1. 用pycharm编写程序
信息

单行与多行注释

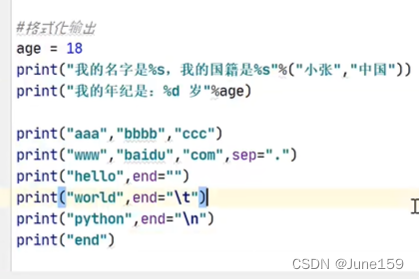
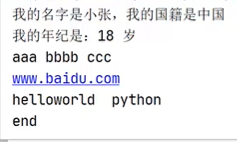
输出输出
2.条件判断语句
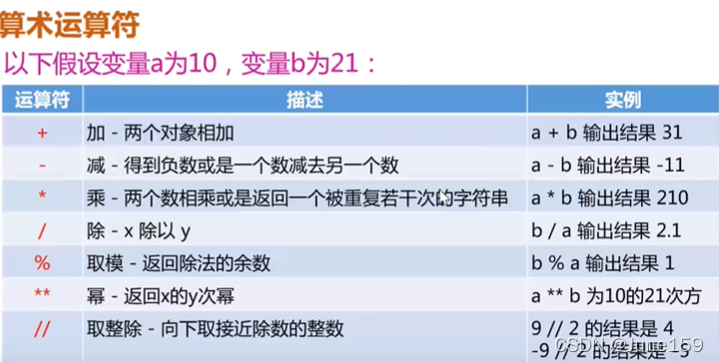
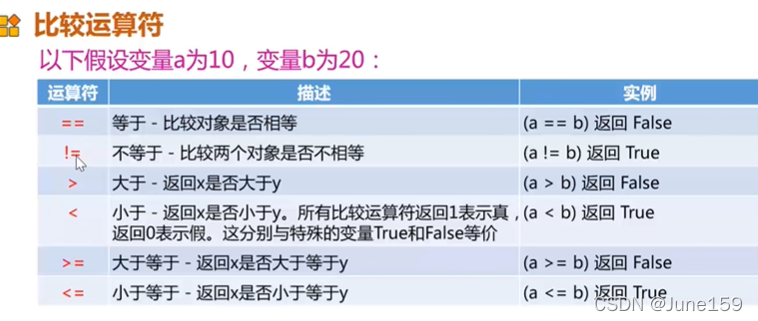
强制类型转化和输入

