程序被其他程序翻译成不同的格式
之前列举的Hello World 的C语言程序的生命周期是以一种高级语言开始的,因为它能轻松被人读懂。然而,为了在系统中运行这段程序,每段C语言代码必须被其他程序翻译并且装载到底层机器语言的指令序列中。稍后这些指令集被打包成可执行程序并且保存在硬盘中。目标程序也可以被称为可执行目标文件。
在Unix系统中,翻译从源代码到目标文件的动作是由编译器驱动来完成的。
linux> gcc -o hello hello.c
在这里的GCC编译器驱动读取这段hello.c文件并且翻译成可执行目标文件hello。 翻译的执行由四个有序阶段过程组成,对应下图。程序要执行的这四个阶段(预处理器、编译器、汇编器、链接器)统称为编译系统。
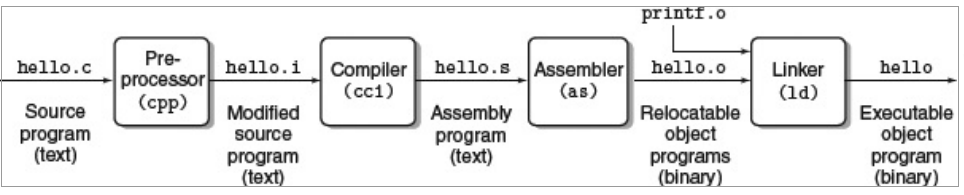
预处理器阶段。
预处理器会从C程序源码的’#‘开始编辑。例如,C语言程序的第一行’#include <studio.h>'代码,那么预处理器就知道把stdio.h库的头文件放在程序内容当中。处理后的结果是另外一种形式的C程序,一般会是.i后缀。
编译阶段。
编译器接下来会把hello.i翻译成包括汇编语言程序的hello.s。程序包括以下Main函数定义:
1 main:
2 subq $8, %rsp
3 movl $.LCO, %edi
4 call puts
5 movl $0, %eax
6 addq $8, %rsp
7 ret
在文本框中2-7行在定义描述中的是低级机器语言指令。汇编语言之所以有如此用户,是因为它可以针对不同的高级语言和不同的编译器都有相同的输出结果。例如,C编译器和Fortan编译器在相同的汇编语言中都生成了相同的输出文件。
GNU项目
GCC是GNU(GNU’s Not Unix的简称)是多个有价值的开发工具之一。GNU是由Richard Stallman在1984年创建的免税项目,并致力于发展完善的类Unix系统,并且源码可以不受限制地修改和传播。项目会开发出包括Unix操作系统的所有主要组件的环境,除了Linux项目独大发展的内核。
GNU环境包括EMACS编辑器、GCC编译器、GDB调试器、汇编器、链接器、二进度处理和其他组件。GCC编译器可以支持各种语言,并且在不同的机器可以生成代码。支持语言包括C、C++,Fortan,GNU项目是一个巨大的成功,但是常常被忽略。现代开源行动(跟Linux都有关系)本身的优越理念就源自于GNU项目的开源软件概念。Linux有很多著名的工具是GNU项目的,并且为Linux内核服务。
链接器阶段。
注意下这段C语言程序的printf函数,这是每一个编译器的C语言标准库都会提供的。printf函数部分会抽离并且预编译成printf.o文件,并且合并到hello.o程序中。链接器负责处理合并操作。合并后的结果就是可执行程序,并准备装载到内存和在系统中运行。
英文原文:
1.2 Programs Are Translated by Other Programs into Different Forms
The hello program begins life as a high-level C program because it can be read and understood by human beings in that form. However,in order to run hello.c on the system, the individual C statements must be translated by other programs into a sequence of low-level machine-language instructions. These instructions are then packaged in a form called an executable object program and stored as a binary disk file. Object programs are also referred to as executable objectfiles.On a Unix system, the translation from source file to object file is performed by a compiler driver:
linux> gcc -o hello hello.c
Here, the GCC compiler driver reads the source file hello.c and translates it into an executable object file hello . The translation is performed in the sequence of four phases shown in Figure 1.3 . The programs that perform the four phases (preprocessor, compiler,assembler, and linker) are known collectively as the compilation system.
Preprocessing phase. The preprocessor (cpp) modifies the original C program according to directives that begin with the ` # 'character. For example, the #include <stdio.h> command in line1 of hello.c tells the preprocessor to read the contents of the system header file stdio.h and insert it directly into the programtext. The result is another C program, typically with the .i suffix.
Compilation phase. The compiler ( cc1 ) translates the text filehello.i into the text file hello.s , which contains an assemblylanguage program. This program includes the following definitionof function main :
1 main:
2 subq $8, %rsp
3 movl $.LCO, %edi
4 call puts
5 movl $0, %eax
6 addq $8, %rsp
7 ret
Each of lines 2-7 in this definition describes one low-level machinelanguage instruction in a textual form. Assembly language is useful because it provides a common output language for different compilers for different high-level languages. For example, Ccompilers and Fortran compilers both generate output files in the same assembly language.
Assembly phase. Next, the assembler ( as ) translates hello.sinto machine-language instructions, packages them in a form known as a relocatable object program, and stores the result in theobject file hello.o. This file is a binary file containing 17 bytes to encode the instructions for function main. If we were to viewhello.o with a text editor, it would appear to be gibberish.
Aside The GNU project
GCC is one of many useful tools developed by the GNU(short for GNU’s Not Unix) project. The GNU project is tax-exempt charity started by Richard Stallman in 1984, witthe ambitious goal of developing a complete Unix-like system whose source code is unencumbered by restrictionson how it can be modified or distributed. The GNU project has developed an environment with all the major components of a Unix operating system, except for the kernel, which was developed separately by the Linuxproject.
The GNU environment includes the EMACS editor,GCC compiler, GDB debugger, assembler, linker, utilities for manipulating binaries, and other components. The GCC compiler has grown to support many different languages,with the ability to generate code for many different machines. Supported languages include C, C++, Fortran,The GNU project is a remarkable achievement, and yet it is often overlooked. The modern open-source movement (commonly associated with Linux) owes its intellectual origins to the GNU project’s notion of free software (“free” as in “free speech,” not “free beer”). Further, Linux owes much of its popularity to the GNU tools, which provide the environment for the Linux kernel.
Linking phase. Notice Notice that our hello program calls theprintf function, which is part of the standard C library provided byevery C compiler. The printf function resides in a separate precompiled object file called printf.o , which must somehow be merged with our hello.o program. The linker ( ld ) handles this merging. The result is the hello file, which is an executable objectfile (or simply executable) that is ready to be loaded into memoryand executed by the system.





















 135
135

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








