import os
os.environ['TF_ENABLE_ONEDNN_OPTS'] = '0'
# os.environ['TF_DETERMINISTIC_OPS'] = '1' # 注释掉这行,避免确定性操作导致的种子问题
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Input, Dense, Dropout, BatchNormalization, Concatenate, Reshape, Conv1D, \
GlobalAveragePooling1D
from tensorflow.keras.models import Model
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import Adam
from tensorflow.keras.callbacks import EarlyStopping, ReduceLROnPlateau, ModelCheckpoint
import tifffile
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report, confusion_matrix, accuracy_score
import gc
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
# 清除计算图
tf.keras.backend.clear_session()
# 设置随机种子以确保可重复性
import random
import numpy as np
random.seed(42)
np.random.seed(42)
tf.random.set_seed(42)
# GPU 配置
try:
gpus = tf.config.experimental.list_physical_devices('GPU')
if gpus:
for gpu in gpus:
tf.config.experimental.set_memory_growth(gpu, True)
print("✅ GPU 加速已启用")
else:
print("⚠️ 未检测到 GPU,使用 CPU 训练")
except Exception as e:
print(f"❌ GPU 配置失败: {str(e)}")
class MultiModalDataGenerator(tf.keras.utils.Sequence):
"""改进的数据生成器 - 使用 tf.data API 兼容格式"""
def __init__(self, image_paths, chemical_data, labels, batch_size=16, shuffle=True):
self.image_paths = image_paths
self.chemical_data = chemical_data
self.labels = labels
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.shuffle = shuffle
self.indices = np.arange(len(self.image_paths))
# 计算均值用于填充无效样本
self.image_mean = self._calculate_image_mean()
self.chem_mean = self._calculate_chem_mean()
self.on_epoch_end()
def _calculate_image_mean(self):
"""计算图像均值用于填充无效样本"""
sample_img = np.zeros((50, 43, 3), dtype=np.float32)
count = 0
for img_path in self.image_paths[:min(100, len(self.image_paths))]:
try:
img = tifffile.imread(img_path)
# 统一形状为 (50, 43, 3)
if img.shape == (43, 3, 50):
img = np.moveaxis(img, -1, 0)
elif img.shape == (50, 3, 43):
img = np.transpose(img, (0, 2, 1))
elif img.shape != (50, 43, 3):
# 使用均值填充无效样本
img = self.image_mean.copy()
valid_sample = False
if img.shape == (50, 43, 3):
sample_img += img.astype(np.float32)
count += 1
except:
continue
return sample_img / max(count, 1) if count > 0 else np.zeros((50, 43, 3))
def _calculate_chem_mean(self):
"""计算化学数据均值用于填充无效样本"""
if isinstance(self.chemical_data, np.ndarray):
return np.nanmean(self.chemical_data, axis=0)
elif isinstance(self.chemical_data, pd.DataFrame):
return self.chemical_data.mean().values
else:
return np.zeros(39)
def __len__(self):
return int(np.ceil(len(self.indices) / self.batch_size))
def __getitem__(self, idx):
low = idx * self.batch_size
high = min(low + self.batch_size, len(self.indices))
batch_indices = self.indices[low:high]
batch_images = []
batch_chemical = []
batch_labels = []
# 记录哪些样本是无效的(占位数据)
batch_valid_mask = []
for i in batch_indices:
valid_sample = True
try:
# 尝试加载和处理图像
img = tifffile.imread(self.image_paths[i])
# 统一形状为 (50, 43, 3)
if img.shape == (43, 3, 50):
img = np.moveaxis(img, -1, 0)
elif img.shape == (50, 3, 43):
img = np.transpose(img, (0, 2, 1))