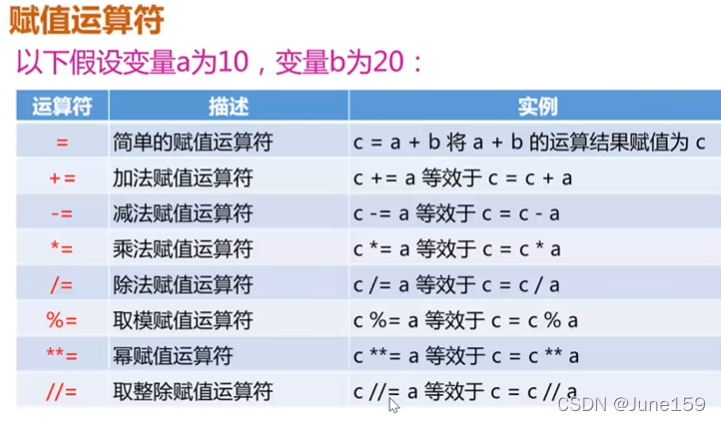


3.循环控制语句
for
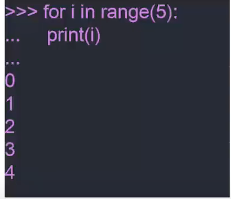

while

break和continue

4.字符串
有单引号双引号三引号
单引号单词
双引号句子
三引号段落
遇到字符串里有引号时,可以用转义字符\来防止报错

起始位置,结束位置,字符串的加减乘除,输入的转义

解编码


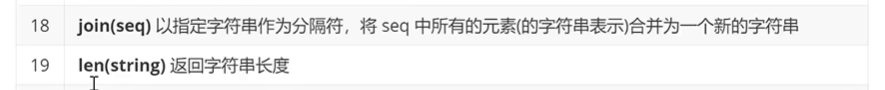

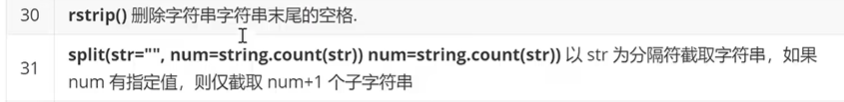
5.列表上

列表增加

列表删除

# -*- coding = utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 22/4/22 19:41
# @Author : Justha
# @File : 列表.py
# @Software: PyCharm
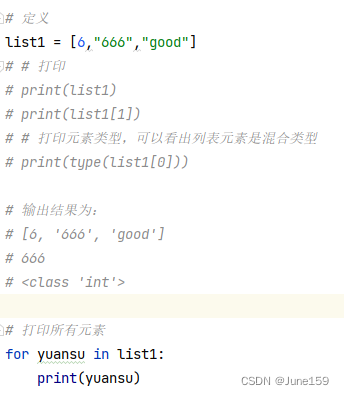
# 定义
list1 = [6," 666","good"]
list2 = ["英语","数学"]
# # 打印
# print(list1)
# print(list1[1])
# # 打印元素类型,可以看出列表元素是混合类型
# print(type(list1[0]))
# 输出结果为:
# [6, '666', 'good']
# 666
# <class 'int'>
# 打印所有元素
for yuansu in list1:
print(yuansu)
# append,extend,insert,del,pop,remove,
# # append将列表作为一个元素加在末尾
# list1.append(list2)
# print(list1)
# # 输出结果为 [6, ' 666', 'good', ['英语', '数学']]
# # extend将一个列表中所有元素分别一次添加到末尾
# list1.extend(list2)
# print(list1)
# # 输出结果为 [6, ' 666', 'good', '英语', '数学']
# # insert指定两个参数,一个为插入位置的下标,另一个为要插入的元素
# list1.insert(1,"插入插入")
# print(list1)
# # 输出结果为 [6, '插入插入', ' 666', 'good']
# # del删除整个列表
# del list1
# # pop删除列表的下标位置处元素
# list1.pop(1)
# print(list1)
# # 输出为 [6, 'good']
6.列表下
# -*- coding = utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 22/4/25 11:54
# @Author : Justha
# @File : 6列表2.py
# @Software: PyCharm
# 查找在不在 in not in
# 索引 index
# 数数 count
# 反转 reverse
# 排序 sort
list1=[6,666,"good","bad",6]
# # 查找在不在 in not in
# if "good" in list1:
# print("yes!")
# if "great" not in list1:
# print("no")
# # good在列表下标[1,3)中的是否有,如果有,则返回在整个列表的下表,如果没有,则报错
# #并且只会返回索引到的第一个
# print(list1.index("good",1,3))
# # count数数有多少个
# print(list1.count(6))
# # reverse反转列表
# print(list1)
# list1.reverse()
# print(list1)
# # 输出结果为:
# # [6, 666, 'good', 'bad', 6]
# # [6, 'bad', 'good', 666, 6]
# # sort排序列表(降序),并可加入reverse=true来反向排序(升序)
# list2=[2,3,7,1,5,8]
# print(list2)
# list2.sort()
