目录
1.6 输入和输出
1.6.1 读取输入
要想通过控制台进行输入,首先需要创造一个Scanner对象,并与标准输入流 System.in 关联。
package com.qcby.第三章基础;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
//连续输入,分割用换行或者空格
int a = in.nextInt();
int b = in.nextInt();
int c = in.nextInt();
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(b);
System.out.println(c);
//连续输入字符串,只能用换行
//如果字符串输入前面还有其他输入(不是字符串类型),那么该字符串会把换行符读走
int d = in.nextInt();
String a1 = in.nextLine();
String b1 = in.nextLine();
String c1 = in.nextLine();
System.out.println(d);
System.out.println(a1);
System.out.println(b1);
System.out.println(c1);
}
}- java.util.Scanner 5.0
- Scanner(InputStreamin)
- String nextLine()
- String next()
- int nextInt()
- edouble nextDouble()
- boolean hasNext()
- boolean hasNextInt()
- boolean hasNextDouble()
2、java.lang.System 1.0
- static Console console() 6
3、java.io.Console 6
- static char[] readPassword(String prompt,0bject...args)
- static String readLine(String prompt,Object...args)
1.6.2 格式化输出
double x = 10000.0/3.0;
System.out.print(x);//3333.33……5 会将x对应的数据类型所允许的最大非0数字位输出
//printf使用规则同C语言
System.out.printf("%8.2f",x);//3333.33
System.out.printf("Hello,%s.Next year,you'll be %d",name,age);每一个以%开始的格式说明符会用相应的参数代替。
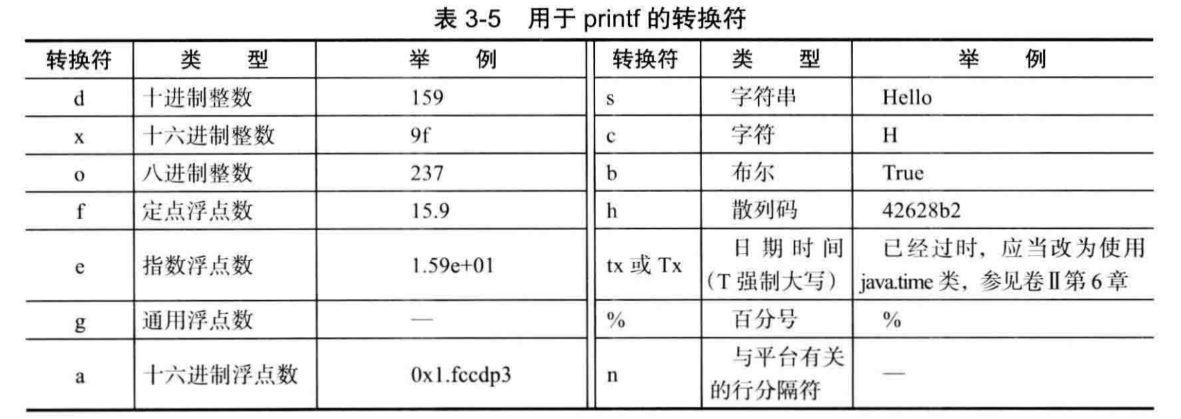
其他各种格式见P76。
1.6.3 文件输入与输出
见Java核心技术卷I 暂略。
1.7 控制流程
1.7.1 块作用域
块(即复合语句)是指由一对大括号括起来的若干条Java语句。块确定了变量的作用域。一个块可以嵌套在另一个块中。
1.7.2 条件语句
if-else、if-else if-……-else。
1.7.3 循环
while(……){}、do{}while(……);
1.7.4 确定循环
for(初始化;检测(循环继续的条件);更新)、for-each
//for-each循环 优点:不用考虑遍历时,循环的边界条件
int[] arr = {1,5,7,10};
//x会依次表示数组里面的每一项
for(int x:arr) {
System.out.println(x);
}
String[] arr2 = {"aa","bb","cc"};
for(String x:arr2) {
System.out.println(x);
}
int[][] arr3 = {{1,2},{5,8}};
for(int[] x:arr3) {
for(int y:x) {
System.out.println(y);
}
}1.7.5 多查选择:switch语句
switch语句将从与选项值相匹配的case标签处开始执行,直到遇到break语句,或者执行到switch语句的结束处为止。如果没有相匹配的case标签,而有default子句,那么就会执行这个子句。
int a = 8;
//switch击穿:每一个case都没有加break,那么当第一个满足条件的case语句执行完后,
//不会退出Switch语句,会把后面的每一个case语句里面的内容都执行一遍,即使不满足条件。
switch(a) {
case 5:
System.out.println("555");
//break;
case 8:
System.out.println("888");
//break;
case 10:
System.out.println("aaa");
//break;
default:
System.out.println("xxx");
//break;
}
1.7.6 中断控制流程语句
break:跳出当前循环。
带标签的break语句:跳出多重循环。标签必须放在希望跳出的最外层循环之前并且必须紧跟一个冒号。

continue:跳过循环体的剩余部分。
for(int i=0;i<=5;i++) {
if(i==3) continue;
System.out.println(i);
}
1.8 大数值
- 如果基本的整数和浮点数精度不能够满足需求,那么可以使用java.myth包中的两个很有用的类:BigInteger 和 BigDecimal。这两个类可以处理包含任意长度数字序列的数值。BigInteger 类实现了任意精度的整数运算,BigDecimal 实现了任意精度的浮点数运算。
- 使用静态的valueOf方法可以将普通的数值装换为大数值:
BigInteger a = BigInteger.valueOf(100);
3、对于大数值,应使用 add 和 multiply 方式实现 + 和 *。
BigInteger c = a.add(b);//c = a + b
BigInteger d = c.multiply(b.add(BigInteger.valueOf(2)));//d = c*(b + 2)4、常用方法
- java.math.Biglnteger 1.1
BigInteger add(BigInteger other)
BigInteger subtract(BigInteger other)
BigInteger multiply(BigInteger other)
BigInteger divide(BigInteger other)
BigInteger mod(BigInteger other)
返回这个大整数和另一个大整数other的和、差、积、商以及余数。
int compareTo(BigInteger other)
如果这个大整数与另一个大整数other相等,返回0;如果这个大整数小于另一个大整数other,返回负数;否则,返回正数。
static BigInteger valueOf(long x)
返回值等于x的大整数。
- java.math.BigDecimal
BigDecimal add(BigDecimal other)
BigDecimal subtract(BigDecimal other)
BigDecimal multiply(BigDecimal other)
BigDecimal divide(BigDecimal other RoundingMode mode) 5.0
返回这个大实数与另一个大实数other的和、差、积、商。要想计算商,必须给出舍入方式(rounding mode)。RoundingMode.HALF_UP是在学校中学习的四舍五入方式(即,数值0到4舍去,数值5到9进位)。它适用于常规的计算。有关其他的舍入方式请参看API文档。
int compareTo(BigDecimal other)
如果这个大实数与另一个大实数相等,返回0;如果这个大实数小于另一个大实数,返回负数;否则,返回正数。
static BigDecimal valueOf(long x)
static BigDecimal value0f(1ong x,int scale)
返回值为x或x/10^scale的一个大实数。





















 8万+
8万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








