Mybatis-Plus是一个能简化我们开发的数据库框架,官网对其的描述如下

首先我强烈推荐在IDEA上安装一个MybatisX插件,这个插件能提供许多便捷的功能,用了你就会发现它的好。
使用Mybatis-Plus之前我们需要引入Mybatis-Plus的依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.5.1</version>
</dependency>
然后我们可以选择在在 Spring Boot 启动类中添加 @MapperScan 注解,扫描 Mapper 文件夹:
这样我们就不必在每个mapper类上面添加@Mapper注解了
@SpringBootApplication
@MapperScan("com.kk.admin.mapper")
public class SpringBootDemo04AdminApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootDemo04AdminApplication.class, args);
}
}
编写一个User实体类(这里我们使用了Lombok来简化代码)
如果数据库表名与实体类名不一致,我们可以在实体类上添加@TableName(“表名”)注解来指明该实体类对应那个数据库表
/**
* @Author Kk
* @Date 2022/2/3 21:16
* @Description
*/
@Data
public class User {
//以下是数据库字段
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String email;
}
编写UserMapper接口(我们完全不要在接口中定义任何方法,只需要继承BaseMapper接口就行)在泛型中传入我们要操作的实体类对象User
/**
* @Author Kk
* @Date 2022/2/7 21:08
* @Description
*/
@Mapper
public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper<User> {
}
编写UserService接口(MyBatis-Plus不仅能简化我们Mapper层的代码,Service的代码也能帮助我们简化)
我们只需要继承IService接口
/**
* @Author Kk
* @Date 2022/2/7 21:30
* @Description
*/
public interface UserService extends IService<User> {
}
编写UserService实现类UserServiceImpl(同时,我们的实现类中并不需要实现接口中的诸多方法,我们只需要继承ServiceImpl类就行,这是官方提供的IService的实现类)
/**
* @Author Kk
* @Date 2022/2/7 21:30
* @Description
*/
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<UserMapper, User> implements UserService {
}
以下是ServiceImpl的部分源码(因此我们在上面泛型中传入UserMapper与User两个参数)
/**
* IService 实现类( 泛型:M 是 mapper 对象,T 是实体 )
*
* @author hubin
* @since 2018-06-23
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public class ServiceImpl<M extends BaseMapper<T>, T> implements IService<T> {
protected Log log = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
@Autowired
protected M baseMapper;
然后我们可以在Controller中编写请求来测试一下
/**
