TcpServer class的功能是管理accept(2)获得的TcpConnection。TcpServer是供用户直接使用的,生命期由用户控制。
一、上下文类关系图
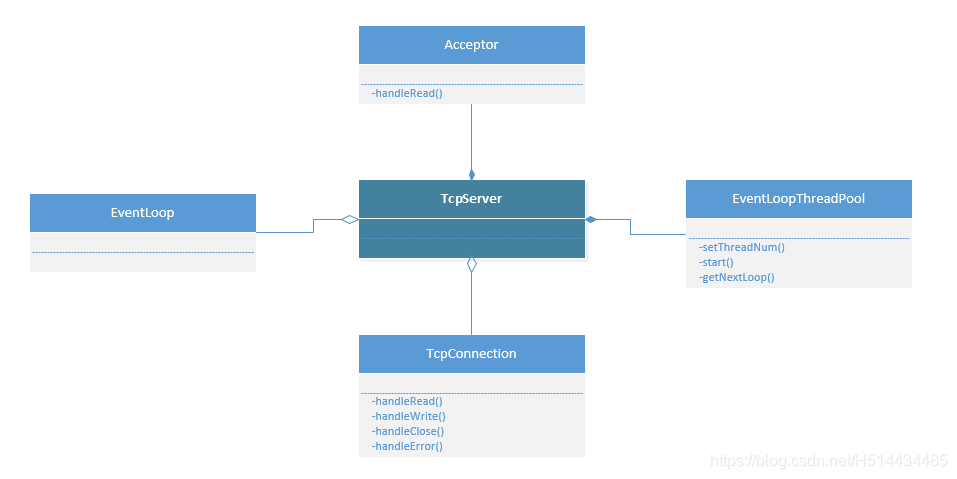
- Acceptor,供TcpServer内部使用,用于获得新连接的fd。
- EventLoop,用户最开始初始化的Loop程序。
- TcpConnection,TcpServer对每一个新来的连接都会创建一个TcpConnection。
- EventLoopThreadPool,初始化线程池,每个新的TcpConnection对应线程池中一个线程(如果用户创建了线程池的话)。
二、使用举例
#include "TcpServer.h"
#include "EventLoop.h"
#include "InetAddress.h"
#include <stdio.h>
void onConnection(const muduo::TcpConnectionPtr& conn)
{
if (conn->connected())
{
printf("onConnection(): tid=%d new connection [%s] from %s\n",
muduo::CurrentThread::tid(),
conn->name().c_str(),
conn->peerAddress().toHostPort().c_str());
}
else
{
printf("onConnection(): tid=%d connection [%s] is down\n",
muduo::CurrentThread::tid(),
conn->name().c_str());
}
}
void onMessage(const muduo::TcpConnectionPtr& conn,
muduo::Buffer* buf,
muduo::Timestamp receiveTime)
{
printf("onMessage(): tid=%d received %zd bytes from connection [%s] at %s\n",
muduo::CurrentThread::tid(),
buf->readableBytes(),
conn->name().c_str(),
receiveTime.toFormattedString().c_str());
printf("onMessage(): [%s]\n", buf->retrieveAsString().c_str());
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
printf("main(): pid = %d\n", getpid());
muduo::InetAddress listenAddr(9981);
muduo::EventLoop loop;
muduo::TcpServer server(&loop, listenAddr);
server.setConnectionCallback(onConnection);
server.setMessageCallback(onMessage);
if (argc > 1) {
server.setThreadNum(atoi(argv[1]));
}
server.start();
loop.loop();
}
- 设置本地网络地址。
- 初始化全局EventLoop。
- 设置连接Or断开回调、设置消息到达回调。
- 设置线程池大小。
- 启动服务。
- EventLoop循环执行。
三、源码分析
TcpServer.h
class TcpServer : boost::noncopyable
{
public:
typedef boost::function<void(EventLoop*)> ThreadInitCallback;
//TcpServer(EventLoop* loop, const InetAddress& listenAddr);
TcpServer(EventLoop* loop,
const InetAddress& listenAddr,
const string& nameArg);
~TcpServer(); // force out-line dtor, for scoped_ptr members.
const string& hostport() const { return hostport_; }
const string& name() const { return name_; }
/// Set the number of threads for handling input.
