本篇主要介绍一下Redisson 的基本使用 和它的 分布锁的源码分析 包括 lua 脚本 和 watch 看门狗源码

Redisson 是什么
Redisson - 是一个高级的分布式协调Redis客服端,能帮助用户在分布式环境中轻松实现一些Java的对象,Redisson、Jedis、Lettuce 是三个不同的操作 Redis 的客户端,Jedis、Lettuce 的 API 更侧重对 Reids 数据库的 CRUD(增删改查),而 Redisson API 侧重于分布式开发 , 最常用就可以使用Redisson 提供的分布式锁的功能
Redisson 的基本使用
引入Redisson 的依赖
<!-- 原生,本章使用-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.redisson</groupId>
<artifactId>redisson</artifactId>
<version>3.13.6</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 另一种Spring集成starter,本章未使用 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.redisson</groupId>
<artifactId>redisson-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.13.6</version>
</dependency>
Redisson基本配置
Redisson的基本配置是 通过创建一个 Config 对象然后用于创建 RedissonClient , 后续操作都是通过RedissonClient来进行的
@Configurationpublic
class RedissionConfig {
@Value("${spring.redis.host}")
private String redisHost;
@Value("${spring.redis.password}")
private String password;
private int port = 6379;
@Bean
public RedissonClient getRedisson() {
Config config = new Config();
//config.useSentinelServers();使用哨兵模式
//config.useClusterServers();使用集群模式
//使用单节点
config.useSingleServer()
.setAddress("redis://" + redisHost + ":" + port)
.setPassword(password);
config.setCodec(new JsonJacksonCodec());
return Redisson.create(config);
}}
Redisson 分布式锁使用
可以看到 只需要通过 lock.tryLock() 和 lock.unlock() 就可以实现分布式锁的控制流程了
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
public void deduct() {
RLock lock = redissonClient.getLock("lock");
try {
// 1.获取redis 锁
if (lock.tryLock(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) {
try {
// 2.获取库存
String stock = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get("iphone14");
if (stock != null) {
// 3.比较并且扣减库存
long stockCount = Long.parseLong(stock);
if (stockCount > 0) {
// 4.设置库存
stringRedisTemplate
.opsForValue()
.set("iphone14", String.valueOf(--stockCount));
}
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
压测验证
先把 iphone14 库存设置为5000

通过ab 压测看一下
ab -c 100 -n 5000 http://127.0.0.1:10010/deduct
可以看到 控制了并发问题


Redisson 源码分析 (加锁/解锁/看门狗)
#源码分析
加锁 源码分析
加锁方法lock 或者 tryLock 都会调用 tryAcquireAsync 异步获取锁, 最终执行lua脚本的方法是 tryLockInnerAsync
如果leaseTime 传了 则不会开启看门狗

RedissonLock.tryAcquireAsync() >RedissonLock. tryLockInnerAsync()

解锁 源码分析
unlock()方法释放锁 最终会调用 unlockAsync , 最终执行lua脚本的方法是 unlockInnerAsync

RedissonLock.unlockAsync() >RedissonLock. unlockInnerAsync() 返回null 表示 释放的锁不存在
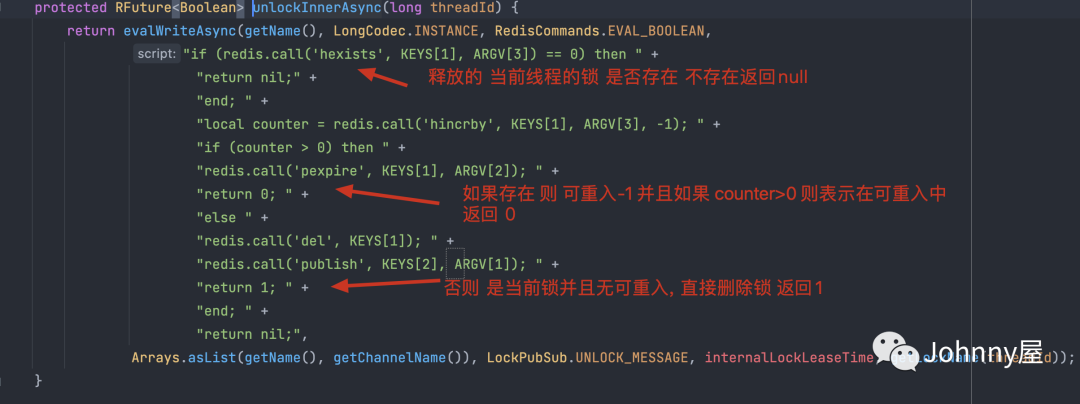
看门狗源码分析



可以看到 任务的调度是使用的 netty 实现的时间轮算法的工具 HashedWheelTimer [[Netty时间轮算法的实现HashedWheelTimer 和源码分析]]
netty的实现的是粗粒度的 当任务调度跨度很大会有空推问题 但是在看门狗这个应用中没问题 kafka 时间轮算法的还有 它提供的是 多纬度的 解决了空推问题 [[Kafka时间轮算法]]


总结
本篇主要介绍了 Redisson 的基本使用, 并且使用它的分布式锁功能控制了抢库存业务逻辑, 最后分析了 Redisson的 RedissonLock的加锁解锁和 看门狗机制的源码分析 , 看门狗任务调度使用的netty的时间轮算法,同样实现时间轮算法的还有 kafka , kafka它提供的是多维度时间轮 解决了 netty 时间轮的 空推问题 有兴趣可以了解一下... [[Netty时间轮算法的实现HashedWheelTimer 和源码分析]][[Kafka时间轮算法]]
最后
如果感觉本文对你有帮助,点赞关注支持一下,想要了解更多Java后端,大数据,算法领域最新资讯可以关注我公众号【架构师老毕】私信666还可获取更多Java后端,大数据,算法PDF+大厂最新面试题整理+视频精讲




















 2008
2008

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








