前面[读书笔记]Spring中IOC容器中FileSystemXmlApplicationContext的初始化详解我们以FileSystemXmlApplicationContext为例,讲解了其Resource定位的问题解决方案,即以FileSystem方式存在的Resource的定位实现。这里我们继续学习BeanDefinition的载入和解析。
Bean的定义主要有BeanDefinition描述,如下图说明了这些类的层次关系:
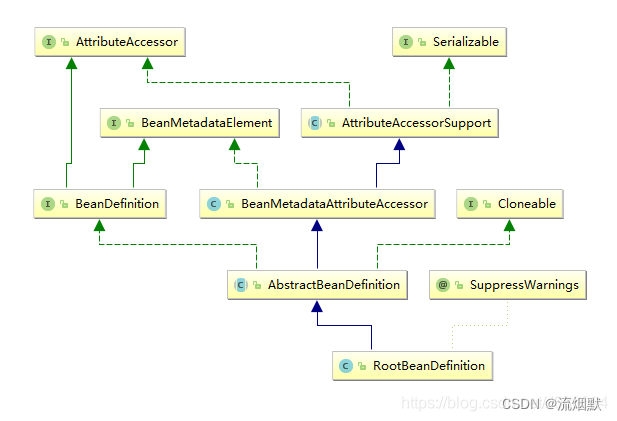
Bean的定义就是完整的描述了在Spring的配置文件中你定义的节点中所有的信息,包括各种子节点。当Spring成功解析你定义的一个节点后,在Spring的内部他就被转化 成BeanDefinition对象。以后所有的操作都是对这个对象完成的。
Bean的解析过程非常复杂,功能被分的很细,因为这里需要被扩展的地方很多,必须保证有足够的灵活性,以应对可能的变化。Bean的解析主要就是对Spring配置文件的解析。这个解析过程主要通过 下图中的类完成:
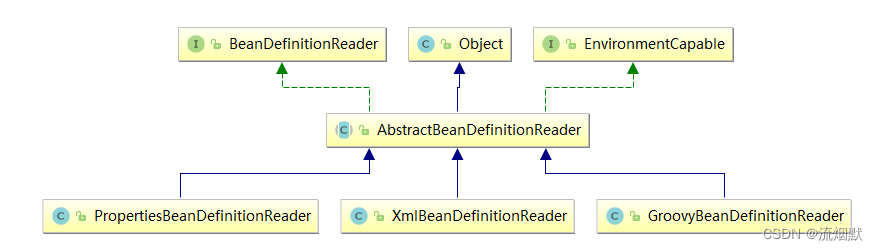
【1】BeanDefinition载入的前置流程
对IOC容器来说,这个载入过程相当于把定义的BeanDefinition在IOC容器中转化成一个Spring内部表示的数据结构的过程。IOC容器对Bean的管理和依赖注入功能的实现,是通过对其持有的BeanDefinition进行各种相关操作来完成的。这些BeanDefinition数据再IOC容器中通过一个HashMap来保持和维护。
在开始分析前,先回到IOC容器的初始化入口,也就是refresh方法。这个方法最初是在FileSystemXmlApplicationContext的构造函数中被调用的,它的调用标志着容器初始化的开始,这些初始化对象就是BeanDefinition数据。
public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(
String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, @Nullable ApplicationContext parent)
throws BeansException {
super(parent);
setConfigLocations(configLocations);
if (refresh) {
refresh();
}
}
AbstractApplicationContext#refresh
该方法详细地描述了整个ApplicationContext的初始化过程,比如BeanFactory的更新、MessageSource和PostProcessor的注册等等
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
//设置BeanFactory的后置处理
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
// 调用BeanFactory的后置处理器,这些后置处理器是在Bean定义中向容器注册的
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
//注册Bean的后置处理器,其将会在bean创建过程中调用
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
// 对上下文中的消息源进行初始化
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
// 初始化上下文中的事件机制
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
// 初始化其他特殊的bean
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
// 检查监听bean并将这些bean向容器中注册
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
// 实例化所有的(non-lazy-init)单例对象
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
//发布容器事件,结束Refresh过程
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
//为了防止Bean资源占用,在异常处理中销毁已经在前面过程中生成的单件Bean
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
// 重置 active 标识
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext#refreshBeanFactory
在这个方法中创建了BeanFactory。在创建IOC容器前,如果已经有容器存在,那么需要把已有的容器销毁和关闭,保证在refresh以后使用的是新建立起来的IOC容器。
@Override
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException {
if (hasBeanFactory()) {
destroyBeans();
closeBeanFactory();
}
try {
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory();
beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());
customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// 启动对BeanDefinition的载入
loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex);
}
}
这里的loadBeanDefinitions是个抽象方法。如果是xml环境下,那么这里将会调用AbstractXmlApplicationContext中的实现。如下所示,其将会初始化读取器XmlBeanDefinitionReader 并进行设置,然后启动读取器来完成BeanDefinition在IOC容器中的载入。
@Override
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException {
// Create a new XmlBeanDefinitionReader for the given BeanFactory.