# print(list2)
# list2.sort(reverse=1)
# print(list2)
## 输出为:
# [2, 3, 7, 1, 5, 8]
# [1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 8]
# [8, 7, 5, 3, 2, 1]
# 综合应用:
# eg1:办公室分配问题
# allRoom=[[],[],[]]
# people=["A","B","C","D","E","F","G"]
#
# import random
# for man in people:
# index=random.randint(0,2)
# allRoom[index].append(man)
# i=1
# for room in allRoom:
# if len(room) != 0:
# print("办公室%d有%d人,分别为:" % (i, len(room)), end="")
# else:
# print("办公室%d有%d人,太惨了吧!" % (i, len(room)), end="")
# for man in room:
# print("%s," % man, end="")
# print("\n")
# i +=1
# eg2:打印商品菜单
products=[["iphone18",6888],["redMiK90",5000],["苹果",25],["旺仔牛奶",4],["棒棒冰",1]]
i=1
for product in products:
if len(product[0]) in (1,2,3,4):
print("%d\t%s\t\t%d"%(i, product[0], product[1]))
else:
print("%d\t%s\t%d"%(i,product[0],product[1]))
i +=1
cast=[]
list=[]
while True :
print("你想买什么鸭?\n")
x=input()
if x=="q":
break
else:
int(x)
cast.append(int(x))
print("还有吗,")
for j in cast:
list.append(products[j-1])
print("好的,您的最后清单为:")
print(cast)
print(list)
k=1
for product2 in list:
if len(product2[0]) in (1, 2, 3, 4):
print("%d\t%s\t\t%d" % (k, product2[0], product2[1]))
else:
print("%d\t%s\t%d" % (k, product2[0], product2[1]))
k += 1
7.元组
# -*- coding = utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 22/4/26 10:53
# @Author : Justha
# @File : 7元组上.py
# @Software: PyCharm
# 定义增删改查
# 定义 单个元素必须末尾加上逗号,以表现其为元组
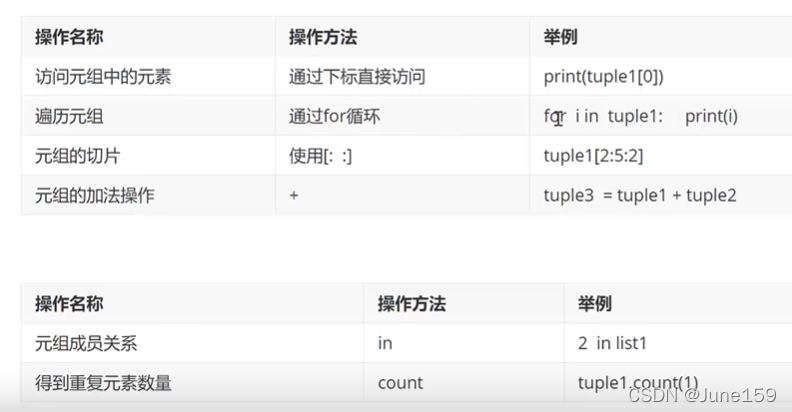
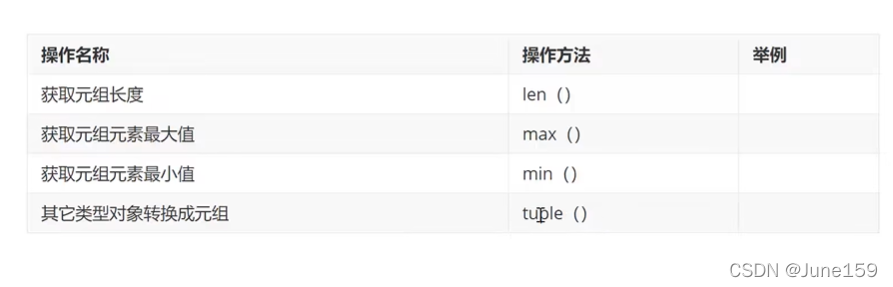
tup1 = ("lll",)
tup2=(6,666)
print(type(tup1))
print(type(tup2))
# 输出 <class 'tuple'>
# 增
tup3=tup1+tup2
print(tup3)
# 输出 ('lll', 6, 666)
# 改
del tup1
# 查
print(tup3[2])
# 切片 左闭右开
tup4=tup3+tup3+tup3
print(tup4[0:6:1])
print(tup4[0:6:2])
# 输出
# ('lll', 6, 666, 'lll', 6, 666)
# ('lll', 666, 6)
# 遍历
for ys in tup3:
print(ys)
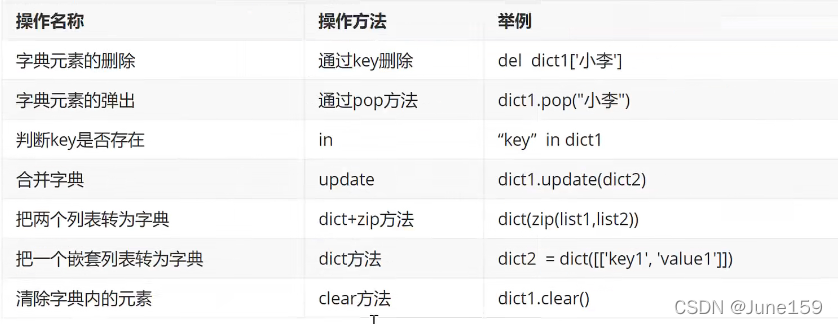
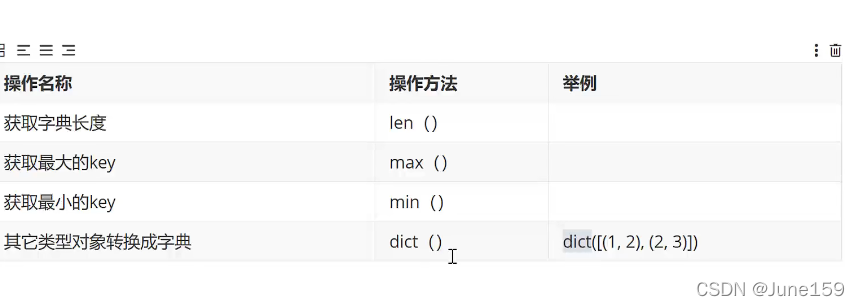
8.字典

