通过综合案例,我们来了解和学习在开发Web程序时,前端程序和后端程序以及数据库三者之间是如何交互、如何协作的,而通过综合案例也来掌握通过接口文档开发服务端接口的能力。
目录
一、准备工作
1. 需求说明
2. 环境搭建
3. 开发规范
二、部门管理
1. 查询部门
2. 前后端联调
3. 删除部门
4. 新增部门
三、员工管理
1. 分页查询
2. PageHelper分页插件
3. 条件分页查询
4. 删除员工
四、员工信息
1. 新增员工
2. 文件上传
2.1 简介
2.2 本地存储
2.3 阿里云OSS
3. 修改员工
3.1 查询回显
3.2 修改员工信息
五、配置文件
1. 参数配置化
2. yml配置文件
3. @ConfigurationProperties注解
一、准备工作
1. 需求说明
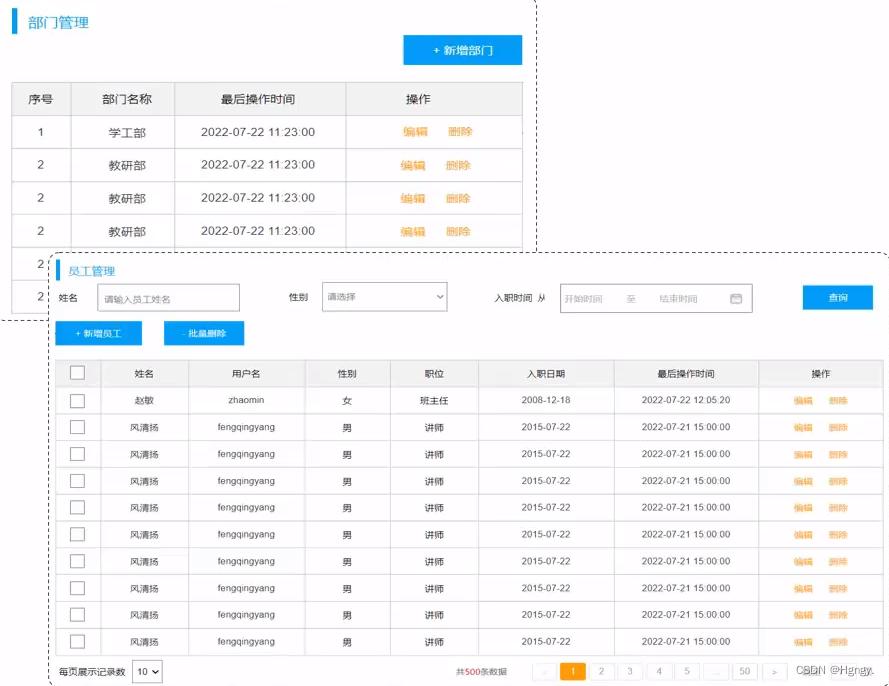 | 部门管理:
|
员工管理:
|
2. 环境搭建
-
准备数据库表(dept、emp) 。```
– 部门管理
create table dept(
id int unsigned primary key auto_increment comment ‘主键ID’,
name varchar(10) not null unique comment ‘部门名称’,
create_time datetime not null comment ‘创建时间’,
update_time datetime not null comment ‘修改时间’
) comment ‘部门表’;insert into dept (id, name, create_time, update_time) values(1,‘学工部’,now(),now()),(2,‘教研部’,now(),now()),(3,‘咨询部’,now(),now()), (4,‘就业部’,now(),now()),(5,‘人事部’,now(),now());
– 员工管理(带约束)
create table emp (
id int unsigned primary key auto_increment comment ‘ID’,
username varchar(20) not null unique comment ‘用户名’,
password varchar(32) default ‘123456’ comment ‘密码’,
name varchar(10) not null comment ‘姓名’,
gender tinyint unsigned not null comment ‘性别, 说明: 1 男, 2 女’,
image varchar(300) comment ‘图像’,
job tinyint unsigned comment ‘职位, 说明: 1 班主任,2 讲师, 3 学工主管, 4 教研主管, 5 咨询师’,
entrydate date comment ‘入职时间’,
dept_id int unsigned comment ‘部门ID’,
create_time datetime not null comment ‘创建时间’,
update_time datetime not null comment ‘修改时间’
) comment ‘员工表’;INSERT INTO emp
(id, username, password, name, gender, image, job, entrydate,dept_id, create_time, update_time) VALUES
(1,‘jinyong’,‘123456’,‘金庸’,1,‘1.jpg’,4,‘2000-01-01’,2,now(),now()),
(2,‘zhangwuji’,‘123456’,‘张无忌’,1,‘2.jpg’,2,‘2015-01-01’,2,now(),now()),
(3,‘yangxiao’,‘123456’,‘杨逍’,1,‘3.jpg’,2,‘2008-05-01’,2,now(),now()),
(4,‘weiyixiao’,‘123456’,‘韦一笑’,1,‘4.jpg’,2,‘2007-01-01’,2,now(),now()),
(5,‘changyuchun’,‘123456’,‘常遇春’,1,‘5.jpg’,2,‘2012-12-05’,2,now(),now()),
(6,‘xiaozhao’,‘123456’,‘小昭’,2,‘6.jpg’,3,‘2013-09-05’,1,now(),now()),
(7,‘jixiaofu’,‘123456’,‘纪晓芙’,2,‘7.jpg’,1,‘2005-08-01’,1,now(),now()),
(8,‘zhouzhiruo’,‘123456’,‘周芷若’,2,‘8.jpg’,1,‘2014-11-09’,1,now(),now()),
(9,‘dingminjun’,‘123456’,‘丁敏君’,2,‘9.jpg’,1,‘2011-03-11’,1,now(),now()),
(10,‘zhaomin’,‘123456’,‘赵敏’,2,‘10.jpg’,1,‘2013-09-05’,1,now(),now()),
(11,‘luzhangke’,‘123456’,‘鹿杖客’,1,‘11.jpg’,5,‘2007-02-01’,3,now(),now()),
(12,‘hebiweng’,‘123456’,‘鹤笔翁’,1,‘12.jpg’,5,‘2008-08-18’,3,now(),now()),
(13,‘fangdongbai’,‘123456’,‘方东白’,1,‘13.jpg’,5,‘2012-11-01’,3,now(),now()),
(14,‘zhangsanfeng’,‘123456’,‘张三丰’,1,‘14.jpg’,2,‘2002-08-01’,2,now(),now()),
(15,‘yulianzhou’,‘123456’,‘俞莲舟’,1,‘15.jpg’,2,‘2011-05-01’,2,now(),now()),
(16,‘songyuanqiao’,‘123456’,‘宋远桥’,1,‘16.jpg’,2,‘2007-01-01’,2,now(),now()),
(17,‘chenyouliang’,‘123456’,‘陈友谅’,1,‘17.jpg’,NULL,‘2015-03-21’,NULL,now(),now()); -
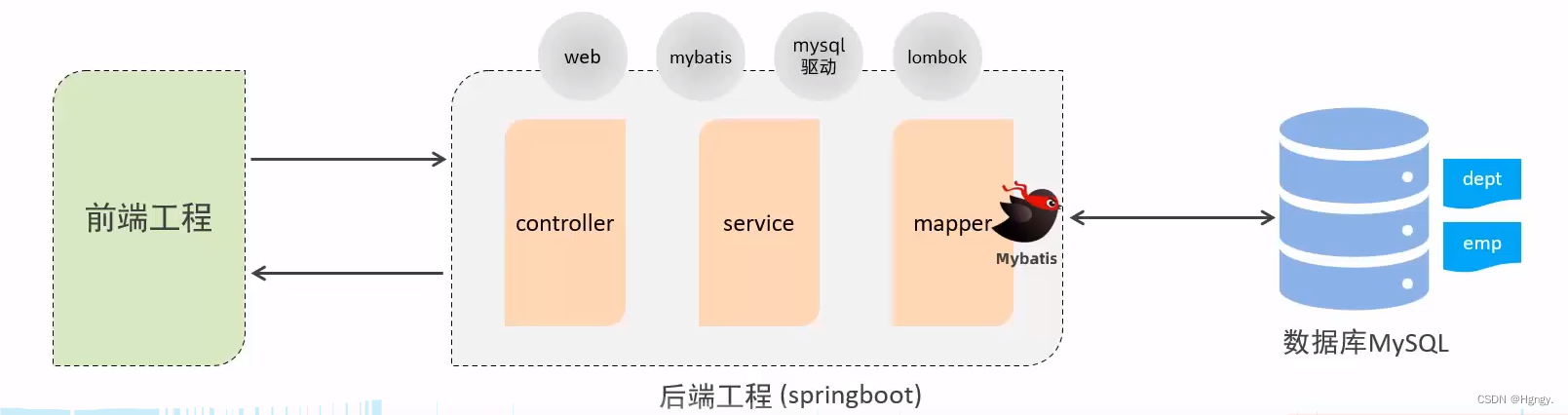
创建springboot工程,引入对应的起步依赖(web、mybatis、mysql驱动、lombok)配置文件。
-
application.properties中引入mybatis的配置信息,准备对应的实体类。
-
准备对应的Mapper、Service(接口、实现类)、Controller基础结构。
3. 开发规范
案例基于当前最为主流的前后端分离模式进行开发。在开发每一功能接口时仔细阅读接口文档并严格遵守接口文档进行开发,才能保证我们开发的功能可以顺利与前端对接。而在本案例中,前后端交互使用的是 Restful 风格接口。
REST (REpresentational State Transfer),表述性状态转换,它是一种软件架构风格
-
传统风格:```
http://localhost : 8080/user/getById?id=1 //GET:查询ia为1的用户
http://localhost : 8080/user/saveUser //POST:新增用户
http://localhost :8080/user/updateUser //POST:修改用户
http://localhost :8080/user/deleteUser?id=1 //GET:删除id为1的用户 -
**REST风格:**URL定位资源、HTTP动词描述操作```
http://localhost:8080/users/1 //GET:查询id为1的用户
http://localhost:8080/users //POST:新增用户
http://localhost:8080/users //PUT:修改用户
http://localhost:8080/users/1 //DELETE:删除id为1的用户
注意事项:
- REST是风格,是约定方式,约定不是规定,可以打破。
- 描述模块的功能通常使用复数,也就是加s的格式来描述,表示此类资源,而非单个资源。如:users、emps、books …
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Result {
private Integer code;//响应码,1 代表成功; 0 代表失败
private String msg; //响应信息 描述字符串
private Object data; //返回的数据
//增删改 成功响应
public static Result success(){
return new Result(1,"success",null);
}
//查询 成功响应
public static Result success(Object data){
return new Result(1,"success",data);
}
//失败响应
public static Result error(String msg){
return new Result(0,msg,null);
}
}
二、部门管理
1. 查询部门
- 查询全部数据(由于部门数据比较少,不考虑分页)。

