图片分类
一.配置环境
我们用的环境是win10+anaconda+pycharm
1.安装anaconda
2.安装完成后,创建适用于tensorflow的虚环境,在anaconda prompt中输入以下命令
添加映像
- conda config --add channels https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/free/
- conda config --set show_channel_urls yes
创建虚环境(tensorflow不支持Python3.7,我们这里使用python3.5,将该环境命名为fi
- conda create -n fi python=3.5
启动虚环境
- activate fi
安装tensorflow
- pip install --upgrade --ignore-installed tensorflow
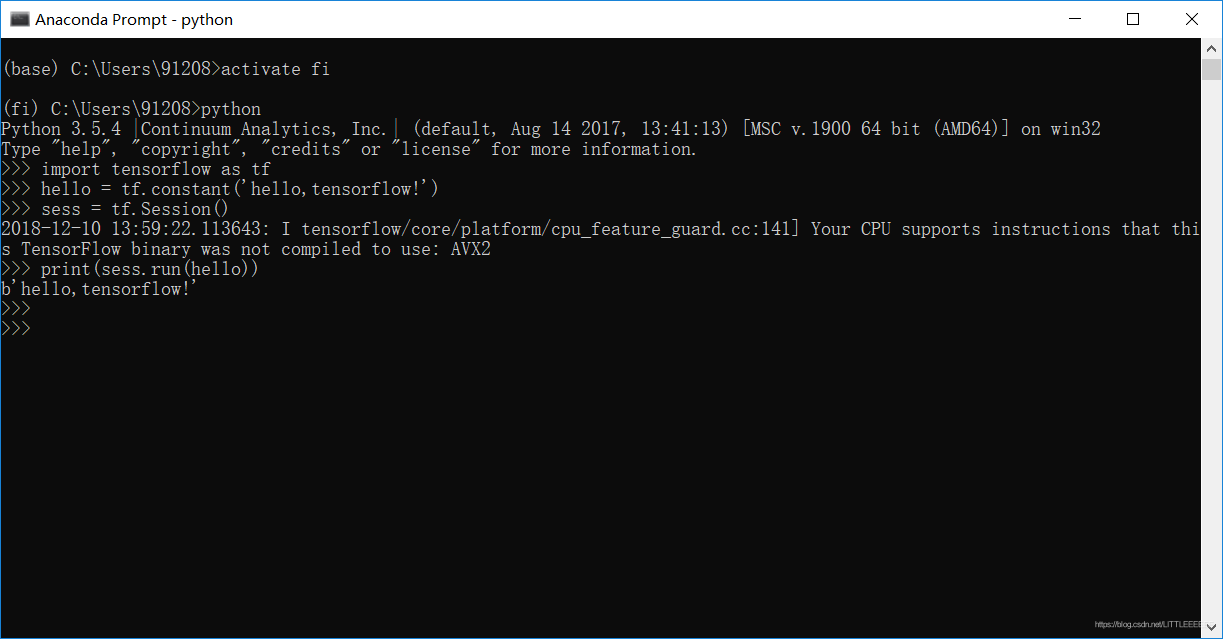
3.测似是否安装成功
- 在anaconda prompt中的fi虚环境里启动python(输入python)
- 测试代码如下
- import tensorflow as tf
- hello = tf.constant('Hello, TensorFlow!')
