引言:线性表是n个具有相同特性的数据元素的有限序列,常见的线性表:顺序表、链表、栈、队列、字符串...
线性表在逻辑上是线性结构,也就说是连续的一条直线。但是在物理结构上并不一定是连续的, 线性表在物理上存储时,通常以数组和链式结构的形式存储
顺序表
(1)概念
顺序表是用一段物理地址连续的存储单元依次存储数据元素的线性结构,一般情况下采用数组存
储。在数组上完成数据的增删查改
(2)结构
顺序表又分为静态顺序表和动态顺序表
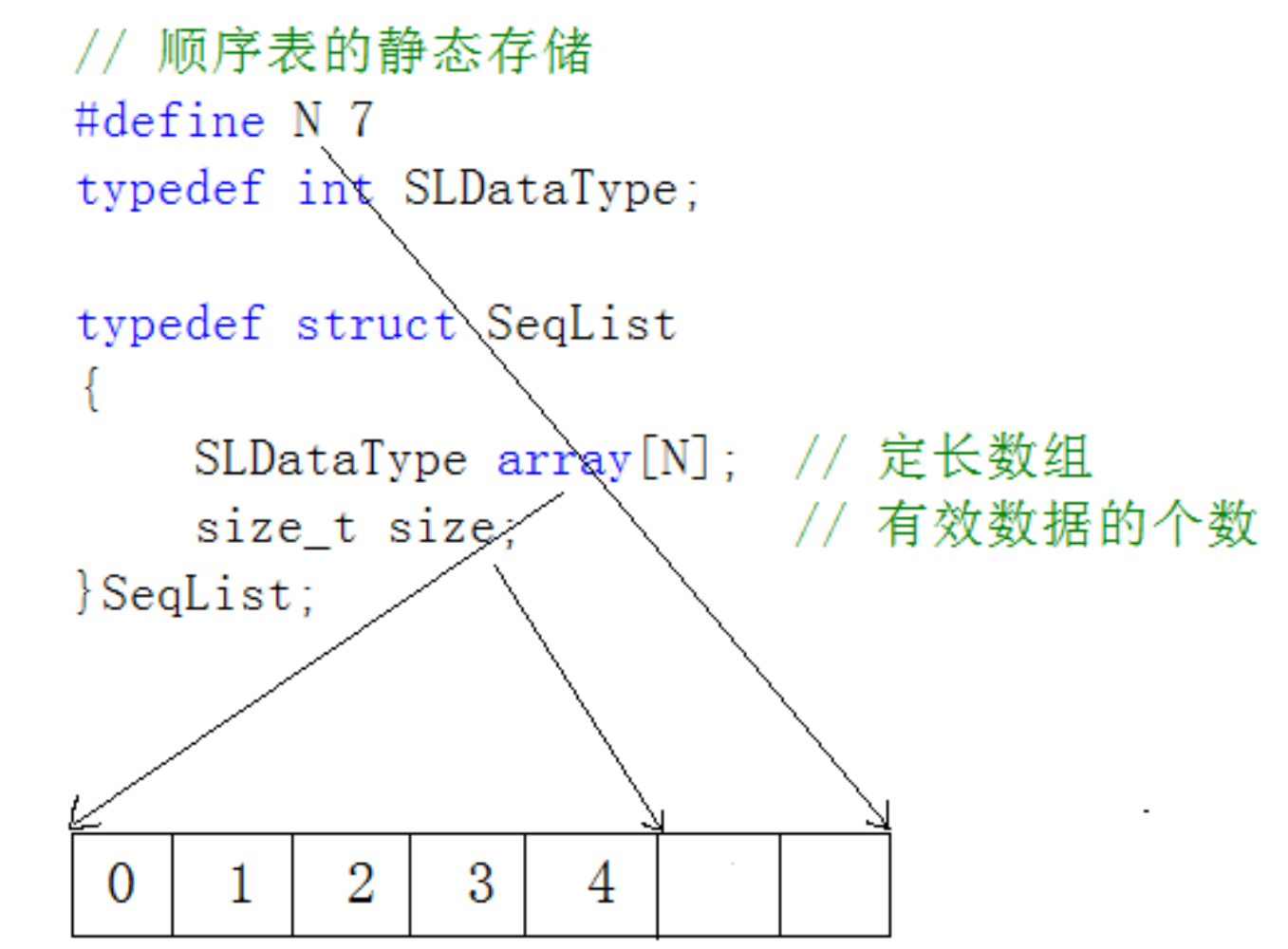
但是静态数据表也是有弊端的,空间开大了浪费,开小了又不够,所以一般采用动态顺序表

(3)接口实现,一般用三个文件分别来放置声明、定义、测试代码
声明
SeqList.h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
//静态的顺序表
// 给小了不够,给大了浪费
//#define N 10//定义空间大小
//typedef int SLDatatype;//定义顺序表类型
//struct SeqList
//{
// SLDatatype a[N];
// SLDatatype size;//记录有效数据
//};
//动态顺序表
typedef int SLDatatype;//定义顺序表类型
typedef struct SeqList
{
SLDatatype* a;
SLDatatype size;//存储有效数据个数
SLDatatype capacity;//容量大小
}SL;
//STL命名风格
void SLInit(SL* psl);//初始化
void SLDestory(SL* psl);//销毁
void SLPushBack(SL* psl, SLDatatype x);//尾插
void SLPushFront(SL* psl, SLDatatype x);//头插
void SLPopBack(SL* psl);//尾删
void SLPopFront(SL* psl);//头删
void SLCheckCapacity(SL* psl);//检查容量大小
void SLPrint(SL* psl);//打印
void SLInsert(SL* psl,int pos, SLDatatype x);//任意位置插入
void SLErase(SL* psl, int pos);//任意位置删除
int SLFind(SL* psl, SLDatatype x);//查找
void SLModify(SL* psl, int pos, SLDatatype x);//修改
定义
SeqList.c
#include"SeqList.h"
void SLInit(SL* psl)
{
assert(psl);
psl->a = (SLDatatype*)malloc(sizeof(SLDatatype) * 4);
if (psl->a == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail\n");
return;
}
psl->capacity = 4;
psl->size = 0;
}
void SLPrint(SL* psl)
{
assert(psl);
for (int i = 0; i < psl->size; i++)
{
printf("%d ", psl->a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
void SLCheckCapacity(SL* psl)
{
assert(psl);
if (psl->size == psl->capacity)
{
int* temp = (SLDatatype*)realloc(psl->a,sizeof(SLDatatype) * psl->capacity * 2);
if (temp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail\n");
return;
}
psl->a = temp;
psl->capacity *= 2;
}
}
void SLDestory(SL* psl)
{
assert(psl);
free(psl->a);
psl->a = NULL;
psl->capacity = psl->size = 0;
}
void SLPushBack(SL* psl, SLDatatype x)//尾插
{
assert(psl);
//psl->a[psl->size++}=x;
//容量不够怎么办
/*SLCheckCapacity(psl);
psl->a[psl->size] = x;
psl->size++;*/
SLInsert(psl, psl->size, x);
}
void SLPushFront(SL* psl, SLDatatype x)//头插
{
assert(psl);
SLCheckCapacity(psl);
int end = psl->size - 1;
while (end >=0)
{
psl->a[end + 1] = psl->a[end];
--end;
}
psl->a[0] = x;
psl->size++;
//SLInsert(psl, 0, x);
}
void SLPopBack(SL* psl)//尾删
{
assert(psl);
