P177
#include<stdio.h>
int main (void) {
const int FREEZING=0;
float tem;
int colddays=0;
int alldays=0;
while(scanf("%f",&tem)==1)
{
alldays++;
if(tem<FREEZING)
{
colddays++;
}
}
if(alldays!=0)
{
printf("%d days total,%.1f%% were below freezing",
alldays,100.0*colddays/alldays);
if(alldays==0)
{
printf("no data");
}
return 0;
}
}

ifelse
if(expression)
statement1
else
statement2
ch=getchar(); //== scanf("%c",&ch);
putchar(ch(; // = printf("%c",ch);
P181 CYpher1
#include<stdio.h>
#define SPACE ' '
int main(void){
char ch;
ch=getchar();
while(ch !='\n')
{
if(ch == SPACE)
putchar(ch);
else
putchar(ch+1);
ch=getchar();
}
putchar(ch);
return 0;
}

//while((ch=getchar())!=‘\n’){
}
C语言有一系列专门处理字符的函数,包含在ctype.h中
#include<stdio.h>
#include<ctype.h>
int main(void){
char ch;
while((ch=getchar())!='\n'){
if(isalpha(ch)){
putchar(ch+1);
}else{
putchar(ch);
}
}
return 0;
}


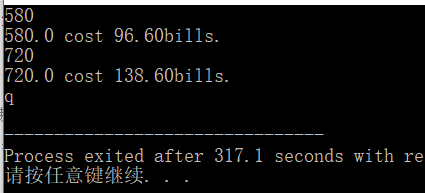
多重选择ifelse
#include<stdio.h>
#define RATE1 0.13
#define RATE2 0.15
#define RATE3 0.3 //前三个级别的费率
#define RATE4 0.34 //前四个级别的费率
#define BREAK1 360
#define BREAK2 468
#define BREAK3 720 //电费划分的三个级别
#define BASE1 (RATE1*BREAK1) //使用360度
#define BASE2 (BASE1+(RATE2*(BREAK2-BREAK1)))
#define BASE3 (BASE1+BASE2+(RATE3*(BREAK3-BREAK2)))
int main(void){
double kwh; //使用的电
double bill; //需要交的电费
while(scanf("%lf",&kwh)){ //lf对应double
if(kwh<=BREAK1){
bill=RATE1*kwh;
} else if(kwh<=BREAK2){
bill=BASE1+(kwh-BREAK1)*RATE2;
} else if(kwh<=BREAK3){
bill=BASE2+(kwh-BREAK2)*RATE3;
} else
bill=BASE3+(kwh-BREAK3)*RATE4;
printf("%.1f cost %1.2fbills.\n",kwh,bill);
}
return 0;
}
显示约数
#include<stdio.h>
int main(void){
int num=144;
int div;
for(div=2;(div*div)<=num;div++)
if(num%div==0)
printf("%d可以被%d和%d整除\n",num,div,num/div);
return 0;
}
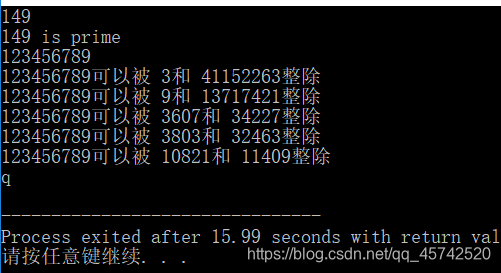
P189 约数计算
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
int main(void){
int num; //待测试的素数
int div; //可能的约数
bool isprime ; //素数标记
while(scanf("%d",&num)==1){
for(div=2,isprime=true;(div*div)<=num;div++){
if(num % div==0){
if((div*div)!=num){
printf("%d可以被 %d和 %d整除\n",num,div,num/div);
}
else{
printf("%d可以被 %d整除\n",num,div);
}
isprime=false;
}
}
if(isprime){
printf("%d is prime\n",num);
}
}
return 0;
}
**P190chcount **//计算除引号外其他字符的数量
#include<stdio.h>
#define PERIOD '.'
