Radar Installation
| Time Limit: 1000MS | Memory Limit: 10000K | |
| Total Submissions: 69114 | Accepted: 15506 |
Description
Assume the coasting is an infinite straight line. Land is in one side of coasting, sea in the other. Each small island is a point locating in the sea side. And any radar installation, locating on the coasting, can only cover d distance, so an island in the
sea can be covered by a radius installation, if the distance between them is at most d.
We use Cartesian coordinate system, defining the coasting is the x-axis. The sea side is above x-axis, and the land side below. Given the position of each island in the sea, and given the distance of the coverage of the radar installation, your task is to write a program to find the minimal number of radar installations to cover all the islands. Note that the position of an island is represented by its x-y coordinates.
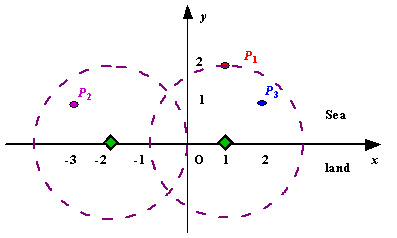
Figure A Sample Input of Radar Installations
We use Cartesian coordinate system, defining the coasting is the x-axis. The sea side is above x-axis, and the land side below. Given the position of each island in the sea, and given the distance of the coverage of the radar installation, your task is to write a program to find the minimal number of radar installations to cover all the islands. Note that the position of an island is represented by its x-y coordinates.

Figure A Sample Input of Radar Installations
Input
The input consists of several test cases. The first line of each case contains two integers n (1<=n<=1000) and d, where n is the number of islands in the sea and d is the distance of coverage of the radar installation. This is followed by n lines each containing
two integers representing the coordinate of the position of each island. Then a blank line follows to separate the cases.
The input is terminated by a line containing pair of zeros
The input is terminated by a line containing pair of zeros
Output
For each test case output one line consisting of the test case number followed by the minimal number of radar installations needed. "-1" installation means no solution for that case.
Sample Input
3 2 1 2 -3 1 2 1 1 2 0 2 0 0
Sample Output
Case 1: 2 Case 2: 1
题目大意:在平面上有n个点,告诉你圆的半径为d,求在x轴上最少需要几个点可以使得以这些点为圆心,半径为d的圆覆盖所有的n个点
思路:对于每一个点,找出他所对应的最左雷达位置与最右雷达位置,便有n个区间,从左向右遍历判断下一个区间能否与上一个区间的交集重合,若能重合则可共用同一个雷达。若能公用一个雷达则更新交集范围。注意d<0的情形,另外若|y|>d则可判断-1
实现代码:
//************************************************************************//
//*Author : Handsome How *//
//************************************************************************//
//#pragma comment(linker, "/STA CK:1024000000,1024000000")
#pragma warning(disable:4996)
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <deque>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <bitset>
#include <algorithm>
#include <functional>
#include <numeric>
#include <utility>
#include <complex>
#include <sstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <ctime>
#include <cassert>
#define fur(i,a,b) for(int i=(a);i<=(b);i++)
#define furr(i,a,b) for(int i=(a);i>=(b);i--)
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int MAXN = 1000 + 20;
struct Node
{
double l;
double r;
}len[MAXN];
bool compare(Node A, Node B)
{
if (A.l != B.l)return A.l < B.l;
else return A.r < B.r;
}
int main()
{
//freopen("E:\\data.in", "r", stdin);
//freopen("E:\\data.out", "w", stdout);
int n,kase=0;
double d;
while (scanf("%d%lfd", &n,&d) != EOF)
{
if(n == 0 && d == 0)break;
printf("Case %d: ",++kase);
bool legal = true;
double x, y,t;
fur(i, 0, n-1)
{
scanf("%lf%lf", &x,&y);
if (y > d || y < d*(-1.0))legal = false; //最高点能否被雷达范围覆盖
t = sqrt(d*d - y*y);
len[i].l = x - t;
len[i].r = x + t;
}
if (d < 0) { printf("-1\n"); continue; }
if(legal==false) { printf("-1\n"); continue; }
sort(len, len + n, compare);
//fur(i, 0, n - 1)printf("%lf %lf\n", len[i].l, len[i].r);
int last = 0,cnt=1;
fur(i, 1, n - 1)
{
if (len[i].l <= len[last].r)
{
len[last].l = max(len[last].l, len[i].l);
len[last].r = min(len[last].r, len[i].r);
continue; //交集的更新
}
last = i; //新开一个区间
cnt++;
}
printf("%d\n",cnt);
}
return 0;
}





 本文介绍了一种算法,用于解决在平面坐标系中如何利用最少数量的雷达安装位置来覆盖所有岛屿的问题。通过计算每个岛屿对应的雷达覆盖范围,采用区间合并的方法,实现了雷达位置的最优布局。
本文介绍了一种算法,用于解决在平面坐标系中如何利用最少数量的雷达安装位置来覆盖所有岛屿的问题。通过计算每个岛屿对应的雷达覆盖范围,采用区间合并的方法,实现了雷达位置的最优布局。
















 1817
1817

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