* 从数据库中查出user表中的用户进行展示
* @param pn 翻页携带参数(表示当前页)
* @param model
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/dynamicTable")
public String dynamicTable(@RequestParam(value = "pn",defaultValue = "1") Integer pn,Model model){
//从数据库中查出user表中的用户进行展示
List<User> list = userService.list();
// model.addAttribute("users",list);
//分页构造函数(当前页,每页显示条数)
Page<User> userPage = new Page<>(pn, 2);
//分页查询的结果(翻页对象,实体对象封装操作类(可以为null))
Page<User> page = userService.page(userPage, null);
//当前页码
long current = page.getCurrent();
//分页总数
long pages = page.getPages();
//数据总条数
long total = page.getTotal();
List<User> records = page.getRecords();
model.addAttribute("page",page);
return "table/dynamic_table";
}
编辑前端代码,将数据渲染到页面中
<tr class="gradeX odd" th:each="user:${page.records}">
<td th:text="${user.id}">id</td>
<td th:text="${user.name}">Internet
Explorer 4.0
</td>
<td th:text="${user.age}">age</td>
<td th:text="${user.email}">email</td>
<td>
<a th:href="@{/user/delete/{id}(id=${user.id},pn=${page.current})}" class="btn btn-danger btn-sm" type="button">删除</a>
</td>
</tr>
测试结果:
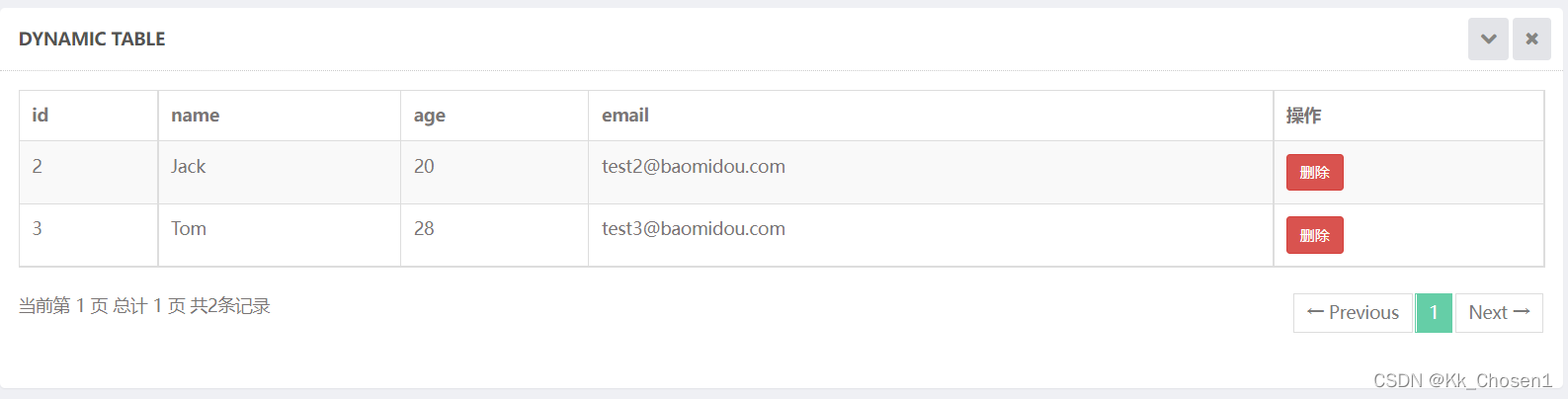
测试根据id删除:
为了实现删除一条数据后依旧停留在当前页面,我们可以在请求中携带一个当前页码的参数,然后通过重定向发送过去
@GetMapping("/user/delete/{id}")
public String deleteUserByID(@PathVariable("id") Long id,
@RequestParam("pn") Integer pn,
RedirectAttributes redirectAttributes){
userService.removeById(id);
//重定向携带参数
redirectAttributes.addAttribute("pn",pn);
return "redirect:/dynamicTable";
}
测试效果如下:
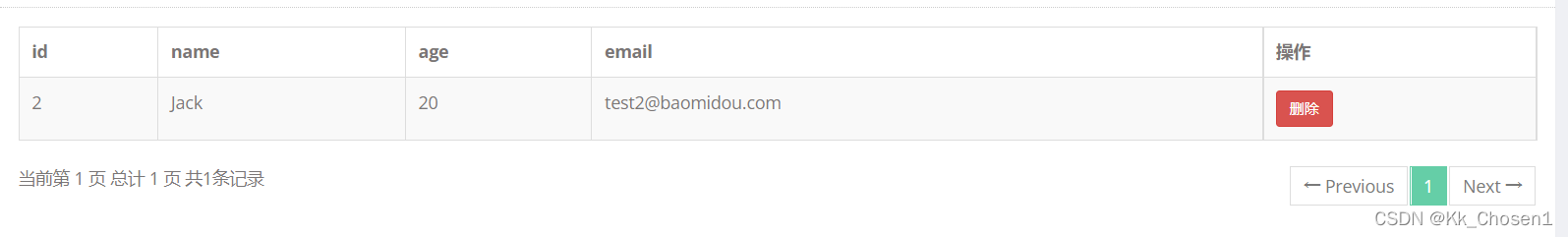








 本文介绍了如何在SpringBoot项目中集成Mybatis-Plus,包括依赖引入、Mapper与Service的简化、@MapperScan和泛型使用。通过实例演示了如何实现实体类映射、数据查询与CRUD操作,让开发者快速上手数据库开发。
本文介绍了如何在SpringBoot项目中集成Mybatis-Plus,包括依赖引入、Mapper与Service的简化、@MapperScan和泛型使用。通过实例演示了如何实现实体类映射、数据查询与CRUD操作,让开发者快速上手数据库开发。
















 1029
1029

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