// 创建XmlBeanDefinitionReader 并通过回调设置到beanFactory
XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);
// Configure the bean definition reader with this context's
// resource loading environment.
beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment());
//为XmlBeanDefinitionReader 设置ResourceLoader,默认是DefaultResourceLoader
beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this);
beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this));
// Allow a subclass to provide custom initialization of the reader,
// then proceed with actually loading the bean definitions.
initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader);
loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader);
}
具体载入过程委托给XmlBeanDefinitionReader 来处理(本文环境中BeanDefinition是通过xml来定义的)。
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) throws BeansException, IOException {
Resource[] configResources = getConfigResources();
if (configResources != null) {
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configResources);
}
String[] configLocations = getConfigLocations();
if (configLocations != null) {
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocations);
}
}
那么到这里我们总结一下。我们可以看到在初始化FileSystemXmlApplicationContext的过程中是通过调用IOC容器的refresh来启动整个BeanDefinition的载入过的,这个初始化是通过定义的XmlBeanDefinitionReader来完成的。同时,我们也知道实际使用的IOC容器是DefaultListableBeanFactory,具体的Resource载入在XmlBeanDefinitionReader读入BeanDefinition实现。
因为Spring可以对应不同形式的BeanDefinition,那么可以根据需要使用XmlBeanDefinitionReader或者其他种类的BeanDefinitionReader来完成数据的载入工作。
【2】BeanDefinition的载入
AbstractBeanDefinitionReader的loadBeanDefinitions方法如下所示,在AbstractBeanDefinitionReader中并没有实现loadBeanDefinitions(resources)方法,该方法具体实现在XmlBeanDefinitionReader中。
@Override
public int loadBeanDefinitions(String... locations) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.notNull(locations, "Location array must not be null");
int count = 0;
for (String location : locations) {
count += loadBeanDefinitions(location);
}
return count;
}
// 上面方法会调用下面这个方法
@Override
public int loadBeanDefinitions(String... locations) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.notNull(locations, "Location array must not be null");
int count = 0;
for (String location : locations) {
count += loadBeanDefinitions(location);
}
return count;
}
// 上面方法会调用下面这个方法
@Override
public int loadBeanDefinitions(String location) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
return loadBeanDefinitions(location, null);
}
// 上面方法会调用下面这个方法
public int loadBeanDefinitions(String location, @Nullable Set<Resource> actualResources) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = getResourceLoader();
if (resourceLoader == null) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Cannot load bean definitions from location [" + location + "]: no ResourceLoader available");
}
if (resourceLoader instanceof ResourcePatternResolver) {
// Resource pattern matching available.
try {
Resource[] resources = ((ResourcePatternResolver) resourceLoader).getResources(location);
// 继续从这里进入
int count = loadBeanDefinitions(resources);
if (actualResources != null) {
Collections.addAll(actualResources, resources);
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Loaded " + count + " bean definitions from location pattern [" + location + "]");
}
return count;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Could not resolve bean definition resource pattern [" + location + "]", ex);
}
}
else {
// Can only load single resources by absolute URL.
