = 8 # 信号集
sa_restorer = 12 # 恢复函数指针,参见linux/signal.c程序。
nr_system_calls = 74 # 该版本的Linux内核的系统调用总数
# 在使用软驱时收到了并行打印机中断,但现在可以不管它。
.globl system_call,sys_fork,timer_interrupt,sys_execve
.globl hd_interrupt,floppy_interrupt,parallel_interrupt
.globl device_not_available, coprocessor_error
.align 2 # 内存4字节对齐(2^2=4)
bad_sys_call: # 错误的系统调用号从这里返回。
movl $-1,%eax # eax中置-1,退出中断。
iret
.align 2
reschedule: # 重新执行调度程序入口。调度程序schedule在(kernel/sched.c,104行)。
pushl $ret_from_sys_call # 将ret_from_sys_call的地址入栈(101行)。
jmp schedule
.align 2
system_call:
cmpl $nr_system_calls-1,%eax # 调用号如果超出范围的话,就在eax中置-1,并退出。
ja bad_sys_call
push %ds # 保存原段寄存器值。
push %es
push %fs
pushl %edx # ebx,ecx,edx入栈。里面都放着系统调用相应的C语言函数的调用参数。
pushl %ecx #
pushl %ebx # to the system call
movl $0x10,%edx # ds、es指向内核数据段(全局描述符表中的数据段描述符)。
mov %dx,%ds
mov %dx,%es
movl $0x17,%edx # fs指向局部数据段(全局描述符表中的数据段描述符)。
mov %dx,%fs
# 调用地址=sys_call_table+调用号(%eax)*4。对应C程序中的sys_call_table在include/linux/sys.h中,
# 其中定义了系统调用的C语言函数地址数组sys_call_table,一共是74个。
call *sys_call_table(,%eax,4)
pushl %eax # 把系统调用返回值入栈。
movl current,%eax # 取当前任务数据结构地址到eax里面
# 检查任务状态和时间片是否为0。也即,查看当前任务是不是就绪状态,如果不在就绪状态,(state!=0)就去执行调度程序。
# 如果在就绪状态,但是时间片用完了(counter==0),则也去执行调度程序。
cmpl $0,state(%eax) # state 查看任务状态
jne reschedule
cmpl $0,counter(%eax) # counter 查看任务时间片是否为0
je reschedule
# 以下这段代码执行从系统调用C函数返回后,对信号量进行识别处理。
ret_from_sys_call:
# 首先判断当前任务是不是task[0],如果是,就直接返回。因为task[0]是初始化任务,
# 它没有信号量,所以不需要处理信号量。
movl current,%eax # task[0] cannot have signals
cmpl task,%eax
je 3f
# 通过对原调用程序代码选择符的检查来判断调用程序是否是内核中的任务(例如任务0)。如果是,直接退出。
# 如果不是,就需要进行信号量的处理。
# 这里比较选择符是否为普通用户代码段的选择符0x000f(RPL=3,局部表,第1个段(代码段)),如果不是则跳转退出中断程序。
cmpw $0x0f,CS(%esp) # 检查旧代码段是否为内核态?是就退出。
jne 3f
cmpw $0x17,OLDSS(%esp) # 检查旧栈段是否为用户态?不在就退出。
jne 3f
# 下面这段代码的用途是首先取当前任务结构中的信号位图(32位,每一位代表一种信号),然后用任务结构中的信号阻塞(屏蔽) 码,
# 阻塞不允许的信号位,取的数值最小的信号值,再把原信号位图中该信号对应的位复位(置0),最后将该信号值作为参数之一调用do_signal().
# do_signal()在(kernel/signal.c,82行)中,其参数包括13个入栈的信息。
movl signal(%eax),%ebx # 取信号位图->ebx,每1位代表1种信号,共32个信号。
movl blocked(%eax),%ecx # 取阻塞(屏蔽)信号位图->ecx。
notl %ecx # 每位取反。
andl %ebx,%ecx # 获得许可的信号位图
bsfl %ecx,%ecx # 从低位(位0)开始扫描位图,看是否有1的位。如有,则ecx保留该位的偏移值(即第几位 0-31)
je 3f
btrl %ecx,%ebx # 复位该信号(ebx含有原signal位图)。
movl %ebx,signal(%eax) # 重新保存signal位图信息->current->signal.