@RestController
public class DeptController {
@Autowired
private DeptService deptService;
//@RequestMapping(value = "/depts",method = RequestMethod.GET); 指定请求方式为GET
@GetMapping("/depts")
public Result list(){
//调用Service查询部门数据
List<Dept> deptList = deptService.list();
return Result.success(deptList);
}
}
public interface DeptService {
/**
*
* 查询全部部门数据
*/
List<Dept> list();
}
@Service
public class DeptServiceImpl implements DeptService {
@Autowired
private DeptMapper deptMapper;
/**
* 查询全部部门数据
*/
@Override
public List<Dept> list() {
return deptMapper.list();
}
}
@Mapper
public interface DeptMapper {
/**
* 查询全部部门数据
*/
@Select("select * from dept;")
List<Dept> list();
}
2. 前后端联调
- 将资料中提供的 “前端工程” 文件夹中的压缩包,拷贝到一个没有中文不带空格的目录下,解压 nginv-1.22.0-tlias.zip。
- 启动nginx,访问测试:http://localhost:90
3. 删除部门
- 弹出确认框,提示 “您确定要删除该部门的信息吗?” 如果选择确定,则删除该部门,删除成功后,重新刷新列表页面。如果选择了取消,则不执行任何操作。

@RestController
public class DeptController {
@Autowired
private DeptService deptService;
/**
* 删除部门信息
*/
@DeleteMapping("/depts/{id}")
public Result delete(@PathVariable Integer id){
//log.info("根据id删除部门:{}",id);
//调用Service删除部门数据
deptService.delete(id);
return Result.success();
}
}
public interface DeptService {
/**
*
* 删除部门数据
*/
void delete(Integer id);
}
@Service
public class DeptServiceImpl implements DeptService {
@Autowired
private DeptMapper deptMapper;
/**
* 删除部门数据
*
*/
@Override
public void delete(Integer id) {
deptMapper.deleteById(id);
}
}
@Mapper
public interface DeptMapper {
/**
* 根据id删除部门数据
*/
@Delete("delete from dept where id = #{id}")
void deleteById(Integer id);
}
4. 新增部门
- 点击新增部门,会打开新增部门的页面。
- 部门名称,必填,唯一,长度为2-10位。

@RestController
public class DeptController {
@Autowired
private DeptService deptService;
/**
* 新增部门信息
*
*/
@PostMapping("/depts")
public Result add(@RequestBody Dept dept){
//log.info("新增部门:{}",dept);
//调用Service新增部门数据
deptService.add(dept);
return Result.success();
}
}
public interface DeptService {
/**
*
* 新增部门数据
*/
void add(Dept dept);
}
@Service
public class DeptServiceImpl implements DeptService {
@Autowired
private DeptMapper deptMapper;
/**
* 新增部门数据
*
*/
@Override
public void add(Dept dept) {
dept.setCreateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
dept.setUpdateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
deptMapper.insert(dept);
}
}
@Mapper
public interface DeptMapper {
/**
* 新增部门信息
*/
@Insert("insert into dept(name,create_time,update_time) values(#{name},#{createTime},#{updateTime}) ")
void insert(Dept dept);
}
三、员工管理
1. 分页查询
- 设置请求参数默认值:@RequestParam(defaultvalue=“7”)
在之前的MySQL学习中,我们知道使用 limit 关键字 实现分页查询。
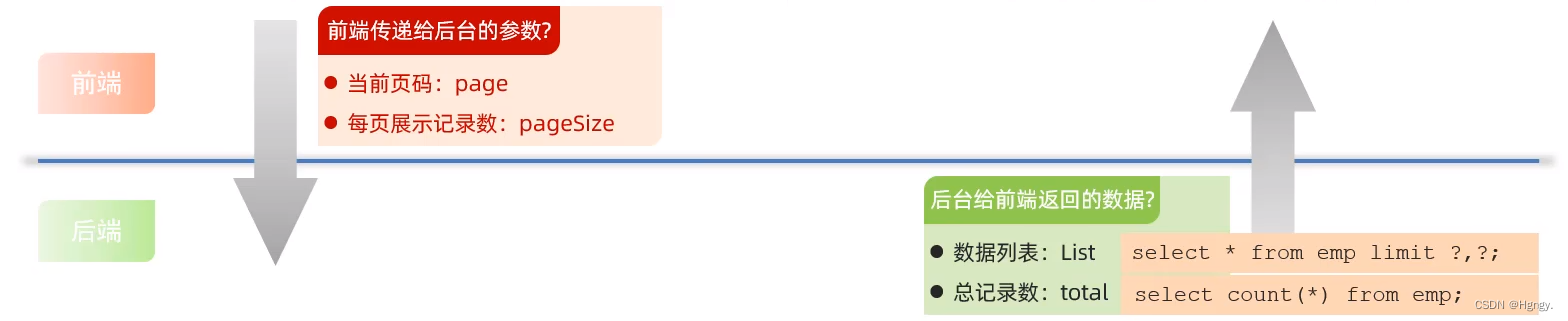
服务端给客户端响应数据最终是我们所设置的Controller方法的返回值,而一个方法只能有一个返回值,而员工列表和记录数类型不一样,所以我们需要将这两项数据封装成一个实现类。
@Date
public class PageBean{
private Long tocal; //总记录数
private List rows; //当前页数据列表
}