Resource resource = resourceLoader.getResource(location);
// 继续从这里进入
int count = loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
if (actualResources != null) {
actualResources.add(resource);
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Loaded " + count + " bean definitions from location [" + location + "]");
}
return count;
}
}
XmlBeanDefinitionReader.loadBeanDefinitions
如下所示,在读取器中得到代表xml文件的Resource,因为这个Resource对象封装了对xml文件的IO操作,所以读取器可以在打开IO流后得到xml的文件对象。有了这个文件对象以后,就可以按照Spring的Bean定义规则来对这个xml的文档树进行解析了。
@Override
public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
return loadBeanDefinitions(new EncodedResource(resource));
}
public int loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.notNull(encodedResource, "EncodedResource must not be null");
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Loading XML bean definitions from " + encodedResource);
}
Set<EncodedResource> currentResources = this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.get();
if (!currentResources.add(encodedResource)) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Detected cyclic loading of " + encodedResource + " - check your import definitions!");
}
//这里得到xml文件,并得到IO的inputsource准备进行读取
try (InputStream inputStream = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream()) {
InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(inputStream);
if (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null) {
inputSource.setEncoding(encodedResource.getEncoding());
}
return doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource());
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"IOException parsing XML document from " + encodedResource.getResource(), ex);
}
finally {
currentResources.remove(encodedResource);
if (currentResources.isEmpty()) {
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.remove();
}
}
}
具体的读取过程可以在doLoadBeanDefinitions方法中找到,这是从特定的XML文件中实际载入BeanDefinition的地方。
// XmlBeanDefinitionReader#doLoadBeanDefinitions
protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
try {
// 获取xml文档对象
Document doc = doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource);
// 解析文档对象,注册BeanDefinition
int count = registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Loaded " + count + " bean definitions from " + resource);
}
return count;
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (SAXParseException ex) {
throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Line " + ex.getLineNumber() + " in XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex);
}
catch (SAXException ex) {
throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex);
}
catch (ParserConfigurationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Parser configuration exception parsing XML from " + resource, ex);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"IOException parsing XML document from " + resource, ex);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Unexpected exception parsing XML document from " + resource, ex);
}
}
在以前项目中,我们有时需要XML文件解析异常就是在这里抛出的。上面方法的核心就是两句话:得到xml文件的文档对象,然后解析文档对象注册BeanDefinition到容器中。
// 得到文档对象·
Document doc = doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource);
// 解析文档对象,注册BeanDefinition
int count = registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource);
得到文档对象是由DefaultDocumentLoade完成的,其会通过一个DocumentBuilder来解析inputSource得到Document。(可以看到在开源框架中比如spring、mybatis等都大量使用了builder这种建造者设计模式)。
protected Document doLoadDocument(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource) throws Exception {
return this.documentLoader.loadDocument(inputSource, getEntityResolver(), this.errorHandler,
getValidationModeForResource(resource), isNamespaceAware());
}
@Override
public Document loadDocument(InputSource inputSource, EntityResolver entityResolver,
ErrorHandler errorHandler, int validationMode, boolean namespaceAware) throws Exception {
DocumentBuilderFactory factory = createDocumentBuilderFactory(validationMode, namespaceAware);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Using JAXP provider [" + factory.getClass().getName() + "]");
}
DocumentBuilder builder = createDocumentBuilder(factory, entityResolver, errorHandler);
return builder.parse(inputSource);
}
【3】BeanDefinition的注册
//XmlBeanDefinitionReader.registerBeanDefinitions
public int registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
// DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader 对象XML的BeanDefinition进行解析
BeanDefinitionDocumentReader documentReader = createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader();
// 已经存在的BeanDefinition数量
int countBefore = getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount();
// 具体解析过程
documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource));
// 本次新注册的BeanDefinition数量
return getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount() - countBefore;
}