incl %ecx # 将信号调整为从1开始的数(1-32)
pushl %ecx # 信号值入栈作为调用do_signal的参数之一
call do_signal # 调用c函数信号处理程序(kernel/signal.c,82行)
popl %eax # 弹出信号值。
3: popl %eax
popl %ebx
popl %ecx
popl %edx
pop %fs
pop %es
pop %ds
iret
# int16--下面这段代码处理协处理器发出的出错信号。跳转执行c函数match_error()
# (kernel/math/math_emulate.c ,82),返回后跳转到ret_from_sys_call处继续执行。
.align 2
coprocessor_error:
push %ds
push %es
push %fs
pushl %edx
pushl %ecx
pushl %ebx
pushl %eax
movl $0x10,%eax # ds,es置为指向内核数据段
mov %ax,%ds
mov %ax,%es
movl $0x17,%eax
mov %ax,%fs # fs置为指向局部数据段(出错程序的数据段)。
# 把下面调用你返回的地址入栈。
pushl $ret_from_sys_call
# 执行C函数math_error(),(kernel/math/math_emulate.c ,37行)
jmp math_error
# int7--若设备不存在或协处理器不存在。
# 若控制寄存器CRO的EM标志置位,则**当CPU执行一个转移指令时**就会引发该中断,这样就可以有机会让这个中断处理程序模拟转移指令(169行)
# CR0 的TS标志是在CPU执行任务转换时设置的。TS可以用来确定什么时候协处理器中的内容和CPU正在执行的任务不匹配了。
# 当CPU在运行一个转移指令时,发现TS置位了,就会引发该中断。此时就恢复新任务的协处理器执行状态(165行)。
# 参见(kernel/sched.c,77行)中的说明,该中断最后将转移到标号ret_from_sys_call处执行(检测并处理信号)。
.align 2
device_not_available:
push %ds
push %es
push %fs
pushl %edx
pushl %ecx
pushl %ebx
pushl %eax
movl $0x10,%eax # ds、es置为指向内核数据段
mov %ax,%ds
mov %ax,%es
movl $0x17,%eax # fs置为指向局部数据段(出错程序的数据段)
mov %ax,%fs
pushl $ret_from_sys_call # 把下面跳转或调用的返回地址入栈。
clts # clear TS so that we can use math
movl %cr0,%eax
testl $0x4,%eax # EM (math emulation bit)
je math_state_restore # 如果不是EM引起的中断,则回复新任务协处理器状态,执行
pushl %ebp # C函数math_state_restore()(kernel.sched.c,77)
pushl %esi
pushl %edi
call math_emulate # 调用C函数math_emulate(kernel/math/math_emulate.c,18行)
popl %edi
popl %esi
popl %ebp
ret
# int32--(int 0x20)时钟中断处理程序。中断频率为100hz,也就是100次/秒。(include/linux/sched.h,5)
# 定时芯片8253/8254是在(kernel/sched.c,406)处初始化的。因此这里的jifiies每10ms加1.
# 这段代码将jiffies增加1,发送结束中断执行给8259控制器,然后用当前特权级作为参数调用C函数do_timer(long cpl)。
# 当调用返回时转去检测并处理信号。
.align 2
timer_interrupt:
push %ds # save ds,es and put kernel data space
push %es # into them. %fs is used by _system_call
push %fs
pushl %edx # we save %eax,%ecx,%edx as gcc doesn’t
pushl %ecx # save those across function calls. %ebx
pushl %ebx # is saved as we use that in ret_sys_call
pushl %eax
movl $0x10,%eax # ds、es置为指向内核数据段
mov %ax,%ds
mov %ax,%es
movl $0x17,%eax # fs置为指向局部数据段(出错程序的数据段)
mov %ax,%fs
incl jiffies
# 由于初始化中断控制芯片时,没有采用自动EOI,所以这里需要发指令结束该硬件中断。
movb $0x20,%al # EOI to interrupt controller #1
outb %al,$0x20 # 操作命令字OCW2送0x20端口。
movl CS(%esp),%eax
# 下面3句从选择符中取出当前特权级(0或3)并压入堆栈,作为do_timer的参数。
andl $3,%eax # %eax is CPL (0 or 3, 0=supervisor)
pushl %eax
