目录
0.分析
1).概念:
通俗的讲就是一个线程的池子,可以循环的完成任务的一组线程集合
2).必要性:
我们平时创建一个线程,完成某一个任务,等待线程的退出。但当需要创建大量的线程时,假设T1为创建线程时间,T2为在线程任务执行时间,T3为线程销毁时间,当 T1+T3 > T2,这时候就不划算了,使用线程池可以降低频繁创建和销毁线程所带来的开销,任务处理时间比较短的时候这个好处非常显著。
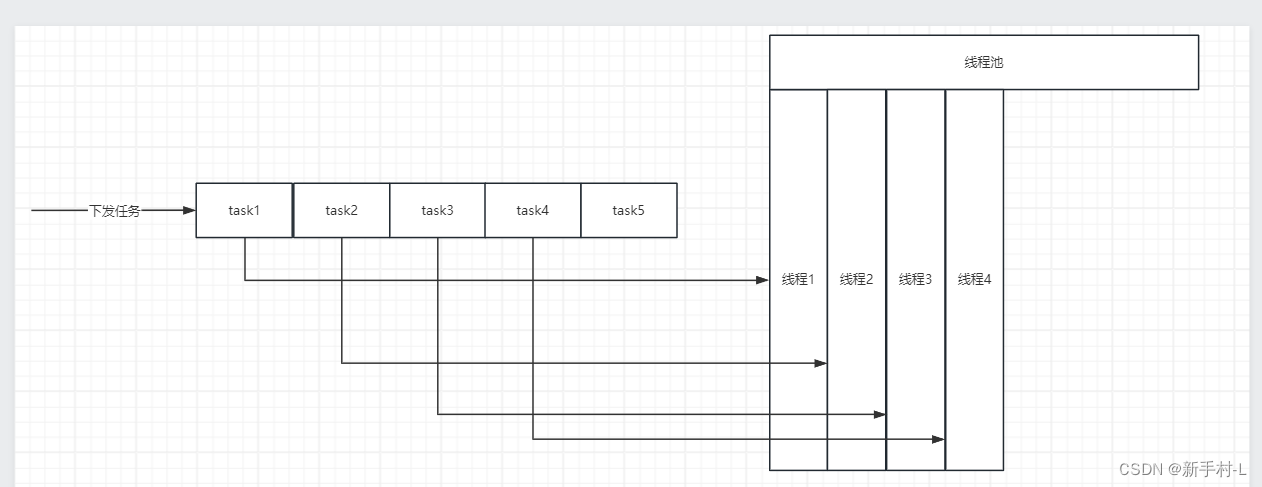
3).基本结构
任务队列,存储需要处理的任务,由工作线程来处理这些任务
线程池工作线程,它是任务队列任务的消费者,等待新任务的信号
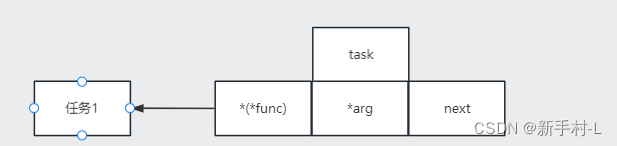
4).任务节点创建
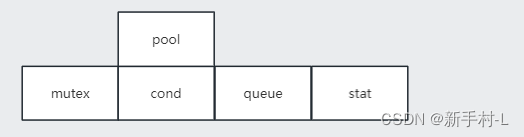
5).线程池创建
1.结构体创建
1).任务节点结构
typedef struct Task{
void *(*(func))(int arg);
int arg;
struct Task *next;
}t;2).线程池.临界资源的结构体
typedef struct ThreadPool{
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
pthread_cond_t cond;
t *queue;
int stat;
pthread_t tid[N];
}threadpool;
threadpool *pool;2.线程池初始化
void pool_init(void)
{
//printf("pool_init run >>>\n");
pool = (threadpool *)malloc(sizeof(threadpool));
pthread_mutex_init(&pool->mutex, NULL);
pthread_cond_init(&pool->cond, NULL);
pool->queue = NULL;
pool->stat = 0;
for(int i=0; i<N; i++)
{
pthread_create(&pool->tid[i], NULL, my_thread, (void *)i);
}
//printf("pool_init end >>>\n");
}3.工作线程
void *my_thread(void *arg)
{
//printf("my_thread run %d >>>\n", arg);
while(1)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutex);
pthread_cond_wait(&pool->cond, &pool->mutex);
t *q = pool->queue;
pool->queue = pool->queue->next;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutex);
// run my_task
q->func(q->arg);
pool->stat--;
}
//printf("my_thread end %d >>>\n", arg);
}4.添加任务
void pool_add_task(int arg)
{
//printf("pool_add_task run %d >>>\n",arg);
t *newtask;
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutex);
while(pool->stat >= N)
{
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutex);
usleep(10000);
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutex);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutex);
newtask = (t*)malloc(sizeof(t));
newtask->func = my_task;
newtask->arg = arg;
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutex);
t *q = pool->queue;
if(NULL == pool->queue)
{
pool->queue = newtask;
}else{
while(q->next != NULL)
{
q = q->next;
}
q->next = newtask;
}
pool->stat++;
pthread_cond_signal(&pool->cond);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutex);
//printf("pool_add_task end %d >>>\n",arg);
}void *my_task(void *arg)
{
printf("my_stask run %d >>>\n", (int)arg);
}5.线程的销毁
void pool_destroy(void)
{
// printf("pool_destroy run >>>\n");
t *del_task;
while(pool->queue != NULL)
{
del_task = pool->queue;
pool->queue = pool->queue->next;
free(del_task);
}
pthread_mutex_destroy(&pool->mutex);
pthread_cond_destroy(&pool->cond);
free(pool);
// printf("pool_destroy end >>>\n");
}6.程序
