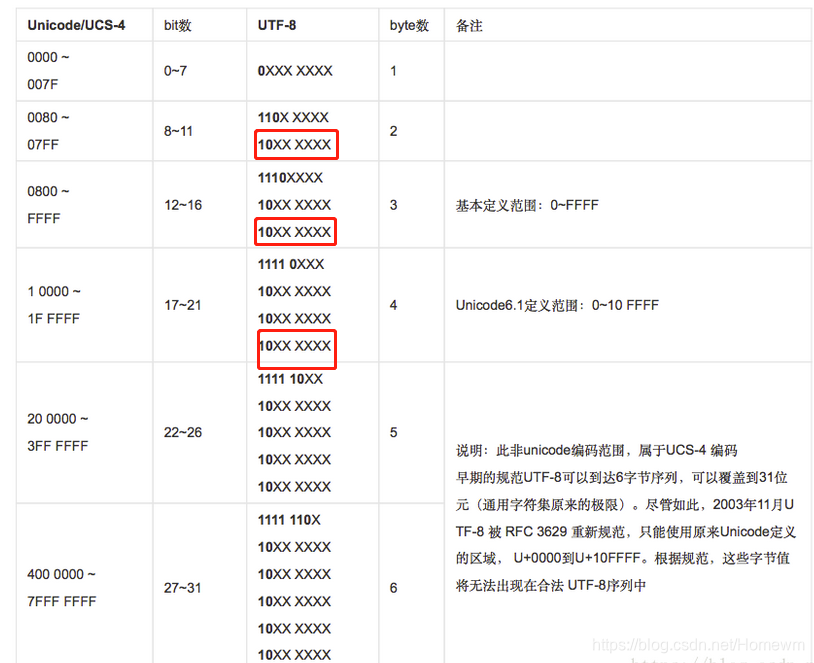
首先了解一下UTF-8编码格式,UTF8算是一种自适应的,长度不定,兼容ASCII编码。

 byte数为5、6的都不使用了,讨论前面的byte数为1、2、3、4的四种情况。
byte数为5、6的都不使用了,讨论前面的byte数为1、2、3、4的四种情况。
def detectUTF8(file_name):
state = 0
line_num = 0
file_obj = open(file_name)
all_lines = file_obj.readlines()
file_obj.close()
for line in all_lines:
line_num += 1
line_len = len(line)
for index in range(line_len):
if state == 0:
if ord(line[index])&0x80 == 0x00:#上表中的第一种情况
state = 0
elif ord(line[index])&0xE0 == 0xC0:#上表中的第二种情况
state = 1
elif ord(line[index])&0xF0 == 0xE0:#上表中的第第三种
state = 2
elif ord(line[index])&0xF8 == 0xF0:#上表中的第第四种
state = 3
else:
print "%s isn't a utf8 file,line:\t"%file_name+str(line_num)
sys.exit(1)
else:
if not ord(line[index])&0xC0 == 0x80:
print "%s isn't a utf8 file in line:\t"%file_name+str(line_num)
sys.exit(1)
state -= 1或许很多人会很疑惑为什么下面这句话是0xC0==0x80?直接看下表被圈的红色框中,是为了确保index指向的byte的首位为1
if not ord(line[index])&0xC0 == 0x80:
参考链接:
https://www.cnblogs.com/ferraborghini/p/4951102.html
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/liyadian/article/details/81228458







 本文介绍了如何在Python中判断文件或字符串是否采用UTF-8编码。UTF-8是一种自适应编码,不使用byte数为5、6的情况,主要关注1、2、3、4 byte的情况。通过检查字节序列的特定模式来验证UTF-8编码,例如检查字节首位是否为1。
本文介绍了如何在Python中判断文件或字符串是否采用UTF-8编码。UTF-8是一种自适应编码,不使用byte数为5、6的情况,主要关注1、2、3、4 byte的情况。通过检查字节序列的特定模式来验证UTF-8编码,例如检查字节首位是否为1。
















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