BeanDefinition的载入分成两部分,首先通过调用XML的解析器得到document对象,但这些document对象并没有按照Spring的Bean对象进行解析。在完成通用的xml解析后,才是按照Spring的Bean规则进行解析的地方,这个按照Spring的Bean规则进行解析的过程是在BeanDefinitionDocumentReader 中实现的,默认是DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader 。
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, XmlReaderContext readerContext) {
this.readerContext = readerContext;
doRegisterBeanDefinitions(doc.getDocumentElement());
}
① doRegisterBeanDefinitions
注册过程又分为两个重要步骤: 解析元素节点得到BeanDefinition,然后注入到容器中。
DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader的几个成员变量(常量):
public static final String BEAN_ELEMENT = BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.BEAN_ELEMENT; // bean
public static final String NESTED_BEANS_ELEMENT = "beans";
public static final String ALIAS_ELEMENT = "alias";
public static final String NAME_ATTRIBUTE = "name";
public static final String ALIAS_ATTRIBUTE = "alias";
public static final String IMPORT_ELEMENT = "import";
public static final String RESOURCE_ATTRIBUTE = "resource";
public static final String PROFILE_ATTRIBUTE = "profile";
@Nullable
private XmlReaderContext readerContext;
// 拥有BeanDefinitionParserDelegate
@Nullable
private BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate;
doRegisterBeanDefinitions放入如下所示:
protected void doRegisterBeanDefinitions(Element root) {
// Any nested <beans> elements will cause recursion in this method. In
// order to propagate and preserve <beans> default-* attributes correctly,
// keep track of the current (parent) delegate, which may be null. Create
// the new (child) delegate with a reference to the parent for fallback purposes,
// then ultimately reset this.delegate back to its original (parent) reference.
// this behavior emulates a stack of delegates without actually necessitating one.
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parent = this.delegate; // 当前的delegate作为parent,可能为null
this.delegate = createDelegate(getReaderContext(), root, parent); // 创建新的delegate
if (this.delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
String profileSpec = root.getAttribute(PROFILE_ATTRIBUTE);
if (StringUtils.hasText(profileSpec)) {
String[] specifiedProfiles = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(
profileSpec, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS);
// We cannot use Profiles.of(...) since profile expressions are not supported
// in XML config. See SPR-12458 for details.
if (!getReaderContext().getEnvironment().acceptsProfiles(specifiedProfiles)) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Skipped XML bean definition file due to specified profiles [" + profileSpec +
"] not matching: " + getReaderContext().getResource());
}
return;
}
}
}
// xml预处理,默认为空;允许用户自定义元素类型,在正式处理开始前,将其转换为标准的Spring BeanDefinition
preProcessXml(root);
// 核心入口
parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate);
// xml后置处理,默认为空,允许用户覆盖
postProcessXml(root);
// 最终将delegate重置
this.delegate = parent;
}
解析顶级元素节点,如import 、alias 、bean等。通过判断是否DefaultNameSpace区别Spring Xml元素节点还是自定义元素。
/**
* Parse the elements at the root level in the document:
* "import", "alias", "bean".
* @param root the DOM root element of the document
*/
protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
// 获取当前节点的字节点,循环调用parseDefaultElement 或者parseCustomElement
NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nl.item(i);
if (node instanceof Element) {
Element ele = (Element) node;
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) {
parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate);
}
else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(ele);
}
}
}
}
else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(root);
}
}
节点解析过程是一个递归过程,如果nodeName==‘beans’,那么会递归调用doRegisterBeanDefinitions方法。
// DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader#parseDefaultElement
private void parseDefaultElement(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
// 解析import
if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, IMPORT_ELEMENT)) {
importBeanDefinitionResource(ele);
}
// 解析 alias
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, ALIAS_ELEMENT)) {
processAliasRegistration(ele);
}
// 解析 bean
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, BEAN_ELEMENT)) {
processBeanDefinition(ele, delegate);
}
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, NESTED_BEANS_ELEMENT)) {
// recurse
doRegisterBeanDefinitions(ele);
}
}
我们以Bean节点为例学习BeanDefinition的获取与注入。
② processBeanDefinition
处理给定的元素节点,解析得到BeanDefinition并注入到容器。DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader的processBeanDefinition方法如下所示:
// DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader#processBeanDefinition
protected void processBeanDefinition(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
BeanDefinitionHolder bdHolder = delegate.parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele);
if (bdHolder != null) {
bdHolder = delegate.decorateBeanDefinitionIfRequired(ele, bdHolder);
try {
// Register the final decorated instance.