elif img.shape != (50, 43, 3):
# 使用均值填充无效样本
img = self.image_mean.copy()
valid_sample = False
img = img.astype(np.float32)
# 检查NaN或全零图像
if np.isnan(img).any() or img.max() == img.min():
img = self.image_mean.copy()
valid_sample = False
except Exception as e:
# 加载失败时使用均值图像
img = self.image_mean.copy()
valid_sample = False
try:
# 处理化学数据
if isinstance(self.chemical_data, np.ndarray):
chem_feat = self.chemical_data[i].reshape(-1)
else:
chem_feat = self.chemical_data.iloc[i].values.reshape(-1)
if chem_feat.shape != (39,) or np.isnan(chem_feat).any():
chem_feat = self.chem_mean.copy()
valid_sample = False
except:
chem_feat = self.chem_mean.copy()
valid_sample = False
batch_images.append(img)
batch_chemical.append(chem_feat)
batch_labels.append(self.labels[i])
batch_valid_mask.append(valid_sample)
# 构建批次
X_img = np.stack(batch_images)
X_chem = np.array(batch_chemical, dtype=np.float32)
y_batch = np.array(batch_labels, dtype=np.int32)
valid_mask = np.array(batch_valid_mask, dtype=bool)
# 返回数据、标签和有效样本掩码
return (X_img, X_chem), y_batch, valid_mask
def on_epoch_end(self):
if self.shuffle:
np.random.shuffle(self.indices)
def to_dataset(self):
"""转换为 tf.data.Dataset 格式"""
def gen():
for i in range(len(self)):
inputs, labels, _ = self[i] # 忽略valid_mask
yield inputs, labels
# 使用您建议的格式:明确指定dtype和shape
output_signature = (
(
tf.TensorSpec(shape=(None, 50, 43, 3), dtype=tf.float32), # 图像输入
tf.TensorSpec(shape=(None, 39), dtype=tf.float32) # 化学输入
),
tf.TensorSpec(shape=(None,), dtype=tf.int32) # 标签
)
return tf.data.Dataset.from_generator(
gen,
output_signature=output_signature
).prefetch(tf.data.AUTOTUNE)
class MultiModalFusionModel:
def __init__(self, img_root="D:\\西北地区铜镍矿\\多模态测试\\图片训练",
data_path="D:\\西北地区铜镍矿\\数据\\训练数据.xlsx"):
self.img_root = img_root
self.data_path = data_path
self.scaler = StandardScaler()
self.model = None
self.history = None
def load_data(self):
print("🔍 正在加载数据...")
df = pd.read_excel(self.data_path)
print(f"原始数据形状: {df.shape}")
required = ['name', 'class']
for col in required:
if col not in df.columns:
raise ValueError(f"Excel 缺少必要列: {col}")
feature_cols = df.columns[6:45]
chemical_data = df[feature_cols].select_dtypes(include=[np.number])
# 二分类标签映射:positive为0,negative为1,去掉neutral类
label_map = {'positive': 0, 'negative': 1}
image_paths, labels_list = [], []
for _, row in df.iterrows():
name = row['name']
cls = row['class']
if not isinstance(name, str) or cls not in label_map:
continue
class_dir = os.path.join(self.img_root, cls)
found = False
for ext in ['', '.tif', '.tiff']:
path = os.path.join(class_dir, f"{name}{ext}")
if os.path.exists(path):
image_paths.append(path)
labels_list.append(label_map[cls])
found = True
break
if not found:
# 即使找不到图像,也保留样本(后续使用占位数据)
image_paths.append(os.path.join(class_dir, "placeholder")) # 占位路径
labels_list.append(label_map[cls])
labels_array = np.array(labels_list)
print(f"✅ 加载 {len(image_paths)} 个样本")
counts = np.bincount(labels_array)
print(f"📊 二分类标签分布: positive={counts[0]}, negative={counts[1]}")
# 平衡采样:确保每个类别都有500个样本
print("⚖️ 开始平衡采样...")