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define N 10
// task
typedef struct Task{
void *(*(func))(int arg);
int arg;
struct Task *next;
}t;
typedef struct ThreadPool{
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
pthread_cond_t cond;
t *queue;
int stat;
pthread_t tid[N];
}threadpool;
threadpool *pool;
void *my_thread(void *arg)
{
//printf("my_thread run %d >>>\n", arg);
while(1)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutex);
pthread_cond_wait(&pool->cond, &pool->mutex);
t *q = pool->queue;
pool->queue = pool->queue->next;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutex);
// run my_task
q->func(q->arg);
pool->stat--;
}
//printf("my_thread end %d >>>\n", arg);
}
void *my_task(void *arg)
{
printf("my_stask run %d >>>\n", (int)arg);
}
void pool_add_task(int arg)
{
//printf("pool_add_task run %d >>>\n",arg);
t *newtask;
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutex);
while(pool->stat >= N)
{
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutex);
usleep(10000);
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutex);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutex);
newtask = (t*)malloc(sizeof(t));
newtask->func = my_task;
newtask->arg = arg;
pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutex);
t *q = pool->queue;
if(NULL == pool->queue)
{
pool->queue = newtask;
}else{
while(q->next != NULL)
{
q = q->next;
}
q->next = newtask;
}
pool->stat++;
pthread_cond_signal(&pool->cond);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutex);
//printf("pool_add_task end %d >>>\n",arg);
}
void pool_init(void)
{
//printf("pool_init run >>>\n");
pool = (threadpool *)malloc(sizeof(threadpool));
pthread_mutex_init(&pool->mutex, NULL);
pthread_cond_init(&pool->cond, NULL);
pool->queue = NULL;
pool->stat = 0;
for(int i=0; i<N; i++)
{
pthread_create(&pool->tid[i], NULL, my_thread, (void *)i);
}
//printf("pool_init end >>>\n");
}
void pool_destroy(void)
{
// printf("pool_destroy run >>>\n");
t *del_task;
while(pool->queue != NULL)
{
del_task = pool->queue;
pool->queue = pool->queue->next;
free(del_task);
}
pthread_mutex_destroy(&pool->mutex);
pthread_cond_destroy(&pool->cond);
free(pool);
// printf("pool_destroy end >>>\n");
}
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
pool_init();
sleep(5);
for(int i=1; i<=20; i++)
{
pool_add_task(i);
}
sleep(5);
pool_destroy();
}



 本文介绍了线程池的概念,阐述了在大量线程创建场景中使用线程池的优势,并详细展示了线程池的结构、任务节点创建、线程池初始化、工作线程、任务添加以及线程销毁的实现过程。
本文介绍了线程池的概念,阐述了在大量线程创建场景中使用线程池的优势,并详细展示了线程池的结构、任务节点创建、线程池初始化、工作线程、任务添加以及线程销毁的实现过程。
















 1293
1293

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