//这里是向IOC容器注册解析得到的BeanDefinition的地方。
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(bdHolder, getReaderContext().getRegistry());
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
getReaderContext().error("Failed to register bean definition with name '" +
bdHolder.getBeanName() + "'", ele, ex);
}
// Send registration event.
// 在BeanDefinition向IOC容器注册完以后,发送消息
getReaderContext().fireComponentRegistered(new BeanComponentDefinition(bdHolder));
}
}
BeanDefinitionHolder 的生成是通过对Document文档树的内容进行解析完成的,解析过程是由BeanDefinitionParserDelegate实现的,这个解析是与Spring对BeanDefinition的配置规则紧密相关的。BeanDefinition的处理结果是由BeanDefinitionHolder 持有的,这个BeanDefinitionHolder 除了持有BeanDefinition外,还持有其他与BeanDefinition的使用相关的信息,比如Bean的名字、别名集合等。得到BeanDefinitionHolder就意味着BeanDefinition是通过BeanDefinitionParserDelegate对xml元素的信息按照Spring的Bean规则进行解析得到的。
public class BeanDefinitionHolder implements BeanMetadataElement {
// 解析得到的BeanDefinition
private final BeanDefinition beanDefinition;
private final String beanName;
@Nullable
private final String[] aliases;
//...
}
我们先看一下获取BeanDefinitionHolder 的过程,然后再分析registerBeanDefinition过程。
③ parseBeanDefinitionElement(Element ele, @Nullable BeanDefinition containingBean)
@Nullable
public BeanDefinitionHolder parseBeanDefinitionElement(Element ele, @Nullable BeanDefinition containingBean) {
// 元素的ID属性
String id = ele.getAttribute(ID_ATTRIBUTE);
// 元素的name属性
String nameAttr = ele.getAttribute(NAME_ATTRIBUTE);
// 获取别名
List<String> aliases = new ArrayList<>();
if (StringUtils.hasLength(nameAttr)) {
String[] nameArr = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(nameAttr, MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS);
aliases.addAll(Arrays.asList(nameArr));
}
// beanName == id
String beanName = id;
if (!StringUtils.hasText(beanName) && !aliases.isEmpty()) {
beanName = aliases.remove(0);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No XML 'id' specified - using '" + beanName +
"' as bean name and " + aliases + " as aliases");
}
}
if (containingBean == null) {
checkNameUniqueness(beanName, aliases, ele);
}
// 这个方法会引发对Bean元素的详细解析
AbstractBeanDefinition beanDefinition = parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele, beanName, containingBean);
if (beanDefinition != null) {
if (!StringUtils.hasText(beanName)) {
try { // 如果beanName不存在,则生成一个BeanName
if (containingBean != null) {
beanName = BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.generateBeanName(
beanDefinition, this.readerContext.getRegistry(), true);
}
else {
beanName = this.readerContext.generateBeanName(beanDefinition);
// Register an alias for the plain bean class name, if still possible,
// if the generator returned the class name plus a suffix.
// This is expected for Spring 1.2/2.0 backwards compatibility.