- sess = tf.Session()
- print(sess.run(hello))
4.部署pycharm
- pycharm的安装过程不再详述,首先new project-pure python,创建一个python项目
- File-settings-project,将之前设置的虚环境地址配置到pycharm中
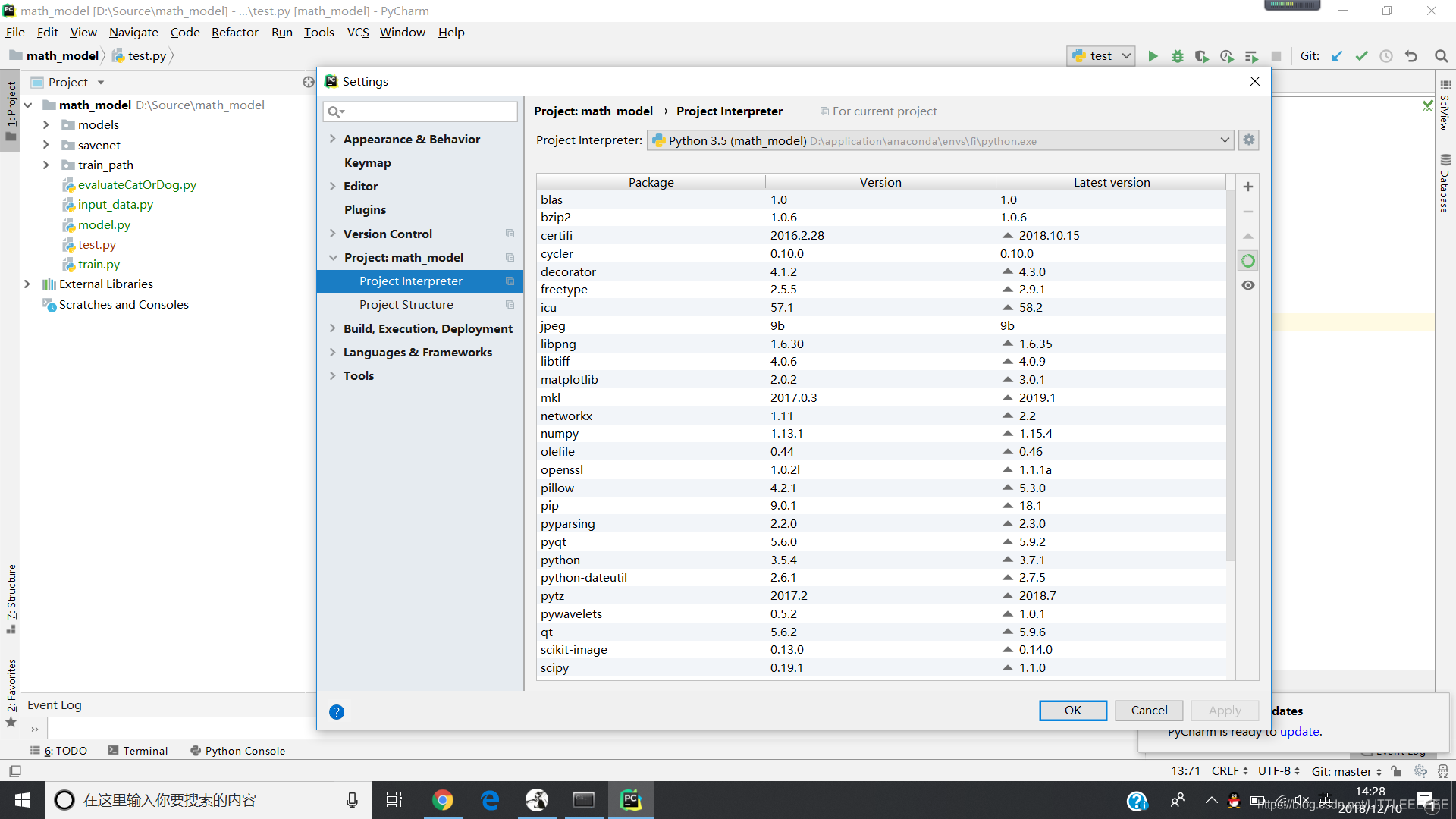
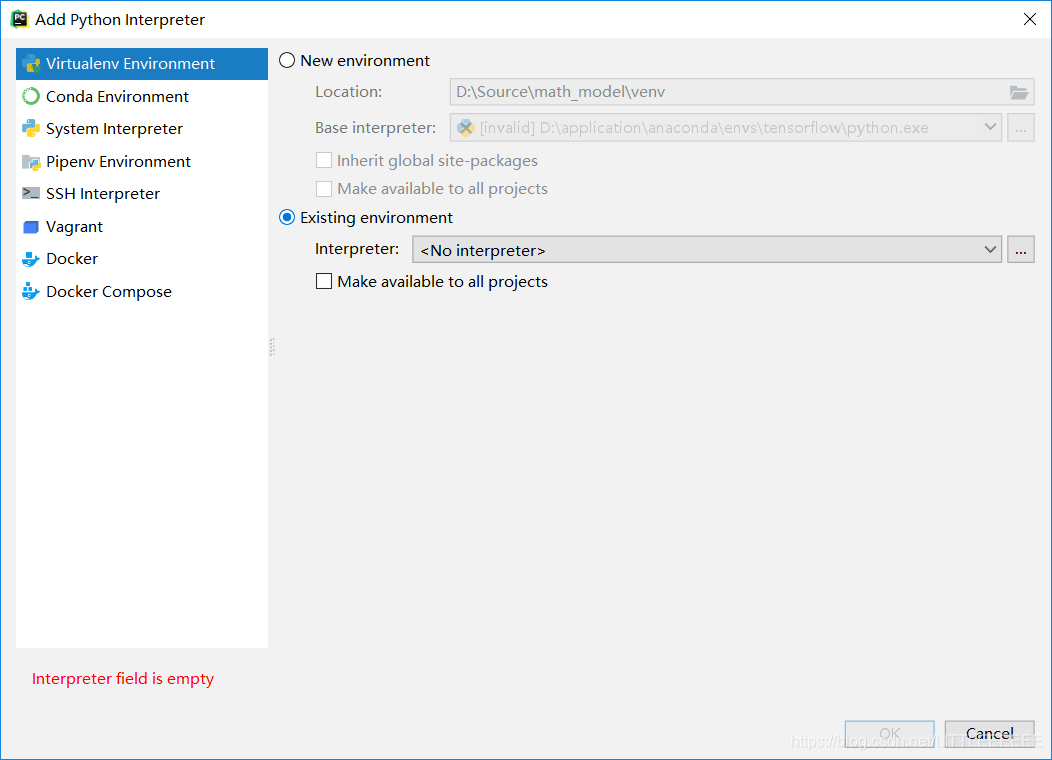
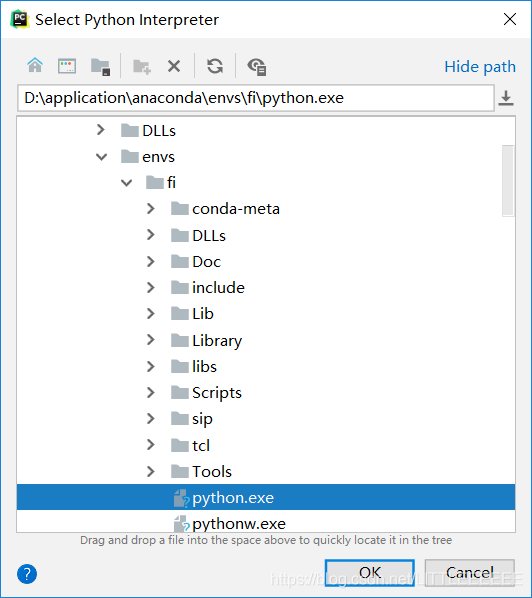
pycharm配置完成
二.项目:
项目要求是分析图片是否经过了颜色修改
数据集来自imagenet
input_data.py
#我们的图片文件夹中是原图片和经过颜色修改过后的图片混在一起,文件名可以区分,我们先把图片分别择出来,添加标签
import tensorflow as tf
import os
import numpy as np
def get_files(file_dir):
fakes = []
label_fakes = []
trues = []
label_trues = []
for file in os.listdir(file_dir):
name = file.split(sep='.')