# do_timer(CPL)执行任务切换、计时等工作,在kernel/sched.c,305行实现。
call do_timer # 'do_timer(long CPL)' does everything from
addl $4,%esp # task switching to accounting ... 在进行任务切换时,用于调整栈指针
jmp ret_from_sys_call
# 这是sys_execve()系统调用。取中断调用程序的代码指针作为参数调用C函数do_exevce()。
# do_exevce()在(fs/exec.c,182行)。
.align 2
sys_execve:
lea EIP(%esp),%eax
pushl %eax
call do_execve
addl $4,%esp # 丢弃调用时压入栈的EIP值。
ret
# sys_fork()调用,用于创建`子进程`,时system_call功能2。原型在include/linux/sys.h中。
# 首先调用C函数find_empty_process(),取得一个进程号pid。若返回负数则说明当前任务数组已满。
# 然后调用copy_process()复制进程。
.align 2
sys_fork:
call find_empty_process # 调用find_empty_process(),(kernel/fork.c,135行)
testl %eax,%eax
js 1f
push %gs
pushl %esi
pushl %edi
pushl %ebp
pushl %eax
call copy_process # 调用copy_process(),(kernel/fork.c,68行)
addl $20,%esp # 丢弃这里的所有压栈内容。将指针向上移动20字节。
1: ret
# int46--(int 0x2E)硬盘中断处理程序。响应硬件中断请求IRQ14。
# 当硬盘操作完成或出错就会发出此中断信号。(kernel/blk_drv_hd.c).
# 首先向8259A中断控制从芯片发送结束硬件中断指令(EOI),然后取变量do_hd中的函数指针放入edx寄存器中,
# 并置do_hd为null,接着判断dex函数指针是否为空。如是,则给edx赋值指向unexpected_hd_interrupt(),
# 用于显示出错信息。随后向8259A主芯片送EOI指令,并调用edx中指针指向的函数:read_intr()、write_intr()
# 或 unexpected_hd_interrupt()。
hd_interrupt:
pushl %eax
pushl %ecx
pushl %edx
push %ds
push %es
push %fs
movl $0x10,%eax # ds、es置为内核数据段。
mov %ax,%ds
mov %ax,%es
movl $0x17,%eax # fs置为指向局部数据段(出错程序的数据段)
mov %ax,%fs
# 由于初始化中断控制芯片时没有采用自动EOI,所以这里需要发指令结束该硬件中断。
movb $0x20,%al
outb %al,$0xA0 # EOI to interrupt controller #1 # 送从8259A中断控制从芯片
jmp 1f # give port chance to breathe # 起到一个简单的延时作用
1: jmp 1f
1: xorl %edx,%edx
xchgl do_hd,%edx
testl %edx,%edx
jne 1f
movl $unexpected_hd_interrupt,%edx
1: outb %al,$0x20
call *%edx # "interesting" way of handling intr. 调用hc指向的C函数。
pop %fs
pop %es
pop %ds
popl %edx
popl %ecx
popl %eax
iret
# int38--(int 0x26)软盘驱动器中断处理程序,响应硬件中断请求IRQ6.
# 其处理过程与上面对硬盘的处理基本一样(kernel/blk_drv_floppy.c)
# 首先向8259A主芯片发送结束硬件中断指令(EOI),然后取变量do_floppy中的函数指针放入edx寄存器中,
# 并置do_floppy为null,接着判断edx函数指针是否为空。如是,则给edx赋值指向unexpected_floppy_interrupt(),
# 用于显示出错信息。随后向8259A主芯片送EOI指令,并调用eax中指针指向的函数:
# rw_interrupt()、seek_interrupt、recal_interrupt、reset_interrupt或者unexpect_floppy_interrupt。
floppy_interrupt:
pushl %eax
pushl %ecx
pushl %edx
push %ds
push %es
push %fs
movl $0x10,%eax # ds、es置为内核数据段。
mov %ax,%ds
mov %ax,%es
movl $0x17,%eax # fs置为指向局部数据段(出错程序的数据段)
mov %ax,%fs
movb $0x20,%al
outb %al,$0x20 # EOI to interrupt controller #1 送主8259A中断控制主芯片EOI指令(结束硬件中断)。
xorl %eax,%eax 下一句do_floppy为一函数指针,将被赋值实际处理C函数程序。放到eax寄存器后就将do_floopy指针变量置空。
xchgl do_floppy,%eax
testl %eax,%eax # 测试函数指针是否=NULL?