int main(void){
char ch;
int charcount =0;
while((ch=getchar())!=PERIOD){
if(ch!='"'&&ch!='\'')
charcount++;
}
printf("there are %d non-quote characters.\n",charcount);
return 0;
}
7.3.2优先级
- !的优先级比乘法还高
- &&运算符的优先级高于||
- &&和||的优先级都高于赋值运算符而低于关系运算符
e.g. a>b&&b>c||c>d 相当于 (a>b) && (b>c) || (c>d)
7.3.3求值顺序
7.3.4范围
&&可以用于测试范围
if(ch>='a'&&ch<='z'){
printf("that is a lowercase character");
}
==可以使用ctype.h中的islower()函数
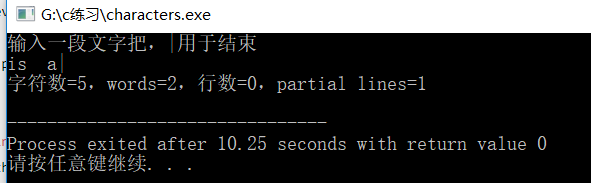
7.4一个统计单词的程序
#include<stdio.h>
#include<ctype.h>
//使用isspace()函数来判断是哦复位空白字符,功能等于
//c==''||c=='\n'||c=='\t';
#include<stdbool.h>
#define STOP '|'
int main (void){
char c; //读入字符
char prev; //读入的签一个字符
long n_char=0L; //字符数
int n_lines=0; //行数
int n_words=0; //单词数
int p_lines=0; //不完整的行数
bool inword=false; //如果c在单词中则inword为true
prev='\n'; //用于识别完整的行
printf("输入一段文字把,|用于结束\n");
while((c=getchar())!=STOP){
n_char++; //统计字符数
if(c=='\n')
n_lines++; //统计行
if(!isspace(c)&&!inword){
inword=true; //开始一个新单词
n_words++; //统计单词
}
if(isspace(c)&&inword) {
inword=false;
}
prev=c;
}
if(prev!='\n'){
p_lines=1;
}
printf("字符数=%ld,words=%d,行数=%d,",
n_char,n_words,n_lines);
printf("partial lines=%d\n",p_lines);
return 0;
}
7.5条件运算符:?
?是if else 的一种快捷表达方式
x=(y<0)?-y:y;
等同于
if(y<0)
x=-y;
else
y=y;
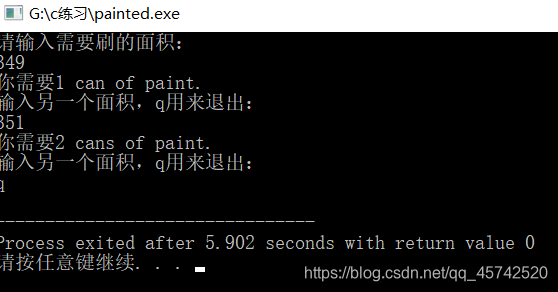
#include<stdio.h>
#define COVERAGE 350 //每罐油漆可以刷的面积
int main(void){
int feet; //尺 ,面积
int cans;
printf("请输入需要刷的面积: \n");
while(scanf("%d",&feet)==1){
cans=feet/COVERAGE;
cans+=(feet%COVERAGE==0)?0:1;
printf("你需要%d %s of paint.\n",cans,cans==1?"can":"cans");
printf("输入另一个面积,q用来退出:\n");
}
return 0;
}
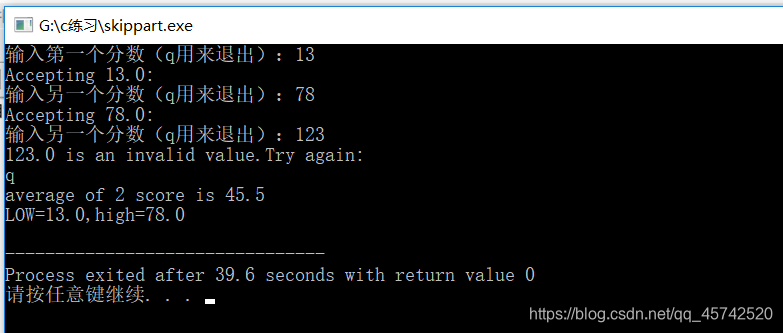
7.5循环辅助语句:continue,break
continue和break语句可以根据循环体的测试结果来忽略一部分循环内容,甚至结束循环。
三种循环都可以使用continue语句。执行到该语句时会跳过本次迭代的剩余部分,并开始下一轮迭代
#include<stdio.h>
int main(void){
const float MIN=0.0f;
const float MAX=100.0f;