if 'rich' in name[0]:
fakes.append(file_dir + file)
label_fakes.append(0)
else:
trues.append(file_dir + file)
label_trues.append(1)
image_list = np.hstack((fakes, trues))
label_list = np.hstack((label_fakes, label_trues))
# print('There are %d cats\nThere are %d dogs' %(len(cats), len(dogs)))
# 多个种类分别的时候需要把多个种类放在一起,打乱顺序,这里不需要
# 把标签和图片都放倒一个 temp 中 然后打乱顺序,然后取出来
temp = np.array([image_list, label_list])
temp = temp.transpose()
# 打乱顺序
np.random.shuffle(temp)
# 取出第一个元素作为 image 第二个元素作为 label
image_list = list(temp[:, 0])
label_list = list(temp[:, 1])
label_list = [int(i) for i in label_list]
return image_list, label_list
# 测试 get_files
#imgs , label = get_files('D://Source//math_model//train_path//add//')
#for i in imgs:
# print("img:",i)
#for i in label:
# print('label:',i)
# 测试 get_files end
# image_W ,image_H 指定图片大小,batch_size 每批读取的个数 ,capacity队列中 最多容纳元素的个数
def get_batch(image, label, image_W, image_H, batch_size, capacity):
# 转换数据为 ts 能识别的格式
image = tf.cast(image, tf.string)
label = tf.cast(label, tf.int32)
# 将image 和 label 放倒队列里
input_queue = tf.train.slice_input_producer([image, label])
label = input_queue[1]
# 读取图片的全部信息
image_contents = tf.read_file(input_queue[0])
# 把图片解码,channels =3 为彩色图片, r,g ,b 黑白图片为 1 ,也可以理解为图片的厚度
image = tf.image.decode_jpeg(image_contents, channels=3)
# 将图片以图片中心进行裁剪或者扩充为 指定的image_W,image_H
image = tf.image.resize_image_with_crop_or_pad(image, image_W, image_H)
# 对数据进行标准化,标准化,就是减去它的均值,除以他的方差
image = tf.image.per_image_standardization(image)
# 生成批次 num_threads 有多少个线程根据电脑配置设置 capacity 队列中 最多容纳图片的个数 tf.train.shuffle_batch 打乱顺序,
image_batch, label_batch = tf.train.batch([image, label], batch_size=batch_size, num_threads=64, capacity=capacity)
# 重新定义下 label_batch 的形状
label_batch = tf.reshape(label_batch, [batch_size])
# 转化图片
image_batch = tf.cast(image_batch, tf.float32)
return image_batch, label_batch
#模型构建
# coding=utf-8
import tensorflow as tf
# 结构
# conv1 卷积层 1
# pooling1_lrn 池化层 1
# conv2 卷积层 2
# pooling2_lrn 池化层 2
# local3 全连接层 1
# local4 全连接层 2
# softmax 全连接层 3
def inference(images, batch_size, n_classes):
with tf.variable_scope('conv1') as scope:
# 卷积盒的为 3*3 的卷积盒,图片厚度是3,输出是16个featuremap
weights = tf.get_variable('weights',
shape=[3, 3, 3, 16],
dtype=tf.float32,
initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.1, dtype=tf.float32))
biases = tf.get_variable('biases',
shape=[16],
dtype=tf.float32,
initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.1))
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(images, weights, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
pre_activation = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
conv1 = tf.nn.relu(pre_activation, name=scope.name)
with tf.variable_scope('pooling1_lrn') as scope:
pool1 = tf.nn.max_pool(conv1, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME', name='pooling1')
norm1 = tf.nn.lrn(pool1, depth_radius=4, bias=1.0, alpha=0.001 / 9.0, beta=0.75, name='norm1')
with tf.variable_scope('conv2') as scope:
weights = tf.get_variable('weights',
shape=[3, 3, 16, 16],
dtype=tf.float32,
initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.1, dtype=tf.float32))
biases = tf.get_variable('biases',
shape=[16],
dtype=tf.float32,
initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.1))
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(norm1, weights, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
pre_activation = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
conv2 = tf.nn.relu(pre_activation, name='conv2')
