结构
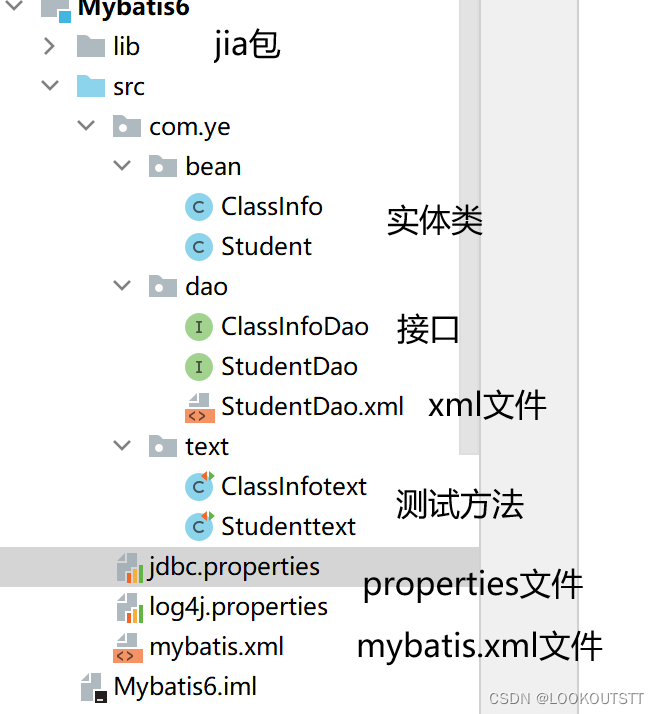
一、jdbc.properties文件
Properties文件是java中很常用的一种配置文件,文件后缀为“.properties”,属文本文件,文件的内容格式是“键=值”的格式,可以用“#”作为注释,java编程中用到的地方很多,运用配置文件,可以便于java深层次的解耦。例如java应用通过JDBC连接数据库时,通常需要在代码中写数据库连接字符串,下面贴出java通过JDBC连接数据库的代码(以mysql为例):
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver";//mysql提供的Driver接口的实现类
//此处为"jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/mydb"的简化形式,mydb为数据库名
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/mydb
jdbc.user=root
jdbc.password=root
以上代码连接mysql数据库没有任何问题,但是我想换成Oracle数据库,问题就来了,不是不能改,而是我必须得到java源代码中修改代码,这样的硬代码耦合在java中一般不这么做(菜鸟程序员有可能)。所以,为了达到解耦的目的,我们可以用配置文件来储存数据库的连接字符串。下面贴一份保存数据库连接字符串的properties配置文件 jdbc.properties:
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/mydb
jdbc.user=root
jdbc.password=root
这样我们就可以通过加载properties配置文件来连接数据库,达到深层次的解耦目的,如果想要换成oracle或是DB2,我们只需要修改配置文件即可,不用修改任何代码就可以更换数据库。
二.log4j.properties文件
log4j.rootLogger=TRACE,stdout
log4j.appender.stdout=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.stdout.Target=System.err
log4j.appender.stdout.layout=org.apache.log4j.SimpleLayout
log4j.appender.logfile=org.apache.log4j.FileAppender
log4j.appender.logfile.File=wocao.log
log4j.appender.logfile.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.logfile.layout.ConversionPattern=%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss} %F %p %m%n
log4j.logger.mapperNS =TRACE
log4j.logger.com.mybatis=DEBUG
log4j.logger.com.mybatis.common.jdbc.SimpleDataSource=DEBUG
log4j.logger.com.mybatis.common.jdbc.ScriptRunner=DEBUG
log4j.logger.com.mybatis.sqlmap.engine.impl.SqlMapClientDelegate=DEBUG
log4j.logger.java.sql.Connection=DEBUG
log4j.logger.java.sql.Statement=DEBUG
log4j.logger.java.sql.PreparedStatement=DEBUG
log4j.logger.java.sql.ResultSet=DEBUG
log4j.logger.org.springframework=error