/**
* 员工管理Controller
*/
//@Slf4j - lombok日志
@RestController
public class EmpController {
@Autowired
private EmpService empService;
@GetMapping("/emps")
public Result page(@RequestParam(defaultValue = "1") Integer page,@RequestParam(defaultValue = "10") Integer pageSize){
//log.info("分页查询:参数:{},{}",page,pageSize);
//调用Service分页查询
PageBean pageBean = empService.page(page,pageSize);
return Result.success(pageBean);
}
}
public interface EmpService {
/**
*
* 分页查询获取列表数据
*/
PageBean page(Integer page , Integer pageSize);
}
@Service
public class EmpServiceImpl implements EmpService {
@Autowired
private EmpMapper empMapper;
@Override
public PageBean page(Integer page, Integer pageSize) {
//获取总记录数
Long count = empMapper.count();
//获取分页查询结果列表
Integer start = (page - 1) * pageSize;
List<Emp> empList = empMapper.page(start,pageSize);
//封装pagebean对象
PageBean pageBean = new PageBean(count,empList);
return pageBean;
}
}
@Mapper
public interface EmpMapper {
/**
*查询总记录数
*/
@Select("select count(*) from emp")
public Long count();
/**
*
* 分页查询获取列表数据
*/
@Select("select * from emp limit #{start},#{pageSize}")
public List<Emp> page(Integer start,Integer pageSize);
}
2. PageHelper分页插件
在上述分页查询操作中,我们定义两条Sql语句获取指定页码数据列表和总记录数,这是原始的分页查询方式,可以看到步骤固定,代码繁琐。
所以第三方组织就提供了专门实现分页查询操作功能的插件,而目前MyBatis框架中最流行的就是PageHelper分页插件 。
-
引入依赖:```
<dependency> <groupId>com.github.pagehelper</groupId> <artifactId>pagehelper-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>1.4.2</version> </dependency> -
分页代码:```
@Service
public class EmpServiceImpl implements EmpService {
@Autowired
private EmpMapper empMapper;
@Override
public PageBean page(Integer page, Integer pageSize){
//设置分页参数
PageHelper.startPage(page,pageSize);
//执行查询
List empList = empMapper.list();
Page p = (Page) empList;
//封装pagebean对象
PageBean pageBean = new PageBean(p.getTotal(),p.getResult());
return pageBean;
}
}@Mapper
public interface EmpMapper {
/**
* 员工信息查询
*/
@Select(“select * from emp”)
public List list();
}
3. 条件分页查询
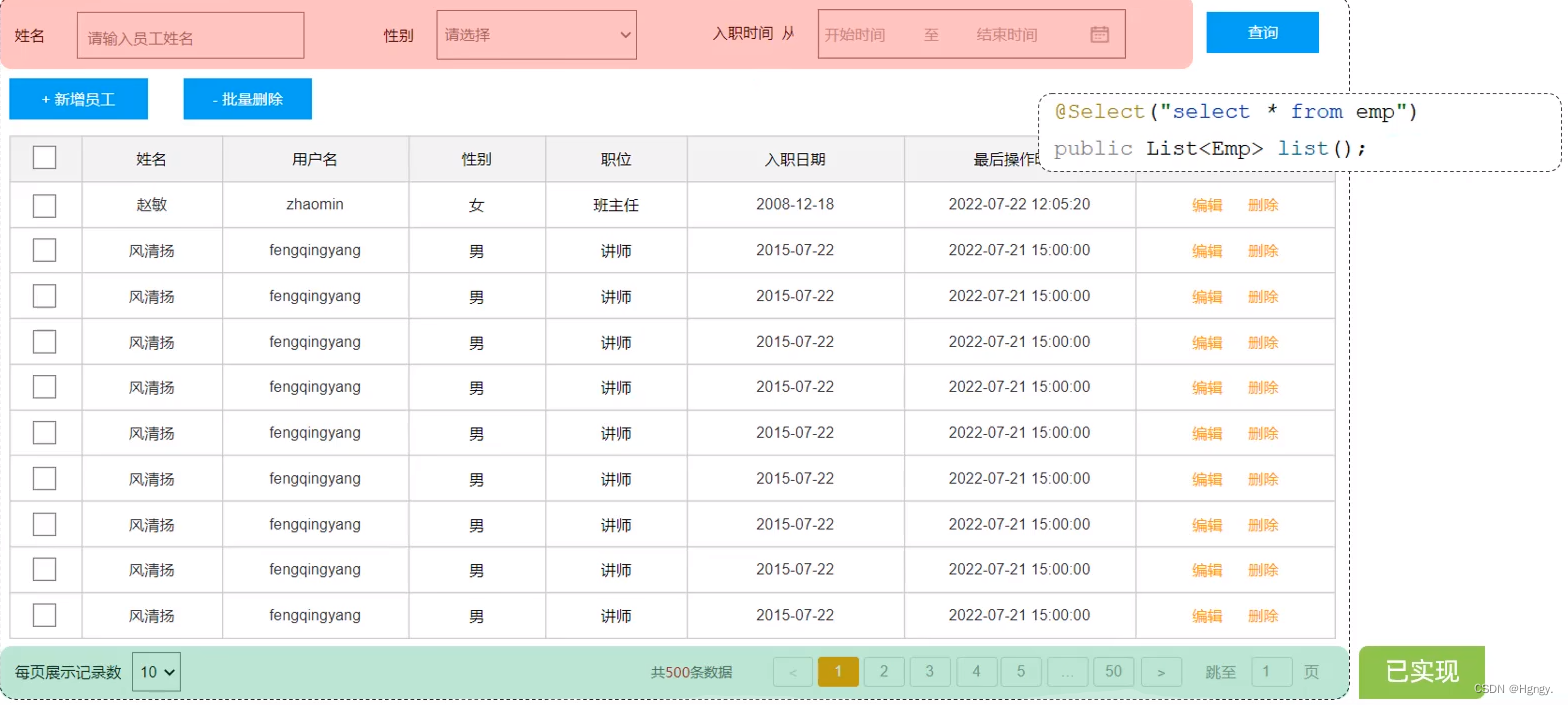
在上述分页查询代码基础上添加条件即可。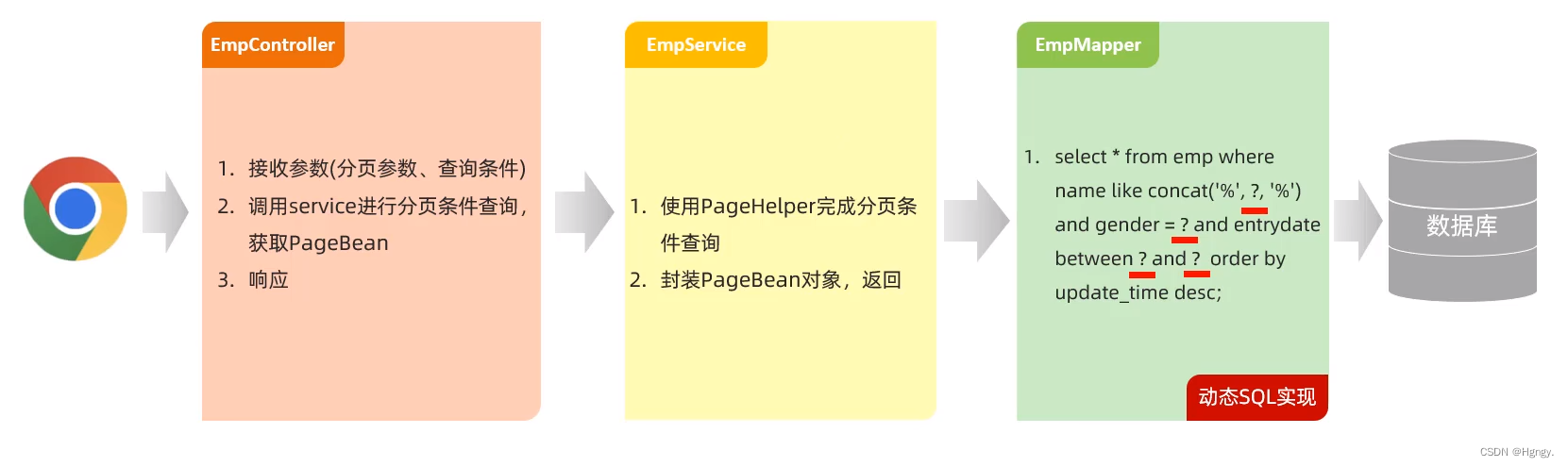
@RestController
public class EmpController {
@Autowired
private EmpService empService;
@GetMapping("/emps")
public Result page(
@RequestParam(defaultValue = "1") Integer page,
@RequestParam(defaultValue = "10") Integer pageSize,
String name, Short gender,
@DateTimeFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd") LocalDate begin,
@DateTimeFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd") LocalDate end){
