2020-8-24 多线程操作
1.多线程简述:
a.时间片轮流 每个进程轮流使用CPU
b.按照进程优先级使用CPU,如:车载,军工软件…

2.QThread介绍


3.流程
添加新文件-新建类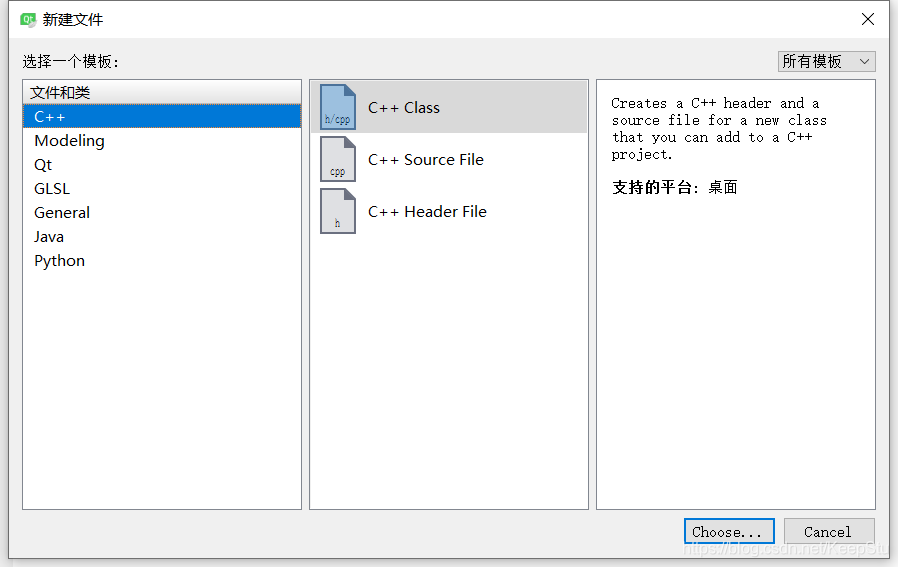
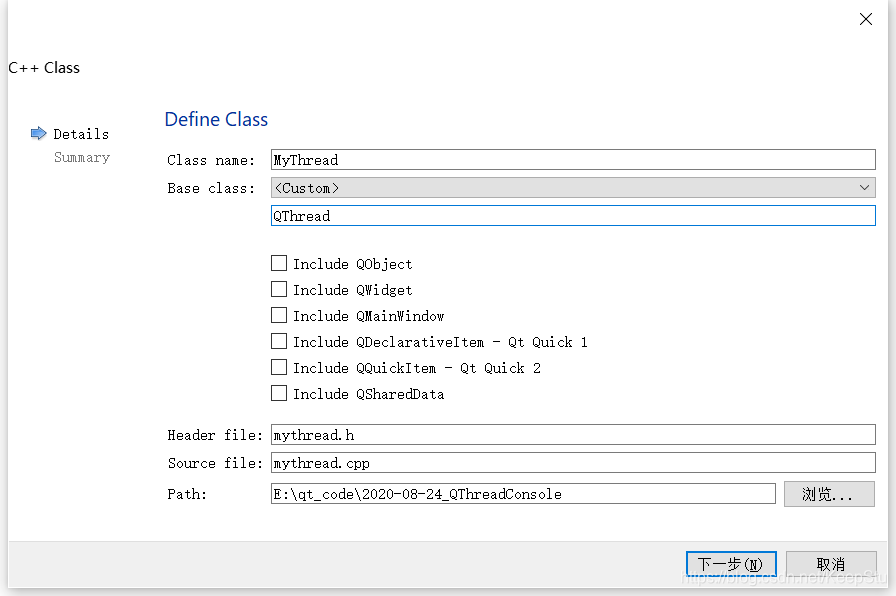
类定义
添加头文件#include <QThread>
在头文件中声明宏Q_OBJECT,这样才支持信号与槽
#ifndef MYTHREAD_H
#define MYTHREAD_H
#include <QThread>
class MyThread : public QThread
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
MyThread();
};
#endif // MYTHREAD_H
4.实现run()函数
声明:
protected:
virtual void run();
5.代码
mythread.h
#ifndef MYTHREAD_H
#define MYTHREAD_H
#include <QThread>
#include <QString>
#include <QDebug>
class MyThread : public QThread
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
MyThread();
void setThreadName(QString name);
protected:
virtual void run();
private:
QString threadName;
};
#endif // MYTHREAD_H
main.cpp
#include <QCoreApplication>
#include "mythread.h"//加入自拟的线程类
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QCoreApplication a(argc, argv);
qDebug()<<QThread::currentThreadId();//打印主线程ID
MyThread thread1;//定义一个线程对象
thread1.setThreadName("thread1");
thread1.start();//运行线程1
MyThread thread2;
thread2.setThreadName("thread2");
thread2.start();//运行线程2
//每个线程有线程的ID
return a.exec();
}
mythread.cpp
#include "mythread.h"
MyThread::MyThread()//构造函数
{
//打印当前线程的ID
qDebug()<<"MyThread()"<<threadName<<QThread::currentThreadId();
}
void MyThread::setThreadName(QString name)
{
threadName=name;
qDebug()<<"setThreadName()"<<threadName<<QThread::currentThreadId();
}
void MyThread::run()//run函数内的都会独立开辟线程
{
qDebug()<<"run()"<<threadName<<QThread::currentThreadId();
//exec();//只让线程执行一次
while(true) //一般IO操作会使用while,如果满足条件即进入while轮询,如果不满足条件就阻塞,只运行外部线程
{
qDebug()<<"run()while"<<threadName<<QThread::currentThreadId();
qDebug()<<"thread:"<<threadName;
sleep(1);//睡眠1ms,让出权限
}
}
6.分析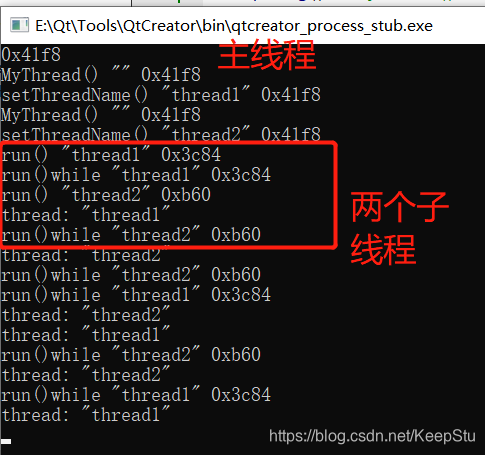
7.线程中的connect信号与槽的连接