log4j.logger.org.apache=ERROR
log4j.logger.org.mybatis=DEBUG 三.Mybatis.xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<!--配置环境信息===就是配置连接数据库的参数
default:指定配置的环境信息的id,表示默认连接该环境
-->
<properties resource="jdbc.properties">
<!-- 项目的配置名称-->
</properties>
<settings>
<setting name="logImpl" value="log4j"/>
</settings>
<typeAliases>
<!-- 加载com.baen.Emp包中的所有的类,给类默认起名别为类的名字但首字母小写 -->
<package name="com.ye.bean"/>
</typeAliases>
<environments default="mysql">
<environment id="mysql">
<!--配置事务的处理方式:模式使用JDBC的事务处理-->
<transactionManager type="jdbc"></transactionManager>
<!--数据源的默认type设置为pooled,表示使用连接池-->
<dataSource type="pooled">
<property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.user}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<package name="com.ye.dao"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>四.创建两个表的实体类


五.创建ClassInfoDao接口使用注解@Slelect、@Insert、@delect、@完成增删改查
public interface ClassInfoDao {
//全查
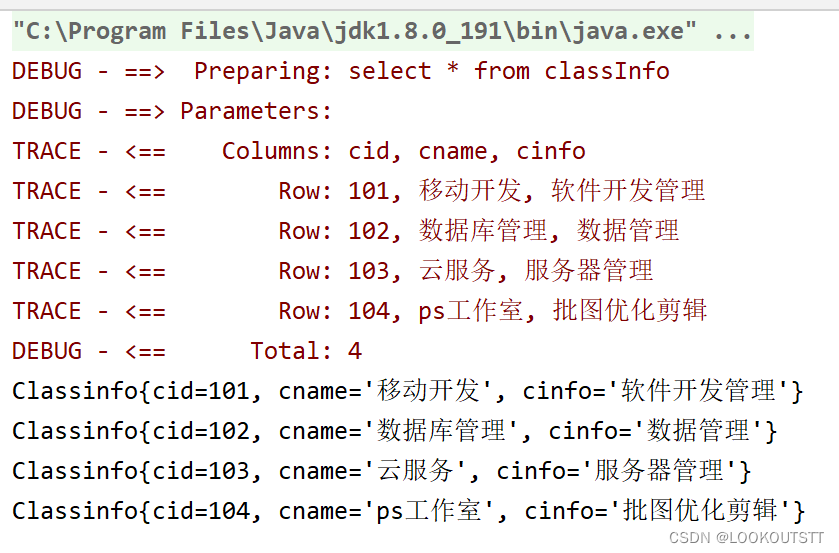
@Select("select * from classInfo")
List<ClassInfo> selectAd();
//根据编号查询
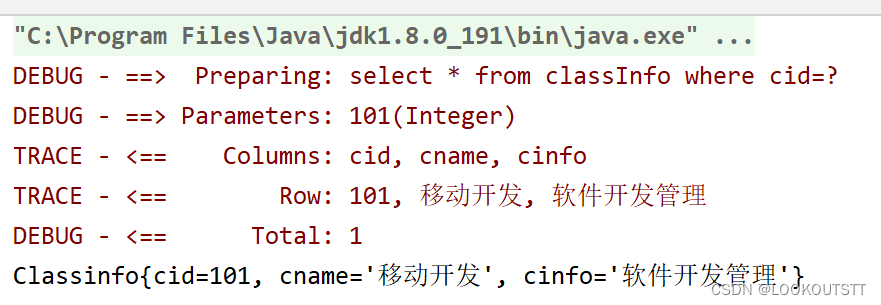
@Select("select * from classInfo where cid=#{cid}")
ClassInfo selectByCid(int cid);
//添加
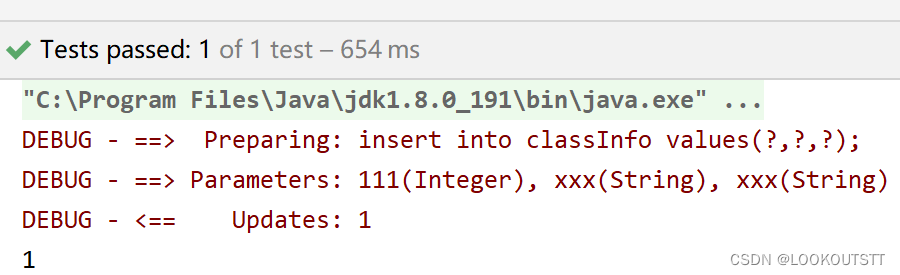
@Insert("insert into classInfo values(#{cid},#{cname},#{cinfo});")
int insert(ClassInfo classInfo);
//删除
@Delete("DELETE FROM classInfo WHERE cid=#{cid}")
int delete(int cid);
}注解就像修饰符一样,使用时在其前面增加@符号,用于修饰包、类、构造方法、域、方法、参数以及局部变量的声明,这些信息被存在注解的“name=values”键值对中。注解不影响程序代码的运行,无论增加还是删除注解,代码都始终如一的执行。
使用Annotation之前(甚至在使用之后),XML被广泛的应用于描述元数据。不知何时开始一些应用开发人员和架构师发现XML的维护越来越糟糕了。他们希望使用一些和代码紧耦合的东西,而不是像XML那样和代码是松耦合的(在某些情况下甚至是完全分离的)代码描述。
假如你想为应用设置很多的常量或参数,这种情况下,XML是一个很好的选择,因为它不会同特定的代码相连。如果你想把某个方法声明为服务,那么使用Annotation会更好一些,因为这种情况下需要注解和方法紧密耦合起来,开发人员也必须认识到这点。
六.测试
package com.ye.text;
import com.ye.bean.ClassInfo;