//log.info("分页查询:参数:{},{},{},{},{},{}",page,pageSize,name,gender,begin,end);
//调用Service分页查询
PageBean pageBean = empService.page(page,pageSize,name,gender,begin,end);
return Result.success(pageBean);
}
}
public interface EmpService {
/**
*
* 分页查询获取列表数据
*/
PageBean page(Integer page , Integer pageSize,String name, Short gender,LocalDate begin, LocalDate end);
}
@Service
public class EmpServiceImpl implements EmpService {
@Autowired
private EmpMapper empMapper;
@Override
public PageBean page(Integer page, Integer pageSize, String name, Short gender, LocalDate begin, LocalDate end){
//设置分页参数
PageHelper.startPage(page,pageSize);
//执行查询
List<Emp> empList = empMapper.list(name, gender, begin, end);
Page<Emp> p = (Page<Emp>) empList;
//封装pagebean对象
PageBean pageBean = new PageBean(p.getTotal(),p.getResult());
return pageBean;
}
}
@Mapper
public interface EmpMapper {
public List<Emp> list(String name, Short gender, LocalDate begin, LocalDate end);
}
<!-- EmpMapper.xml-->
<mapper namespace="com.itheima.mapper.EmpMapper">
<!-- 条件查询-->
<select id="list" resultType="com.itheima.pojo.Emp">
select *
from emp
<where>
<if test="name != null">
name like concat('%', #{name}, '%')
</if>
<if test="gender != null">
and gender = #{gender}
</if>
<if test="begin != null and end != null">
and entrydate between #{begin} and #{end}
</if>
</where>
order by update_time desc
</select>
</mapper>
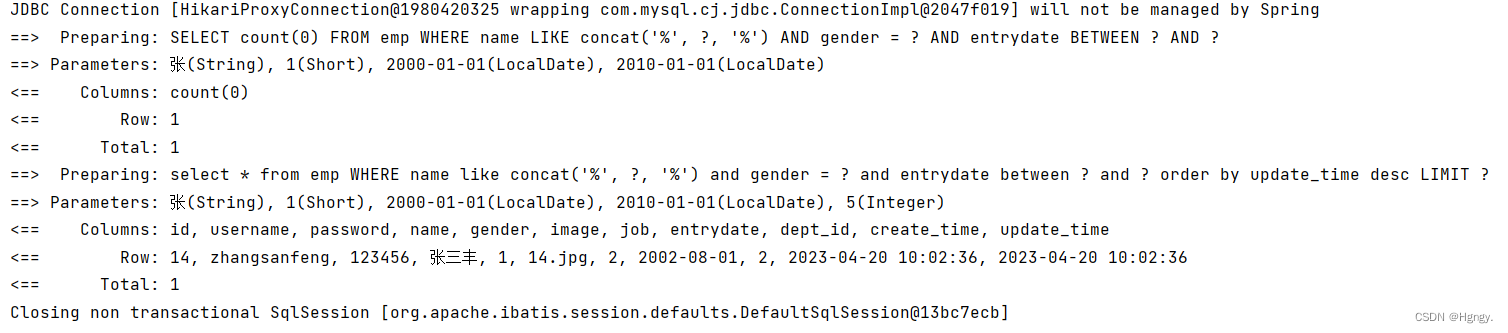
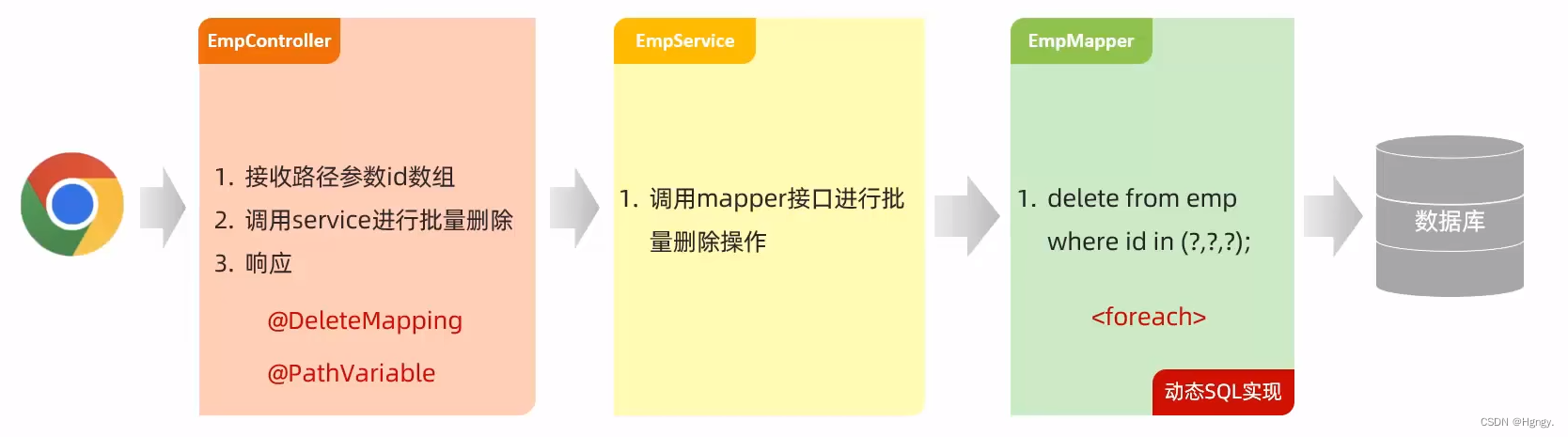
4. 删除员工
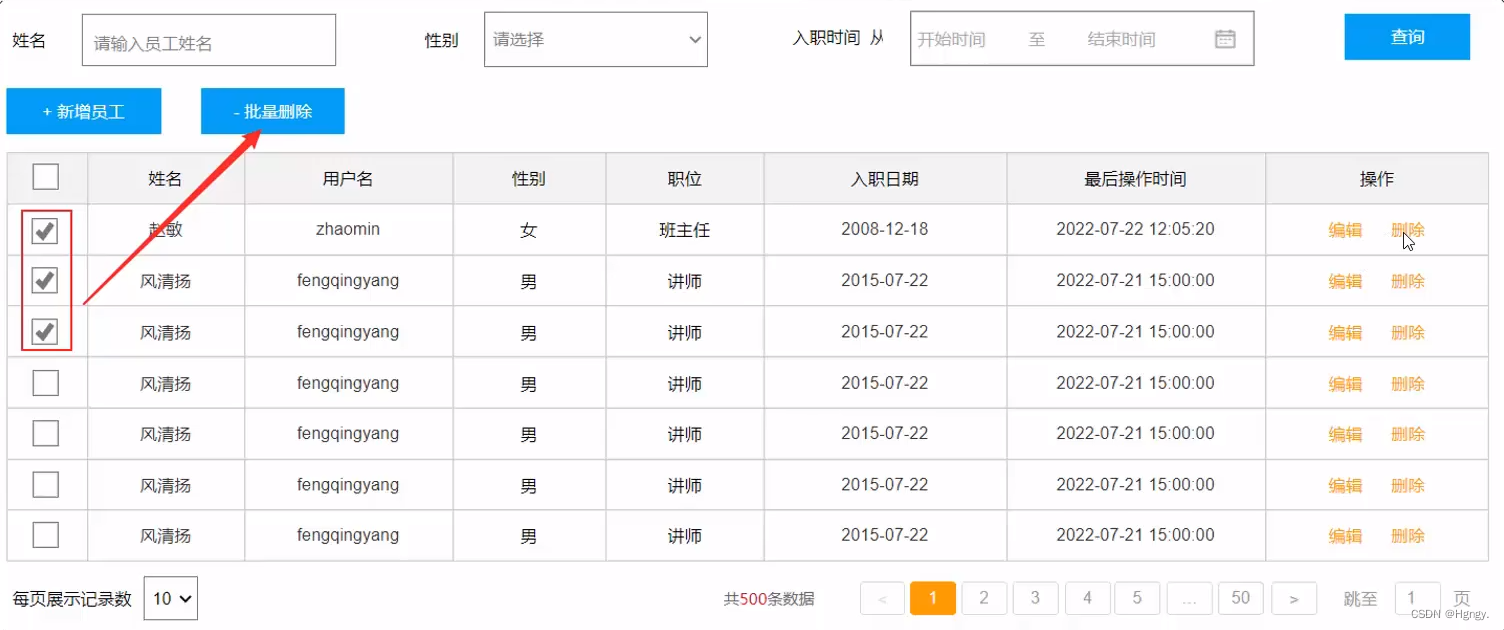
**思考问题:**是否要开发删除和批量删除两个接口?
- 如果我们仅仅开发一个批量删除的接口是可行的,因为删除一条元素也是特殊的批量删除。
@RestController
public class EmpController {
@Autowired
private EmpService empService;
/**
* 删除员工
*/
@DeleteMapping("/emps/{ids}")
public Result delete(@PathVariable List<Integer> ids){
//log.info("删除员工:{},",ids);
empService.delete(ids);
return Result.success();
}
}
public interface EmpService {
void delete(List<Integer> ids);
}
@Service
public class EmpServiceImpl implements EmpService {
@Override
public void delete(List<Integer> ids) {
empMapper.delete(ids);
}
}
@Mapper
public interface EmpMapper {
void delete(List<Integer> ids);
}
<!-- EmpMapper.xml-->
<mapper namespace="com.itheima.mapper.EmpMapper">
<!-- 批量删除操作-->
<delete id="delete">
delete
from emp
where id in
<foreach collection="ids" item="id" separator="," open="(" close=")">
#{id}
</foreach>
</delete>
</mapper>
四、员工信息
1. 新增员工
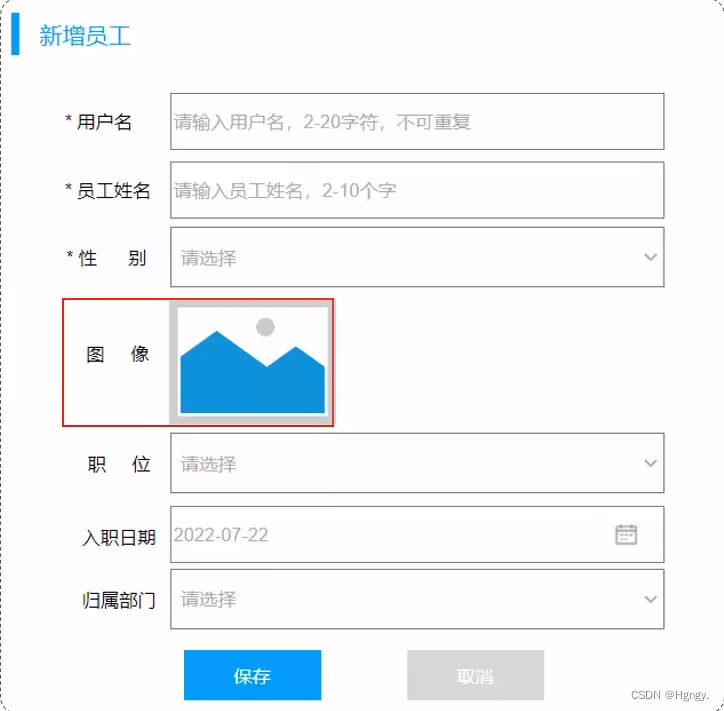
该小节我们针对于员工基本信息的录入,图像的上传第二小节再进行仔细介绍。

