前言
如果说CHM的源码对并发分片和CAS操作运用的淋漓尽致,那么ABQ则是Lock & Condition类的使用参考书~
阻塞队列的应用
见名知义,ABQ是基于数组实现的阻塞队列。
大家常用的MQ、Kafka使得程序之间实现解耦。同理,阻塞队列使得线程之间进行数据通信与解耦。
举一个熟悉场景——用户注册成功后,增加积分。通常,我们可以通过MQ来实现注册、积分操作的异步与解耦。但假如我们的程序规模比较小,采用阻塞队列会更加方便。
- 改造前的代码逻辑
public class UserService {
public boolean register(){
User user=new User();
user.setName("Jeremy");
addUser(user);//注册用户
sendPoints(user);//增加积分
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new UserService().register();
}
private void addUser(User user){
System.out.println("添加用户: "+user);
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void sendPoints(User user){
System.out.println("发送积分给指定用户:"+user);
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
- 改造后的逻辑
public class UserService {
private final ExecutorService single = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
private volatile boolean isRunning = true;
ArrayBlockingQueue arrayBlockingQueue=new
ArrayBlockingQueue(10);
{
init();
}
public void init(){
single.execute(()->{
while(isRunning){
try {
//阻塞的方式获取队列中的数据
User user=(User)arrayBlockingQueue.take();
sendPoints(user);
} catch (InterruptedException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
public boolean register(){
User user=new User();
user.setName("Mic");
addUser(user);
arrayBlockingQueue.add(user);//添加到异步
队列
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new UserService().register();
}
private void addUser(User user){
System.out.println("添加用户: "+user);
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void sendPoints(User user){
System.out.println(" 发送积分给指定用户:"+user);
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
- 优化后流程图
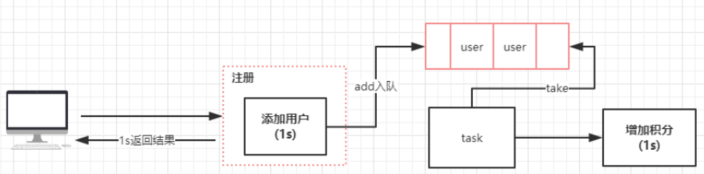
修改之后的代码在性能 & 耦合度方面都有提高。
阻塞队列主要应用于生产者、消费者场景中。
JUC中的阻塞队列
| 阻塞队列 | 原理 |
|---|---|
| ArrayBlockingQueue | 数组实现的有界阻塞队列,FIFO |
| LinkedBlockingQueue | 链表实现的有界阻塞队列,FIFO |
| PriorityBlockingQueue | 支持优先级排序的无界阻塞队列,可通过实体类实现compareTo()或构造参数Comparator实现排序 |
| DelayQueue | 优先级排序的无界阻塞队列 |
| SynchronousQueue | 不存储元素的阻塞队列 |
| LinkedTransferQueue | 链表实现的无界阻塞队列 |
| LinkedBlockingDeque | 链表实现的双向阻塞队列 |
阻塞队列的操作方法
阻塞队列中,插入和删除操作都提供了四种处理方式。
- 插入操作
add(e)→ 队列满了,继续插入会报错,IllegalStateExceptionoffer(e)→ 返回元素是否成功插入,成功返回trueput(e)→ 队列满了,生产者继续put,会阻塞生产者线程,直到队列可用offer(e,time,unit)→ 队列满了继续添加元素,则生产者线程被阻塞指定时间,超时后,线程退出
- 移除操作
remove()→ 队列为空,返回false;移除成功,返回truepoll()→ 队列为空,返回nulltake()→ 队列为空,阻塞take(),直到队列中有数据消费poll(time,unit)→ 队列为空,等待指定时间,在获取数据
ABQ源码分析
构造方法
ABQ提供三个构造方法:
- capacity → 队列长度
public ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity) {
this(capacity, false);//默认非公平锁
}
- fair → 是否为公平的阻塞队列
public ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity, boolean fair) {
if (capacity <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
this.items = new Object[capacity];
lock = new ReentrantLock(fair);//重入锁,出队&入队持有同一把锁
notEmpty = lock.newCondition();//初始化非空等待队列
notFull = lock.newCondition();//初始化非满等待队列
}
- 接受初始数据
Add方法
add() → 父类AbstractQueue的add()
public boolean add(E e) {
return super.add(e);//调用父类的模板方法 → 解决通用性问题
}
AbstractQueue的add()
public boolean add(E e) {
if (offer(e))//调用offer()
