DNA sequence
Time Limit : 15000/5000ms (Java/Other) Memory Limit : 32768/32768K (Java/Other)
Total Submission(s) : 15 Accepted Submission(s) : 7
Font: Times New Roman | Verdana | Georgia
Font Size: ← →
Problem Description
The twenty-first century is a biology-technology developing century. We know that a gene is made of DNA. The nucleotide bases from which DNA is built are A(adenine), C(cytosine), G(guanine), and T(thymine). Finding the longest common subsequence between DNA/Protein
sequences is one of the basic problems in modern computational molecular biology. But this problem is a little different. Given several DNA sequences, you are asked to make a shortest sequence from them so that each of the given sequence is the subsequence
of it.
For example, given "ACGT","ATGC","CGTT" and "CAGT", you can make a sequence in the following way. It is the shortest but may be not the only one.
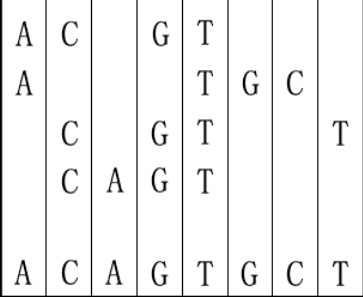
For example, given "ACGT","ATGC","CGTT" and "CAGT", you can make a sequence in the following way. It is the shortest but may be not the only one.

Input
The first line is the test case number t. Then t test cases follow. In each case, the first line is an integer n ( 1<=n<=8 ) represents number of the DNA sequences. The following k lines contain the k sequences, one per line. Assuming that the length of any
sequence is between 1 and 5.
Output
For each test case, print a line containing the length of the shortest sequence that can be made from these sequences.
Sample Input
1 4 ACGT ATGC CGTT CAGT
Sample Output
8
————————————————————————————————————————————————
题意:从n个串中找出一个最短的公共串(也许应该说序列吧,因为不要求连续,即只要保持相对顺序就好)。
分析:迭代加深搜索,就是每次都限制了DFS的深度,若搜不到答案,则加深深度,继续搜索,这样就防止了随着深度不断加深而进行的盲目搜索,而且,对于这种求最短长度之类的题目,只要找到可行解,即是最优解了。所以就这样敲完代码了,敲完之后,悲剧TLE。
少了一步十分重要的剪枝,就是每次DFS的时候,都要判断一下,当前的深度+最少还有加深的深度是否大于限制的长度,若是,则退回。
分析:迭代加深搜索,就是每次都限制了DFS的深度,若搜不到答案,则加深深度,继续搜索,这样就防止了随着深度不断加深而进行的盲目搜索,而且,对于这种求最短长度之类的题目,只要找到可行解,即是最优解了。所以就这样敲完代码了,敲完之后,悲剧TLE。
少了一步十分重要的剪枝,就是每次DFS的时候,都要判断一下,当前的深度+最少还有加深的深度是否大于限制的长度,若是,则退回。
#include <iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<queue>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
char s[10][10];
int n,mx,flag;
char ch[5]={'A','T','C','G'};
void dfs(int deep,int *cnt)
{
if(flag)
return;
int sum=0;
int maxlen=0;
int a;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
{
a=strlen(s[i])-cnt[i];
sum=sum+a;
maxlen=max(maxlen,a);
}
if(maxlen+deep>mx)
return;
if(sum==0)
{
flag=1;
return;
}
int fl=0;
int next[10];
for(int i=0; i<4; i++)
{
for(int j=0; j<n; j++)
{
if(s[j][cnt[j]]==ch[i])
{
fl=1;
next[j]=cnt[j]+1;
}
else
next[j]=cnt[j];
}
if(fl)
{
dfs(deep+1,next);
}
if(flag)
return;
}
}
int main()
{
int o,k;
int cnt[10];
scanf("%d",&o);
while(o--)
{
scanf("%d",&n);
mx=0;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
{
scanf("%s",s[i]);
k=strlen(s[i]);
mx=max(mx,k);
}
memset(cnt,0,sizeof(cnt));
flag=0;
for(int i=0; i<40; i++)
{
dfs(0,cnt);
if(flag)
break;
mx++;
}
printf("%d\n",mx);
}
return 0;
}







 本文介绍了一个生物信息学问题,即如何从多个DNA序列中构造出一个最短的序列,使得每个原始序列都是该序列的子序列。通过迭代加深搜索算法,并结合有效的剪枝策略来解决这一问题。
本文介绍了一个生物信息学问题,即如何从多个DNA序列中构造出一个最短的序列,使得每个原始序列都是该序列的子序列。通过迭代加深搜索算法,并结合有效的剪枝策略来解决这一问题。
















 301
301

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