# -*- coding = utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 22/4/26 11:36
# @Author : Justha
# @File : 8字典.py
# @Software: PyCharm
# 定义 访问 get方法 遍历
# 增删改查
# 定义
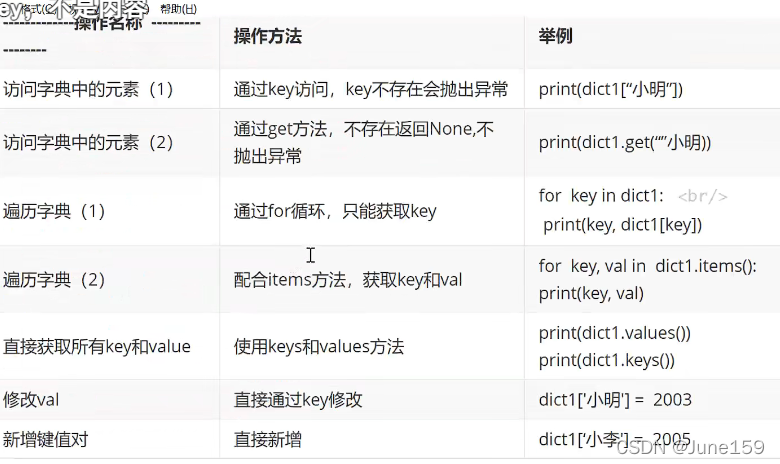
dict1 = {"name":666 , "age":15}
# print(type(dict1))
# 访问
# print(dict1["name"])
#
# # get方法
# # 不用get就会报错 print(dict1["id"])
# print(dict1.get("id"))
# # 在后面添加参数可将none改成参数
# print(dict1.get("id",111))
# 遍历
# 遍历键
for key in dict1.keys():
print(key)
# 遍历值
for value in dict1.values():
print(value)
# 遍历键值对
for key,value in dict1.items():
print(key,value)
# # 增
# dict1["id"]=100001
# print(dict1)
#
# # 删
# # 删单个元素 del
# del dict1["id"]
# print(dict1)
# # 清除所有 clear()
# dict1.clear()
# print(dict1)
# 改
dict1["name"]="newname"
print(dict1["name"])
# 查
# 访问?
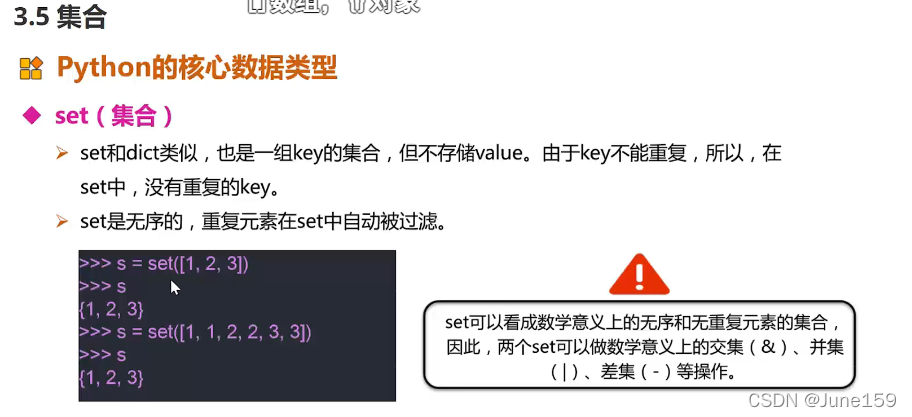
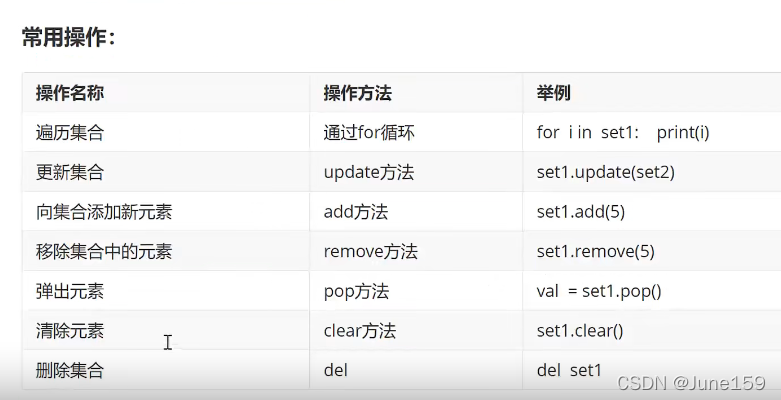
9.集合

