为什么需要图计算?
许多大数据以大规模图或网络的形式呈现
许多非图结构的大数据,常会被转换为图模型进行分析
图数据结构很好的表达了数据之间的关联性
图(Graph)的基本概念
图是由顶点集合(vertex)及顶点间关系集合(边edge)组成的一种网状数据结构
通常表示为二元组:Graph =(V,E)
可以对事物之间的关系建模
应用场景
在地图应用中寻找最短路径
社交网络关系
网页间超链接关系
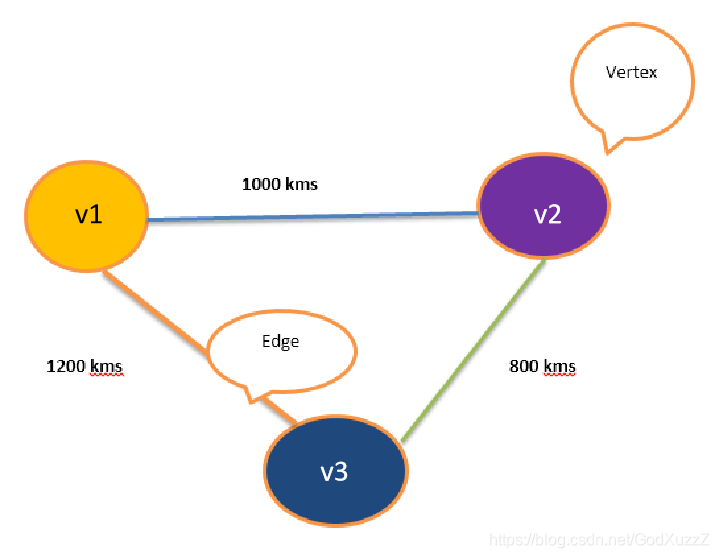
图的术语
顶点(Vertex)
边(Edge)
Graph = (V,E)
集合V={v1,v2,v3}
集合E={(v1,v2),(v1,v3),(v2,v3)}
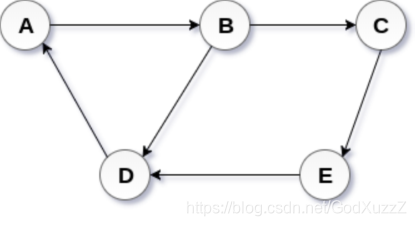
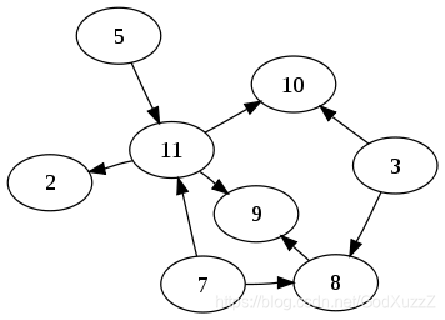
有向图
G = {V,E}
V = {A,B,C,D,E}
E = {<A,B>,<B,C>,<B,D>,<C,E>,<D,A>,<E,D>}
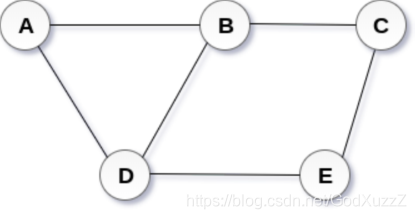
无向图
G = {V,E}
V = {A,B,C,D,E}
E = {(A,B),(B,C),(B,D),(C,E),(D,A),(E,D)}
有环图
包含一系列顶点连接的回路(环路)
无环图
DAG即为有向无环图
度:一个顶点所有边的数量
出度:指从当前顶点指向其他顶点的边的数量
入度:其他顶点指向当前顶点的边的数量
图的经典表示法
邻接矩阵

1、对于每条边,矩阵中响应单元格值为1
2、对于每个循环,矩阵中响应单元格值为2,方便再行或列上求得顶点度数
Spark GraphX简介
GraphX是Spark提供分布式图计算API
GraphX特点:
基于内存实现了数据的复用与快速读取
通过弹性分布式属性图同意了图视角与表视图
与Spark Streaming、Spark SQL 与Spark MLlib等无缝衔接
GraphX核心抽象
弹性分布式属性图(Resilient Distributed Property Graph)
顶点和边都带有属性的有向多重图
一份物理存储,两种视图
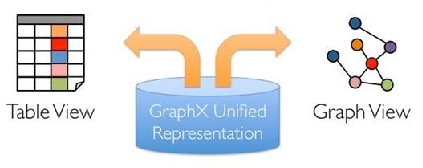
对Graph视图的所有操作,最终都会转换成其关联的Table视图的RDD操作来完成
GraphX API
Graph [VD,ED]
VertexRDD [VD]
EdgeRDD [ED]
EdgeTrilet [ED,VD]
Edge:样例类
VertexId:Long的别名
class Graph[VD, ED] {
val vertices: VertexRDD[VD]
val edges: EdgeRDD[ED]
val triplets: RDD[EdgeTriplet[VD, ED]]
}
import org.apache.spark.graphx._
val vertices:RDD[(VertexId,Int)] = sc.makeRDD(Seq((1L,1),(2L,2),(3L,3)))
val edges = sc.makeRDD(Seq(Edge(1L,2L,1),Edge(2L,3L,2)))
val graph = Graph(vertices,edges) // Graph[Int,Int]?
import org.apache.spark.graphx.GraphLoader
// 加载边列表文件创建图,文件每行描述一条边,格式:srcId dstId。顶点与边的属性均为1
val graph = GraphLoader.edgeListFile(sc,"file:///opt/spark/data/graphx/followers.txt")