return true;
else
throw new IllegalStateException("Queue full");
}
offer方法
- 判断添加数据是否为空
- 添加重入锁
- 判断队列长度,如果队列长度=数组长度,表示满了,直接返回false
- 否则,调用
enqueue()将元素添加到队列
public boolean offer(E e) {
checkNotNull(e);//对请求数据作判断
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
if (count == items.length)
return false;
else {
enqueue(e);
return true;
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
enqueue方法
核心逻辑,通过putIndex索引直接将元素添加到数组队列中。
private void enqueue(E x) {
// assert lock.getHoldCount() == 1;
// assert items[putIndex] == null;
final Object[] items = this.items;
items[putIndex] = x;//通过putIndex对数据赋值
//当putIndex等于数组长度时,将putIndex重置为0
if (++putIndex == items.length)
putIndex = 0;
count++;//记录队列元素的个数
//唤醒notEmpty队列中的线程
//表明当前队列中元素不为空,如果存在消费者线程阻塞,就可以开始取元素了
notEmpty.signal();
}
这里需要注意的是,putIndex超过数组长度时,重新从数组头节点插入数据,但并不会出现数据覆盖的情况。这是因为:
- 元素个数由count统计。满了后,无法继续添加,会报错。
- 队列中的元素会有消费者通过
take()等方法获取,获取后会从队列中移除。
put方法
队列满了,会阻塞。
public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException {
checkNotNull(e);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
//等待时,可中断的锁
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (count == items.length)
//队列满了的情况下,当前线程会被挂起,加入到notFull等待队列
notFull.await();
enqueue(e);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
take方法
有就删除,没有就阻塞。
public E take() throws InterruptedException {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (count == 0)
notEmpty.await();//队列为空,加入notEmpty等待队列
return dequeue();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
dequeue方法
出队列,删除队列头部元素并返回给客户端索引值。
private E dequeue() {
// assert lock.getHoldCount() == 1;
// assert items[takeIndex] != null;
final Object[] items = this.items;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E x = (E) items[takeIndex];//默认获取0位置元素
items[takeIndex] = null;//将该位置元素设置为空
if (++takeIndex == items.length)//拿到数组最大值,索引重置为0
takeIndex = 0;
count--;//元素个数递减
if (itrs != null)
itrs.elementDequeued();//更新迭代器中元素
notFull.signal();//触发 因队列满了导致阻塞的notFull等待队列
return x;
}
itrs.elementDequeued()
remove方法
移除一个指定元素。
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) return false;
final Object[] items = this.items;//获取数组元素
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();//获得锁
try {
if (count > 0) {//如果队列不为空
//获取下一个添加元素时索引
final int putIndex = this.putIndex;
//获取当前要移除元素索引
int i = takeIndex;
do {
//从takeIndex下标开始,找到要被删除的元素
if (o.equals(items[i])) {
removeAt(i);//移除指定元素
return true;//返回执行结果
}
//当前删除索引+1后,判断是否与数组长度相等
//若为true,说明索引已到数组尽头,重置为0
if (++i == items.length)
i = 0;
} while (i != putIndex);//继续查找,直到最后一个元素
}
return false;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
总结
ABQ的设计也是精妙的。
- 通过成员变量
count获取队列中元素个数 - 通过两个阻塞队列
notEmpty、notFull控制添加和获取元素时的阻塞 - 两个阻塞队列与ABQ之间通过Condition的
await()&signal()完成通信





 本文深入解析了ABQ(ArrayBlockingQueue)的工作原理,包括其构造方法、核心操作如add、offer、put和take,以及内部实现细节。通过对比改造前后的代码逻辑,展示了ABQ在提高程序性能和降低耦合度方面的优势。
本文深入解析了ABQ(ArrayBlockingQueue)的工作原理,包括其构造方法、核心操作如add、offer、put和take,以及内部实现细节。通过对比改造前后的代码逻辑,展示了ABQ在提高程序性能和降低耦合度方面的优势。
















 560
560

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