String beanClassName = beanDefinition.getBeanClassName();
if (beanClassName != null &&
beanName.startsWith(beanClassName) && beanName.length() > beanClassName.length() &&
!this.readerContext.getRegistry().isBeanNameInUse(beanClassName)) {
aliases.add(beanClassName);
}
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Neither XML 'id' nor 'name' specified - " +
"using generated bean name [" + beanName + "]");
}
}
catch (Exception ex) {
error(ex.getMessage(), ele);
return null;
}
}
String[] aliasesArray = StringUtils.toStringArray(aliases);
// 根据BeanDefinition beanName以及别名集合实例化得到BeanDefinitionHolder
return new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDefinition, beanName, aliasesArray);
}
return null;
}
parseBeanDefinitionElement方法是一个复杂的过程,主要是对其他属性的解析。对bean元素进行解析的过程,也就是BeanDefinition依据XML的<bean>定义被创建的过程。这个BeanDefinition可以看成是对<bean>定义的抽象,这个数据抽象中封装的数据大多都是与<bean>定义相关的,如长江的init-method、destroy-method、factory-method等等。
④ parseBeanDefinitionElement(Element ele, String beanName, @Nullable BeanDefinition containingBean)
在这个解析过程中,我们可以看到对Bean定义的相关处理,比如对元素attribute值的处理,对元素属性值的处理,对构造函数值的处理等等。
@Nullable
public AbstractBeanDefinition parseBeanDefinitionElement(
Element ele, String beanName, @Nullable BeanDefinition containingBean) {
this.parseState.push(new BeanEntry(beanName));
//这里只读取定义的<bean>属性中设置的class名字,然后载入到BeanDefinition中去,只是做个记录
//并不涉及对象的实例化过程,对象的实例化过程实际是在依赖注入时完成的。
String className = null;
if (ele.hasAttribute(CLASS_ATTRIBUTE)) {
className = ele.getAttribute(CLASS_ATTRIBUTE).trim();
}
String parent = null;
if (ele.hasAttribute(PARENT_ATTRIBUTE)) {
parent = ele.getAttribute(PARENT_ATTRIBUTE);
}
try {
// 这里生成需要的BeanDefinition对象,为Bean定义信息的载入做准备 这里会抛出异常
AbstractBeanDefinition bd = createBeanDefinition(className, parent);
// 这里对当前的Bean元素进行属性解析,并设置description的信息
parseBeanDefinitionAttributes(ele, beanName, containingBean, bd);
bd.setDescription(DomUtils.getChildElementValueByTagName(ele, DESCRIPTION_ELEMENT));
// 解析meta 元素
parseMetaElements(ele, bd);
// Parse lookup-override sub-elements of the given bean element.
parseLookupOverrideSubElements(ele, bd.getMethodOverrides());
// Parse replaced-method sub-elements of the given bean element.
parseReplacedMethodSubElements(ele, bd.getMethodOverrides());
//解析构造函数
parseConstructorArgElements(ele, bd);
// 解析属性设置
parsePropertyElements(ele, bd);
parseQualifierElements(ele, bd);
bd.setResource(this.readerContext.getResource());
bd.setSource(extractSource(ele));
return bd;
} // 这些异常是在createBeanDefinition时进行的,对Bean进行检查比如类是否能够找到
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
error("Bean class [" + className + "] not found", ele, ex);
}
catch (NoClassDefFoundError err) {
error("Class that bean class [" + className + "] depends on not found", ele, err);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
error("Unexpected failure during bean definition parsing", ele, ex);
}
finally {
this.parseState.pop();
}
return null;
}
上面是具体生成BeanDefinition的地方。以parsePropertyElements为例,从属性元素集合到具体的每一个属性元素以及对应的属性值,根据解析结果,对这些属性值的处理会被封装成PropertyValue对象并设置到BeanDefinition中。Array、List、Set、Map、Prop等各种元素都会在这里被解析生成对应的数据对象,比如ManagedList、ManagedArray、ManagedSet等。这些Managed类是Spring对具体的BeanDefinition的数据封装。
经过元素的逐层解析,我们在xml文件定义的BeanDefinition就被整个载入到了IOC容器中,并在容器中建立了数据映射。在IOC容器中建立了对应的数据结构或者说可以看成是pojo对象在IOC容器中的抽象,这些数据结构可以以AbstractBeanDefinition为入口,让IOC容器执行索引、查询和操作。
经过以上的载入过程,IOC容器大致完成了管理bean对象的数据准备工作(或者说是初始化过程)。但是重要的依赖注入实际上在这个时候还没有发生。现在IOC容器BeanDefinition中存在的还是一些静态的配置信息,严格的说这时候的容器还没有完全起作用,要完全发挥容器的作用,还需完成数据向容器的注册。
⑤ registerBeanDefinition
注册为IOC容器提供了更友好的使用方式,在DefaultListableBeanFactory中,是通过一个HashMap来持有载入的BeanDefinition的。
/** Map of bean definition objects, keyed by bean name. */
private final Map<String, BeanDefinition> beanDefinitionMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256);
我们再回头看DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader的processBeanDefinition方法。在解析得到BeanDefinition后,会返回一个BeanDefinitionHolder 。此时就会调用BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(bdHolder, getReaderContext().getRegistry());触发BeanDefinition的注册。
// DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader#processBeanDefinition
protected void processBeanDefinition(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
BeanDefinitionHolder bdHolder = delegate.parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele);
if (bdHolder != null) {
bdHolder = delegate.decorateBeanDefinitionIfRequired(ele, bdHolder);
try {
// Register the final decorated instance.