jne 1f # 如空,则使指针指向unexpected_floppy_interrupt()。
movl $unexpected_floppy_interrupt,%eax
1: call *%eax # "interesting" way of handling intr. 调用do_floppy指向的C函数。
pop %fs
pop %es
pop %ds
popl %edx
popl %ecx
popl %eax
iret
# int 39--(int 0x27)并行端口中断处理程序,对应的响应硬件中断请求IRQ7.
parallel_interrupt: # 内核版本尚未实现,这里只是发送EOI指令。
pushl %eax
movb $0x20,%al
outb %al,$0x20
popl %eax
iret
4.源码完整版
/*
* linux/kernel/system_call.s
*
* (C) 1991 Linus Torvalds
*/
/*
* system_call.s contains the system-call low-level handling routines.
* This also contains the timer-interrupt handler, as some of the code is
* the same. The hd- and flopppy-interrupts are also here.
*
* NOTE: This code handles signal-recognition, which happens every time
* after a timer-interrupt and after each system call. Ordinary interrupts
* don't handle signal-recognition, as that would clutter them up totally
* unnecessarily.
*
* Stack layout in 'ret_from_system_call':
*
* 0(%esp) - %eax
* 4(%esp) - %ebx
* 8(%esp) - %ecx
* C(%esp) - %edx
* 10(%esp) - %fs
* 14(%esp) - %es
* 18(%esp) - %ds
* 1C(%esp) - %eip
* 20(%esp) - %cs
* 24(%esp) - %eflags
* 28(%esp) - %oldesp
* 2C(%esp) - %oldss
*/
SIG_CHLD = 17
EAX = 0x00
EBX = 0x04
ECX = 0x08
EDX = 0x0C
FS = 0x10
ES = 0x14
DS = 0x18
EIP = 0x1C
CS = 0x20
EFLAGS = 0x24
OLDESP = 0x28
OLDSS = 0x2C
state = 0 # these are offsets into the task-struct.
counter = 4
priority = 8
signal = 12
sigaction = 16 # MUST be 16 (=len of sigaction)
blocked = (33*16)
# offsets within sigaction
sa_handler = 0
sa_mask = 4
sa_flags = 8
sa_restorer = 12
nr_system_calls = 74
/*
* Ok, I get parallel printer interrupts while using the floppy for some
* strange reason. Urgel. Now I just ignore them.
*/
.globl system_call,sys_fork,timer_interrupt,sys_execve
.globl hd_interrupt,floppy_interrupt,parallel_interrupt
.globl device_not_available, coprocessor_error
.align 2
bad_sys_call:
movl $-1,%eax
iret
.align 2
reschedule:
pushl $ret_from_sys_call
jmp schedule
.align 2
system_call:
cmpl $nr_system_calls-1,%eax
ja bad_sys_call
push %ds
push %es
push %fs
pushl %edx
pushl %ecx # push %ebx,%ecx,%edx as parameters
pushl %ebx # to the system call
movl $0x10,%edx # set up ds,es to kernel space
mov %dx,%ds
mov %dx,%es
movl $0x17,%edx # fs points to local data space
mov %dx,%fs
call *sys_call_table(,%eax,4)
pushl %eax
movl current,%eax
cmpl $0,state(%eax) # state
jne reschedule
cmpl $0,counter(%eax) # counter
je reschedule
ret_from_sys_call:
movl current,%eax # task[0] cannot have signals
cmpl task,%eax
je 3f
cmpw $0x0f,CS(%esp) # was old code segment supervisor ?
jne 3f
cmpw $0x17,OLDSS(%esp) # was stack segment = 0x17 ?