///
/// Always accepts new connection in loop's thread.
/// Must be called before @c start
/// @param numThreads
/// - 0 means all I/O in loop's thread, no thread will created.
/// this is the default value.
/// - 1 means all I/O in another thread.
/// - N means a thread pool with N threads, new connections
/// are assigned on a round-robin basis.
void setThreadNum(int numThreads); //设置线程池中线程个数
void setThreadInitCallback(const ThreadInitCallback& cb) //设置线程初始化回调函数,一般用于启动线程服务时,初始化调用这得一些资源数据。
{ threadInitCallback_ = cb; }
/// Starts the server if it's not listenning.
///
/// It's harmless to call it multiple times.
/// Thread safe.
void start(); //开始TcpServer服务
/// Set connection callback.
/// Not thread safe.
void setConnectionCallback(const ConnectionCallback& cb) //设置链路连接Or断开时的回调
{ connectionCallback_ = cb; }
/// Set message callback.
/// Not thread safe.
void setMessageCallback(const MessageCallback& cb) //设置消息回调
{ messageCallback_ = cb; }
/// Set write complete callback.
/// Not thread safe.
void setWriteCompleteCallback(const WriteCompleteCallback& cb) //设置写完成回调
{ writeCompleteCallback_ = cb; }
private:
/// Not thread safe, but in loop
void newConnection(int sockfd, const InetAddress& peerAddr); //新连接到达时调用的方法
/// Thread safe.
void removeConnection(const TcpConnectionPtr& conn); //移除一个连接
/// Not thread safe, but in loop
void removeConnectionInLoop(const TcpConnectionPtr& conn); //移除一个连接,用TcpConnection所在的loop
typedef std::map<string, TcpConnectionPtr> ConnectionMap; //KV映射
EventLoop* loop_; // the acceptor loop //当前的loop
const string hostport_; //端口
const string name_; //名称
boost::scoped_ptr<Acceptor> acceptor_; // avoid revealing Acceptor //数据接收器
boost::scoped_ptr<EventLoopThreadPool> threadPool_; //用于loop的线程池
ConnectionCallback connectionCallback_; //连接回调
MessageCallback messageCallback_; //消息回调
WriteCompleteCallback writeCompleteCallback_; //写完成回调
ThreadInitCallback threadInitCallback_; //线程初始化回调
bool started_; //开始标志
// always in loop thread
int nextConnId_; //下一个连接ID
ConnectionMap connections_; //开启的连接映射表
};
//TcpServer初始化流程
//a、赋值网络信息和名称。
//b、新建一个用于接收连接的Acceptor。
//c、创建一个线程池。
//d、设置默认的心理回调和消息回调。
//e、启动状态默认false、下一个连接ID默认1
TcpServer::TcpServer(EventLoop* loop,
const InetAddress& listenAddr,
const string& nameArg)
: loop_(CHECK_NOTNULL(loop)),
hostport_(listenAddr.toIpPort()),
name_(nameArg),
acceptor_(new Acceptor(loop, listenAddr)),
threadPool_(new EventLoopThreadPool(loop)),
connectionCallback_(defaultConnectionCallback),
messageCallback_(defaultMessageCallback),
started_(false),
nextConnId_(1)
{
//当有连接到来时,设置TcpServer的新连接回调函数
acceptor_->setNewConnectionCallback(