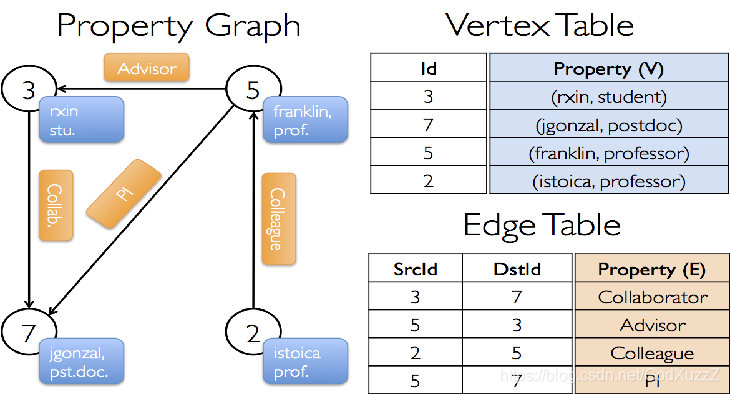
属性用户合作关系属性图
顶点属性
用户名、职业
边属性
合作关系
构建用户社交网络关系
顶点:用户名、年龄
边:打call次数
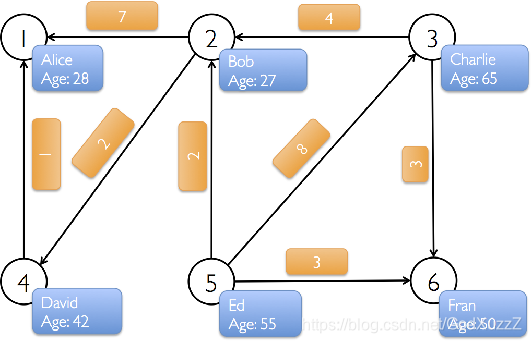

找出大于30岁的用户
graph.vertices.filter{case(id,(name,age)) => age > 30}.collect
假设打call超过5次,表示真爱。请找出他们
查看图信息
顶点数量
边数量
度、入度、出度
class Graph[VD,ED] {
val numEdges:Long
val numVertices:Long
val inDegrees:VertexRDD[Int]
val outDegrees:VertexRDD[Int]
val degrees:VertexRDD[Int]
}
图的算子
属性算子
类似于RDD的map操作
class Graph[VD,ED] {
def mapVertices[VD2](map:(VertexId,VD) => VD2):Graph[VD2,ED]
def mapEdges[ED2](map:Edge[ED] => ED2):Graph[VD,ED2]
def mapTrilets[ED2](map:EdgeTrilet[VD,ED] => ED2):Graph[VD,ED2]
}
val t1_graph = tweeter_graph.mapVertices{ case(vertexId,(name,age)) => (vertexId,name)}
val t2_graph = tweeter_graph.mapVertices{ (vertexId,attr) => (vertexId,attr._1)}
val t3_graph = tweeter_graph.mapEdges(e => Edge(e.srcId,e.dstId,e.attr*7.0))
结构算子
class Graph[VD,ED] {
def reverse:Graph[VD,ED]
def subgraph(epred:EdgeTrilet[VD,ED] => Boolean,vpred:(VertexId,VD) => Boolean):Graph[VD,ED]
}
val t1_graph = tweeter_graph.reverse
val t2_graph = tweeter_graph.subgraph(vpred=(id,attr)=>attr._2<65) //attr:(name,age)
join算子:从外部的RDDs加载数据,修改顶点属性
class Graph[VD, ED] {
def joinVertices[U](table: RDD[(VertexId, U)])(map: (VertexId, VD, U) => VD): Graph[VD, ED]
def outerJoinVertices[U, VD2](table: RDD[(VertexId, U)])(map: (VertexId, VD, Option[U]) => VD2)
: Graph[VD2, ED]
}
val tweeters_comps:RDD[(VertexId,String)]= sc.parallelize(Array((1L, "kgc.cn"), (2L, "berkeley.edu"), (3L, "apache.org")))
val t_graph = tweeter_graph.joinVertices(tweeters_comps)((id, v, cmpy) => (v._1 + " @ " + cmpy, v._2))