import com.ye.dao.ClassInfoDao;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.List;
public class ClassInfotext {
InputStream stream=null;
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder builder=null;
SqlSessionFactory factory=null;
SqlSession sqlSession=null;
ClassInfoDao Info=null;
@Before
public void inif() throws IOException {
stream= Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis.xml");
builder=new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();
factory=builder.build(stream);
sqlSession=factory.openSession();
Info=sqlSession.getMapper(ClassInfoDao.class);
}
//全查
@Test
public void selectAdd(){
List<ClassInfo> classInfos = Info.selectAd();
for (ClassInfo classInfo : classInfos) {
System.out.println(classInfo);
}
}
//根据编号查询
@Test
public void selectByCid(){
ClassInfo classInfo = Info.selectByCid(101);
System.out.println(classInfo);
}
//添加
@Test
public void insert(){
ClassInfo classInfo=new ClassInfo();
classInfo.setCid(111);
classInfo.setCname("xxx");
classInfo.setCinfo("xxx");
int insert = Info.insert(classInfo);
System.out.println(insert);
}
//删除
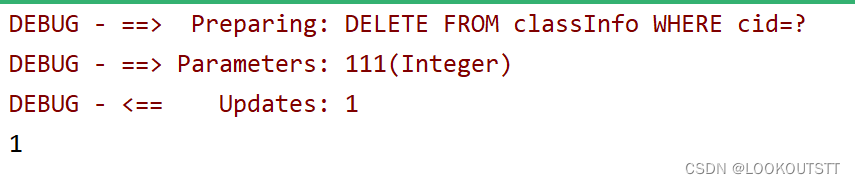
@Test
public void delete(){
int delete = Info.delete(111);
System.out.println(delete);
}
@After
public void distriy() throws IOException {
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
stream.close();
}
}
试图
七.创建StudentDao接口完成一对一多表联查,和动态修改模糊查询
public interface StudentDao {
List<Student> selectAll();
List<Student> seach(Student student);
int update(Student student);
}创建Student.xml
resultType可以把查询结果封装到pojo类型中,但必须pojo类的属性名和查询到的数据库表的字段名一致。
如果sql查询到的字段与pojo的属性名不一致,则需要使用resultMap将字段名和属性名对应起来,进行手动配置封装,将结果映射到pojo中
resultMap
resultMap可以实现将查询结果映射为复杂类型的pojo,比如在查询结果映射对象中包括pojo和list实现一对一查询和一对多查询。
先在Mapper文件中,配置基本的sql语句
<!-- 查询所有的订单数据 -->
<!-- resultMap:填入配置的resultMap标签的id值 -->
