前言
在操作List集合的时候,习惯用for each循环操作。这次项目中根据业务逻辑需要删除符合条件的元素,元素删除后,继续next操作,抛出了ConcurrentModificationException异常。下面,重现异常,看看异常是怎么发生的,怎么避免。
测试代码
异常的发生
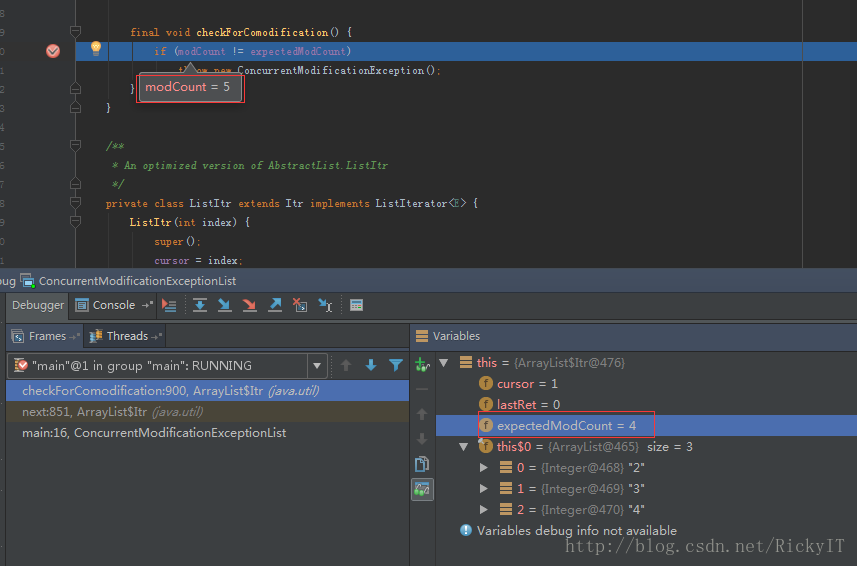
ConcurrentModificationException异常是在这里抛出的。当modCount != expectedModCount为true的时候抛出。
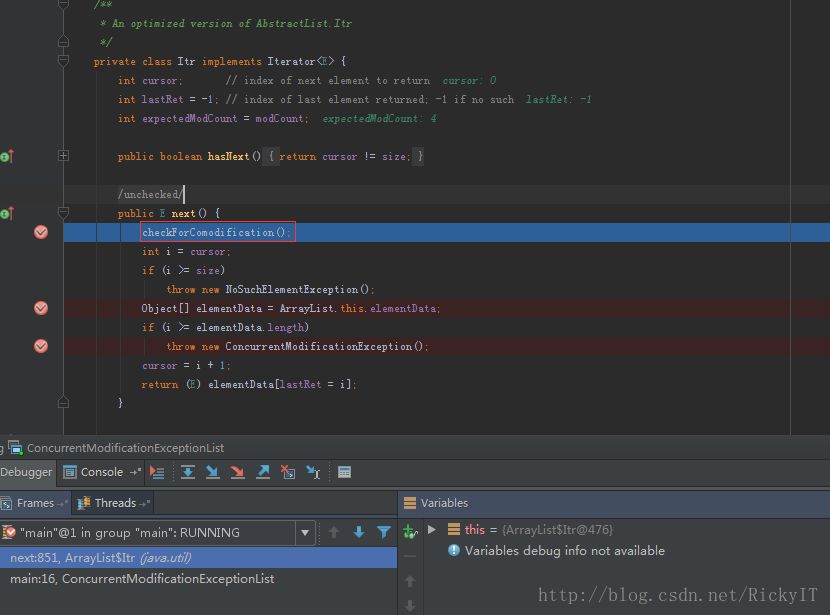
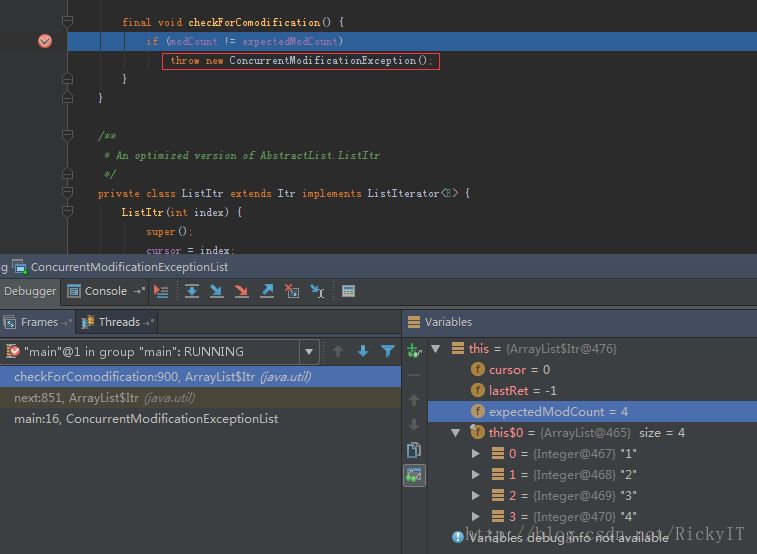
原因
上述异常为什么会发生,来看一下源码中的删除动作。
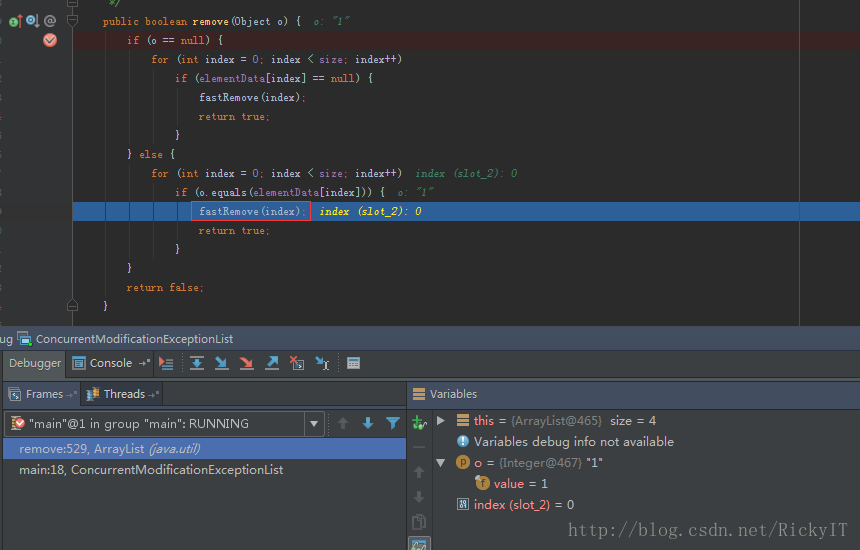