t_graph.vertices.collect
val s_graph = tweeter_graph.outerJoinVertices(tweeters_comps)((id, v, cmpy) => (v._1 + " @ " + cmpy, v._2))
s_graph.vertices.collect
val conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("ghx").setMaster("local[*]")
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
// 建立所有的点
val vects = sc.makeRDD(Seq((3L,("rxin","stu")),(5L,("zs","prof")),(2L,("ls","prof")),(7L,("xx","pst"))))
// 建立所有的边
val edges = sc.makeRDD(Seq(Edge(2L,5L,"ts"),Edge(5L,3L,"zd"),Edge(5L,7L,"pi"),Edge(3L,7L,"collab")))
// 建立图
val graph = Graph(vects,edges)
// 新的点
val newPoint = sc.parallelize(Array((3L,"hehe"),(5L,"xixi"),(4L,"cici")))
// graph.joinVertices(newPoint)((id,src,newval) => (src._1+"@"+newval,src._2)).vertices.foreach(f => println(f._2))
graph.outerJoinVertices(newPoint)((id,src,newval) => (src._1+"@"+newval,src._2)).vertices.foreach(f => println(f._2))
/*(xx,pst) (xx@None,pst)
(zs@xixi,prof) (zs@Some(xixi),prof)
(ls,prof) (ls@None,prof)
(rxin@hehe,stu) (rxin@Some(hehe),stu)
*/
GraphX API应用
计算用户粉丝数量
case class User(name:String,age:Int,inDeg:Int,outDeg:Int)
// 修改顶点属性
val initialUserGraph:Graph[User,Int] = tweeter_graph.mapVertices {
case(id,(name,age)) => User(name,age,0,0)
}
// 将顶点入度、出度存入顶点属性中
val userGraph = initialUserGraph.outerJoinVertices(initialUserGraph.inDegrees){
case(id,u,inDegOpt) => User(u.name,u.age,inDegOpt.getOrElse(0),u.outDeg)}.outJoinVertices(initialuserGraph.outDegrees){
case(id,u,outDegOpt) => User(u.name,u.age,u.inDeg,outDegOpt.getOrElse(0))
}
// 顶点的入度即为粉丝数量
for((id,property) <- userGraph.vertices.collect)
println(s"User $id ${property.name} and is liked by ${property.inDeg} people.")