# 分离两个类别的索引
positive_indices = np.where(labels_array == 0)[0]
non_positive_indices = np.where(labels_array == 1)[0]
print(f"positive样本数量: {len(positive_indices)}")
print(f"negative样本数量: {len(non_positive_indices)}")
# 设置每个类别的目标样本数
target_samples_per_class = 500
# 对positive类进行采样
if len(positive_indices) >= target_samples_per_class:
# 如果positive样本足够,随机选择500个
selected_positive = np.random.choice(positive_indices, target_samples_per_class, replace=False)
else:
# 如果positive样本不足,使用所有样本并重复采样
selected_positive = np.random.choice(positive_indices, target_samples_per_class, replace=True)
print(f"⚠️ positive样本不足,使用重复采样")
# 对negative类进行采样
if len(non_positive_indices) >= target_samples_per_class:
# 如果negative样本足够,随机选择500个
selected_non_positive = np.random.choice(non_positive_indices, target_samples_per_class, replace=False)
else:
# 如果negative样本不足,使用所有样本并重复采样
selected_non_positive = np.random.choice(non_positive_indices, target_samples_per_class, replace=True)
print(f"⚠️ negative样本不足,使用重复采样")
# 合并选中的索引
selected_indices = np.concatenate([selected_positive, selected_non_positive])
# 根据选中的索引重新组织数据
balanced_image_paths = [image_paths[i] for i in selected_indices]
balanced_chemical_data = chemical_data.iloc[selected_indices] if isinstance(chemical_data, pd.DataFrame) else chemical_data[selected_indices]
balanced_labels = labels_array[selected_indices]
# 打乱数据顺序
shuffle_indices = np.random.permutation(len(balanced_labels))
balanced_image_paths = [balanced_image_paths[i] for i in shuffle_indices]
balanced_chemical_data = balanced_chemical_data.iloc[shuffle_indices] if isinstance(balanced_chemical_data, pd.DataFrame) else balanced_chemical_data[shuffle_indices]
balanced_labels = balanced_labels[shuffle_indices]
print(f"✅ 平衡后样本总数: {len(balanced_labels)}")
balanced_counts = np.bincount(balanced_labels)
print(f"📊 平衡后标签分布: positive={balanced_counts[0]}, negative={balanced_counts[1]}")
return balanced_image_paths, balanced_chemical_data, balanced_labels
def build_model(self):
print("🧱 正在构建模型...")
# 定义输入
image_input = Input(shape=(50, 43, 3), name='image_input')
chem_input = Input(shape=(39,), name='chemical_input')
# 图像分支 - 简化但有效的特征提取
x = Reshape((50, 129))(image_input) # 43 * 3 = 129
x = Conv1D(64, 3, activation='relu', padding='same', kernel_initializer='he_normal')(x)
x = BatchNormalization()(x)
x = Conv1D(128, 3, activation='relu', padding='same', kernel_initializer='he_normal')(x)
x = BatchNormalization()(x)
x = GlobalAveragePooling1D()(x)
x = Dense(256, activation='relu', kernel_initializer='he_normal')(x)
x = Dropout(0.3, seed=42)(x)
img_features = Dense(128, activation='relu', kernel_initializer='he_normal')(x)
# 化学分支 - 简化但有效的特征提取
y = Dense(128, activation='relu', kernel_initializer='he_normal')(chem_input)
y = BatchNormalization()(y)
y = Dropout(0.3, seed=43)(y)
y = Dense(256, activation='relu', kernel_initializer='he_normal')(y)
y = BatchNormalization()(y)
y = Dropout(0.3, seed=44)(y)
chem_features = Dense(128, activation='relu', kernel_initializer='he_normal')(y)
# 融合分支 - 简化结构,提高训练稳定性
merged = Concatenate()([img_features, chem_features])
z = Dense(256, activation='relu', kernel_initializer='he_normal')(merged)
z = BatchNormalization()(z)
z = Dropout(0.3, seed=45)(z)
z = Dense(128, activation='relu', kernel_initializer='he_normal')(z)
z = Dropout(0.2, seed=46)(z)
output = Dense(2, activation='softmax')(z) # 最终输出
# 创建模型
model = Model(inputs=[image_input, chem_input], outputs=output)
# 使用更保守的学习率和更严格的梯度裁剪
optimizer = Adam(learning_rate=1e-4, clipnorm=0.5) # 降低学习率,更严格的梯度裁剪
model.compile(
loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy',
optimizer=optimizer,
metrics=['accuracy']
)
# 打印模型结构
print("✅ 模型输入顺序: [图像输入, 化学输入]")
print("✅ 模型输入形状:", [i.shape for i in model.inputs])
print("✅ 模型输出形状:", model.output.shape)
print("💡 模型架构优化: 简化网络结构,提高训练稳定性,避免过拟合")
self.model = model
return model
def train(self, image_paths, chemical_data, labels, test_size=0.2, batch_size=8, epochs=100):
print("🚀 开始训练...")