# pool2 and norm2
with tf.variable_scope('pooling2_lrn') as scope:
norm2 = tf.nn.lrn(conv2, depth_radius=4, bias=1.0, alpha=0.001 / 9.0, beta=0.75, name='norm2')
pool2 = tf.nn.max_pool(norm2, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 1], strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME', name='pooling2')
with tf.variable_scope('local3') as scope:
reshape = tf.reshape(pool2, shape=[batch_size, -1])
dim = reshape.get_shape()[1].value
weights = tf.get_variable('weights',
shape=[dim, 128],
dtype=tf.float32,
initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.005, dtype=tf.float32))
biases = tf.get_variable('biases',
shape=[128],
dtype=tf.float32,
initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.1))
local3 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(reshape, weights) + biases, name=scope.name)
# local4
with tf.variable_scope('local4') as scope:
weights = tf.get_variable('weights',
shape=[128, 128],
dtype=tf.float32,
initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.005, dtype=tf.float32))
biases = tf.get_variable('biases',
shape=[128],
dtype=tf.float32,
initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.1))
local4 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(local3, weights) + biases, name='local4')
# softmax
with tf.variable_scope('softmax_linear') as scope:
weights = tf.get_variable('softmax_linear',
shape=[128, n_classes],
dtype=tf.float32,
initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.005, dtype=tf.float32))
biases = tf.get_variable('biases',
shape=[n_classes],
dtype=tf.float32,
initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.1))
softmax_linear = tf.add(tf.matmul(local4, weights), biases, name='softmax_linear')
return softmax_linear
def losses(logits, labels):
with tf.variable_scope('loss') as scope:
cross_entropy = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits \
(logits=logits, labels=labels, name='xentropy_per_example')
loss = tf.reduce_mean(cross_entropy, name='loss')
tf.summary.scalar(scope.name + '/loss', loss)
return loss
def trainning(loss, learning_rate):
with tf.name_scope('optimizer'):
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=learning_rate)
global_step = tf.Variable(0, name='global_step', trainable=False)
train_op = optimizer.minimize(loss, global_step=global_step)
return train_op
def evaluation(logits, labels):
with tf.variable_scope('accuracy') as scope:
correct = tf.nn.in_top_k(logits, labels, 1)
correct = tf.cast(correct, tf.float16)
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(correct)
tf.summary.scalar(scope.name + '/accuracy', accuracy)
return accuracy
import os
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
import input_data
import model
N_CLASSES = 2 # 2个输出神经元,[1,0] 或者 [0,1]猫和狗的概率
IMG_W = 208 # 重新定义图片的大小,图片如果过大则训练比较慢
IMG_H = 208
BATCH_SIZE = 32 # 每批数据的大小
CAPACITY = 256
MAX_STEP = 20000 # 训练的步数,应当 >= 10000
learning_rate = 0.0001 # 学习率,建议刚开始的 learning_rate <= 0.0001
def run_training():
# 数据集
train_dir = 'D://Source//math_model//train_path//add//' # My dir--20170727-csq
# logs_train_dir 存放训练模型的过程的数据,在tensorboard 中查看
logs_train_dir = 'D://Source//math_model//models//'
# 获取图片和标签集
train, train_label = input_data.get_files(train_dir)
# 生成批次
train_batch, train_label_batch = input_data.get_batch(train,
train_label,
IMG_W,
IMG_H,
BATCH_SIZE,
CAPACITY)
# 进入模型
train_logits = model.inference(train_batch, BATCH_SIZE, N_CLASSES)
# 获取 loss
train_loss = model.losses(train_logits, train_label_batch)
# 训练
train_op = model.trainning(train_loss, learning_rate)