谁是网络红人
需求说明
数据:twitter-graph-data.txt
格式:((User… , …) , (User… , …))
- (User… , …) = (用户名,用户ID)
- 第一个用户表示被跟随者(followee)
- 第二个用户表示跟随者(follower)
创建图并计算每个用户的粉丝数量
找出网络红人
val conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("fans")
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
var rdd = sc.textFile("twitter_graph_data.txt").cache()
val pattern = """([a-zA-Z0-9]+),([0-9]+)""".r
val vects = rdd.flatMap(str => {
pattern.findAllIn(str).map(e => {
val ff = e.split(",")
(ff(1).toLong,ff(0))
})
}).distinct()
val pattern1 = """\(\([a-zA-Z0-9]+,([0-9]+)\),\([a-zA-Z0-9]+,([0-9]+)\)\)""".r
val edges = rdd.flatMap(str => {
val matches = pattern1.findAllMatchIn(str)
matches.map(x => (Edge(x.group(1).toLong,x.group(2).toLong,1)))
})
var graph = Graph(vects,edges)
val in = graph.inDegrees.repartition(1).sortBy(-_._2).take(3)
sc.makeRDD(in).join(vects).foreach(println)
PageRank in GraphX
PageRank(PR)算法
用于评估网页链接的质量和数量,以确定该网页的重要性和权威性的相对分数,范围0到10
从本质上讲,PageRank是找出途中顶点(网页链接)的重要性
GraphX提供了PageRank API用于计算图的PageRank
class Graph[VD,ED]{
def pageRank(tol:Double,resetProb:Double=0.15):Graph[Double,Double]
}
PageRank应用
找出用户社交网络中最重要的用户
val tweeters = Array((1L,("Alice",28)),(2L,("Bob",27)),(3L,("Charlie",65)),(4L,("David",42)),(5L,("Ed",55)),(6L,("Fran",50)))
val vertexRDD:RDD[(Long,(String,Int))] = spark.sparkContext.parallelize(tweeters)
val followRelations = Array(Edge[Int](2L,1L,7),Edge[Int](2L,4L,2),Edge[Int](3L,2L,4),Edge[Int](3L,6L,3),Edge[Int](4L,1L,1),Edge[Int](5L,2L,2),Edge[Int](5L,3L,2),Edge[Int](5L,6L,3))