boost::bind(&TcpServer::newConnection, this, _1, _2));
}
//析构的过程就是释放TcpConnection
TcpServer::~TcpServer()
{
loop_->assertInLoopThread();
LOG_TRACE << "TcpServer::~TcpServer [" << name_ << "] destructing";
for (ConnectionMap::iterator it(connections_.begin());
it != connections_.end(); ++it)
{
TcpConnectionPtr conn = it->second;
it->second.reset();//引用减一
conn->getLoop()->runInLoop(
boost::bind(&TcpConnection::connectDestroyed, conn));
conn.reset();
}
}
//设置EventLoop使用的线程池个数
void TcpServer::setThreadNum(int numThreads)
{
assert(0 <= numThreads);
threadPool_->setThreadNum(numThreads);
}
//开启TcpServer服务
void TcpServer::start()
{
if (!started_)
{
started_ = true;
threadPool_->start(threadInitCallback_);
}
if (!acceptor_->listenning())
{
//开启下接收器的监听
loop_->runInLoop(
boost::bind(&Acceptor::listen, get_pointer(acceptor_)));
}
}
//新连接到达时调用的处理回调
void TcpServer::newConnection(int sockfd, const InetAddress& peerAddr)
{
//检测是否在当前线程
loop_->assertInLoopThread();
//新连接到来时,要从线程池中去一个EventLoop给新的连接使用
EventLoop* ioLoop = threadPool_->getNextLoop();
//a、组织下新连接的名称TcpServerName:端口#ID号
//b、默认将下一个ID号加1
char buf[32];
snprintf(buf, sizeof buf, ":%s#%d", hostport_.c_str(), nextConnId_);
++nextConnId_;
string connName = name_ + buf;
LOG_INFO << "TcpServer::newConnection [" << name_
<< "] - new connection [" << connName
<< "] from " << peerAddr.toIpPort();
InetAddress localAddr(sockets::getLocalAddr(sockfd));
//创建一个新的TcpConnection
//传入参数有:
//Loop、
//新连接的名称
//连接socket
//当前服务地址
//远程连接地址
// FIXME poll with zero timeout to double confirm the new connection
// FIXME use make_shared if necessary
TcpConnectionPtr conn(new TcpConnection(ioLoop,
connName,
sockfd,
localAddr,
peerAddr));
//保存当前连接
connections_[connName] = conn;
//设置连接回调(连接断开和关闭都会调用)
conn->setConnectionCallback(connectionCallback_);
//设置消息回调
conn->setMessageCallback(messageCallback_);
//设置写完成回调
conn->setWriteCompleteCallback(writeCompleteCallback_);
//设置关闭回调,移除对应的TcpConnection
conn->setCloseCallback(
boost::bind(&TcpServer::removeConnection, this, _1)); // FIXME: unsafe
//调用连接建立方法(初始化状态,启动Channdel开始读等 )
ioLoop->runInLoop(boost::bind(&TcpConnection::connectEstablished, conn));
}
void TcpServer::removeConnection(const TcpConnectionPtr& conn)
{
// FIXME: unsafe
loop_->runInLoop(boost::bind(&TcpServer::removeConnectionInLoop, this, conn));
}
//在每个TcpConnection所在线程内部去销毁当前连接
void TcpServer::removeConnectionInLoop(const TcpConnectionPtr& conn)
{
loop_->assertInLoopThread();
LOG_INFO << "TcpServer::removeConnectionInLoop [" << name_
<< "] - connection " << conn->name();
size_t n = connections_.erase(conn->name());
(void)n;
