2)java自带的Annotation
通过上面的示例,我们能理解:@interface 用来声明 Annotation,@Documented 用来表示该 Annotation 是否会出现在 javadoc 中, @Target 用来指定 Annotation 的类型,@Retention 用来指定 Annotation 的策略。
理解这一点之后,我们就很容易理解 java 中自带的 Annotation 的实现类,即 Annotation 架构图的右半边。如下图:
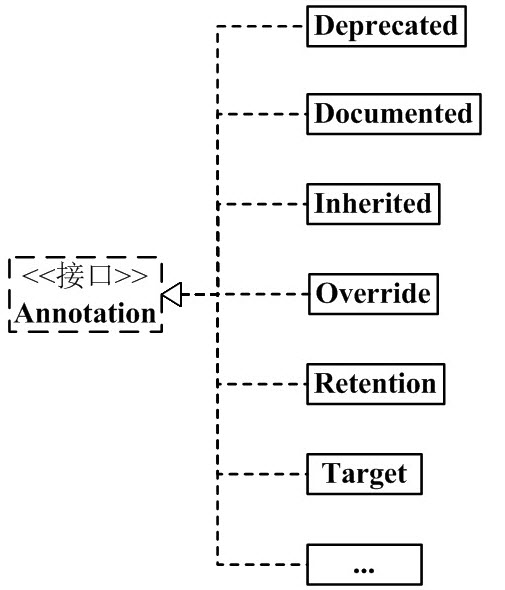
java 常用的 Annotation:
@Deprecated -- @Deprecated 所标注内容,不再被建议使用。
@Override -- @Override 只能标注方法,表示该方法覆盖父类中的方法。
@Documented -- @Documented 所标注内容,可以出现在javadoc中。
@Inherited -- @Inherited只能被用来标注“Annotation类型”,它所标注的Annotation具有继承性。
@Retention -- @Retention只能被用来标注“Annotation类型”,而且它被用来指定Annotation的RetentionPolicy属性。
@Target -- @Target只能被用来标注“Annotation类型”,而且它被用来指定Annotation的ElementType属性。
@SuppressWarnings -- @SuppressWarnings 所标注内容产生的警告,编译器会对这些警告保持静默。由于 "@Deprecated 和 @Override" 类似,"@Documented, @Inherited, @Retention, @Target" 类似;下面,我们只对 @Deprecated, @Inherited, @SuppressWarnings 这 3 个 Annotation 进行说明。







 本文介绍了Java中的注解(Annotation)及其使用,重点关注了@Deprecated用于标记过时功能,@Inherited使子类继承Annotation,@SuppressWarnings用于消除特定警告。此外,还提到了其他核心Annotation的作用,如@Documented, @Retention和@Target。适合作为Java初学者或有经验开发者巩固知识的参考资料。
本文介绍了Java中的注解(Annotation)及其使用,重点关注了@Deprecated用于标记过时功能,@Inherited使子类继承Annotation,@SuppressWarnings用于消除特定警告。此外,还提到了其他核心Annotation的作用,如@Documented, @Retention和@Target。适合作为Java初学者或有经验开发者巩固知识的参考资料。
 https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1qL411u7eE?from=search&seid=5395319662329838164&spm_id_from=333.337.0.0
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1qL411u7eE?from=search&seid=5395319662329838164&spm_id_from=333.337.0.0















 641
641

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