# -*- coding = utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 22/4/27 10:45
# @Author : Justha
# @File : 9集合.py
# @Software: PyCharm
# 定义访问增删改查
# 定义
set1=set([2,4,6,7,8])
print(type(set1))
# # 访问(因为集合无序,所以只有遍历)
# for i in set1:
# print(i)
#
# # 增
# set1.add(666)
# for i in set1:
# print(i)
# 删
set1.remove(6)
for i in set1:
print(i)
# 改查
# 无
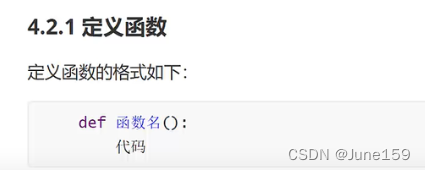
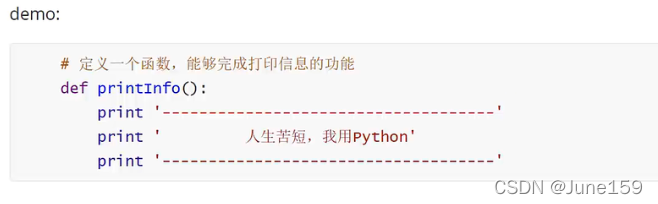
10.函数
# -*- coding = utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 22/4/27 16:16
# @Author : Justha
# @File : 10函数.py
# @Software: PyCharm
# 带参数 带返回值 带多个返回值
# 四道小题(见csdn)
# 局部变量 全局变量
# 不带参数
def divideLine():
print("-"*50)
divideLine()
# 带参数、返回值
def toAdd(a,b):
return a+b
print(toAdd(6,66))
# 带多个返回值
def toDivide(a,b):
return a//b,a%b
# 直接输出
print(toDivide(68,6))
# 先赋值再输出
c,d=toDivide(68,6)
print("商为:%d,余数为:%d"%(c,d))
# # eg1
# def line2():
# print("--"*40)
#
# eg2
# def nline2():
# n=input()
# n=int(n)
# while n>0:
# line2()
# n -=1
# nline2()
#
# eg3
# def addFunc(a,b,c):
# return a+b+c
#
# eg4
# def aver(a,b,c):
# return addFunc(a,b,c)/3.0
#
# print(aver(6,7,8))
# 有局部用局部,有全局用全局;局部不保存,全局会保存
# 使用全局用global
a = 666
def func1():
global a
a +=100
def func2():
a=999
func1()
print(a)
func2()
print(a)
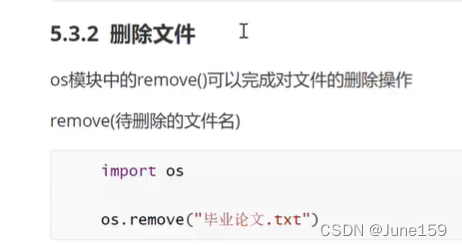
11.文件操作




# -*- coding = utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 22/4/27 17:06
# @Author : Justha
# @File : 11文件.py
# @Software: PyCharm
# 打开关闭、读写
# # 打开关闭
# f= open("demotxt.txt","w")
#
# f.close()
# 写(每次写会将之前的删掉)
f= open("demotxt.txt",'w')
f.write("李白乘舟将欲行\n忽闻岸上踏歌声\n桃花潭水深千尺\n不及汪伦送我情")
f.close()
# 读 read readline readlines
f = open("demotxt.txt",'r')
print(f.read(5))
f.close()
f = open("demotxt.txt",'r')
print(f.readline())
f.close()
f = open("demotxt.txt",'r')
print(f.readlines())
f.close()
f = open("demotxt.txt",'r')
for i in f.readlines():
print(i)
f.close()
12.异常处理

# -*- coding: gbk -*-
# @Time : 22/4/27 17:30
# @Author : Justha
# @File : 唉嘿文件.py
# @Software: PyCharm
try:
num +=5
except NameError as result:
print(result)
finally:
print("程序运行完毕")
# Exception




 这篇博客涵盖了Python的基础知识,包括注释、条件判断、循环控制、字符串操作、列表操作、元组、字典和集合的使用,以及函数定义和文件操作。还涉及了异常处理和简单的代码实践示例,适合Python初学者入门学习。
这篇博客涵盖了Python的基础知识,包括注释、条件判断、循环控制、字符串操作、列表操作、元组、字典和集合的使用,以及函数定义和文件操作。还涉及了异常处理和简单的代码实践示例,适合Python初学者入门学习。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