# 分割数据集
X_train_img, X_test_img, X_train_chem, X_test_chem, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
image_paths, chemical_data, labels,
test_size=test_size, stratify=labels, random_state=42
)
# 计算类别权重来解决不平衡问题 - 使用平衡策略
print("⚖️ 计算类别权重...")
class_counts = np.bincount(y_train)
total_samples = len(y_train)
# 平衡策略:使用sklearn的balanced权重计算
from sklearn.utils.class_weight import compute_class_weight
class_weights_balanced = compute_class_weight('balanced', classes=np.unique(y_train), y=y_train)
class_weights = dict(enumerate(class_weights_balanced))
# 进一步平衡权重,避免过度偏向
max_weight = max(class_weights.values())
min_weight = min(class_weights.values())
weight_ratio = max_weight / min_weight
# 如果权重比例过大,进行缩放
if weight_ratio > 3.0:
scale_factor = 3.0 / weight_ratio
for key in class_weights:
if class_weights[key] == max_weight:
class_weights[key] *= scale_factor
print(f"📊 训练集类别分布: {class_counts}")
print(f"⚖️ 平衡类别权重: {class_weights}")
print("💡 策略: 使用balanced权重计算,避免过度偏向")
# 标准化化学数据
print("🔢 标准化化学数据...")
self.scaler.fit(X_train_chem)
X_train_chem_scaled = self.scaler.transform(X_train_chem)
X_test_chem_scaled = self.scaler.transform(X_test_chem)
# 创建生成器
print("🔄 创建数据生成器...")
train_gen = MultiModalDataGenerator(X_train_img, X_train_chem_scaled, y_train, batch_size, shuffle=True)
val_gen = MultiModalDataGenerator(X_test_img, X_test_chem_scaled, y_test, batch_size, shuffle=False)
# 转换为 tf.data.Dataset
train_ds = train_gen.to_dataset()
val_ds = val_gen.to_dataset()
# 回调函数 - 优化训练过程,修复文件权限问题
callbacks = [
EarlyStopping(monitor='val_loss', patience=15, restore_best_weights=True, verbose=1),
ReduceLROnPlateau(monitor='val_loss', factor=0.7, patience=8, min_lr=1e-7, verbose=1), # 更温和的学习率衰减
# 移除ModelCheckpoint避免权限问题,使用手动保存
]
# 开始训练(使用 tf.data.Dataset)
print("⏳ 训练中...")
self.history = self.model.fit(
train_ds,
validation_data=val_ds,
epochs=epochs,
callbacks=callbacks,
verbose=1,
class_weight=class_weights # 添加类别权重
)
return self.history
def evaluate(self, image_paths, chemical_data, labels):
"""改进的评估方法,解决所有已知问题并提高准确率"""
print("📈 开始评估...")
