class Bowl{
Bowl(int marker){
System.out.println(“Bowl(” + marker + “)”);
}
void f1(int marker) {
System.out.println(“f1(” + marker + “)”);
}
}
class Table{
static Bowl bowl1 = new Bowl(1);
Table(){
System.out.println(“Table()”);
bowl2.f1(1);
}
void f2(int marker) {
System.out.println(“f2(” + marker + “)”);
}
static Bowl bowl2 = new Bowl(2);
}
class Cupboard{
Bowl bowl3 = new Bowl(3) ;
static Bowl bowl4 = new Bowl(4);
Cupboard(){
System.out.println(“Cupboard()”);
bowl4.f1(2);
}
void f3(int marker) {
System.out.println(“f3(” + marker + “)” );
}
static Bowl bowl5 = new Bowl(5);
}
public class _572 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(“Creating new Cupboard() in main”);
new Cupboard();
System.out.println(“Creating new Cupboard() in main”);
new Cupboard();
table.f2(1);
cupboard.f3(1);
}
static Table table = new Table();
static Cupboard cupboard = new Cupboard();
}
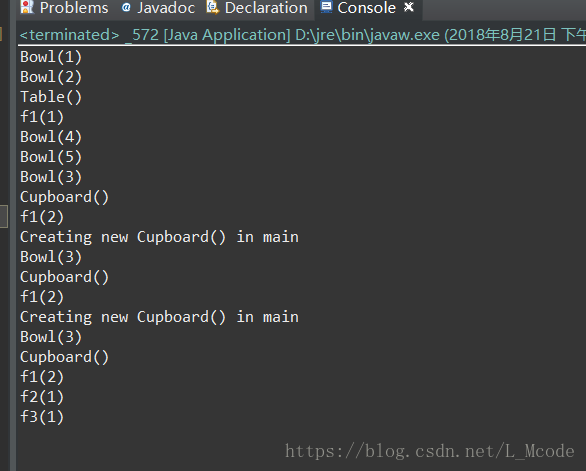





 本文通过一个Java示例程序展示了不同类中构造器和静态成员变量的初始化顺序及方法调用过程。重点关注了静态成员变量的创建与初始化、构造器的作用以及静态上下文中方法的调用。
本文通过一个Java示例程序展示了不同类中构造器和静态成员变量的初始化顺序及方法调用过程。重点关注了静态成员变量的创建与初始化、构造器的作用以及静态上下文中方法的调用。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