<select id="selectAll" resultMap="studentMap">
select * from student
</select>
配置resultMap标签,映射不同的字段和属性名
<!-- resultMap最终还是要将结果映射到pojo上,type就是指定映射到哪一个pojo -->
<!-- id:设置ResultMap的id -->
<resultMap id="studentMap" type="com.ye.bean.Student">
<!-- 定义主键 ,非常重要。如果是多个字段,则定义多个id -->
<!-- property:主键在pojo中的属性名 -->
<!-- column:主键在数据库中的列名 -->
<id property="id" column="id" />
<!-- 定义普通属性 -->
<association property="classInfo"
select="com.ye.dao.ClassInfoDao.selectByCid" column="cid"/>
</resultMap>
结果就可以封装到pojo类型中
使用resultMap进行关联查询
一对一查询
一对一数据模型:订单用户
一个订单信息只会是一个人下的订单,所以从查询订单信息出发关联查询用户信息为一对一查询。如果从用户信息出发查询用户下的订单信息则为一对多查询,因为一个用户可以下多个订单。
改造pojo类
在订单类中添加User属性,User属性是一个引用类型,用于存储关联查询的用户信息,因为关联关系是一对一,所以只需要添加单个属性即可
配置Mapper.xml配置文件
OrderMapper.xml
先使用id和result属性,映射order类的结果集,然后在使用association映射关联对象User的结果集
<resultMap id="studentMap" type="com.ye.bean.Student">
<id property="sid" column="sid"/>
<result property="sname" column="sname"/>
<result property="sex" column="sex"/>
<result property="phone" column="phone"/>
<result property="address" column="address"/>
<
<!-- association :配置一对一属性 -->
<!-- property:order里面的User属性名 -->
<!-- javaType:属性类型 -->
<association property="classInfo" select="com.ye.dao.ClassInfoDao.selectByCid" column="cid"/>
</resultMap>
<!-- 一对一关联,查询订单,订单内部包含用户属性 -->
<select id="selectAll" resultMap="studentMap">
select * from student
</select>
测试
@Test
public void selectAdd(){
List<Student> students = student.selectAll();
for (Student student1 : students) {
System.out.println(student1);
}
}试图

八.动态sql
动态SQL
可以根据具体的参数条件,来对SQL语句进行动态拼接。
比如在以前的开发中,由于不确定查询参数是否存在,许多人会使用类似于where 1 = 1 来作为前缀,然后后面用AND拼接要查询的参数,这样,就算要查询的参数为空,也能够正确执行查询,如果不加1 = 1,则如果查询参数为空,SQL语句就会变成SELECT * FROM student where,SQL不合法。
mybatis里的动态标签主要有
if
当满足test条件时,才会将<if>标签内的SQL语句拼接上去。
where