float score;
float total=0.0f;
int n=0;
float min=MAX;
float max=MIN;
printf("输入第一个分数(q用来退出):");
while (scanf("%f",&score)==1){
if(score<MIN||score>MAX){
printf("%0.1f is an invalid value.Try again:\n",score);
continue;
}
printf("Accepting %0.1f:\n",score);
min=(score<min)?score:min;
max=(score>max)?score:max;
total+=score;
n++;
printf("输入另一个分数(q用来退出):");
}
if(n>0){
printf("average of %d score is %0.1f\n",n,total/n);
printf("LOW=%0.1f,high=%0.1f\n",min,max);
}
else
printf("no valid scores were entered.\n");
return 0;
}
- 对于while和do while循环来说,continue的下一个行为是对循环的测试表达式求值,跳过count++
#include<stdio.h>
int main (void){
int count =0;
char ch;
for(count=0;count<10;count++){
ch=getchar();
if(ch=='\n')
continue;
putchar(ch);
}
return 0;
}
2.对于for循环来说,continue之后的下一个行为是对更新表达式求值
7.6.2break语句
程序执行到break语句会终止包含他的循环,并进入程序的下一阶段
#include<stdio.h>
int main(void){
float length,width;
printf("enter the length of reactangle:\n");
while(scanf("%f",&length)==1)
{
printf("length=%.2f:",length);
printf("enter its width:\n");
if(scanf("%f",&width)!=1)
break;
printf("width=%.2f:\n",width);
printf("area=%.2f:\n",length*width);
}
printf("done.\n");
return 0;
}
在for循环中break与continue不同,遇到break后会直接执行循环后的第一条语句
多重选择switch’和break
对于需要在多个选项中选择的程序,可以用if else if 来完成,但大多数情况下,使用switch更为方便快捷。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<ctype.h>
int main(Void){
char ch;
printf("give a letter of the alphabet,and i will give");
printf("an animal name\nbeginning with that letter\n");
printf("please type in a letter ;type # to end my act.\n");
while((ch=getchar())!='#'){
if(ch=='\n')
continue;
if(islower(ch)){
switch(ch)
{
case'a': printf("argali\n"); break;
case 'b': printf("babirusa\n"); break;
//只测试到b
default: printf("that is a stumper\n"); //switch结束
}
}else{
printf("我只接受小写字母\n");
}
while(getchar()!='\n')
continue;
printf("请输入另一个字母或#\n");