8.对同一资源操作的线程锁
QMutex(一种线程安全方式)
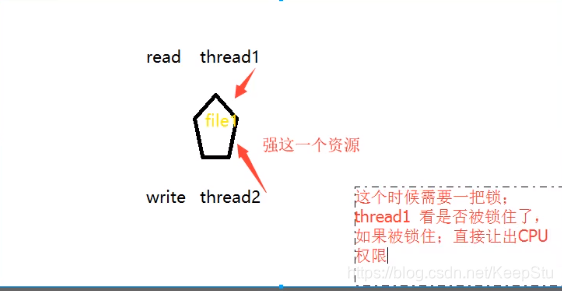
注意:线程锁QMutex必须为全局变量,不要写入类成员变量中

未加锁的运行结果:
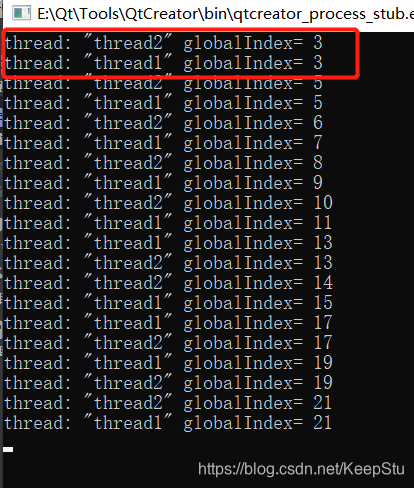
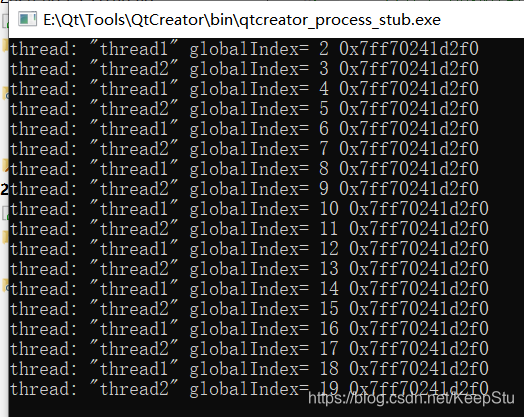
加入全局锁之后:
代码:
mythread.h
#ifndef MYTHREAD_H
#define MYTHREAD_H
#include <QThread>
#include <QString>
#include <QDebug>
#include <QMutex>
class MyThread : public QThread
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
MyThread();
void setThreadName(QString name);
protected:
virtual void run();
private:
QString threadName;
};
#endif // MYTHREAD_H
main.cpp
#include <QCoreApplication>
#include "mythread.h"//加入自拟的线程类
#include <QMutex>
QMutex globalMutex;//定义一个全局锁
int globalIndex=1;//定义一个全局变量
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QCoreApplication a(argc, argv);
MyThread thread1;//定义一个线程对象
thread1.setThreadName("thread1");
thread1.start();//运行线程1
MyThread thread2;
thread2.setThreadName("thread2");
thread2.start();//运行线程2
//每个线程有线程的ID
return a.exec();
}
mythread.cpp
#include "mythread.h"
extern int globalIndex;//使用全局变量
extern QMutex globalMutex;//使用全局锁
MyThread::MyThread()//构造函数
{
}
void MyThread::setThreadName(QString name)
{
threadName=name;
}
void MyThread::run()//run函数内的都会独立开辟线程
{
//exec();//只让线程执行一次
while(true) //一般IO操作会使用while,如果满足条件即进入while轮询,如果不满足条件就阻塞,只运行外部线程
{
globalMutex.lock();//先锁住
globalIndex++;
//qDebug()<<"run()while"<<threadName<<QThread::currentThreadId();
qDebug()<<"thread:"<<threadName<<"globalIndex="<<globalIndex<<&globalMutex;//&globalMutex表示da'yin打印锁对象的地址,看看是不是同一把锁
globalMutex.unlock();//解锁对资源的操作
sleep(1);//睡眠1ms,让出权限
}
}







 本文详细介绍了在Qt中实现多线程操作的方法,包括QThread的使用、线程的创建与启动,以及如何通过线程锁QMutex来解决多线程环境下对同一资源操作的问题,确保数据的安全性和一致性。
本文详细介绍了在Qt中实现多线程操作的方法,包括QThread的使用、线程的创建与启动,以及如何通过线程锁QMutex来解决多线程环境下对同一资源操作的问题,确保数据的安全性和一致性。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