# 获取准确率
train__acc = model.evaluation(train_logits, train_label_batch)
# 合并 summary
summary_op = tf.summary.merge_all()
sess = tf.Session()
# 保存summary
train_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(logs_train_dir, sess.graph)
saver = tf.train.Saver()
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
coord = tf.train.Coordinator()
threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess, coord=coord)
try:
for step in np.arange(MAX_STEP):
if coord.should_stop():
break
_, tra_loss, tra_acc = sess.run([train_op, train_loss, train__acc])
if step % 50 == 0:
print('Step %d, train loss = %.2f, train accuracy = %.2f%%' % (step, tra_loss, tra_acc * 100.0))
summary_str = sess.run(summary_op)
train_writer.add_summary(summary_str, step)
if step % 2000 == 0 or (step + 1) == MAX_STEP:
# 每隔2000步保存一下模型,模型保存在 checkpoint_path 中
checkpoint_path = os.path.join(logs_train_dir, './model.ckpt')
saver.save(sess, checkpoint_path, global_step=step)
except tf.errors.OutOfRangeError:
print('Done training -- epoch limit reached')
finally:
coord.request_stop()
coord.join(threads)
sess.close()
# train
run_training()
以上训练后设置的是每2000步保存一次模型,保存模型的文件夹最好在项目文件夹中
evaluate.py
# coding=utf-8
import tensorflow as tf
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
import model
import os
#加载模型判断图片真假
def evaluate_one_image(image_array,dir):
with tf.Graph().as_default():
BATCH_SIZE = 1 # 因为只读取一副图片 所以batch 设置为1
N_CLASSES = 2 # 2个输出神经元,[1,0] 或者 [0,1] 假和真的概率
# 转化图片格式
image = tf.cast(image_array, tf.float32)
# 图片标准化
image = tf.image.per_image_standardization(image)
# 图片原来是三维的 [208, 208, 3] 重新定义图片形状 改为一个4D 四维的 tensor
image = tf.reshape(image, [1,208, 208, 3])
logit = model.inference(image, BATCH_SIZE, N_CLASSES)
# 因为 inference 的返回没有用激活函数,所以在这里对结果用softmax 激活
logit = tf.nn.softmax(logit)
# 用最原始的输入数据的方式向模型输入数据 placeholder
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[208, 208, 3])
# 我门存放模型的路径
logs_train_dir = 'D://Source//math_model//models//'
# 定义saver
saver = tf.train.Saver()
with tf.Session() as sess:
#将模型加载到sess 中
ckpt = tf.train.get_checkpoint_state(logs_train_dir)
if ckpt and ckpt.model_checkpoint_path:
global_step = ckpt.model_checkpoint_path.split('/')[-1].split('-')[-1]
saver.restore(sess, ckpt.model_checkpoint_path)
else:
print('模型加载失败,,,文件没有找到')
# 将图片输入到模型计算
prediction = sess.run(logit, feed_dict={x: image_array})
# 获取输出结果中最大概率的索引
max_index = np.argmax(prediction)
#print(str(dir)+str(prediction))
if max_index == 0:
print(str(dir)+'假的概率 %.6f' % prediction[:, 0])
else:
print(str(dir)+'真的概率 %.6f' % prediction[:, 1])
# 测试
train = 'D://Source//math_model//train_path//test//'
files = os.listdir(train)
n = len(files)
for x in range(0,n):
img_dir = os.path.join(train, files[x])
image = Image.open(img_dir).convert("RGB")
image = image.resize([208, 208])
image = np.array(image)
evaluate_one_image(image,img_dir)
完成!
参考博客
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/u012052268/article/details/74202439?tdsourcetag=s_pcqq_aiomsg
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/u012373815/article/details/78768727




 本文介绍了在Windows 10环境下,利用Anaconda创建虚拟环境并配置TensorFlow,通过PyCharm建立Python项目进行图片分类。项目数据集来源于ImageNet,主要包含input_data.py、model.py和train.py等文件,模型每2000步保存一次,最终通过evaluate.py进行评估。
本文介绍了在Windows 10环境下,利用Anaconda创建虚拟环境并配置TensorFlow,通过PyCharm建立Python项目进行图片分类。项目数据集来源于ImageNet,主要包含input_data.py、model.py和train.py等文件,模型每2000步保存一次,最终通过evaluate.py进行评估。
















 1009
1009

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








