一、概念
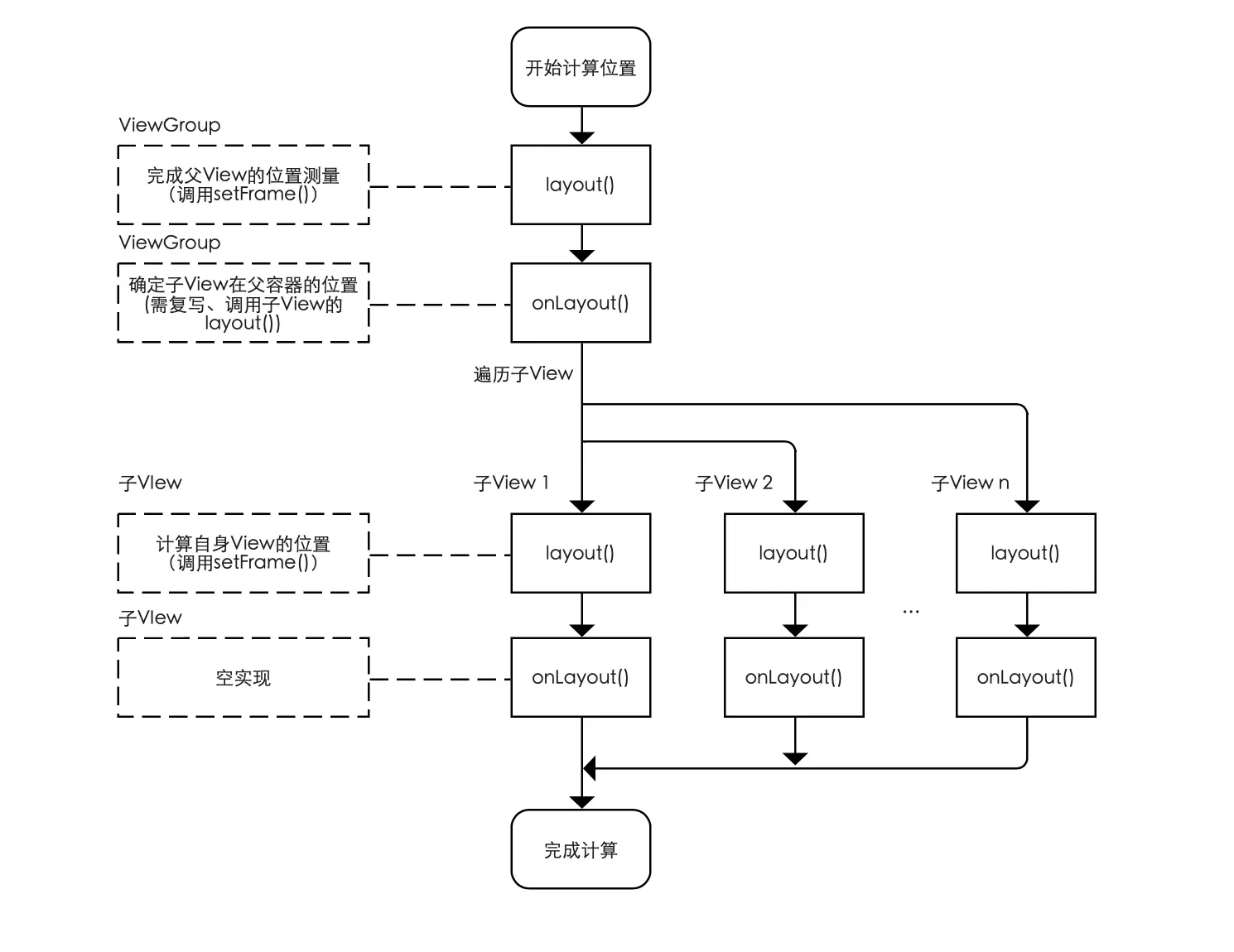
View 由于没有子元素因此它的 onLayout() 是个空实现。自定义 ViewGroup 时需要重写 onLayout() 方法,遍历并计算每一个子元素四条边到父容器的距离,然后调用子元素的 layout() 传递过去。
|
override fun onLayout(changed: Boolean, left: Int, top: Int, right: Int, bottom: Int) {...} 形参changed为当前控件大小和位置是否改变了(很耗性能,父容器宽高的改变和子控件请求刷新都会被系统频繁调用),其它为控件自身四边到父容器的距离。 |
override fun onLayout(changed: Boolean, l: Int, t: Int, r: Int, b: Int) {
val childLeft = 0
val childTop = 0
val childRight = 0
val childBottom = 0
//遍历子元素
for (i in 0 Uuntil childCount) {
val childView = getChildAt(i)
//获取测量后的子元素宽高
val childMeasuredWidth = childView.measuredWidth
val childMeasuredHeight = childView.measuredHeight
//计算子元素四边到父容器的距离(结合在onMeasure()中保存的一些全局数据)
//TODO...
//确定了子元素在父容器中的位置,调用子元素的 layout() 传递过去
childView.layout(childLeft, childTop, childRight, childBottom)
}
}
1.1 getMeasuredXXX() 和 getXXX() 区别
一般情况下是相等的,除了重写 layout() 进行了修改。
|
getMeasuredWidth() getMeasuredHeight() |
getWidth() getHeight() |
| 获取测量后的值 | 获取布局后的值(名字中省略了Layouted) |
| 在 measure() 结束后就可以获取到,供后续布局使用。 | 在 layout() 执行后才能获取到,是控件真正的最终尺寸。 |
| 通过 setMeasuredDimension( ) 进行设置的。 | 通过视图右边坐标减去左边坐标计算出来的。 |





 文章详细介绍了在自定义ViewGroup时如何重写onLayout方法,遍历并计算子元素的位置。onLayout中计算每个子元素的四边距离,并调用子元素的layout方法。同时提到了getMeasuredWidth和getWidth的区别,前者是在measure阶段获取测量后的值,后者在layout之后提供最终尺寸。
文章详细介绍了在自定义ViewGroup时如何重写onLayout方法,遍历并计算子元素的位置。onLayout中计算每个子元素的四边距离,并调用子元素的layout方法。同时提到了getMeasuredWidth和getWidth的区别,前者是在measure阶段获取测量后的值,后者在layout之后提供最终尺寸。

















 633
633

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