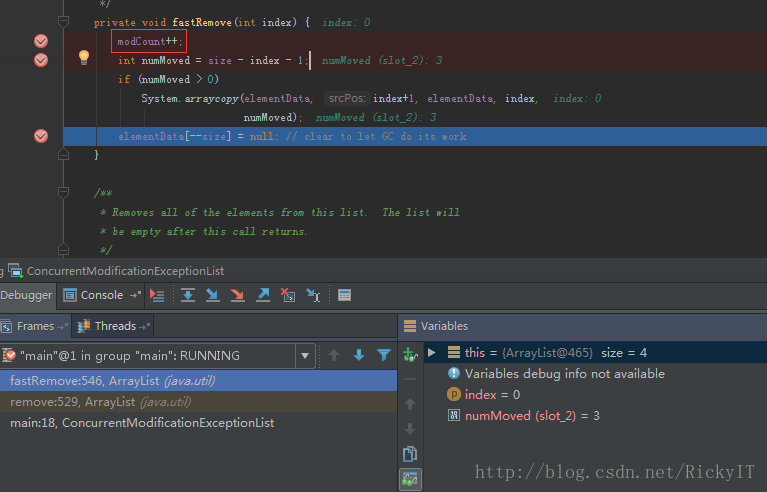
在执行删除动作前modCount自加1。在下个元素做checkForComodification的时候异常就抛出了。
异常的解决
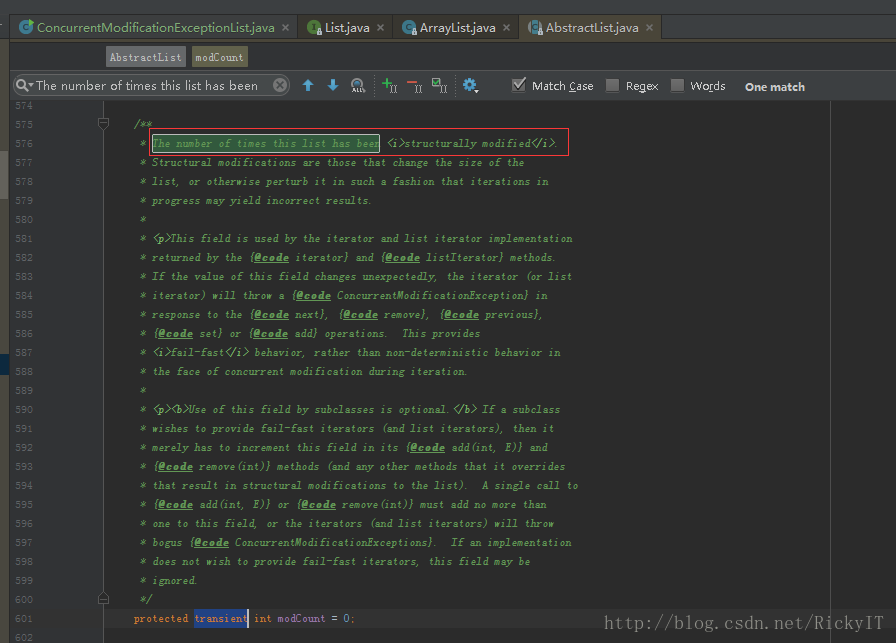
查看源码,modCount是在ArrayList的父类AbstractList中定义的,modCount记录list被修改的次数。在iterator和实现iterator的list中,进行next(),remove()、previous、set、add操作时,modCount的值被意外改变,将抛出异常ConcurrentModificationException。关于异常的解决,网上也有很多的方法,参考文末。
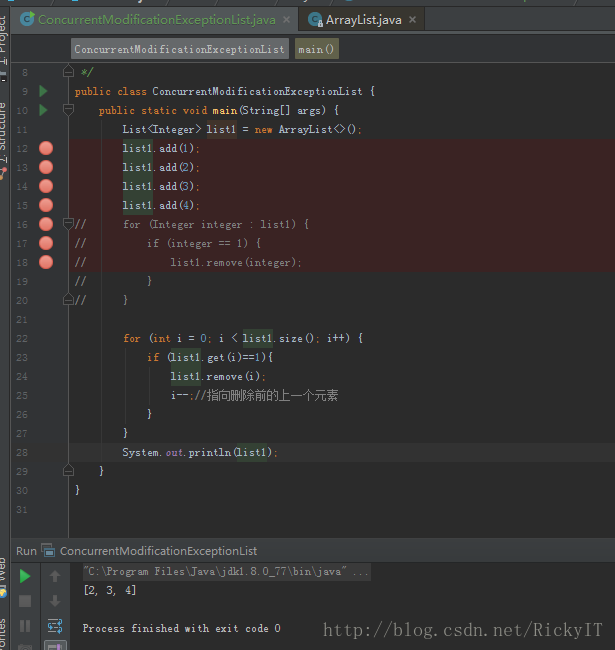