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(bdHolder, getReaderContext().getRegistry());
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
getReaderContext().error("Failed to register bean definition with name '" +
bdHolder.getBeanName() + "'", ele, ex);
}
// Send registration event.
getReaderContext().fireComponentRegistered(new BeanComponentDefinition(bdHolder));
}
}
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils#registerBeanDefinition
public static void registerBeanDefinition(
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
// Register bean definition under primary name.
// 获取BeanName
String beanName = definitionHolder.getBeanName();
// 注册BeanDefinition
registry.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, definitionHolder.getBeanDefinition());
// Register aliases for bean name, if any.
String[] aliases = definitionHolder.getAliases();
if (aliases != null) {
for (String alias : aliases) {
// 注册别名
registry.registerAlias(beanName, alias);
}
}
}
真正的注册DefaultListableBeanFactory#registerBeanDefinition
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.hasText(beanName, "Bean name must not be empty");
Assert.notNull(beanDefinition, "BeanDefinition must not be null");
if (beanDefinition instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {
try {
((AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDefinition).validate();
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Validation of bean definition failed", ex);
}
}
// 根据beanName尝试获取一个已经存在的BeanDefinition
BeanDefinition existingDefinition = this.beanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);
if (existingDefinition != null) {
if (!isAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding()) {
throw new BeanDefinitionOverrideException(beanName, beanDefinition, existingDefinition);
}
else if (existingDefinition.getRole() < beanDefinition.getRole()) {
// e.g. was ROLE_APPLICATION, now overriding with ROLE_SUPPORT or ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Overriding user-defined bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with a framework-generated bean definition: replacing [" +
existingDefinition + "] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
else if (!beanDefinition.equals(existingDefinition)) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Overriding bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with a different definition: replacing [" + existingDefinition +
"] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
else {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Overriding bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with an equivalent definition: replacing [" + existingDefinition +
"] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
}
else {
if (hasBeanCreationStarted()) {
// Cannot modify startup-time collection elements anymore (for stable iteration)
synchronized (this.beanDefinitionMap) { //synchronized 加锁
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
List<String> updatedDefinitions = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames.size() + 1);
updatedDefinitions.addAll(this.beanDefinitionNames);
updatedDefinitions.add(beanName);
this.beanDefinitionNames = updatedDefinitions;
removeManualSingletonName(beanName);
}
}
else {
// Still in startup registration phase
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
this.beanDefinitionNames.add(beanName);
removeManualSingletonName(beanName);
}
this.frozenBeanDefinitionNames = null;
}
if (existingDefinition != null || containsSingleton(beanName)) {
resetBeanDefinition(beanName);
}
else if (isConfigurationFrozen()) {
clearByTypeCache();
}
}
上面当把bean的名字存入到beanDefinitionNames的同时,把beanName作为map的key,把BeanDefinition作为value存入到IOC容器持有的beanDefinitionMap。
完成了BeanDefinition的注册,就完成了IOC容器的初始化过程。此时,在使用的IOC容器DefaultListableBeanFactory中已经建立了整个Bean的配置信息,而且这些BeanDefinition已经可以被容器使用了,它们都在beanDefinitionMap里被检索和使用。这些信息是容器建立依赖反转的基础,有了这些基础数据才可以完成依赖注入。





 本文详细介绍了Spring框架中BeanDefinition的载入与解析过程,包括BeanDefinition的注册及BeanDefinitionHolder的生成,深入剖析了XmlBeanDefinitionReader与DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader的工作原理。
本文详细介绍了Spring框架中BeanDefinition的载入与解析过程,包括BeanDefinition的注册及BeanDefinitionHolder的生成,深入剖析了XmlBeanDefinitionReader与DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader的工作原理。

















 898
898

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