jne 3f
movl signal(%eax),%ebx
movl blocked(%eax),%ecx
notl %ecx
andl %ebx,%ecx
bsfl %ecx,%ecx
je 3f
btrl %ecx,%ebx
movl %ebx,signal(%eax)
incl %ecx
pushl %ecx
call do_signal
popl %eax
3: popl %eax
popl %ebx
popl %ecx
popl %edx
pop %fs
pop %es
pop %ds
iret
.align 2
coprocessor_error:
push %ds
push %es
push %fs
pushl %edx
pushl %ecx
pushl %ebx
pushl %eax
movl $0x10,%eax
mov %ax,%ds
mov %ax,%es
movl $0x17,%eax
mov %ax,%fs
pushl $ret_from_sys_call
jmp math_error
.align 2
device_not_available:
push %ds
push %es
push %fs
pushl %edx
pushl %ecx
pushl %ebx
pushl %eax
movl $0x10,%eax
mov %ax,%ds
mov %ax,%es
movl $0x17,%eax
mov %ax,%fs
pushl $ret_from_sys_call
clts # clear TS so that we can use math
movl %cr0,%eax
testl $0x4,%eax # EM (math emulation bit)
je math_state_restore
pushl %ebp
pushl %esi
pushl %edi
call math_emulate
popl %edi
popl %esi
popl %ebp
ret
.align 2
timer_interrupt:
push %ds # save ds,es and put kernel data space
push %es # into them. %fs is used by _system_call
push %fs
pushl %edx # we save %eax,%ecx,%edx as gcc doesn't
pushl %ecx # save those across function calls. %ebx
pushl %ebx # is saved as we use that in ret_sys_call
pushl %eax
movl $0x10,%eax
mov %ax,%ds
mov %ax,%es
movl $0x17,%eax
mov %ax,%fs
incl jiffies
movb $0x20,%al # EOI to interrupt controller #1
outb %al,$0x20
movl CS(%esp),%eax
andl $3,%eax # %eax is CPL (0 or 3, 0=supervisor)
pushl %eax
call do_timer # 'do_timer(long CPL)' does everything from
addl $4,%esp # task switching to accounting ...
jmp ret_from_sys_call
.align 2
sys_execve:
lea EIP(%esp),%eax
pushl %eax
call do_execve
addl $4,%esp
ret
.align 2
sys_fork:
call find_empty_process
testl %eax,%eax
js 1f
push %gs
pushl %esi
pushl %edi
pushl %ebp
pushl %eax
call copy_process
addl $20,%esp
1: ret
hd_interrupt:
pushl %eax
pushl %ecx
pushl %edx
push %ds
push %es
push %fs
movl $0x10,%eax
mov %ax,%ds
mov %ax,%es
movl $0x17,%eax
mov %ax,%fs
movb $0x20,%al
outb %al,$0xA0 # EOI to interrupt controller #1
jmp 1f # give port chance to breathe
1: jmp 1f
1: xorl %edx,%edx
xchgl do_hd,%edx
testl %edx,%edx
jne 1f
movl $unexpected_hd_interrupt,%edx
1: outb %al,$0x20
call *%edx # "interesting" way of handling intr.
pop %fs
pop %es
pop %ds
popl %edx
popl %ecx
popl %eax
iret
floppy_interrupt:
pushl %eax
pushl %ecx
pushl %edx
push %ds
push %es
push %fs
movl $0x10,%eax
mov %ax,%ds
mov %ax,%es
movl $0x17,%eax
mov %ax,%fs
movb $0x20,%al
outb %al,$0x20 # EOI to interrupt controller #1
xorl %eax,%eax
xchgl do_floppy,%eax
testl %eax,%eax
jne 1f
movl $unexpected_floppy_interrupt,%eax
1: call *%eax # "interesting" way of handling intr.
pop %fs
pop %es
pop %ds
popl %edx
popl %ecx
popl %eax
iret
parallel_interrupt:
pushl %eax
movb $0x20,%al
outb %al,$0x20
popl %eax
iret
5.源码图像版
6.源码注释版图像

专注讲解Linux中的常用命令,共计发布100+文章。
本系列将精讲Linux0.11内核中的每一个文件,共计会发布100+文章。
😉【Linux102】11-kernel/vsprintf.c
😉【Linux102】12-include/stdarg.h
和Linux内核102系列不同,本系列将会从全局描绘Linux内核的各个模块,而非逐行源码分析,适合想对Linux系统有宏观了解的家人阅读。
😉【Linux】Linux概述1-linux对物理内存的使用
关于小希
😉嘿嘿嘿,我是小希,专注Linux内核领域,同时讲解C语言、汇编等知识。
我的微信:C_Linux_Cloud,期待与您学习交流!

加微信请备注哦
小希的座右铭:
别看简单,简单也是难。别看难,难也是简单。我的文章都是讲述简单的知识,如果你喜欢这种风格:
下一期想看什么?在评论区留言吧!我们下期见!





















 1227
1227

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