val edgeRDD = spark.sparkContext.parallelize(followRelations)
val graph:Graph[(String,Int),Int] = Graph(vertexRDD,edgeRDD)
val ranks = graph.pageRank(0.0001)
ranks.vertices.sortBy(_._2,false).collect
需求说明
- 现有followers.txt、users.txt,通过followers.txt创建图,并使用PageRank算法找出图中最重要的用户,输出用户名称与重要程度
val conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("fans")
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
val graph = GraphLoader.edgeListFile(sc,"followers.txt")
val ranks = graph.pageRank(0.0001).vertices
val users = sc.textFile("user.txt").map{ line =>
val fields = line.split(",")
(fields(0).toLong,fields(1))
}
val ranksByUsername = users.join(ranks).map {
case (id,(username,rank)) => (username,rank)
}
ranksByUsername.repartition(1).sortBy(_._2).foreach(println)
连通分量
连通分量是一个子图,其中任何两个顶点通过一条或一系列边相互连接,其顶点是原始图顶点集的子集,其边是原始图边集的子集
class Graph[VD,ED]{
def connectedComponents():Graph[VertexID,ED]
}
Pregel概述
Pregel是Google提出的用于大规模分布式图计算框架
- 图遍历(BFS)
- 单源最短路径(SSSP)
- PageRank计算
Pregel的计算由一系列迭代组成,称为supersteps
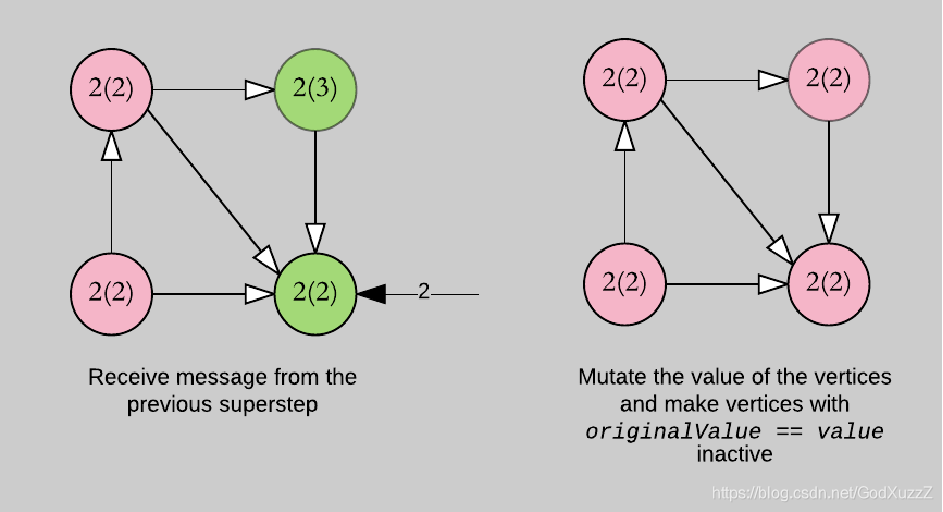
Pregel迭代过程
- 每个顶点从上一个superstep接收入站消息
- 计算顶点新的属性值
- 在下一个superstep中向相邻的顶点发送消息
- 当没有剩余消息时,迭代结束。
Pregel计算过程-初始化
需求说明:求出图中最小值

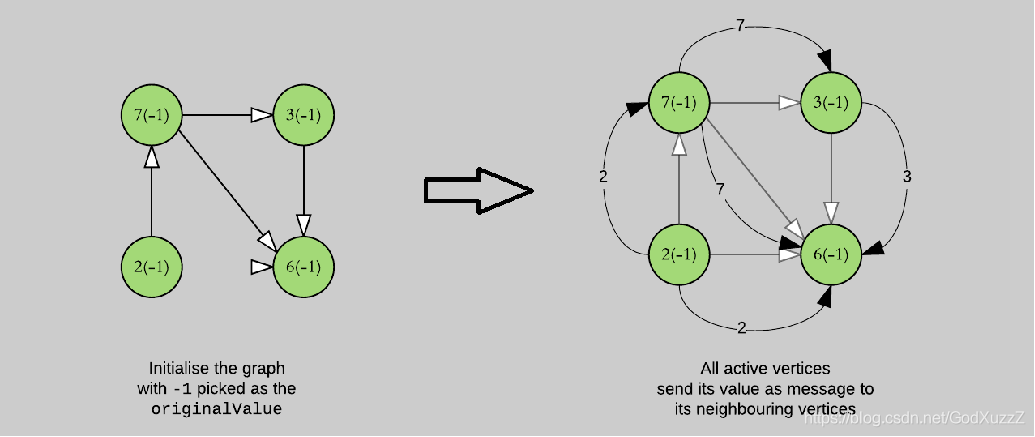
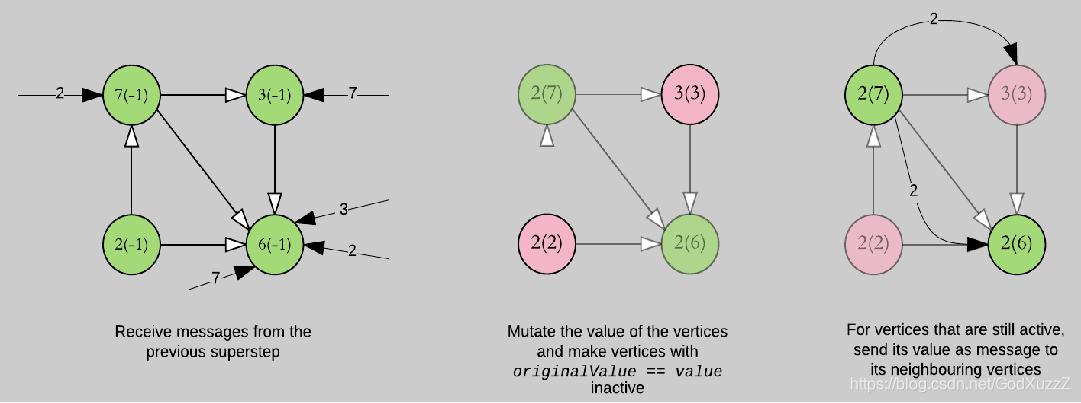
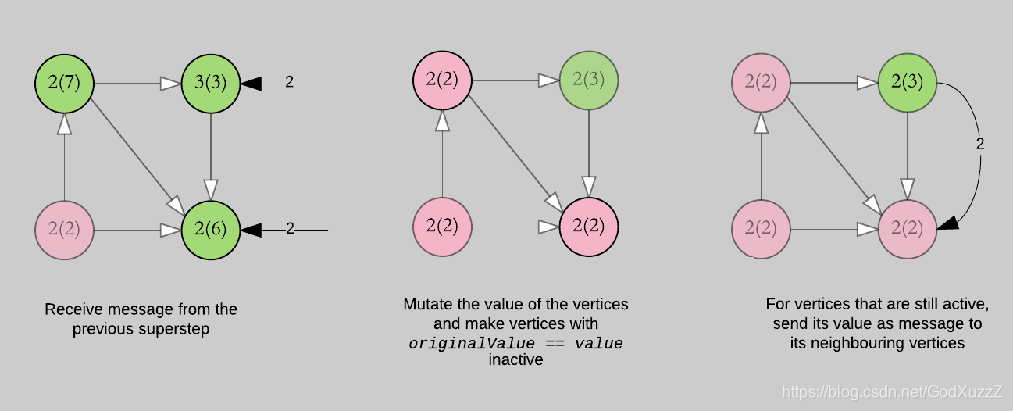
val conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("shortest").setMaster("local[*]")
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
val vects = Array(
(1L,("Alice",28)),
(2L,("Bob",27)),