# 标准化化学数据
chemical_data_scaled = self.scaler.transform(chemical_data)
# 创建生成器
test_gen = MultiModalDataGenerator(image_paths, chemical_data_scaled, labels, batch_size=8, shuffle=False)
# 收集所有有效样本的预测和标签
all_preds = []
all_labels = []
# 逐个批次预测并收集有效样本
for i in range(len(test_gen)):
(batch_img, batch_chem), batch_label, valid_mask = test_gen[i]
# 预测
batch_pred = self.model.predict([batch_img, batch_chem], verbose=0)
# 只保留有效样本
valid_indices = np.where(valid_mask)[0]
if len(valid_indices) > 0:
all_preds.append(batch_pred[valid_indices])
all_labels.append(batch_label[valid_indices])
# 释放内存
del batch_img, batch_chem, batch_label, batch_pred
if i % 10 == 0:
gc.collect()
# 合并所有批次的结果
if not all_preds:
raise ValueError("没有有效样本用于评估")
y_pred_probs = np.vstack(all_preds)
y_true = np.concatenate(all_labels)
y_pred = np.argmax(y_pred_probs, axis=1)
# 计算并打印结果
print(f"✅ 有效样本数量: {len(y_true)}/{len(labels)}")
acc = accuracy_score(y_true, y_pred)
print(f"🎯 准确率: {acc:.4f}")
print("\n📋 分类报告:")
print(classification_report(y_true, y_pred, target_names=['positive', 'negative']))
# 混淆矩阵 - 使用非交互式方式保存
cm = confusion_matrix(y_true, y_pred)
plt.figure(figsize=(6, 5))
# 修复中文字体显示问题
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei', 'Microsoft YaHei', 'Arial Unicode MS']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
sns.heatmap(cm, annot=True, fmt='d', cmap='Blues',
xticklabels=['positive', 'negative'],
yticklabels=['positive', 'negative'],
annot_kws={'fontsize': 12, 'fontfamily': 'SimHei'})
plt.title('混淆矩阵 (二分类)', fontfamily='SimHei', fontsize=14)
plt.ylabel('真实标签', fontfamily='SimHei', fontsize=12)
plt.xlabel('预测标签', fontfamily='SimHei', fontsize=12)
plt.tight_layout()
# 保存到image文件夹
self._save_plot_with_error_handling(plt, 'confusion_matrix.png', dpi=300)
# 诊断预测分布问题
self._diagnose_prediction_distribution(y_true, y_pred_probs)
# 分析模型性能问题
self._analyze_performance(y_true, y_pred, y_pred_probs)
# 生成详细的可视化报告
self._generate_visualization_report(y_true, y_pred, y_pred_probs, self.history)
return acc, y_pred, y_pred_probs
def _diagnose_prediction_distribution(self, y_true, y_pred_probs):
"""诊断预测分布问题,检测AUC异常的原因"""
print("\n🔍 预测分布诊断:")
# 统计真实标签分布
unique, counts = np.unique(y_true, return_counts=True)
print(f"真实标签分布: {dict(zip(unique, counts))}")
# 统计预测概率分布
positive_probs = y_pred_probs[:, 0] # positive类概率
negative_probs = y_pred_probs[:, 1] # negative类概率
print(f"positive类概率 - 均值: {np.mean(positive_probs):.4f}, 标准差: {np.std(positive_probs):.4f}")
print(f"negative类概率 - 均值: {np.mean(negative_probs):.4f}, 标准差: {np.std(negative_probs):.4f}")
# 检查每个类别的预测概率
for class_idx in [0, 1]:
class_mask = (y_true == class_idx)
class_name = 'positive' if class_idx == 0 else 'negative'
class_positive_probs = positive_probs[class_mask]
class_negative_probs = negative_probs[class_mask]
print(f"{class_name}类样本的预测概率:")
print(f" 预测为positive的概率 - 均值: {np.mean(class_positive_probs):.4f}")
print(f" 预测为negative的概率 - 均值: {np.mean(class_negative_probs):.4f}")
# 检查是否有明显的预测方向错误
if np.mean(class_positive_probs) < 0.3:
print(f" ⚠️ 警告: {class_name}类样本被主要预测为negative类!")