assert(n == 1);
EventLoop* ioLoop = conn->getLoop();
ioLoop->queueInLoop(
boost::bind(&TcpConnection::connectDestroyed, conn));
}
四、关键点总结
1、Acceptor
TcpServer内部使用Acceptor来获得新连接的fd。在TcpServer构造时已设置好Acceptor获得新连接时要调用的回调函数。当新连接到达时,Acceptor会回调TcpServer::newConnection(),后者会创建TcpConnection对象conn,并把它加入到ConnectionMap,设置好callback,再调用conn->connectEstablished()。详细注释可参考上文的源码注释。
2、线程池
说道线程池,先看下Muduo网络框架处理模型,如下:
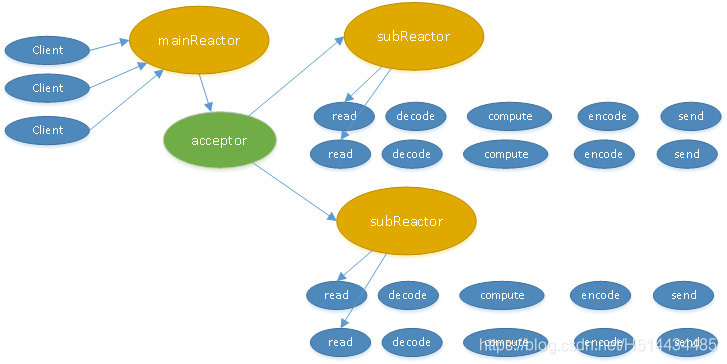
Muoduo服务端所用的思想是one loop per thread,而这个思想实现多线程TcpServer的关键步骤是在新建TcpConnection时从event loop pool中挑选一个loop给TcpConnection用。也就是说多线程TcpServer字段的EventLoop只用来接收新连接(mainReactor),而新连接会用其他EventLoop(subReactor)来执行IO。(单线程TcpServer的EventLoop是与TcpConnecton共享的)。
从以上分析我们就知道线程池(EventLoopThreadPool)存在的意义了。
- 用户通过TcpServer::setThreadNum来设置线程池的个数,如果不设置线程池个数,则TcpServer和TcpConnection共用一个EventLoop,即单线程的。
- Muduo目前采用最简单的round-robin算法来选取pool中的EventLoop,不允许TcpConnection在运行中更换EventLoop。
- 线程池中的每一个线程对应一个subReactor。
3、连接的断开
TcpServer连接的断开分两种,主动和被动。
主动断开:
即TcpServer自身的析构,看源码
//析构的过程就是释放TcpConnection
TcpServer::~TcpServer()
{
loop_->assertInLoopThread();
LOG_TRACE << "TcpServer::~TcpServer [" << name_ << "] destructing";
for (ConnectionMap::iterator it(connections_.begin());
it != connections_.end(); ++it)
{
TcpConnectionPtr conn = it->second;
it->second.reset();//引用减一
conn->getLoop()->runInLoop(
boost::bind(&TcpConnection::connectDestroyed, conn));
conn.reset();
}
}
析构的时候就是调用每个TcpConnection::conectDestroyed()去销毁对应的Channel。
被动断开:
即客户端主动断开连接。
TcpServer在创建TcpConnection的时候,给每个TcpConnection设置了连接断开回调,关闭回调执行流程代码如下:
1、
conn->setCloseCallback(boost::bind(&TcpServer::removeConnection, this, _1));
2、
void TcpServer::removeConnection(const TcpConnectionPtr& conn)
{
// FIXME: unsafe
loop_->runInLoop(boost::bind(&TcpServer::removeConnectionInLoop, this, conn));
}
3、
void TcpServer::removeConnectionInLoop(const TcpConnectionPtr& conn)
{
loop_->assertInLoopThread();
LOG_INFO << "TcpServer::removeConnectionInLoop [" << name_
<< "] - connection " << conn->name();
size_t n = connections_.erase(conn->name());
(void)n;
assert(n == 1);
EventLoop* ioLoop = conn->getLoop();
ioLoop->queueInLoop(
boost::bind(&TcpConnection::connectDestroyed, conn));
}
TcpServer被动关闭连接时和主动断开连接一样,最后都是调用的TcpConnection::connectDestroyed()
先连接TcpConnect的,可参考此篇文章:
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/H514434485/article/details/95108114







 本文深入解析Muduo网络库中的TcpServer组件,介绍其核心功能、使用示例及源码分析,包括Acceptor组件的工作原理、线程池机制及连接断开处理。
本文深入解析Muduo网络库中的TcpServer组件,介绍其核心功能、使用示例及源码分析,包括Acceptor组件的工作原理、线程池机制及连接断开处理。
















 2341
2341

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