(3L,("Charlie",65)),
(4L,("David",42)),
(5L,("Ed",55)),
(6L,("Fran",50))
)
val vertexRdd = sc.makeRDD(vects)
val edges = Array(
Edge(2L,1L,7),
Edge(2L,4L,2),
Edge(3L,2L,4),
Edge(3L,6L,3),
Edge(4L,1L,1),
Edge(2L,5L,2),
Edge(5L,3L,8),
Edge(5L,6L,3)
)
val edgeRDD = sc.makeRDD(edges)
val graph = Graph(vertexRdd,edgeRDD)
val srcVertexId = 5L
val initialGraph = graph.mapVertices{
case(vid,(name,age)) => if(vid ==srcVertexId) 0.0 else Double.PositiveInfinity
}
val pregelGraph = initialGraph.pregel(
Double.PositiveInfinity,
Int.MaxValue,
EdgeDirection.Out
)(
(vid:VertexId,vd:Double,distMsg:Double) => {
val minDist = math.min(vd,distMsg)
println(s"顶点${vid},属性${vd},收到消息${distMsg},合并后的属性${minDist}")
minDist
},
(edgeTriplet:EdgeTriplet[Double,PartitionID]) => {
if(edgeTriplet.srcAttr + edgeTriplet.attr < edgeTriplet.dstAttr) {
println(s"顶点${edgeTriplet.srcId} 给 顶点${edgeTriplet.dstId} 发送消息${edgeTriplet.srcAttr + edgeTriplet.attr}")
Iterator[(VertexId,Double)]((edgeTriplet.dstId,edgeTriplet.srcAttr + edgeTriplet.attr))
} else {
Iterator.empty
}
},
(msg1:Double,msg2:Double) => math.min(msg1,msg2)
)
pregelGraph.triplets.collect().foreach(println)
println(pregelGraph.vertices.collect.mkString("\n"))
sc.stop()
GraphX Pregel API
initialMsg:在“superstep 0”之前发送至顶点的初始消息
maxIterations:将要执行的最大迭代次数
activeDirection:发送消息方向(默认是出边方向:EdgeDirection.Out)
vprog:用户定义函数,用于顶点接收消息
sendMsg:用户定义的函数,用于确定下一个迭代发送的消息及发往何处
mergeMsg:用户定义的函数,在vprog前,合并到达顶点的多个消息
class Graph[VD,ED]{
def pregel[A](initialMsg:A,maxIterations:Int,activeDirection:EdgeDirection)(