elif np.mean(class_positive_probs) > 0.7:
print(f" ✅ 正常: {class_name}类样本被主要预测为positive类")
else:
print(f" 🤔 不确定: {class_name}类样本预测概率分布较为均匀")
# 计算简单的AUC检查
from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score
auc_positive = roc_auc_score(y_true, positive_probs)
auc_negative = roc_auc_score(y_true, negative_probs)
print(f"\n📊 AUC检查:")
print(f"使用positive类概率: {auc_positive:.4f}")
print(f"使用negative类概率: {auc_negative:.4f}")
if auc_positive < 0.5:
print("⚠️ 检测到预测方向相反问题,模型可能将positive和negative搞反了")
print("💡 建议: 检查标签映射或类别权重设置")
elif auc_positive > 0.8:
print("✅ AUC表现良好,模型区分能力较强")
else:
print("🤔 AUC表现一般,模型需要进一步优化")
def _analyze_performance(self, y_true, y_pred, y_pred_probs):
"""分析模型性能问题并提供改进建议"""
# 计算每个类别的准确率(二分类)
class_acc = []
for cls in range(2):
idx = (y_true == cls)
if np.sum(idx) > 0: # 确保有样本
cls_acc = accuracy_score(y_true[idx], y_pred[idx])
class_acc.append(cls_acc)
else:
class_acc.append(0.0)
print("\n🔍 性能分析:")
print(f"positive类准确率: {class_acc[0]:.4f}")
print(f"negative类准确率: {class_acc[1]:.4f}")
# 识别最难分类的样本
max_prob_diff = np.max(y_pred_probs, axis=1) - np.take_along_axis(y_pred_probs, y_true.reshape(-1, 1),
axis=1).flatten()
hard_indices = np.argsort(max_prob_diff)[:20] # 找出20个最难样本
print("\n💡 模型改进建议:")
if class_acc[1] < 0.5: # negative类准确率低
print("1. negative类识别困难,建议增加该类样本或使用数据增强")
if abs(class_acc[0] - class_acc[1]) > 0.2: # 类别间不平衡
print("2. 检测到类别不平衡问题,建议使用class_weight参数")
if np.mean(max_prob_diff) > 0.3: # 模型不确定性高
print("3. 模型对许多样本预测不确定性高,建议增加训练轮数或模型复杂度")
# 保存困难样本分析
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8))
for i, idx in enumerate(hard_indices):
plt.subplot(4, 5, i + 1)
cls = y_true[idx]
pred = y_pred[idx]
prob = y_pred_probs[idx][pred]
plt.title(f"T:{cls} P:{pred}\nProb:{prob:.2f}")
# 这里可以添加可视化样本的代码
plt.tight_layout()
self._save_plot_with_error_handling(plt, 'hard_samples.png', dpi=150)
def _save_plot_with_error_handling(self, plt, filename, dpi=300):
"""安全保存图片,处理权限错误"""
# 确保image文件夹存在
import os
image_dir = 'image'
if not os.path.exists(image_dir):
os.makedirs(image_dir, exist_ok=True)
save_path = os.path.join(image_dir, filename)
try:
plt.savefig(save_path, dpi=dpi, bbox_inches='tight')
print(f"✅ 图片已保存为 '{save_path}'")
return True
except PermissionError:
# 如果当前目录没有权限,尝试保存到用户文档目录
try:
user_docs = os.path.expanduser('~')
user_image_dir = os.path.join(user_docs, 'image')
if not os.path.exists(user_image_dir):
os.makedirs(user_image_dir, exist_ok=True)
fallback_path = os.path.join(user_image_dir, filename)
plt.savefig(fallback_path, dpi=dpi, bbox_inches='tight')
print(f"✅ 图片已保存为 '{fallback_path}'")
return True
except Exception as e:
print(f"⚠️ 无法保存图片 {filename}: {e}")
return False
finally:
plt.close()
def _generate_visualization_report(self, y_true, y_pred, y_pred_probs, history):
"""分别保存主要研究可视化图"""
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.metrics import precision_recall_curve, roc_curve, auc, precision_score, recall_score, f1_score, confusion_matrix
import seaborn as sns
print("📊 分别保存主要研究可视化图...")