既然异常是在iterator和实现iterator的list中发生的,那不使用for each操作,采用for in操作就能避免异常的发生。
代码验证一下
看一下源码:
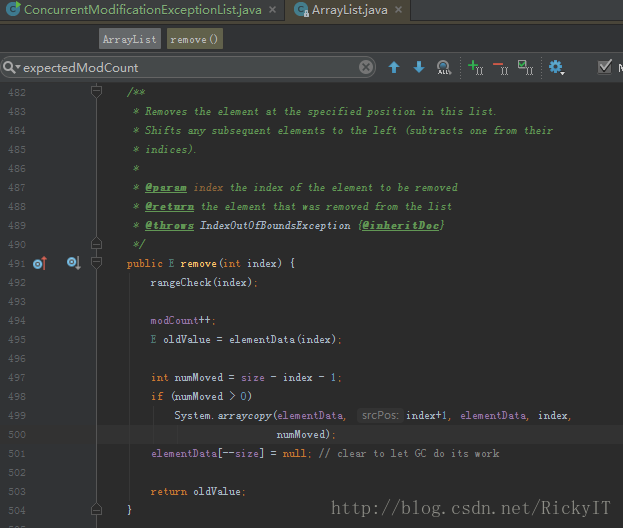
源码中是没有做checkForComodification检查的,也不会发生异常。
参考
Java ConcurrentModificationException异常原因和解决方法
集合迭代时对集合进行修改抛ConcurrentModificationException原因的深究以及解决方案
Java ConcurrentModificationException 异常分析与解决方案




















 2672
2672

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