}
printf("bye\n");
return 0;
}
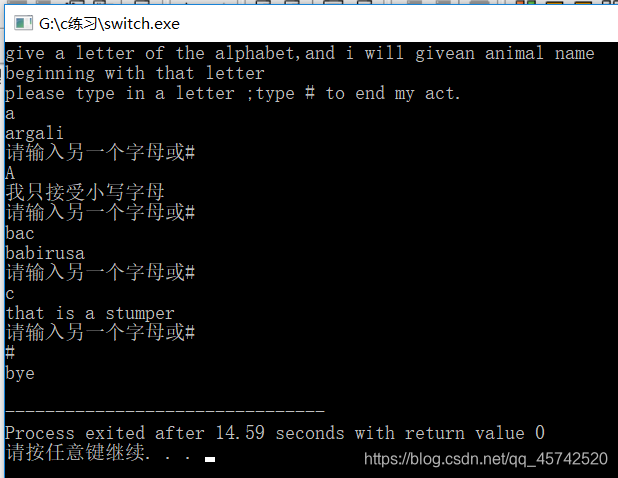
使用break语句,可以使其直接跳出switch语句,否则他将一直执行到default:
- C语言的case一般都指定一个值,而并非是一个范围
- switch在圆括号中的测试表达式的值是整数(或char类型
- case标签必须是整数类型(包括char类型)的常量或整型常量表达式,不可以是变量。
7.7.2只读每行的首字符
while(getchar()!='\n')
7.7.3多重标签
#include<stdio.h>
int main(void){
char ch;
int a,e,i,o,u;
a=e=i=o=u=0;
printf("请输入文字,#用来退出\n");
while((ch=getchar())!='#'){
switch(ch){
case 'a':
case 'A': a++; break;
case 'e':
case 'E': e++; break;
case 'i':
case 'I': i++; break;
case 'o':
case 'O': o++; break;
case 'u':
case 'U': u++; break;
default: break;
}
}
printf("numbles of vowels: A E I O U\n");
printf("%4d%4d%4d%4d",a,e,i,o,u);
return 0;
}
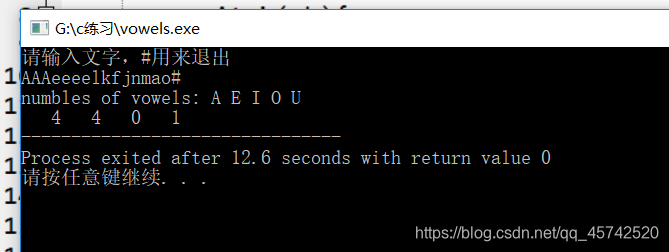
可以在swith语句测试前使用ctype.h中所包含的toupper将字母转换成大写字母而避免使用多重标签
7.7.4 ifelse和swith的选择
- 如果是根据浮点类型的变量或表达式来选择则无无法使用switch
- 如果根据变量在某个范围内决定程序的走向,使用switch就很麻烦
- 使用switch程序通常执行的会快一些,生成的代码较少
7.8goto语句
原则上根本不在C程序中使用goto语句,因为易被滥用
goto语句有两部分:goto和标签名(标签名和变量名相同) goto part2;
想要正常工作,函数中还需包含一条part2:…
使用goto语句的情况(可以使用c语言代替的)
if(size>12) 使用c语言表示:if(size>12){
cost=cost*1.05;
flag=2;
}bill=cost*flag;
}
goto a;
goto b;
a:cost=cost*1.05;
flag=2;
b:bill=cost*flag;
if(ibex>14)
goto a;
sheds=2;
goto b;
a:sheds=3;
b:help=2*sheds;
//USE C
if(ibex>14)
sheds=3;
else
sheds=2;
help=2*sheds;
//不确定循环
readin:scanf("%d,&score"):
if(score<0)
goto stage2;
more statements;
goto readin;
stage2:more stuff
//USE C
scnaf("%d",&score);
while(score<0){
more statement;
scnaf("%d",&score);
}
more stuff;
C可以接受一种goto的用法——出现问题时从一组嵌套循环中跳出(一条break语句只能跳出当前循环)





 本文详细介绍了C语言中的控制语句,包括if-else分支、while和for循环、条件运算符、continue和break的使用,以及switch语句。同时讨论了goto语句的使用场景和避免滥用的原则。
本文详细介绍了C语言中的控制语句,包括if-else分支、while和for循环、条件运算符、continue和break的使用,以及switch语句。同时讨论了goto语句的使用场景和避免滥用的原则。
















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