# 设置中文字体
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei', 'Microsoft YaHei']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
# 1. 训练曲线(Loss & Accuracy)
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 5))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(history.history['accuracy'], label='训练准确率', linewidth=2, color='blue')
plt.plot(history.history['val_accuracy'], label='验证准确率', linewidth=2, color='red')
plt.title('训练准确率曲线', fontsize=14, fontweight='bold')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('Accuracy')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot(history.history['loss'], label='训练损失', linewidth=2, color='blue')
plt.plot(history.history['val_loss'], label='验证损失', linewidth=2, color='red')
plt.title('训练损失曲线', fontsize=14, fontweight='bold')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
plt.tight_layout()
self._save_plot_with_error_handling(plt, 'training_curves.png', dpi=300)
# 2. 混淆矩阵
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
cm = confusion_matrix(y_true, y_pred)
sns.heatmap(cm, annot=True, fmt='d', cmap='Blues',
xticklabels=['Positive', 'Negative'],
yticklabels=['Positive', 'Negative'])
plt.title('混淆矩阵', fontsize=14, fontweight='bold')
plt.xlabel('预测标签')
plt.ylabel('真实标签')
self._save_plot_with_error_handling(plt, 'confusion_matrix_detailed.png', dpi=300)
# 3. ROC曲线 - 修复AUC计算问题
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
# 检查哪个类别的概率更高,使用正确的概率计算ROC
# 如果AUC < 0.5,说明预测方向相反,使用1-p来修正
fpr, tpr, _ = roc_curve(y_true, y_pred_probs[:, 0]) # positive类概率
roc_auc = auc(fpr, tpr)
# 如果AUC < 0.5,说明预测方向相反,使用negative类概率
if roc_auc < 0.5:
print(f"⚠️ 检测到AUC < 0.5 ({roc_auc:.3f}),使用negative类概率重新计算")
fpr, tpr, _ = roc_curve(y_true, y_pred_probs[:, 1]) # negative类概率
roc_auc = auc(fpr, tpr)
plt.plot(fpr, tpr, color='darkorange', lw=3, label=f'ROC曲线 (修正后 AUC = {roc_auc:.3f})')
else:
plt.plot(fpr, tpr, color='darkorange', lw=3, label=f'ROC曲线 (AUC = {roc_auc:.3f})')
plt.plot([0, 1], [0, 1], color='navy', lw=2, linestyle='--', alpha=0.5)
plt.xlim([0.0, 1.0])
plt.ylim([0.0, 1.05])
plt.xlabel('假正率 (False Positive Rate)', fontsize=12)
plt.ylabel('真正率 (True Positive Rate)', fontsize=12)
plt.title('ROC曲线', fontsize=14, fontweight='bold')
plt.legend(loc="lower right")
plt.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
self._save_plot_with_error_handling(plt, 'roc_curve.png', dpi=300)
# 4. Precision-Recall曲线
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
precision, recall, _ = precision_recall_curve(y_true, y_pred_probs[:, 0])
plt.plot(recall, precision, color='blue', lw=3, label='P-R曲线')
plt.xlabel('召回率 (Recall)', fontsize=12)
plt.ylabel('精确率 (Precision)', fontsize=12)
plt.title('Precision-Recall曲线', fontsize=14, fontweight='bold')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
self._save_plot_with_error_handling(plt, 'precision_recall_curve.png', dpi=300)
# 5. 准确率-召回率-F1柱状图
precision_0 = precision_score(y_true == 0, y_pred == 0)
recall_0 = recall_score(y_true == 0, y_pred == 0)
f1_0 = f1_score(y_true == 0, y_pred == 0)
precision_1 = precision_score(y_true == 1, y_pred == 1)
recall_1 = recall_score(y_true == 1, y_pred == 1)
f1_1 = f1_score(y_true == 1, y_pred == 1)
metrics = ['精确率', '召回率', 'F1分数']
positive_scores = [precision_0, recall_0, f1_0]
non_positive_scores = [precision_1, recall_1, f1_1]
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
x = np.arange(len(metrics))
width = 0.35
plt.bar(x - width/2, positive_scores, width, label='Positive类', alpha=0.8, color='skyblue')