@RestController
public class EmpController {
@Autowired
private EmpService empService;
/**
* 新增员工
*/
@PostMapping("/emps")
public Result save(@RequestBody Emp emp){
//log.info("新增员工:{},",emp);
empService.save(emp);
return Result.success();
}
}
public interface EmpService {
void save(Emp emp);
}
@Service
public class EmpServiceImpl implements EmpService {
@Override
public void save(Emp emp) {
emp.setCreateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
emp.setUpdateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
empMapper.insert(emp);
}
}
@Mapper
public interface EmpMapper {
void delete(List<Integer> ids);
}
@Mapper
public interface EmpMapper {
@Insert("insert into emp(username, name, gender, image, job, entrydate, dept_id, create_time, update_time) " +
"values (#{username},#{name},#{gender},#{image},#{job},#{entrydate},#{deptId},#{createTime},#{updateTime})")
void insert(Emp emp);
}
2. 文件上传
2.1 简介
- 文件上传,是指将本地图片、视频、音频等文件上传到服务器,供其他用户浏览或下载的过程。
- 文件上传在项目中应用非常广泛,我们经常发微博、发微信朋友圈都用到了文件上传功能。
① 前端在进行文件上传时,需注意三要素:
- 表单项 type= " file "
- 表单提交方式 post
- 表单的enctype属性 multipart/form-data
<form action="/upload" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
姓名: <input type="text” name="username"<br>
年龄: <input type="text"name="age"><br>
头像: <input type="file" name="image"><br>
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
② 服务端接收文件:MultipartFile
//@slf4j
@RestController
public class UploadController {
@PostMapping("/upload")
public Result upload(String username, Integer age, MultipartFile image){
//log.info("文件上传:{},{},{}",username,age,image);
return Result.success();
}
}
2.2 本地存储
在服务端,接收到上传上来的文件之后,将文件存储在本地服务器磁盘中。
① MultipartFile 常用方法:
| 方法 | 说明 |
| String getOriginalFilename() ; | 获取原始文件名。 |
| void transferTo(File dest) ; | 将接收的文件转存到磁盘文件中。 |
| long getSize() ; | 获取文件的大小,单位:字节。 |
| byte[] getBytes() ; | 获取文件内容的字节数组。 |
| lnputStream getInputStream() ; | 获取接收到的文件内容的输入流。 |
@RestController
public class UploadController {
@PostMapping("/upload")
public Result upload(String username, Integer age, MultipartFile image) throws IOException {
//log.info("文件上传:{},{},{}",username,age,image);
//获取原始文件名 - 1.jpg
String originalFilename= image.getOriginalFilename();
//构造唯一文件名(不重复)-- uuid(通用唯一识别码)
int index = originalFilename.lastIndexOf(".");
String extname = originalFilename.substring(index);
String newFileName = UUID.randomUUID().toString() + extname;
//log.info("新的文件名:{}" , newFileName);
//将文件存储在服务器的磁盘目录中 F:\downloadfile\upload
image.transferTo(new File("F:\\downloadfile\\upload\\"+newFileName));
return Result.success();
}
}
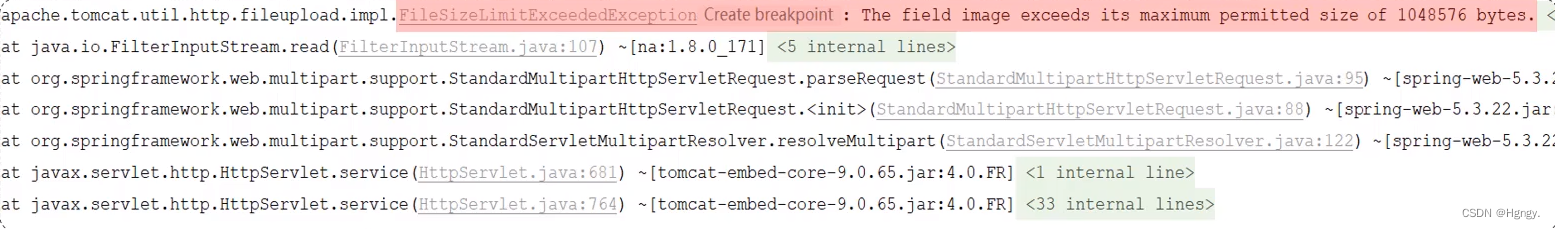
② 在SpringBoot中,文件上传,默认单个文件允许最大大小为 1M。如果需要上传大文件,可以进行如下配置:
#配置单个文件最大上传大小
spring.servlet.multipart.max-file-size=10MB
#配置单个请求最大上传大小(一次请求可以上传多个文件)
spring.servlet.multipart.max-request-size=100MB
**注意问题:**本地存储指将我们上传的文件全部存储在本地磁盘目录当中,但是这种方式在我们实际开发中很少使用,原因如下:
- 全部存储在磁盘目录下,前端页面无法直接访问。
- 项目中上传大量文件到本地磁盘目录下,而磁盘容量有限且不方便扩容又或者磁盘发生错误,损失较大。
2.3 阿里云OSS
① 介绍:
- 阿里云是阿里巴巴集团旗下全球领先的云计算公司,也是国内最大的云服务提供商。
- 阿里云对象存储OSS (Object Storage Service),是一款海量、安全、低成本、高可靠的云存储服务。使用OSS,您可以通过网络随时存储和调用包括文本、图片、音频和视频等在内的各种文件。
- 官网:https://www.aliyun.com/
- 使用步骤:

Bucket:存储空间是用户用于存储对象(Object,就是文件)的容器,所有的对象都必须隶属于某个存储空间。
SDK:Software Development Kit的缩写,软件开发工具包,包括辅助软件开发的依赖(jar包)、代码示例等,都可以叫做SDK。
**② 安装:**参照官方SDK编写入门程序:阿里云对象存储OSS简介
-
添加依赖:```
<dependency> <groupId>com.aliyun.oss</groupId> <artifactId>aliyun-sdk-oss</artifactId> <version>3.15.1</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>javax.xml.bind</groupId> <artifactId>jaxb-api</artifactId> <version>2.3.1</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>javax.activation</groupId> <artifactId>activation</artifactId> <version>1.1.1</version> </dependency> <!-- no more than 2.3.3--> <dependency> <groupId>org.glassfish.jaxb</groupId> <artifactId>jaxb-runtime</artifactId> <version>2.3.3</version> </dependency> -
简单上传文件流代码:```
import com.aliyun.oss.ClientException;
import com.aliyun.oss.OSS;
import com.aliyun.oss.OSSClientBuilder;
import com.aliyun.oss.OSSException;
import com.aliyun.oss.model.PutObjectRequest;
import com.aliyun.oss.model.PutObjectResult;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { // Endpoint以华东1(杭州)为例,其它Region请按实际情况填写。 String endpoint = "https://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com"; // 阿里云账号AccessKey拥有所有API的访问权限,风险很高。强烈建议您创建并使用RAM用户进行API访问或日常运维,请登录RAM控制台创建RAM用户。 String accessKeyId = "yourAccessKeyId"; String accessKeySecret = "yourAccessKeySecret"; // 填写Bucket名称,例如examplebucket。 String bucketName = "examplebucket"; // 填写Object完整路径,完整路径中不能包含Bucket名称,例如exampledir/exampleobject.txt。 String objectName = "exampledir/exampleobject.txt"; // 填写本地文件的完整路径,例如D:\\localpath\\examplefile.txt。 // 如果未指定本地路径,则默认从示例程序所属项目对应本地路径中上传文件流。 String filePath= "D:\\localpath\\examplefile.txt"; // 创建OSSClient实例。 OSS ossClient = new OSSClientBuilder().build(endpoint, accessKeyId, accessKeySecret); try { InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(filePath); // 创建PutObjectRequest对象。 PutObjectRequest putObjectRequest = new PutObjectRequest(bucketName, objectName, inputStream); // 设置该属性可以返回response。如果不设置,则返回的response为空。 putObjectRequest.setProcess("true"); // 创建PutObject请求。 PutObjectResult result = ossClient.putObject(putObjectRequest); // 如果上传成功,则返回200。 System.out.println(result.getResponse().getStatusCode()); } catch (OSSException oe) { System.out.println("Caught an OSSException, which means your request made it to OSS, " + "but was rejected with an error response for some reason."); System.out.println("Error Message:" + oe.getErrorMessage()); System.out.println("Error Code:" + oe.getErrorCode()); System.out.println("Request ID:" + oe.getRequestId()); System.out.println("Host ID:" + oe.getHostId()); } catch (ClientException ce) { System.out.println("Caught an ClientException, which means the client encountered " + "a serious internal problem while trying to communicate with OSS, " + "such as not being able to access the network."); System.out.println("Error Message:" + ce.getMessage()); } finally { if (ossClient != null) { ossClient.shutdown(); } } }}
③ 项目集成:
-
引入阿里云OSS上传文件工具类(由官方的示例代码改造而来)```
package com.itheima.utils;import com.aliyun.oss.OSS;
import com.aliyun.oss.OSSClientBuilder;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.UUID;/**
-
阿里云 OSS 工具类
*/
@Component
public class AliOSSUtils {
private String endpoint = “https://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com”;
private String accessKeyId = “LTAI5tMXhdNWon5c2k4fbSd4”;
private String accessKeySecret = “3fleUo57n8X42mijz6WsCUKznmumw8”;
private String bucketName = “web-tlias”;/**
-
实现上传图片到OSS
*/
public String upload(MultipartFile file) throws IOException {
// 获取上传的文件的输入流
InputStream inputStream = file.getInputStream();// 避免文件覆盖
String originalFilename = file.getOriginalFilename();
String fileName = UUID.randomUUID().toString() + originalFilename.substring(originalFilename.lastIndexOf(“.”));//上传文件到 OSS
OSS ossClient = new OSSClientBuilder().build(endpoint, accessKeyId, accessKeySecret);
ossClient.putObject(bucketName, fileName, inputStream);//文件访问路径
String url = endpoint.split(“//”)[0] + “//” + bucketName + “.” + endpoint.split(“//”)[1] + “/” + fileName;
// 关闭ossClient
ossClient.shutdown();
return url;// 把上传到oss的路径返回
}
-
}
-
-
上传图片接口开发```
//@slf4j
@RestController
public class UploadController {
@Autowired
private AliOSSUtils aliOSSUtils;//阿里云oss上传文件 @PostMapping("/upload") public Result upload(MultipartFile image) throws IOException { //log.info("文件上传文件名:{}",image.getOriginalFilename()); //调用阿里云oss文件上传工具类 String url = aliOSSUtils.upload(image); //log.info("文件上传成功,上传文件url为:{}",url); return Result.success(url); }}
3. 修改员工
3.1 查询回显

