1.JDK 和 JRE 有什么区别?
JDK是java开发工具包,提供了java的开发环境和运行环境。JRE是java运行环境(需要进行环境变量配置后才可以使用),为运行提供了所需的环境。JKD包含了JRE,要想编写java程序就需要安装JDK。
2. == 和 equals 的区别是什么?
==比较两个是不是指向同一个内存地址,equals比较的是字面量、值是不是一致。
示例:
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "123abc";
String s2 = "123abc";
String s3 = "123" + "abc";
String s4 = new String("123abc");
System.out.println(s1==s2);//true
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));//true
System.out.println(s1==s3);//true
System.out.println(s1.equals(s3));//true
System.out.println(s1==s4);//false
System.out.println(s1.equals(s4));//true
}
3. 两个对象的 hashCode()相同,则 equals()也一定为 true,对吗?
不对,“通话”和“重地”的 hashCode相同,而equals返回的则为false,在散列表中,hashcode的哈希值相等并一定能得出键值对相等。
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "通话";
String str2 = "重地";
System.out.println(String.format("str1:%d|str2:%d", str1.hashCode(),str2.hashCode()));//format %d格式化为十进制
System.out.println(str1.equals(str2));
}
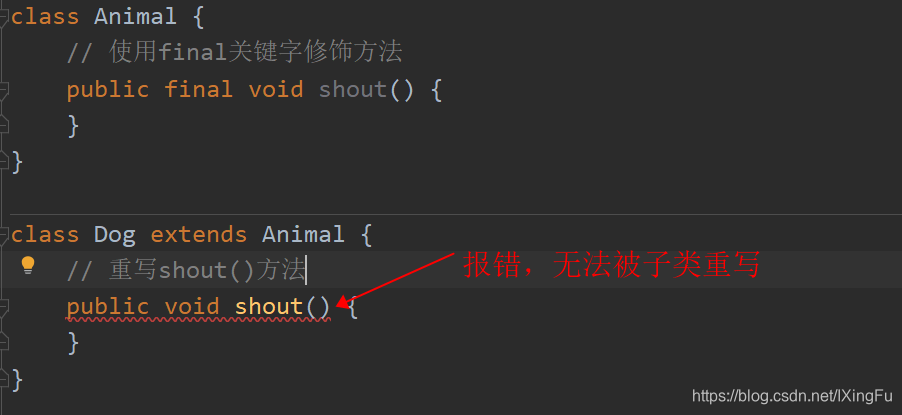
4.final 在 java 中有什么作用?
修饰的类叫最终类,该类不能被继承。修饰方法时改方法为最终方法,无法被子类重写。修饰的变量叫常量,常量必须初始化,初始化之后值就不能被修改。
修饰方法示例:
修饰变量示例:

5. java 中的 Math.round(-1.5) 等于多少?
等于 -1,因为在数轴上取值时,中间值(0.5)向右取整,所以正 0.5 是往上取整,负 0.5 是直接舍弃。
6. String 属于基础的数据类型吗?
不属于基本数据类型,而属于对象,基本数据类型有8种:int、double、boolean、short、long、float、char、byte。
7. java 中操作字符串都有哪些类?它们之间有什么区别?
操作字符串的类有:String、StringBuffer、StringBuilder。
String是不可变的对象,String类的方法都是返回新的String,然后会指向新的String,经常改变字符串内容最好不要使用String。StringBuffer、StringBuilder可以在原对象的基础上进行操作,StringBuffer是线程安全的,公开方法都是synchronized修饰的。StringBuilder是非线程安全的,公开的方法都是同步的。StringBuffer效率不如StringBuilder,但比String要高。在单线程环境下推荐使用StringBuilder,多线程环境下推荐使用 StringBuffer。
8. String str="i"与 String str=new String("i")一样吗?
不一样,因为内存的分配方式不一样。String str="i",java 虚拟机会将其分配到常量池中;而 String str=new String("i") 则会被分到堆内存中。
9.如何将字符串反转?
使用StringBuilder或者StringBuffer的reverse()方法。
实例:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc =new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入一个字符串:");
String s = sc.nextLine();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(s);
sb.reverse();
System.out.println(sb);
}
10. String 类的常用方法都有那些?
1.indexOf():返回指定字符的索引。
public static void main(String[] args) {
String string = "abc123cba";
System.out.println(string.indexOf("i"));//字符串中没有这样的字符,则返回-1。
}
2.charAt():返回指定索引处的字符。
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "www.baidu.com";
char result = s.charAt(5);
System.out.println(result);//索引范围为从0到length()-1。
}
3.replace():字符串替换。
public static void main(String[] args) {
String st = new String("Baidu");
System.out.println("返回值:" + st.replace('B', 'b'));
}
4.trim():去除字符串两端空白。
public static void main(String[] args) {
String st = new String(" www.baidu.com ");
System.out.println("去除两端空白" + st.trim());
}
5.split():分割字符串,返回一个分割后的字符串数组。
public static void main(String[] args) {
String st = new String("Welcome-to-Hangzhou");
String[] str = st.split("-");
for (String s : str) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
6.getBytes():返回字符串的byte类型数组。
public static void main(String[] args) {
String st1 = new String("baidu");
byte[] st2 = st1.getBytes();
System.out.println("返回值:" + st2);
}
7.length():返回字符串长度。
public static void main(String[] args) {
String st = new String("baidu");
System.out.println("字符串长度:" + st.length());
}
8.toLowerCase():将字符串转成小写字母。
public static void main(String[] args) {
String st = new String("BAIDU");
System.out.println(st.toLowerCase());
}
9.toUpperCase():将字符串转成大写字符。
public static void main(String[] args) {
String st = new String("baidu");
System.out.println(st.toUpperCase());
}
10.substring():截取字符串。
public static void main(String[] args) {
String st = new String("Welcome to Hangzhou ");
System.out.println(st.substring(8));
System.out.println(st.substring(8, 19));
}
11.equals():字符串比较。
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "a1";
String s2 = "b2";
String s3 = "c3";
String s4 = "a" + "1";
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));
System.out.println(s1.equals(s3));
System.out.println(s1.equals(s4));
}
11. 抽象类必须要有抽象方法吗?
抽象类中不一定要有抽象方法,包含一个抽象方法的类一定是抽象类。抽象类不允许实例化。
abstract class Dog {
public static void say() {
System.out.println("Wang");
}
}
12. 普通类和抽象类有哪些区别?
普通类是不允许包含抽象方法的,抽象类可以包含抽象方法。普通类可以实例化对象,可以new出来一个对象,抽象类是不允许实例化。




















 7099
7099

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