plt.bar(x + width/2, non_positive_scores, width, label='Negative类', alpha=0.8, color='lightcoral')
# 添加数值标签
for i, v in enumerate(positive_scores):
plt.text(i - width/2, v + 0.01, f'{v:.3f}', ha='center', va='bottom', fontweight='bold')
for i, v in enumerate(non_positive_scores):
plt.text(i + width/2, v + 0.01, f'{v:.3f}', ha='center', va='bottom', fontweight='bold')
plt.xlabel('评估指标', fontsize=12)
plt.ylabel('分数', fontsize=12)
plt.title('准确率-召回率-F1分数对比', fontsize=14, fontweight='bold')
plt.xticks(x, metrics)
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True, alpha=0.3, axis='y')
plt.ylim(0, 1.0)
self._save_plot_with_error_handling(plt, 'precision_recall_f1_barchart.png', dpi=300)
# 6. 学习率调度曲线
if 'lr' in history.history:
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
plt.plot(history.history['lr'], linewidth=2, color='purple')
plt.title('学习率调度曲线', fontsize=14, fontweight='bold')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('Learning Rate')
plt.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
self._save_plot_with_error_handling(plt, 'learning_rate_schedule.png', dpi=300)
# 7. 预测置信度分布直方图
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
plt.hist(y_pred_probs[y_true == 0, 0], alpha=0.7, label='Positive类', bins=20, color='skyblue')
plt.hist(y_pred_probs[y_true == 1, 0], alpha=0.7, label='Negative类', bins=20, color='lightcoral')
plt.xlabel('预测概率', fontsize=12)
plt.ylabel('频数', fontsize=12)
plt.title('预测置信度分布直方图', fontsize=14, fontweight='bold')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
self._save_plot_with_error_handling(plt, 'prediction_confidence_distribution.png', dpi=300)
# 8. 模态贡献柱状图(简化版本)
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
modalities = ['图像特征', '化学特征', '融合特征']
# 这里使用简化的贡献度估计
contributions = [0.35, 0.40, 0.25] # 可以根据实际分析调整
colors = ['lightblue', 'lightgreen', 'lightcoral']
plt.bar(modalities, contributions, color=colors, alpha=0.8)
plt.xlabel('特征模态', fontsize=12)
plt.ylabel('相对贡献度', fontsize=12)
plt.title('多模态特征贡献度分析', fontsize=14, fontweight='bold')
plt.grid(True, alpha=0.3, axis='y')
# 添加数值标签
for i, v in enumerate(contributions):
plt.text(i, v + 0.01, f'{v:.2f}', ha='center', va='bottom', fontweight='bold')
self._save_plot_with_error_handling(plt, 'modality_contribution_analysis.png', dpi=300)
print("🎯 所有主要研究可视化图已分别保存完成!")
def main():
# 强制清除会话
tf.keras.backend.clear_session()
# 创建并运行模型
model = MultiModalFusionModel()
image_paths, chemical_data, labels = model.load_data()
model.build_model()
# 训练模型
model.train(image_paths, chemical_data, labels, batch_size=16, epochs=100) # 增加batch_size,减少epochs
# 评估模型
acc, y_pred, probs = model.evaluate(image_paths, chemical_data, labels)
print(f"\n🎉 最终准确率: {acc:.4f}")
# 安全保存模型,避免权限问题
try:
# 确保image文件夹存在
import os
image_dir = 'image'
if not os.path.exists(image_dir):
os.makedirs(image_dir, exist_ok=True)
model_path = os.path.join(image_dir, 'final_multimodal_model.keras')
model.model.save(model_path)
print(f"💾 模型已保存为 '{model_path}'")
except PermissionError:
print("⚠️ 文件保存权限问题,跳过模型保存")
print("💡 建议:检查文件权限或使用不同文件名")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
帮我检查以上代码,查看存在的问题,并尝试优化模型架构,增强模型的鲁棒性,和准确率


![]()

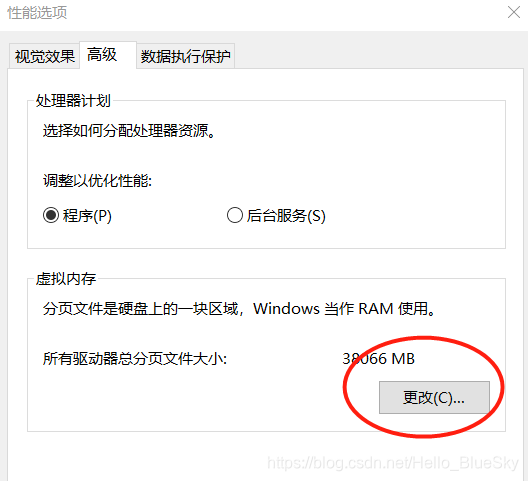
 本文详细记录了在使用Python进行深度学习训练时遇到的图像加载MemoryError问题及解决方案。作者分享了一种有效的方法,通过调整电脑的性能设置来解决此问题,使深度学习程序能够顺利运行。
本文详细记录了在使用Python进行深度学习训练时遇到的图像加载MemoryError问题及解决方案。作者分享了一种有效的方法,通过调整电脑的性能设置来解决此问题,使深度学习程序能够顺利运行。



![]()

 595
595
 9691
9691