<where>标签只会在至少有一个子元素返回了SQL语句时, 才会向SQL语句中添加WHERE,并且如果WHERE之后是以AND或OR开头,会自动将其删掉。
//模糊查询
<select id="seach" parameterType="student" resultMap="studentMap">
select * from student
<where>
<if test="sname!=null and sname!=''">
or sname like concat('%',#{sname},'%')
</if>
<if test="sex!=null and sex!=''">
or sex like concat('%',#{sex},'%')
</if>
<if test="phone!=null and phone!=''">
or phone like concat('%',#{phone},'%')
</if>
<if test="address!=null and address!=''">
or address like concat('%',#{address},'%')
</if>
</where>
</select>
</select>在至少有一个子元素返回了SQL语句时,才会向SQL语句中添加SET,并且如果SET之后是以,开头的话,会自动将其删掉
//修改
<update id="update" parameterType="student">
update student
<set>
<if test="sname!=null and sname!=''">
sname=#{sname},
</if>
<if test="sex!=null and sex!=''">
sex=#{sex},
</if>
<if test="phone!=null and phone!=''">
phone=#{phone},
</if>
<if test="address!=null and address!=''">
address=#{address},
</if>
</set>
where sid=#{sid}
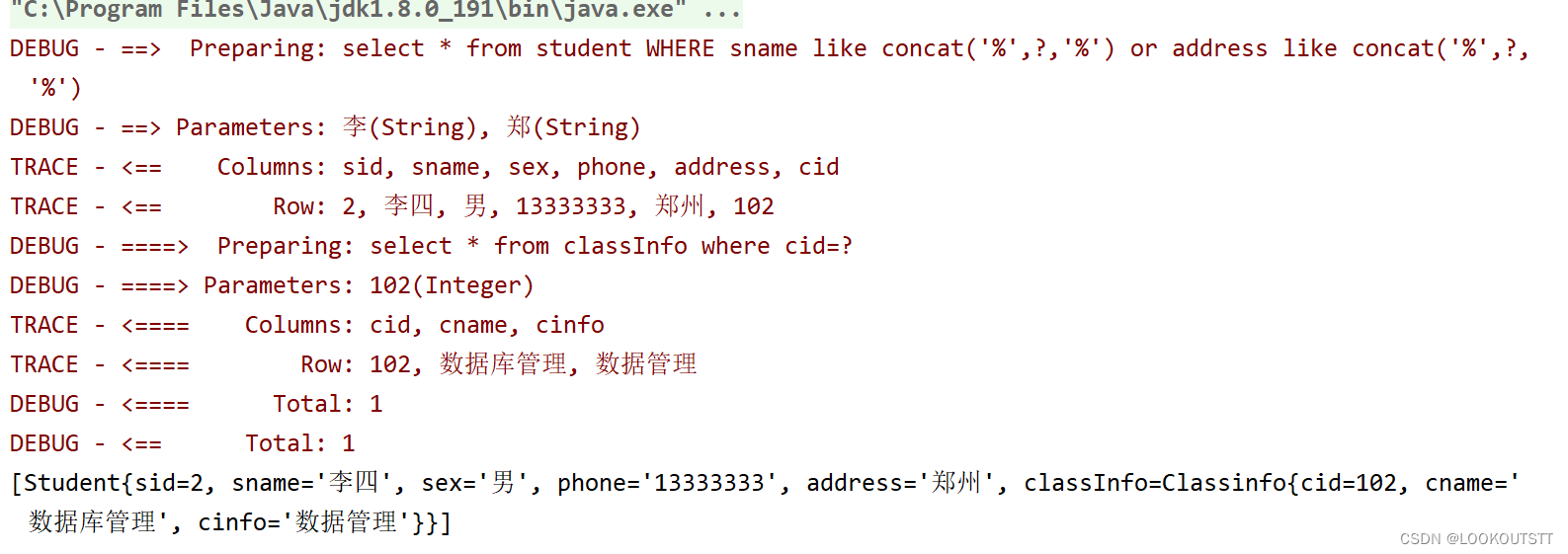
</update><测试模糊查询>
@Test
public void seach(){
Student st=new Student();
st.setSname("李");
st.setAddress("郑");
List<Student> seach = student.seach(st);
System.out.println(seach);
}
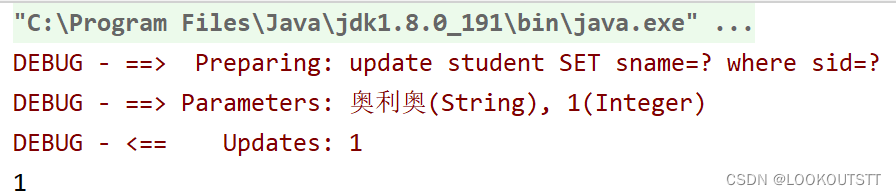
<测试修改>
@Test
public void upd(){
Student st=new Student();
st.setSid(1);
st.setSname("奥利奥");
int update = student.update(st);
System.out.println(update);
}
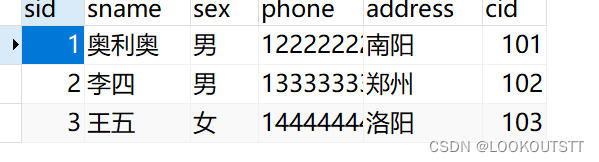
原本数据
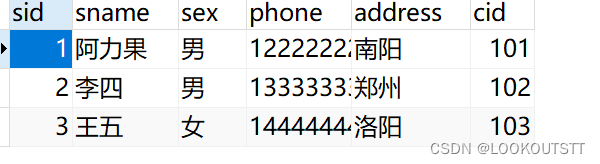
修改后




 本文介绍了使用Java注解配合MyBatis完成数据库的增删改查,以及一对一多表联查的动态SQL。通过jdbc.properties配置数据库连接,使用@Select、@Insert等注解实现DAO接口,同时展示了如何处理字段名与属性名不一致的情况,以及动态SQL的使用,如if和where标签的应用。
本文介绍了使用Java注解配合MyBatis完成数据库的增删改查,以及一对一多表联查的动态SQL。通过jdbc.properties配置数据库连接,使用@Select、@Insert等注解实现DAO接口,同时展示了如何处理字段名与属性名不一致的情况,以及动态SQL的使用,如if和where标签的应用。
















 1711
1711

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