vprog:(VertexID,VD,A) => VD,
sendMsg:EdgeTrilet[VD,ED] => Iteratorp[(VertexID,A)],
mergeMsg:(A,A) => A):Graph[VD,ED]
}
GraphX Pregel应用
需求说明:求出图中最小值
// 创建顶点集RDD
val vertices:RDD[(VertexId,(Int,Int))] = sc.parallelize(Array((1L,(7,-1)),(2L,(3,-1)),(3L,(2,-1)),(4L,(6,-1))))
// 创建边集
val relationships:RDD[Edge[Boolean]] = sc.parallelize(Array(Edge(1L,2L,true),Edge(1L,4L,true),Edge(2L,4L,true),Edge(1L,4L,true),Edge(2L,4L,true),Edge(3L,1L,true),Edge(3L,4L,true)))
// 创建图
val graph = Graph(vertices,relationships)
// Pregel
val minGraph = graph.pregel(initialMsg,Int.MaxValue,EdgeDirection.Out)(vprog,sendMsg,mergeMsg)
minGraph.vertices.collect.foreach{
case(vertexId,(value,original_value)) => println(value)
}
val initialMsg = 9999
// 顶点接收消息
def vprog(vertexId:VertexId,value:(Int,Int),message:Int):(Int,Int) = {
if(message == initialMsg) value else (message min value._1,value._1)
}
// 确定下一个迭代发送的消息及发往何处
def sendMsg(triplet:EdgeTriplet[(Int,Int),Boolean]):Iterator[(VertexId,Int)] = {
val sourceVertex = triplet.srcAttr
if(sourceVertex._1 == sourceVertex._2) Iterator.empty else Iterator((triplet.dstId,sourceVertex._1))
}
// 合并到达顶点的多个消息
def mergeMsg(msg1:Int,msg2:Int):Int = msg1 min msg2 // 求msg1和msg2的最小值
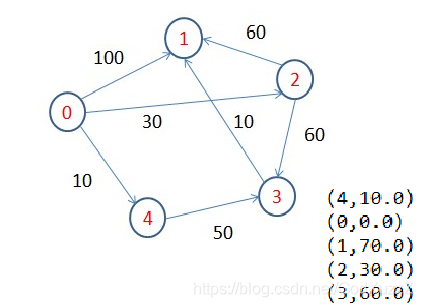
使用Pregel计算单源最短路径
需求说明
求从0到任意点的最短路径(SSSP)
实现思路
初始化Vertex的Message为最大值
将源点(0)的Message设为0
每步每个节点将自己目前的Message加上边的权值发送到相邻节点,每个节点聚合出自身所有消息的最小值
当某一步当中国一个节点Message值无变化,该节点停止迭代




















 511
511

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








