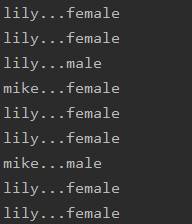
以下所示的代码,由于没有上锁,input在存数据的时候,可能出现赋值了姓名还没有赋值性别就已经被打印的情况。操作共享数据的代码必须加上同步代码块。
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// write your code here
Res r=new Res();
Input in=new Input(r);
Output out=new Output(r);
Thread t1=new Thread(in);
Thread t2=new Thread(out);
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
class Res
{
String name;
String sex;
}
class Input implements Runnable
{
private Res r;
Input(Res r)
{
this.r=r;
}
public void run()
{
boolean flag=true;
while (true)
{
if (flag)
{
r.name = "mike";
r.sex = "male";
flag=false;
}
else
{
r.name = "lily";
r.sex = "female";
flag=true;
}
}
}
}
class Output implements Runnable
{
private Res r;
Output(Res r)
{
this.r=r;
}
public void run()
{
while (true)
{
System.out.println(r.name+"..."+r.sex);
}
}
}
只需要给操作共享数据的代码加上同步代码块,其中锁必须是唯一的,包括Input.class或者r和Output.class都可以。
以下三个函数
wait():
notify() ;
notifyAll () ;
都使用在同步中,因为要对持有监视器(锁)的线程操作。
所以要使用在同步中,因为只有同步才具有锁。
为什么这些操作线程的方法要定义object类中呢?
因为这些方法在操作同步中线程时,都必须要标识它们所操作线程持有的锁,只有同一个锁上的被等待线程,可以被同一个锁上的notify()唤醒。不可以对不同锁中的线程进行唤醒。也就是说,等待和唤醒必须是同一个锁。
class Input implements Runnable
{
private Res r;
Object obj=new Object();
Input(Res r)
{
this.r=r;
}
public void run()
{
int x=1;
while (true)
{
synchronized (r) {
if (x==1) {
r.name = "mike";
r.sex = "male";
} else {
r.name = "lily";
r.sex = "female";
}
x=(x+1)%2;
}
}
}
}
class Output implements Runnable
{
private Res r;
Object obj=new Object();
Output(Res r)
{
this.r=r;
}
public void run()
{
while (true)
{
synchronized (r)
{
System.out.println(r.name + "..." + r.sex);
}
}
}
}
上述的代码还可以优化,可以把锁放在Res类中,同时简化输入、输出类和主函数。
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// write your code here
/*Ticket c=new Ticket();
Thread t1=new Thread(c);
Thread t2=new Thread(c);
t1.start();
c.flag=false;
t2.start();*/
Res r=new Res();
new Thread(new Input(r)).start();
new Thread(new Output(r)).start();
}
}
class Res
{
private String name;
private String sex;
private boolean flag=false;
public synchronized void set(String name,String sex)//需要同步
{
if (flag)
try {
this.wait();
}catch (Exception e) {}
this.name=name;
this.sex=sex;
flag=true;
this.notify();
}
public synchronized void out()//也需要同步
{
if (!flag)
try {
this.wait();
}catch (Exception e) {}
System.out.println(name+"......"+sex);
flag=false;
this.notify();
}
}
class Input implements Runnable
{
private Res r;
Object obj=new Object();
Input(Res r)
{
this.r=r;
}
public void run()
{
int x=1;
while (true)
{
if (x==1)
{
r.set("mike","male");
}
else
{
r.set("lily","female");
}
x=(x+1)%2;
}
}
}




















 869
869

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