SLErase(psl, psl->size );
/*assert(psl->size > 0);
psl->size--;*/
}
void SLPopFront(SL* psl)//头删
{
assert(psl);
SLErase(psl, 0);
/*assert(psl->size > 0);
int start = 0;
while (start<psl->size-1)
{
psl->a[start] = psl->a[start + 1];
start++;
}
psl->size--;*/
/*assert(psl->size > 0);
int start = 1;
while (start < psl->size)
{
psl->a[start - 1] = psl->a[start];
start++:
}
psl->size--;*/
}
void SLInsert(SL* psl, int pos, SLDatatype x)//任意位置插入
{
assert(psl);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= psl->size);
SLCheckCapacity(psl);
int end = psl->size - 1;
while (pos <=end)
{
psl->a[end + 1] = psl->a[end];
end--;
}
psl->a[pos] = x;
psl->size++;
}
void SLErase(SL* psl, int pos)//任意位置删除
{
assert(psl);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= psl->size);
assert(psl->size > 0);
int start = pos + 1;
while (start < psl->size)
{
psl->a[start - 1] = psl->a[start];
start++;
}
psl->size--;
}
//找到返回下标,没找到返回-1
int SLFind(SL* psl, SLDatatype x)//查找
{
assert(psl);
assert(psl->size > 0);
for (int i = 0; i < psl->size; i++)
{
if (psl->a[i] == x)
{
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
void SLModify(SL* psl, int pos, SLDatatype x)//修改
{
assert(psl);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= psl->size);
psl->a[pos] = x;
}
测试代码
test.c
#include"SeqList.h"
void TestSeqList1()
{
//形参的改变不会影响实参
/*SL s;
s.a = NULL;
SLInit(s);*/
//传地址就会影响实参
SL s;
SLInit(&s);
SLPushBack(&s, 1);
SLPushBack(&s, 2);
SLPushBack(&s, 3);
SLPushBack(&s, 4);
SLPrint(&s);
SLDestory(&s);
}
void TestSeqList2()
{
SL s;
SLInit(&s);
SLPushBack(&s, 1);
SLPushBack(&s, 2);
SLPushBack(&s, 3);
SLPushBack(&s, 4);
SLPrint(&s);
SLPushFront(&s, 6);
SLPushFront(&s, 7);
SLPushFront(&s, 8);
SLPushFront(&s, 9);
SLPrint(&s);
SLDestory(&s);
}
void TestSeqList3()
{
SL s;
SLInit(&s);
SLPushBack(&s, 1);
SLPushBack(&s, 2);
SLPushBack(&s, 3);
SLPushBack(&s, 4);
SLPopBack(&s);
SLPrint(&s);
SLPopFront(&s);
SLPrint(&s);
SLPushFront(&s, 2);
SLInsert(&s, 2, 30);
SLPrint(&s);
SLPopBack(&s);
SLPopFront(&s);
SLPrint(&s);
int pos = SLFind(&s, 30);
if (pos != -1)
{
SLErase(&s, pos);
}
SLPrint(&s);
SLDestory(&s);
}
int main()
{
//TestSeqList1();
//TestSeqList2();
TestSeqList3();
return 0;
}
顺序表的弊端
- 增容需要申请新空间,拷贝数据,释放旧空间。会有不小的消耗。
- 增容一般是呈2倍的增长,势必会有一定的空间浪费。例如当前容量为50,满了以后增容到 100,我们再继续插入了5个数据,后面没有数据插入了,那么就浪费了45个数据空间。





















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