@RestController
public class EmpController {
@Autowired
private EmpService empService;
/**
* 根据id查员工
*/
@GetMapping("/emps/{id}")
public Result getById(@PathVariable Integer id){
//log.info("根据id查询员工信息:{}",id);
Emp emp = empService.getById(id);
return Result.success(emp);
}
}
public interface EmpService {
Emp getById(Integer id);
}
@Service
public class EmpServiceImpl implements EmpService {
@Override
public Emp getById(Integer id) {
return empMapper.getById(id);
}
}
@Mapper
public interface EmpMapper {
void delete(List<Integer> ids);
}
@Mapper
public interface EmpMapper {
@Select("select * from emp where id = #{id}")
Emp getById(Integer id);
}
3.2 修改员工信息

@RestController
public class EmpController {
@Autowired
private EmpService empService;
/**
* 更新员工
*/
@PostMapping("/emps")
public Result update(@RequestBody Emp emp){
//log.info("更新员工信息:{}",emp);
empService.update(emp);
return Result.success();
}
}
public interface EmpService {
void update(Emp emp);
}
@Service
public class EmpServiceImpl implements EmpService {
@Override
public void update(Emp emp) {
emp.setUpdateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
empMapper.update(emp);
}
}
@Mapper
public interface EmpMapper {
void delete(List<Integer> ids);
}
<!-- EmpMapper.xml-->
<mapper namespace="com.itheima.mapper.EmpMapper">
<update id="update">
update emp
<set>
<if test=" username!= null">username = #{username},</if>
<if test=" password!= null">password = #{password},</if>
<if test=" name!= null">name = #{name},</if>
<if test=" gender!= null">gender = #{gender},</if>
<if test=" image!= null">image = #{image},</if>
<if test=" job!= null">job = #{job},</if>
<if test=" entrydate!= null">entrydate = #{entrydate},</if>
<if test=" deptId!= null">dept_id = #{deptId},</if>
<if test=" updateTime!= null">update_time = #{updateTime}</if>
</set>
where id = #{id}
</update>
</mapper>
五、配置文件
1. 参数配置化
**问题分析:**上章节中我们采用了阿里云OSS工具类上传文件,在文件上传中我们定义了许多参数,比如阿里云域名、密钥以及存储空间名等。而在之前的开发中我们采用的是硬编码,就会产生问题:不方便维护和管理。
**解决方案:**我们可以把阿里云OSS工具类参数定义在properties配置文件当中。
#阿里云oss配置文件
aliyun.oss.endpoint=https://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com
aliyun.oss.accessKeyId=LTAI5tMXhdNWon5c2k4fbSd4
aliyun.oss.accessKeySecret=3fleUo57n8X42mijz6WsCUKznmumw8
aliyun.oss.bucketName=web-tlias
@Component
public class AliOSSUtils {
@Value("${aliyun.oss.endpoint}")
private String endpoint;
@Value("${aliyun.oss.accessKeyId}")
private String accessKeyId;
@Value("${aliyun.oss.accessKeySecret}")
private String accessKeySecret;
@Value("${aliyun.oss.bucketName}")
private String bucketName;
}
2. yml配置文件
在SpringBoot项目当中支持多种配置方式文件,在之前的学习过程当中,我们一直使用的都是application.properties配置文件,配置文件名是固定的。其实还要其他类型的配置文件:
| 类别 | 内容 | 对比 |
| xml | 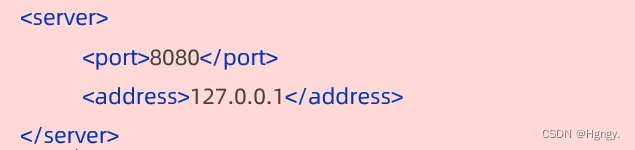 | 臃肿 |
| properties |  | 层次结构不清晰 |
yml / yaml (推荐) |  | 简洁、数据为中心 |
① 基本语法:
- 大小写敏感。
- 数值前边必须有空格,作为分隔符。
- 使用缩进表示层级关系,缩进时,不允许使用Tab键,只能用空格。(idea中会自动将Tab转换为空格)
- 缩进的空格数目不重要,只要相同层级的元素左侧对齐即可。
- #表示注释,从这个字符一直到行尾, 都会被解析器忽略。
② yml数据格式:
-
对象 / Map集合:```
user:
name: zhangsan
age: 18
password: 123456 -
数组 / List / Set集合:```
hobby:- java
- game
- sport
**③ yml配置:**在application.yml中配置上述案例相关的配置项。
spring:
# 数据库连接信息
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/tlias
username: root
password: 123456
# 文件上传配置
servlet:
multipart:
max-file-size: 10MB
max-request-size: 100MB
# Mybatis配置
mybatis:
configuration:
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
map-underscore-to-camel-case: true
# 阿里云oss配置
aliyun:
oss:
endpoint: https://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com
accessKeyId: LTAI5tMXhdNWon5c2k4fbSd4
accessKeySecret: 3fleUo57n8X42mijz6WsCUKznmumw8
bucketName: web-tlias
3. @ConfigurationProperties注解
① 问题分析:
在前面的学习时,我们将阿里云oss中四个参数属性交给properties或者yaml配置文件集中的配置管理,而在工具类中我们要想用到这四个参数就需要在成员变量前加上 @Value注解来注入外部配置文件中的属性值,并且在 @Value注解中使用 ${ } 来指定我们注入的指定值。

但是在实际开发中,如果参数较多,在每一个成员变量前都加上 @Value注解就会繁琐。所以我们又引入了 @ConfigurationProperties注解 。
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "aliyun.oss")
public class AliOSSProperties {
private String endpoint;
private String accessKeyId;
private String accessKeySecret;
private String bucketName;
public AliOSSProperties() {
}
public AliOSSProperties(String endpoint, String accessKeyId, String accessKeySecret, String bucketName) {
this.endpoint = endpoint;
this.accessKeyId = accessKeyId;
this.accessKeySecret = accessKeySecret;
this.bucketName = bucketName;
}
public String getEndpoint() {
return endpoint;
}
public void setEndpoint(String endpoint) {
this.endpoint = endpoint;
}
public String getAccessKeyId() {
return accessKeyId;
}
public void setAccessKeyId(String accessKeyId) {
this.accessKeyId = accessKeyId;
}
public String getAccessKeySecret() {
return accessKeySecret;
}
public void setAccessKeySecret(String accessKeySecret) {
this.accessKeySecret = accessKeySecret;
}
public String getBucketName() {
return bucketName;
}
public void setBucketName(String bucketName) {
this.bucketName = bucketName;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "AliOSSProperties{" +
"endpoint='" + endpoint + '\'' +
", accessKeyId='" + accessKeyId + '\'' +
", accessKeySecret='" + accessKeySecret + '\'' +
", bucketName='" + bucketName + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
@Component
public class AliOSSUtils {
@Autowired
private AliOSSProperties aliOSSProperties;
/**
* 实现上传图片到OSS
*/
public String upload(MultipartFile file) throws IOException {
//获取阿里云oss参数
String endpoint = aliOSSProperties.getEndpoint();
String accessKeyId = aliOSSProperties.getAccessKeyId();
String accessKeySecret = aliOSSProperties.getAccessKeySecret();
String bucketName = aliOSSProperties.getBucketName();
}
**注意:**当我们完成上述操作时,会发现弹出下面提示框,我们可以添加依赖解决问题。但是这个是可选操作,并不影响我们代码的运行。
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId> </dependency>
② @ConfigurationProperties与@Value 对比:
| 相同点 |
|
| 不同点 |
|
Java以前有多火,现在就有多难挤进这条赛道,岗位越来越少,就业人越来越多,技术越来越新,时代越来越进步,这十分要求还在传统Java道路上的人,必须将新兴技术与工作内容结合起来。
Java程序员的未来,到底在哪里
在于深化技术深度、拓展技术广度、向垂直领域深耕、转型管理或产品角色、关注新兴技术领域以及持续学习与适应变化。
这里给大家介绍一个新兴领域技术块,通过AI大模型赋能Java成熟技术栈,提升自己的优势,扩带自己的工作发展,这是一个相对便利的路径,因为Java和大模型是“相互赋能”的
Java作为大模型应用的“基础设施层”
-
模型部署与优化:Java在分布式系统、高并发处理方面的优势,可解决大模型部署的工程化难题。例如:
- 使用Spring Cloud构建大模型服务的微服务架构,实现负载均衡、熔断降级;
- 通过Java的NIO(非阻塞IO)优化模型推理的并发性能,降低延迟;
- 利用Java的JVM调优技术(如GC策略、内存管理)提升模型服务的稳定性。
-
数据管道构建:Java擅长处理结构化数据,可构建大模型训练所需的数据预处理管道。例如:
- 使用Apache Flink(Java实现)实时清洗用户行为日志,生成训练样本;
- 通过Java的JDBC/MyBatis连接数据库,抽取业务数据用于模型微调。
大模型作为Java开发的“智能辅助工具”
-
代码生成与补全:利用大模型(如GitHub Copilot、CodeGeeX)自动生成Java代码片段,减少重复劳动。例如:
- 输入自然语言描述(如“生成一个Spring Boot接口,接收用户ID并返回订单列表”),大模型直接生成可运行的代码;
- 通过大模型分析代码库,自动补全缺失的异常处理逻辑或单元测试。
-
智能调试与优化:大模型可分析Java应用的日志和性能数据,定位问题根源。例如:
- 输入堆栈跟踪信息,大模型识别内存泄漏的代码位置;
- 根据CPU使用率数据,大模型建议优化SQL查询或算法逻辑。
AI不是来替代Java的,而是来重新定义Java工程师的价值。
因此捕获AI,掌握技术是关键,让AI成为我们最便利的工具.
一定要把现有的技术和大模型结合起来,而不是抛弃你们现有技术!掌握AI能力的Java工程师比纯Java岗要吃香的多。
即使现在裁员、降薪、团队解散的比比皆是……但后续的趋势一定是AI应用落地!大模型方向才是实现职业升级、提升薪资待遇的绝佳机遇!
如何学习AGI大模型?
作为一名热心肠的互联网老兵,我决定把宝贵的AI知识分享给大家。 至于能学习到多少就看你的学习毅力和能力了 。我已将重要的AI大模型资料包括AI大模型入门学习思维导图、精品AI大模型学习书籍手册、视频教程、实战学习等录播视频免费分享出来。
因篇幅有限,仅展示部分资料,需要点击下方链接即可前往获取
2025最新版优快云大礼包:《AGI大模型学习资源包》免费分享**
一、2025最新大模型学习路线
一个明确的学习路线可以帮助新人了解从哪里开始,按照什么顺序学习,以及需要掌握哪些知识点。大模型领域涉及的知识点非常广泛,没有明确的学习路线可能会导致新人感到迷茫,不知道应该专注于哪些内容。
我们把学习路线分成L1到L4四个阶段,一步步带你从入门到进阶,从理论到实战。

L1级别:AI大模型时代的华丽登场
L1阶段:我们会去了解大模型的基础知识,以及大模型在各个行业的应用和分析;学习理解大模型的核心原理,关键技术,以及大模型应用场景;通过理论原理结合多个项目实战,从提示工程基础到提示工程进阶,掌握Prompt提示工程。

L2级别:AI大模型RAG应用开发工程
L2阶段是我们的AI大模型RAG应用开发工程,我们会去学习RAG检索增强生成:包括Naive RAG、Advanced-RAG以及RAG性能评估,还有GraphRAG在内的多个RAG热门项目的分析。

L3级别:大模型Agent应用架构进阶实践
L3阶段:大模型Agent应用架构进阶实现,我们会去学习LangChain、 LIamaIndex框架,也会学习到AutoGPT、 MetaGPT等多Agent系统,打造我们自己的Agent智能体;同时还可以学习到包括Coze、Dify在内的可视化工具的使用。

L4级别:大模型微调与私有化部署
L4阶段:大模型的微调和私有化部署,我们会更加深入的探讨Transformer架构,学习大模型的微调技术,利用DeepSpeed、Lamam Factory等工具快速进行模型微调;并通过Ollama、vLLM等推理部署框架,实现模型的快速部署。

整个大模型学习路线L1主要是对大模型的理论基础、生态以及提示词他的一个学习掌握;而L3 L4更多的是通过项目实战来掌握大模型的应用开发,针对以上大模型的学习路线我们也整理了对应的学习视频教程,和配套的学习资料。
二、大模型经典PDF书籍
书籍和学习文档资料是学习大模型过程中必不可少的,我们精选了一系列深入探讨大模型技术的书籍和学习文档,它们由领域内的顶尖专家撰写,内容全面、深入、详尽,为你学习大模型提供坚实的理论基础。(书籍含电子版PDF)

三、大模型视频教程
对于很多自学或者没有基础的同学来说,书籍这些纯文字类的学习教材会觉得比较晦涩难以理解,因此,我们提供了丰富的大模型视频教程,以动态、形象的方式展示技术概念,帮助你更快、更轻松地掌握核心知识。

四、大模型项目实战
学以致用 ,当你的理论知识积累到一定程度,就需要通过项目实战,在实际操作中检验和巩固你所学到的知识,同时为你找工作和职业发展打下坚实的基础。

五、大模型面试题
面试不仅是技术的较量,更需要充分的准备。
在你已经掌握了大模型技术之后,就需要开始准备面试,我们将提供精心整理的大模型面试题库,涵盖当前面试中可能遇到的各种技术问题,让你在面试中游刃有余。

因篇幅有限,仅展示部分资料,需要点击下方链接即可前往获取
























 9443
9443

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








